多重继承、继承与组合、多文件编程实例(C++)
发布时间:2024年01月05日
3.4 多重继承
C++允许一个类从一个或多个基类派生。如果一个类只有一个基类,称为单一继承。如果一个类具有两个或两个以上的基类,就称为多重继承。
class 派生类名:继承方式 基类名1, 派生方式 基类2,...{};

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Phone{ //手机
private:
string m_number;
public:
Phone(const string& number) {
m_number = number;
}
void call(const string& number){
cout << m_number << "打给: " << number << endl;
}
};
class Player{ //播放器
private:
string m_media; //播放器的名称
public:
Player(const string& media){
m_media = media;
}
void play(const string& music){
cout << m_media << "正在播放:" << music << endl;
}
};
class Computer{ //电脑
private:
string m_os; //操作系统的名称
public:
Computer(const string& os){
m_os = os;
}
void run(const string& app){
cout << m_os << "系统正在运行:" << app << endl;
}
};
/* 典型的多重继承 */
class SmarePhone: public Phone, public Player, public Computer{ //智能手机
public:
SmarePhone(const string& number, const string& media, const string& os):Phone(number), Player(media), Computer(os){
}
};
int main(void) {
SmarePhone huawei("15833336666", "MP3", "鸿蒙");
huawei.call("瑞思");
huawei.play("我和我的祖国");
huawei.run("4399合金弹头");
return 0;
}
3.4.1 名字冲突
当两个不同基类拥有同名成员时,容易产生名字冲突问题。
使用作用域限定符解决。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A{
public:
void func(){
cout << "A func()" << endl;
}
};
class B{
public:
void func(){
cout << "B func()" << endl;
}
};
class C: public B, public A {
};
int main(void) {
C c;
//c.func(); //error
c.A::func(); //加作用域限定符 来指定要访问那一个基类中的成员函数
c.B::func();
return 0;
}
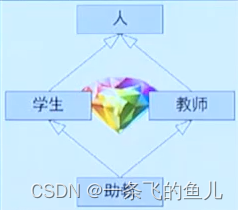
3.4.2 钻石继承与虚继承
钻石继承,一个派生类继承的多个基类又源自一个公共的祖先(公共基类)。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
protected:
int m_data;
public:
A(int data){
m_data = data;
cout << "A(int)" << endl;
}
};
class B: public A{
public:
B(int data):A(data){
cout << "B(int)" << endl;
}
void set(int data){
m_data = data;
}
};
class C: public A{
public:
C(int data):A(data){
cout << "C(int)" << endl;
}
int get(){
return m_data;
}
};
class D: public B, public C {
public:
D(int a, int b):B(a), C(b) {
cout << "D(int,int)" << endl;
}
};
int main(void) {
D d(3,6);
cout << sizeof(D) << endl;
cout << d.get() << endl;//6
d.set(200);//这个位置没有起到作用
cout << d.get() << endl;//6
return 0;
}
//输出结果
myubuntu@ubuntu:~/lv19/cplusplus/dy03$ ./a.out
A(int)
B(int)
A(int)
C(int)
D(int,int)
8
6
6
解决方式:虚继承
虚继承语法:
- 在继承表使用virtual关键字修饰
- 位于继承链表末端子类负责构造公共基类子对象
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
protected:
int m_data;
public:
A(int data){
m_data = data;
cout << "A(int)" << endl;
}
};
class B: virtual public A{
public:
B(int data):A(data){
cout << "B(int)" << endl;
}
void set(int data){
m_data = data;
}
};
class C: virtual public A{
public:
C(int data):A(data){
cout << "C(int)" << endl;
}
int get(){
return m_data;
}
};
class D: public B, public C {
public:
D(int a, int b):B(a), C(b), A(a) {
cout << "D(int,int)" << endl;
}
};
int main(void) {
D d(3,6);
cout << sizeof(D) << endl;
cout << d.get() << endl; //3
d.set(200);
cout << d.get() << endl; //200
return 0;
}
//输出结果
myubuntu@ubuntu:~/lv19/cplusplus/dy03$ ./a.out
A(int)
B(int)
C(int)
D(int,int)
12
3
200
3.5 继承与组合
继承与组合是C++实现代码重用的两种主要方法。
继承是ls-a的关系,比如水果和梨
组合是Has-a的关系,图书馆有图书
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class vehicles{ //交通工具
public:
void load(const string& goods) {
cout << "装载" << goods << endl;
}
};
class tyre{ //轮胎
public:
void run(const string& dest){
cout << "转动方向:" << dest << endl;
}
};
class car : public vehicles{
public:
tyre wheel; //轮子
};
int main(void) {
car c1;
c1.load("金枪鱼");
c1.wheel.run("石家庄");
return 0;
}
3.6 多文件编程实例
/*person.h*/
#ifndef __PERSON_H__
#define __PERSON_H__
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person{
private:
string name;
int age;
public:
Person(const string& name, int age);
void whoami();
};
#endif
/*person.cpp*/
#include "person.h"
Person::Person(const string& name, int age){
this->name = name;
this->age = age;
}
void Person::whoami() {
cout << "我是:" << name << endl;
}
/*student.h*/
#ifndef __STUDENT_H__
#define __STUDENT_H__
#include "person.h"
class Student: public Person{
private:
float score;
public:
Student(const string& name, int age, float score);
void whoami();
};
#endif
/*student.cpp*/
#include "student.h"
Student::Student(const string& name, int age, float score):Person(name, age){
this->score = score;
}
void Student::whoami() {
Person::whoami();
cout << "成绩:" << score << endl;
}
/*main.cpp*/
#include "student.h"
int main(void) {
Student s1("刘铁胆", 19, 88.6);
s1.whoami();
return 0;
}
g++ person.cpp student.cpp main.cpp
./a.out
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36091214/article/details/135416979
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- linux系统和网络(二):进程和系统时间
- 基于SpringBoot+vue的在线视频教育平台的设计与实现,附源码,数据库
- 基于Java SSM框架实现校园网络维修系统项目【项目源码】计算机毕业设计
- WLAN---实验
- 目标检测中的常见指标
- 【漏洞复现】Hikvision综合安防管理平台Fastjson命令执行漏洞
- 数据湖存储解决方案之Iceberg
- WhatsApp business的优势有哪些?
- Spring之依赖注入的方式
- pytorch之torch基础学习