【低照度图像增强系列(3)】EnlightenGAN算法详解与代码实现

前言??
?? 在低照度场景下进行目标检测任务,常存在图像RGB特征信息少、提取特征困难、目标识别和定位精度低等问题,给检测带来一定的难度。
? ? ?🌻使用图像增强模块对原始图像进行画质提升,恢复各类图像信息,再使用目标检测网络对增强图像进行特定目标检测,有效提高检测的精确度。
? ? ? ?本专栏会介绍传统方法、Retinex、EnlightenGAN、SCI、Zero-DCE、IceNet、RRDNet、URetinex-Net等低照度图像增强算法。
👑完整代码已打包上传至资源→低照度图像增强代码汇总资源-CSDN文库
目录
?
🚀一、EnlightenGAN介绍?
相关资料:?
- EnlightenGAN 论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.06972
- EnlightenGAN 论文详细解读:《EnlightenGAN: Deep Light Enhancement withoutPaired Supervision》论文超详细解读(翻译+精读)
- EnlightenGAN 源码:https://github.com/VITA-Group/EnlightenGAN
??1.1?EnlightenGAN简介
目前,基于深度学习的低照度图像增强方法取得了一些不错的成效。但是一直以来存在着一个问题,就是它们大部分都属于监督学习,也就是说需要大量配对数据(paired data)来进行训练,但现实生活中,我们很难获取大量的同场景下的低光和正常光图像来作为数据对。
因此,作者和他的团队提出了一种无监督的生成对抗网络来实现图像增强,即EnlightenGAN。这个模型并不需要配对数据来进行训练,但却能在多种场景下表现良好。为了提高模型性能,同时也弥补数据未成对造成的一些不足,作者和他的团队提出了一系列的新处理方法,包括全局-局部判别器结构,自正则化感知损失,以及自正则注意机制。
??1.2?EnlightenGAN网络结构
下图是EnlightenGAN网络结构。
EnlightenGAN网络结构 = 生成器(带自注意力机制的U-Net)+ 判别器(全局-局部鉴别器)
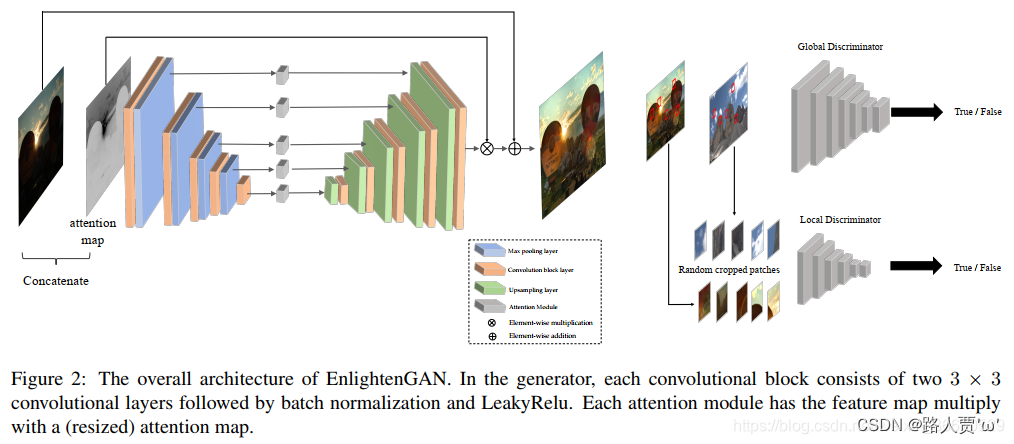
(1)生成器模块??
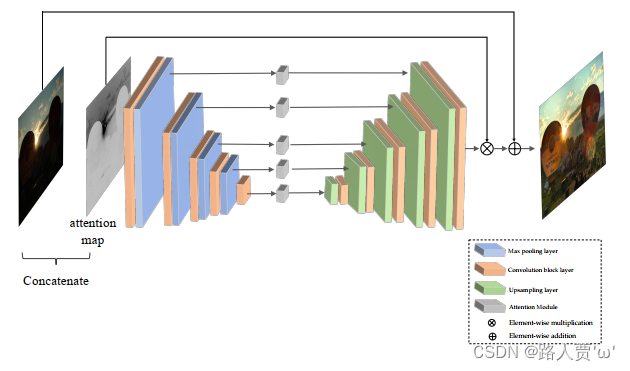
首先,我们来看看生成器模块。
生成器模块就是一个引入了自注意力机制的U-Net,自正则化注意力图的生成方式如下:
-
把输入的RGB图像转为灰度图
-
将灰度图(I)归一化到 [ 0,1 ]
-
运算1 - I(element-wise difference 逐元素作差),突出暗部部分
-
得到了注意力图(attention map),重点关注暗部部分
可以理解为对于光照越弱的地方注意力越强。因为网络中得到的每个特征图大小都不一样,所以这里把注意力图resize为各中间的特征图对应的大小,然后对应相乘最后得到了我们的输出图像。
整个U-Net 生成器由8个卷积块组成,每个卷积块由两个3*3的卷积层和一个BN层和LeakReLU层。
为什么把ReLU层换为LeakyReLU层?
由于稀疏梯度虽然在大多数网络中通常是理想的目标,但是在GAN中,它会妨碍训练过程,影响GAN的稳定性,所以作者的网络中没有maxpool层和ReLU层,而是用LeakReLU层替代ReLU层。
此外,为了减小棋盘效应,作者用一个双线性上采样层+一个卷积层来代替原本的标准反卷积层。
棋盘效应:由于反卷积的”不均匀重叠“,会导致图像中的某部位比别的部位颜色深,造成的伪影看上去像棋盘格子一般。而这种”不均匀重叠“,是因为卷积核(kernel)尺寸不能被步长(stride)整除导致的。
(2)判别器模块??
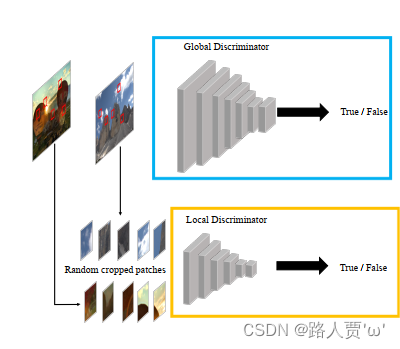
- 全局鉴别器:上面的灰色块,判断生成的图像和真实图像之间的整体光照差异,改善图像的全局光照特征对抗性损失来最小化真实图像和输出图像的光照分布的距离。但全局鉴别器,对于一些暗场景下存在明亮区域的图像,适应性不够。
- 局部鉴别器:下面的灰色块,判断生成的图像和真实图像之间的局部细节差异。改善图像的细节特征,用的 PatchGAN来鉴别真/假 来鉴别真/假。从输出图像和真实图像中随机采样 5 个图像块(上图),来判断是真实图像还是模型增强出来的图像。解决全局鉴别器带来的局部曝光不足或过度的情况了。
(3)损失函数??
相对论鉴别器函数:
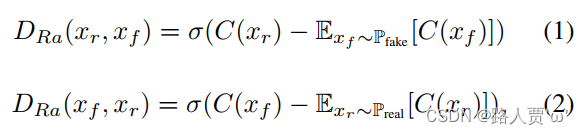
:表示网络
?和
?:是从真实的和伪分布中采样的
:表示S形函数
全局鉴别器D和生成器G的损失函数:
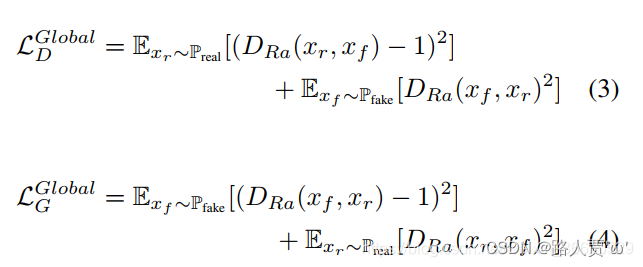
局部鉴别器D和生成器G的损失函数:

自特征保持损失LSFP定义:

表示输入低光图像
表示生成器的增强输出
表示从ImageNet上预训练的VGG16模型中提取的特征图
- i表示第i个最大池化层
- j表示第i个最大池化层之后的第j个卷积层
和
是提取的特征图的维度
EnlightenGAN的整体损失函数:
![]()
🚀二、EnlightenGAN核心代码讲解
这一部分我们主要讲EnlightenGAN模型的网络生成器这部分的核心,也就是models文件夹中的networks.py。
🎄2.1?Functions
① pad_tensor
def pad_tensor(input):
height_org, width_org = input.shape[2], input.shape[3] #获取张量的高度和宽度
divide = 16
if width_org % divide != 0 or height_org % divide != 0:# 判断输入张量的宽度和高度是否不能被divide整除
width_res = width_org % divide
height_res = height_org % divide
if width_res != 0:
width_div = divide - width_res # 需要填充的宽度
pad_left = int(width_div / 2) # 填充的左侧宽度
pad_right = int(width_div - pad_left) # 填充的右侧宽度
else:
pad_left = 0
pad_right = 0
if height_res != 0:
height_div = divide - height_res # 需要填充的高度
pad_top = int(height_div / 2) # 填充的左侧高度
pad_bottom = int(height_div - pad_top) # 填充的右侧高度
else:
pad_top = 0
pad_bottom = 0
padding = nn.ReflectionPad2d((pad_left, pad_right, pad_top, pad_bottom)) # 在输入张量的四个边上进行反射填充
input = padding(input)
else:
pad_left = 0
pad_right = 0
pad_top = 0
pad_bottom = 0
height, width = input.data.shape[2], input.data.shape[3]
assert width % divide == 0, 'width cant divided by stride'
assert height % divide == 0, 'height cant divided by stride'
return input, pad_left, pad_right, pad_top, pad_bottom
这段代码的主要作用是对输入的二维张量进行填充,以确保其高度和宽度能够被指定的divide参数整除。
具体而言,该函数执行以下操作:
- 如果输入张量的宽度或高度不能被
divide整除,计算需要进行填充的数量,并使用反射填充(nn.ReflectionPad2d)对输入进行填充。 - 如果宽度和高度已经能够被
divide整除,则不进行填充。 - 返回填充后的张量以及进行填充的左、右、上、下四个方向的填充量。
主要参数含义:?
width_org和height_org是输入张量的原始宽度和高度。divide是用于指定张量宽度和高度整除性的参数。pad_left、pad_right、pad_top和pad_bottom是填充的左、右、上、下四个方向的填充量。
② pad_tensor_back
def pad_tensor_back(input, pad_left, pad_right, pad_top, pad_bottom):
height, width = input.shape[2], input.shape[3]
return input[:, :, pad_top: height - pad_bottom, pad_left: width - pad_right]这段代码主要作用是与前面 pad_tensor 函数相对应的逆操作,用于反向去除填充。这个函数的目的是从填充后的张量中截取出原始尺寸的部分。
具体来说,函数通过切片操作,从填充后的张量中截取出原始尺寸(不包括填充的部分)的子张量。返回的结果就是去除填充后的张量,恢复到原始尺寸的部分。
这样的操作通常在对图像或特征图进行处理后,需要将其还原到原始尺寸时使用。这可以确保在网络的前向传播和反向传播过程中,输入和输出的尺寸保持一致。
③?weights_init
def weights_init(m):
classname = m.__class__.__name__ # 初始化权重
if classname.find('Conv') != -1:
m.weight.data.normal_(0.0, 0.02) # 卷积层权重正态分布初始化,均值为0,标准差为0.02
elif classname.find('BatchNorm2d') != -1:
m.weight.data.normal_(1.0, 0.02) # 批量归一化层正态分布初始化
m.bias.data.fill_(0) # 批量归一化层偏置项设置为0这段代码主要作用是初始化神经网络模型中的权重。具体来说,它对卷积层和批量归一化层的权重进行初始化。
函数通过遍历模型的每个模块(m),根据模块的类别进行不同的权重初始化。
具体做法如下:
- 如果模块属于卷积层,则将卷积层的权重进行正态分布初始化,均值为0,标准差为0.02。
- 如果模块属于批量归一化层,则将批量归一化层的权重进行正态分布初始化,均值为1,标准差为0.02,并将偏置项设置为0。
(这样的初始化策略有助于在训练初期使得权重处于较小的范围,有助于网络的稳定训练。这是一种常见的初始化方法,尤其在使用卷积和批量归一化的深度学习模型中。)
④ get_norm_layer
def get_norm_layer(norm_type='instance'):
if norm_type == 'batch':
norm_layer = functools.partial(nn.BatchNorm2d, affine=True)
elif norm_type == 'instance':
norm_layer = functools.partial(nn.InstanceNorm2d, affine=False)
elif norm_type == 'synBN':
norm_layer = functools.partial(SynBN2d, affine=True)
else:
raise NotImplementedError('normalization layer [%s] is not found' % norm)
return norm_layer这段代码主要作用是返回指定类型的归一化层。归一化层在深度学习中用于提高训练的稳定性和收敛速度。
函数接受一个参数 norm_type,根据这个参数的值返回不同类型的归一化层。具体来说:
- 如果
norm_type的值为'batch',则返回批量归一化层,并设置affine参数为True。 - 如果
norm_type的值为'instance',则返回实例归一化层,并设置affine参数为False。 - 如果
norm_type的值为'synBN',则返回一个自定义的SynBN2d归一化层,该归一化层也设置affine参数为True。 - 如果
norm_type的值不是上述任何一种,则抛出NotImplementedError异常,表示未找到指定类型的归一化层。
⑤ define_G
def define_G(input_nc, output_nc, ngf, which_model_netG, norm='batch', use_dropout=False, gpu_ids=[], skip=False,
opt=None):
# 定义生成器(全局生成器或局部增强生成器)和特征编码器
netG = None
use_gpu = len(gpu_ids) > 0
norm_layer = get_norm_layer(norm_type=norm)
if use_gpu:
assert (torch.cuda.is_available())
if which_model_netG == 'resnet_9blocks':
netG = ResnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout, n_blocks=9,
gpu_ids=gpu_ids)
elif which_model_netG == 'resnet_6blocks':
netG = ResnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout, n_blocks=6,
gpu_ids=gpu_ids)
elif which_model_netG == 'unet_128':
netG = UnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, 7, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout,
gpu_ids=gpu_ids)
elif which_model_netG == 'unet_256':
netG = UnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, 8, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout,
gpu_ids=gpu_ids, skip=skip, opt=opt)
elif which_model_netG == 'unet_512':
netG = UnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, 9, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout,
gpu_ids=gpu_ids, skip=skip, opt=opt)
elif which_model_netG == 'sid_unet':
netG = Unet(opt, skip)
elif which_model_netG == 'sid_unet_shuffle':
netG = Unet_pixelshuffle(opt, skip)
elif which_model_netG == 'sid_unet_resize':
netG = Unet_resize_conv(opt, skip)
elif which_model_netG == 'DnCNN':
netG = DnCNN(opt, depth=17, n_channels=64, image_channels=1, use_bnorm=True, kernel_size=3)
else:
raise NotImplementedError('Generator model name [%s] is not recognized' % which_model_netG)
if len(gpu_ids) >= 0:
netG.cuda(device=gpu_ids[0])
netG = torch.nn.DataParallel(netG, gpu_ids)
netG.apply(weights_init)
return netG这段代码主要作用是定义了一个生成器网络的创建函数 define_G。这个函数根据指定的参数创建不同类型的生成器网络,支持的生成器类型包括 ResNet 生成器、U-Net 生成器等。此外,函数也支持在 GPU 上运行,并对生成器进行权重初始化。
主要参数:
input_nc:输入通道数。output_nc:输出通道数。ngf:生成器中特征图的数量。which_model_netG:选择的生成器模型的名称。norm:归一化层的类型('batch'、'instance'等)。use_dropout:是否使用 dropout。gpu_ids:指定在哪些 GPU 上运行。skip:是否使用 skip connection(跳跃连接)。opt:其他选项,可能用于某些生成器类型的参数设置。
函数首先根据输入的 which_model_netG 参数选择相应的生成器模型。然后,根据其他参数,如归一化类型、是否使用 dropout 等,构建生成器。最后,将生成器应用权重初始化,如果指定了 GPU,将其移动到 GPU 上,并进行 DataParallel 包装。
⑥ define_D
def define_D(input_nc, ndf, which_model_netD,
n_layers_D=3, norm='batch', use_sigmoid=False, gpu_ids=[], patch=False):
# 定义多层鉴别器
netD = None
use_gpu = len(gpu_ids) > 0
norm_layer = get_norm_layer(norm_type=norm)
if use_gpu:
assert (torch.cuda.is_available())
if which_model_netD == 'basic':
netD = NLayerDiscriminator(input_nc, ndf, n_layers=3, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_sigmoid=use_sigmoid,
gpu_ids=gpu_ids)
elif which_model_netD == 'n_layers':
netD = NLayerDiscriminator(input_nc, ndf, n_layers_D, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_sigmoid=use_sigmoid,
gpu_ids=gpu_ids)
elif which_model_netD == 'no_norm':
netD = NoNormDiscriminator(input_nc, ndf, n_layers_D, use_sigmoid=use_sigmoid, gpu_ids=gpu_ids)
elif which_model_netD == 'no_norm_4':
netD = NoNormDiscriminator(input_nc, ndf, n_layers_D, use_sigmoid=use_sigmoid, gpu_ids=gpu_ids)
elif which_model_netD == 'no_patchgan':
netD = FCDiscriminator(input_nc, ndf, n_layers_D, use_sigmoid=use_sigmoid, gpu_ids=gpu_ids, patch=patch)
else:
raise NotImplementedError('Discriminator model name [%s] is not recognized' %
which_model_netD)
if use_gpu:
netD.cuda(device=gpu_ids[0])
netD = torch.nn.DataParallel(netD, gpu_ids)
netD.apply(weights_init)
return netD这段代码主要作用是定义了一个判别器网络的创建函数 define_D。这个函数根据指定的参数创建不同类型的判别器网络,支持的判别器类型包括基础的多层判别器、带有 n 层的判别器、无归一化的判别器等。
主要参数:
input_nc:输入通道数。ndf:判别器中特征图的数量。which_model_netD:选择的判别器模型的名称。n_layers_D:判别器的层数。norm:归一化层的类型('batch'、'instance'等)。use_sigmoid:是否使用 Sigmoid 函数作为激活函数。gpu_ids:指定在哪些 GPU 上运行。patch:是否使用 patchGAN 结构。
函数首先根据输入的 which_model_netD 参数选择相应的判别器模型。然后,根据其他参数,如归一化类型、是否使用 Sigmoid 等,构建判别器。最后,将判别器应用权重初始化,如果指定了 GPU,将其移动到 GPU 上,并进行 DataParallel 包装。
⑦ print_network
def print_network(net):
num_params = 0
for param in net.parameters():
num_params += param.numel()
print(net)
print('Total number of parameters: %d' % num_params)这段代码主要作用是用于打印神经网络的结构信息和总参数数量。
🎄2.2 Class
①class GANLoss
class GANLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, use_lsgan=True, target_real_label=1.0, target_fake_label=0.0,
tensor=torch.FloatTensor):
super(GANLoss, self).__init__()
self.real_label = target_real_label # 真实标签为1
self.fake_label = target_fake_label # 虚假标签为0
self.real_label_var = None
self.fake_label_var = None
self.Tensor = tensor
if use_lsgan: # 是否使用lsgan的loss损失
self.loss = nn.MSELoss()
else:
self.loss = nn.BCELoss()
def get_target_tensor(self, input, target_is_real): # 获取目标标签张量
target_tensor = None
if target_is_real: # 表示获取真实标签的目标张量
create_label = ((self.real_label_var is None) or
(self.real_label_var.numel() != input.numel()))
if create_label:
real_tensor = self.Tensor(input.size()).fill_(self.real_label)
# 创建一个形状与输入相同的张量,
# 并填充为真实标签值,
# 然后将其封装为不可训练的 PyTorch 变量 Variable,
# 并赋值给 self.real_label_var。
# 最终,返回真实标签变量 self.real_label_var。
self.real_label_var = Variable(real_tensor, requires_grad=False)
target_tensor = self.real_label_var
else: # 表示获取生成标签的目标张量
create_label = ((self.fake_label_var is None) or
(self.fake_label_var.numel() != input.numel()))
if create_label:
fake_tensor = self.Tensor(input.size()).fill_(self.fake_label)
# 创建一个形状与输入相同的张量,
# 并填充为生成标签值,
# 然后将其封装为不可训练的 PyTorch 变量Variable,
# 并赋值给 self.fake_label_var。
# 最终,返回生成标签变量 self.fake_label_var 。
self.fake_label_var = Variable(fake_tensor, requires_grad=False)
target_tensor = self.fake_label_var
return target_tensor
def __call__(self, input, target_is_real):
target_tensor = self.get_target_tensor(input, target_is_real)
return self.loss(input, target_tensor)
这段代码主要作用是定义了一个 GAN 损失的类 GANLoss,用于计算生成对抗网络 (GAN) 的生成器和判别器的损失。
主要参数:
use_lsgan:一个布尔值,表示是否使用均方误差损失(True)还是二进制交叉熵损失(False)。target_real_label:真实标签的目标值,默认为1.0。target_fake_label:生成标签的目标值,默认为0.0。tensor:用于创建标签张量的 PyTorch 张量类型,默认为torch.FloatTensor。
主要方法和属性包括:
loss:根据use_lsgan初始化的时候选择使用 MSELoss 还是 BCELoss。get_target_tensor:用于获取目标标签张量,根据target_is_real和类内部的真假标签值。__call__:计算 GAN 损失,传入输入张量input和一个布尔值target_is_real,表示是否计算真实标签的损失。
② class DiscLossWGANGP
class DiscLossWGANGP():
def __init__(self):
self.LAMBDA = 10
def name(self):
return 'DiscLossWGAN-GP'
def initialize(self, opt, tensor):
# DiscLossLS.initialize(self, opt, tensor)
self.LAMBDA = 10
# def get_g_loss(self, net, realA, fakeB):
# # First, G(A) should fake the discriminator
# self.D_fake = net.forward(fakeB)
# return -self.D_fake.mean()
def calc_gradient_penalty(self, netD, real_data, fake_data):
alpha = torch.rand(1, 1)
alpha = alpha.expand(real_data.size())
alpha = alpha.cuda()
interpolates = alpha * real_data + ((1 - alpha) * fake_data)
interpolates = interpolates.cuda()
interpolates = Variable(interpolates, requires_grad=True)
disc_interpolates = netD.forward(interpolates)
gradients = torch.autograd.grad(outputs=disc_interpolates, inputs=interpolates,
grad_outputs=torch.ones(disc_interpolates.size()).cuda(),
create_graph=True, retain_graph=True, only_inputs=True)[0]
gradient_penalty = ((gradients.norm(2, dim=1) - 1) ** 2).mean() * self.LAMBDA
return gradient_penalty
这段代码主要作用是定义了一个用于计算 Wasserstein GAN with Gradient Penalty (WGAN-GP) 损失的类 DiscLossWGANGP。
主要的方法和属性包括:
__init__:构造函数,初始化LAMBDA参数,该参数用于控制渐变惩罚的强度,默认为10。name:返回损失的名称,这里为 'DiscLossWGAN-GP'。initialize:初始化方法,用于设定一些参数。在这里,对LAMBDA进行了重新设置为10。calc_gradient_penalty:计算渐变惩罚项的方法。该方法接受判别器网络netD、真实数据real_data和生成数据fake_data作为输入。首先,通过插值方法创建一个介于真实数据和生成数据之间的样本集合。然后,计算这些插值样本通过判别器的输出,并计算相对于插值样本的梯度。最终,计算渐变惩罚项,即梯度的范数减1的平方的均值乘以LAMBDA参数。
③ class ResnetGenerator
class ResnetGenerator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_nc, output_nc, ngf=64, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, use_dropout=False, n_blocks=6,
gpu_ids=[], padding_type='reflect'):
assert (n_blocks >= 0)
super(ResnetGenerator, self).__init__()
self.input_nc = input_nc
self.output_nc = output_nc
self.ngf = ngf
self.gpu_ids = gpu_ids
model = [nn.ReflectionPad2d(3),
nn.Conv2d(input_nc, ngf, kernel_size=7, padding=0),
norm_layer(ngf),
nn.ReLU(True)]
n_downsampling = 2
for i in range(n_downsampling):
mult = 2 ** i
model += [nn.Conv2d(ngf * mult, ngf * mult * 2, kernel_size=3,
stride=2, padding=1),
norm_layer(ngf * mult * 2),
nn.ReLU(True)]
mult = 2 ** n_downsampling
for i in range(n_blocks):
model += [
ResnetBlock(ngf * mult, padding_type=padding_type, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout)]
for i in range(n_downsampling):
mult = 2 ** (n_downsampling - i)
model += [nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf * mult, int(ngf * mult / 2),
kernel_size=3, stride=2,
padding=1, output_padding=1),
norm_layer(int(ngf * mult / 2)),
nn.ReLU(True)]
model += [nn.ReflectionPad2d(3)]
model += [nn.Conv2d(ngf, output_nc, kernel_size=7, padding=0)]
model += [nn.Tanh()]
self.model = nn.Sequential(*model)
def forward(self, input):
if self.gpu_ids and isinstance(input.data, torch.cuda.FloatTensor):
return nn.parallel.data_parallel(self.model, input, self.gpu_ids)
else:
return self.model(input)
这段代码主要作用是定义一个生成器网络类 ResnetGenerator,用于实现带残差块的生成器结构。生成器的主要目标是将输入图像转换为目标域的图像。
主要参数和方法包括:
-
__init__:构造函数,定义了生成器的结构。接受一系列参数,包括输入通道数input_nc,输出通道数output_nc,生成器的特征数ngf,规范化层norm_layer,是否使用 dropoutuse_dropout,残差块的数量n_blocks,GPU 设备的列表gpu_ids以及填充类型padding_type。 -
forward:前向传播方法,将输入张量通过生成器网络进行转换。在这里,根据是否使用 GPU,选择在单个 GPU 上运行或在多个 GPU 上并行运行。
生成器的网络结构包括:
- 一个反射填充层 (
ReflectionPad2d),将输入图像进行填充。 - 一个卷积层 (
Conv2d),将填充后的输入映射到特征图,使用 ReLU 激活函数。 - 一系列下采样层 (
Conv2d,规范化层,ReLU 激活函数),通过多个下采样层减小特征图的大小。 - 一系列残差块 (
ResnetBlock),通过多个残差块学习图像的细节和结构。 - 一系列上采样层 (
ConvTranspose2d,规范化层,ReLU 激活函数),通过多个上采样层增加特征图的大小。 - 一个反射填充层 (
ReflectionPad2d)。 - 一个卷积层 (
Conv2d),将最终的特征图映射到输出通道。 - Tanh 激活函数,将输出限制在 -1 到 1 的范围内。
④? class ResnetBlock
class ResnetBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, padding_type, norm_layer, use_dropout):
super(ResnetBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv_block = self.build_conv_block(dim, padding_type, norm_layer, use_dropout)
def build_conv_block(self, dim, padding_type, norm_layer, use_dropout):
conv_block = []
p = 0
if padding_type == 'reflect':
conv_block += [nn.ReflectionPad2d(1)]
elif padding_type == 'replicate':
conv_block += [nn.ReplicationPad2d(1)]
elif padding_type == 'zero':
p = 1
else:
raise NotImplementedError('padding [%s] is not implemented' % padding_type)
conv_block += [nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, kernel_size=3, padding=p),
norm_layer(dim),
nn.ReLU(True)]
if use_dropout:
conv_block += [nn.Dropout(0.5)]
p = 0
if padding_type == 'reflect':
conv_block += [nn.ReflectionPad2d(1)]
elif padding_type == 'replicate':
conv_block += [nn.ReplicationPad2d(1)]
elif padding_type == 'zero':
p = 1
else:
raise NotImplementedError('padding [%s] is not implemented' % padding_type)
conv_block += [nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, kernel_size=3, padding=p),
norm_layer(dim)]
return nn.Sequential(*conv_block)
def forward(self, x):
out = x + self.conv_block(x)
return out这段代码主要作用是定义 ResNet 块的类 ResnetBlock,用于构建生成器中的残差连接块。每个 ResNet 块包含两个卷积层,每个卷积层后跟着归一化层和 ReLU 激活函数。
⑤?class UnetGenerator
class UnetGenerator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_nc, output_nc, num_downs, ngf=64,
norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, use_dropout=False, gpu_ids=[], skip=False, opt=None):
super(UnetGenerator, self).__init__()
self.gpu_ids = gpu_ids
self.opt = opt
# currently support only input_nc == output_nc
assert (input_nc == output_nc)
# construct unet structure
unet_block = UnetSkipConnectionBlock(ngf * 8, ngf * 8, norm_layer=norm_layer, innermost=True, opt=opt)
for i in range(num_downs - 5):
unet_block = UnetSkipConnectionBlock(ngf * 8, ngf * 8, unet_block, norm_layer=norm_layer,
use_dropout=use_dropout, opt=opt)
unet_block = UnetSkipConnectionBlock(ngf * 4, ngf * 8, unet_block, norm_layer=norm_layer, opt=opt)
unet_block = UnetSkipConnectionBlock(ngf * 2, ngf * 4, unet_block, norm_layer=norm_layer, opt=opt)
unet_block = UnetSkipConnectionBlock(ngf, ngf * 2, unet_block, norm_layer=norm_layer, opt=opt)
unet_block = UnetSkipConnectionBlock(output_nc, ngf, unet_block, outermost=True, norm_layer=norm_layer, opt=opt)
if skip == True:
skipmodule = SkipModule(unet_block, opt)
self.model = skipmodule
else:
self.model = unet_block
def forward(self, input):
if self.gpu_ids and isinstance(input.data, torch.cuda.FloatTensor):
return nn.parallel.data_parallel(self.model, input, self.gpu_ids)
else:
return self.model(input)这段代码主要作用是实现 U-Net 生成器的类 UnetGenerator,用于图像到图像的转换任务。
U-Net 生成器的结构包括:
- 通过堆叠多个
UnetSkipConnectionBlock模块实现 U-Net 结构。 - 对于每个下采样,都使用
UnetSkipConnectionBlock模块进行堆叠。 - 最终的输出通道数为
output_nc。
如果设置了 skip 参数为 True,则会使用 SkipModule 对 U-Net 结构进行进一步的封装。
⑥ class SkipModule
class SkipModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, submodule, opt):
super(SkipModule, self).__init__()
self.submodule = submodule
self.opt = opt
def forward(self, x):
latent = self.submodule(x)
return self.opt.skip * x + latent, latent这段代码主要作用是通过SkipModule?模块添加跳跃连接。
⑦ class UnetSkipConnectionBlock
class UnetSkipConnectionBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, outer_nc, inner_nc,
submodule=None, outermost=False, innermost=False, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, use_dropout=False,
opt=None):
super(UnetSkipConnectionBlock, self).__init__()
self.outermost = outermost
downconv = nn.Conv2d(outer_nc, inner_nc, kernel_size=4,
stride=2, padding=1)
downrelu = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)
downnorm = norm_layer(inner_nc)
uprelu = nn.ReLU(True)
upnorm = norm_layer(outer_nc)
if opt.use_norm == 0:
if outermost:
upconv = nn.ConvTranspose2d(inner_nc * 2, outer_nc,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=1)
down = [downconv]
up = [uprelu, upconv, nn.Tanh()]
model = down + [submodule] + up
elif innermost:
upconv = nn.ConvTranspose2d(inner_nc, outer_nc,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=1)
down = [downrelu, downconv]
up = [uprelu, upconv]
model = down + up
else:
upconv = nn.ConvTranspose2d(inner_nc * 2, outer_nc,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=1)
down = [downrelu, downconv]
up = [uprelu, upconv]
if use_dropout:
model = down + [submodule] + up + [nn.Dropout(0.5)]
else:
model = down + [submodule] + up
else:
if outermost:
upconv = nn.ConvTranspose2d(inner_nc * 2, outer_nc,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=1)
down = [downconv]
up = [uprelu, upconv, nn.Tanh()]
model = down + [submodule] + up
elif innermost:
upconv = nn.ConvTranspose2d(inner_nc, outer_nc,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=1)
down = [downrelu, downconv]
up = [uprelu, upconv, upnorm]
model = down + up
else:
upconv = nn.ConvTranspose2d(inner_nc * 2, outer_nc,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=1)
down = [downrelu, downconv, downnorm]
up = [uprelu, upconv, upnorm]
if use_dropout:
model = down + [submodule] + up + [nn.Dropout(0.5)]
else:
model = down + [submodule] + up
self.model = nn.Sequential(*model)
def forward(self, x):
if self.outermost:
return self.model(x)
else:
return torch.cat([self.model(x), x], 1)这段代码主要作用是通过UnetSkipConnectionBlock?模块构建 U-Net 中的下采样和上采样块。它可以包含子模块,并具有跳跃连接。
主要参数:
outer_nc:??输出通道数。inner_nc:??内部通道数。submodule:??可选的子模块。outermost:??是否为最外层模块。innermost:??是否为最内层模块。norm_layer:??规范化层的类型。use_dropout:??是否使用 dropout。opt:? 一些其他选项。
该模块包含以下组件:
- 下采样(卷积、LeakyReLU、规范化)。
- 子模块(如果存在)。
- 上采样(ReLU、转置卷积、Tanh)。
⑧ class NLayerDiscriminator
class NLayerDiscriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_nc, ndf=64, n_layers=3, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, use_sigmoid=False, gpu_ids=[]):
super(NLayerDiscriminator, self).__init__()
self.gpu_ids = gpu_ids
kw = 4
padw = int(np.ceil((kw - 1) / 2))
sequence = [
nn.Conv2d(input_nc, ndf, kernel_size=kw, stride=2, padding=padw),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)
]
nf_mult = 1
nf_mult_prev = 1
for n in range(1, n_layers):
nf_mult_prev = nf_mult
nf_mult = min(2 ** n, 8)
sequence += [
nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult_prev, ndf * nf_mult,
kernel_size=kw, stride=2, padding=padw),
norm_layer(ndf * nf_mult),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)
]
nf_mult_prev = nf_mult
nf_mult = min(2 ** n_layers, 8)
sequence += [
nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult_prev, ndf * nf_mult,
kernel_size=kw, stride=1, padding=padw),
norm_layer(ndf * nf_mult),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)
]
sequence += [nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult, 1, kernel_size=kw, stride=1, padding=padw)]
if use_sigmoid:
sequence += [nn.Sigmoid()]
self.model = nn.Sequential(*sequence)
def forward(self, input):
# if len(self.gpu_ids) and isinstance(input.data, torch.cuda.FloatTensor):
# return nn.parallel.data_parallel(self.model, input, self.gpu_ids)
# else:
return self.model(input)这段代码主要作用是通过NLayerDiscriminator?多层鉴别器模块判别输入图像的真实性。它包含多个卷积层,每一层都包括卷积、规范化和 LeakyReLU 激活函数。
主要参数:
input_nc:? 输入通道数。ndf:? 初始卷积层的输出通道数。n_layers:? 鉴别器包含的卷积层的数量。norm_layer:? 规范化层的类型。use_sigmoid:? 是否在输出层使用 Sigmoid 激活函数。gpu_ids:? GPU 的 ID 列表。
该模块的结构包括:
- 初始卷积层:输入图像经过一个卷积层,然后应用 LeakyReLU 激活函数。
- 多个卷积块:每个卷积块包括卷积层、规范化层和 LeakyReLU 激活函数。这些卷积块用于逐渐降低特征图的空间分辨率。
- 最终卷积层:最后一个卷积块后有一个额外的卷积层,用于生成最终的鉴别输出。
- Sigmoid 激活函数(可选):如果
use_sigmoid为True,则在最后添加 Sigmoid 激活函数。
⑨ class NoNormDiscriminator
class NoNormDiscriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_nc, ndf=64, n_layers=3, use_sigmoid=False, gpu_ids=[]):
super(NoNormDiscriminator, self).__init__()
self.gpu_ids = gpu_ids
kw = 4
padw = int(np.ceil((kw - 1) / 2))
sequence = [
nn.Conv2d(input_nc, ndf, kernel_size=kw, stride=2, padding=padw),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)
]
nf_mult = 1
nf_mult_prev = 1
for n in range(1, n_layers):
nf_mult_prev = nf_mult
nf_mult = min(2 ** n, 8)
sequence += [
nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult_prev, ndf * nf_mult,
kernel_size=kw, stride=2, padding=padw),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)
]
nf_mult_prev = nf_mult
nf_mult = min(2 ** n_layers, 8)
sequence += [
nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult_prev, ndf * nf_mult,
kernel_size=kw, stride=1, padding=padw),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)
]
sequence += [nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult, 1, kernel_size=kw, stride=1, padding=padw)]
if use_sigmoid:
sequence += [nn.Sigmoid()]
self.model = nn.Sequential(*sequence)
def forward(self, input):
# if len(self.gpu_ids) and isinstance(input.data, torch.cuda.FloatTensor):
# return nn.parallel.data_parallel(self.model, input, self.gpu_ids)
# else:
return self.model(input)NoNormDiscriminator 是一个没有规范化层的鉴别器模块。它与 NLayerDiscriminator 的区别在于去除了规范化层,每个卷积层后面直接接 LeakyReLU 激活函数。
?⑩ class FCDiscriminator
class FCDiscriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_nc, ndf=64, n_layers=3, use_sigmoid=False, gpu_ids=[], patch=False):
super(FCDiscriminator, self).__init__()
self.gpu_ids = gpu_ids
self.use_sigmoid = use_sigmoid
kw = 4
padw = int(np.ceil((kw - 1) / 2))
sequence = [
nn.Conv2d(input_nc, ndf, kernel_size=kw, stride=2, padding=padw),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)
]
nf_mult = 1
nf_mult_prev = 1
for n in range(1, n_layers):
nf_mult_prev = nf_mult
nf_mult = min(2 ** n, 8)
sequence += [
nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult_prev, ndf * nf_mult,
kernel_size=kw, stride=2, padding=padw),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)
]
nf_mult_prev = nf_mult
nf_mult = min(2 ** n_layers, 8)
sequence += [
nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult_prev, ndf * nf_mult,
kernel_size=kw, stride=1, padding=padw),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)
]
sequence += [nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult, 1, kernel_size=kw, stride=1, padding=padw)]
if patch:
self.linear = nn.Linear(7 * 7, 1)
else:
self.linear = nn.Linear(13 * 13, 1)
if use_sigmoid:
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
self.model = nn.Sequential(*sequence)
def forward(self, input):
batchsize = input.size()[0]
output = self.model(input)
output = output.view(batchsize, -1)
# print(output.size())
output = self.linear(output)
if self.use_sigmoid:
print("sigmoid")
output = self.sigmoid(output)
return outputFCDiscriminator 是一个基于卷积神经网络的鉴别器模块,用于图像分类任务。它的主要特点是可以根据 patch 参数选择输出全局分类还是局部分类。
???class Unet_resize_conv
class Unet_resize_conv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, opt, skip):
super(Unet_resize_conv, self).__init__()
self.opt = opt
self.skip = skip
p = 1
# self.conv1_1 = nn.Conv2d(4, 32, 3, padding=p)
if opt.self_attention:
self.conv1_1 = nn.Conv2d(4, 32, 3, padding=p)
# self.conv1_1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 32, 3, padding=p)
self.downsample_1 = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.downsample_2 = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.downsample_3 = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.downsample_4 = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
else:
self.conv1_1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 32, 3, padding=p)
self.LReLU1_1 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
if self.opt.use_norm == 1:
self.bn1_1 = SynBN2d(32) if self.opt.syn_norm else nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
self.conv1_2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, 3, padding=p)
self.LReLU1_2 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
if self.opt.use_norm == 1:
self.bn1_2 = SynBN2d(32) if self.opt.syn_norm else nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
self.max_pool1 = nn.AvgPool2d(2) if self.opt.use_avgpool == 1 else nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.conv2_1 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3, padding=p)
self.LReLU2_1 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
if self.opt.use_norm == 1:
self.bn2_1 = SynBN2d(64) if self.opt.syn_norm else nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.conv2_2 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, 3, padding=p)
self.LReLU2_2 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
if self.opt.use_norm == 1:
self.bn2_2 = SynBN2d(64) if self.opt.syn_norm else nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.max_pool2 = nn.AvgPool2d(2) if self.opt.use_avgpool == 1 else nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.conv3_1 = nn.Conv2d(64, 128, 3, padding=p)
self.LReLU3_1 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
if self.opt.use_norm == 1:
self.bn3_1 = SynBN2d(128) if self.opt.syn_norm else nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
self.conv3_2 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, 3, padding=p)
self.LReLU3_2 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
if self.opt.use_norm == 1:
self.bn3_2 = SynBN2d(128) if self.opt.syn_norm else nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
self.max_pool3 = nn.AvgPool2d(2) if self.opt.use_avgpool == 1 else nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.conv4_1 = nn.Conv2d(128, 256, 3, padding=p)
self.LReLU4_1 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
if self.opt.use_norm == 1:
self.bn4_1 = SynBN2d(256) if self.opt.syn_norm else nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
self.conv4_2 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, 3, padding=p)
self.LReLU4_2 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
if self.opt.use_norm == 1:
self.bn4_2 = SynBN2d(256) if self.opt.syn_norm else nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
self.max_pool4 = nn.AvgPool2d(2) if self.opt.use_avgpool == 1 else nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.conv5_1 = nn.Conv2d(256, 512, 3, padding=p)
self.LReLU5_1 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
if self.opt.use_norm == 1:
self.bn5_1 = SynBN2d(512) if self.opt.syn_norm else nn.BatchNorm2d(512)
self.conv5_2 = nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3, padding=p)
self.LReLU5_2 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
if self.opt.use_norm == 1:
self.bn5_2 = SynBN2d(512) if self.opt.syn_norm else nn.BatchNorm2d(512)
# self.deconv5 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(512, 256, 2, stride=2)
self.deconv5 = nn.Conv2d(512, 256, 3, padding=p)
self.conv6_1 = nn.Conv2d(512, 256, 3, padding=p)
self.LReLU6_1 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
if self.opt.use_norm == 1:
self.bn6_1 = SynBN2d(256) if self.opt.syn_norm else nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
self.conv6_2 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, 3, padding=p)
self.LReLU6_2 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
if self.opt.use_norm == 1:
self.bn6_2 = SynBN2d(256) if self.opt.syn_norm else nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
# self.deconv6 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(256, 128, 2, stride=2)
self.deconv6 = nn.Conv2d(256, 128, 3, padding=p)
self.conv7_1 = nn.Conv2d(256, 128, 3, padding=p)
self.LReLU7_1 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
if self.opt.use_norm == 1:
self.bn7_1 = SynBN2d(128) if self.opt.syn_norm else nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
self.conv7_2 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, 3, padding=p)
self.LReLU7_2 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
if self.opt.use_norm == 1:
self.bn7_2 = SynBN2d(128) if self.opt.syn_norm else nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
# self.deconv7 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(128, 64, 2, stride=2)
self.deconv7 = nn.Conv2d(128, 64, 3, padding=p)
self.conv8_1 = nn.Conv2d(128, 64, 3, padding=p)
self.LReLU8_1 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
if self.opt.use_norm == 1:
self.bn8_1 = SynBN2d(64) if self.opt.syn_norm else nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.conv8_2 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, 3, padding=p)
self.LReLU8_2 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
if self.opt.use_norm == 1:
self.bn8_2 = SynBN2d(64) if self.opt.syn_norm else nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
# self.deconv8 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(64, 32, 2, stride=2)
self.deconv8 = nn.Conv2d(64, 32, 3, padding=p)
self.conv9_1 = nn.Conv2d(64, 32, 3, padding=p)
self.LReLU9_1 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
if self.opt.use_norm == 1:
self.bn9_1 = SynBN2d(32) if self.opt.syn_norm else nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
self.conv9_2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, 3, padding=p)
self.LReLU9_2 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)
self.conv10 = nn.Conv2d(32, 3, 1)
if self.opt.tanh:
self.tanh = nn.Tanh()
def depth_to_space(self, input, block_size):
block_size_sq = block_size * block_size
output = input.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
(batch_size, d_height, d_width, d_depth) = output.size()
s_depth = int(d_depth / block_size_sq)
s_width = int(d_width * block_size)
s_height = int(d_height * block_size)
t_1 = output.resize(batch_size, d_height, d_width, block_size_sq, s_depth)
spl = t_1.split(block_size, 3)
stack = [t_t.resize(batch_size, d_height, s_width, s_depth) for t_t in spl]
output = torch.stack(stack, 0).transpose(0, 1).permute(0, 2, 1, 3, 4).resize(batch_size, s_height, s_width,
s_depth)
output = output.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
return output
def forward(self, input, gray):
flag = 0
if input.size()[3] > 2200:
avg = nn.AvgPool2d(2)
input = avg(input)
gray = avg(gray)
flag = 1
# pass
input, pad_left, pad_right, pad_top, pad_bottom = pad_tensor(input)
gray, pad_left, pad_right, pad_top, pad_bottom = pad_tensor(gray)
if self.opt.self_attention:
gray_2 = self.downsample_1(gray)
gray_3 = self.downsample_2(gray_2)
gray_4 = self.downsample_3(gray_3)
gray_5 = self.downsample_4(gray_4)
if self.opt.use_norm == 1:
if self.opt.self_attention:
x = self.bn1_1(self.LReLU1_1(self.conv1_1(torch.cat((input, gray), 1))))
# x = self.bn1_1(self.LReLU1_1(self.conv1_1(input)))
else:
x = self.bn1_1(self.LReLU1_1(self.conv1_1(input)))
conv1 = self.bn1_2(self.LReLU1_2(self.conv1_2(x)))
x = self.max_pool1(conv1)
x = self.bn2_1(self.LReLU2_1(self.conv2_1(x)))
conv2 = self.bn2_2(self.LReLU2_2(self.conv2_2(x)))
x = self.max_pool2(conv2)
x = self.bn3_1(self.LReLU3_1(self.conv3_1(x)))
conv3 = self.bn3_2(self.LReLU3_2(self.conv3_2(x)))
x = self.max_pool3(conv3)
x = self.bn4_1(self.LReLU4_1(self.conv4_1(x)))
conv4 = self.bn4_2(self.LReLU4_2(self.conv4_2(x)))
x = self.max_pool4(conv4)
x = self.bn5_1(self.LReLU5_1(self.conv5_1(x)))
x = x * gray_5 if self.opt.self_attention else x
conv5 = self.bn5_2(self.LReLU5_2(self.conv5_2(x)))
conv5 = F.upsample(conv5, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear')
conv4 = conv4 * gray_4 if self.opt.self_attention else conv4
up6 = torch.cat([self.deconv5(conv5), conv4], 1)
x = self.bn6_1(self.LReLU6_1(self.conv6_1(up6)))
conv6 = self.bn6_2(self.LReLU6_2(self.conv6_2(x)))
conv6 = F.upsample(conv6, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear')
conv3 = conv3 * gray_3 if self.opt.self_attention else conv3
up7 = torch.cat([self.deconv6(conv6), conv3], 1)
x = self.bn7_1(self.LReLU7_1(self.conv7_1(up7)))
conv7 = self.bn7_2(self.LReLU7_2(self.conv7_2(x)))
conv7 = F.upsample(conv7, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear')
conv2 = conv2 * gray_2 if self.opt.self_attention else conv2
up8 = torch.cat([self.deconv7(conv7), conv2], 1)
x = self.bn8_1(self.LReLU8_1(self.conv8_1(up8)))
conv8 = self.bn8_2(self.LReLU8_2(self.conv8_2(x)))
conv8 = F.upsample(conv8, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear')
conv1 = conv1 * gray if self.opt.self_attention else conv1
up9 = torch.cat([self.deconv8(conv8), conv1], 1)
x = self.bn9_1(self.LReLU9_1(self.conv9_1(up9)))
conv9 = self.LReLU9_2(self.conv9_2(x))
latent = self.conv10(conv9)
if self.opt.times_residual:
latent = latent * gray
# output = self.depth_to_space(conv10, 2)
if self.opt.tanh:
latent = self.tanh(latent)
if self.skip:
if self.opt.linear_add:
if self.opt.latent_threshold:
latent = F.relu(latent)
elif self.opt.latent_norm:
latent = (latent - torch.min(latent)) / (torch.max(latent) - torch.min(latent))
input = (input - torch.min(input)) / (torch.max(input) - torch.min(input))
output = latent + input * self.opt.skip
output = output * 2 - 1
else:
if self.opt.latent_threshold:
latent = F.relu(latent)
elif self.opt.latent_norm:
latent = (latent - torch.min(latent)) / (torch.max(latent) - torch.min(latent))
output = latent + input * self.opt.skip
else:
output = latent
if self.opt.linear:
output = output / torch.max(torch.abs(output))
elif self.opt.use_norm == 0:
if self.opt.self_attention:
x = self.LReLU1_1(self.conv1_1(torch.cat((input, gray), 1)))
else:
x = self.LReLU1_1(self.conv1_1(input))
conv1 = self.LReLU1_2(self.conv1_2(x))
x = self.max_pool1(conv1)
x = self.LReLU2_1(self.conv2_1(x))
conv2 = self.LReLU2_2(self.conv2_2(x))
x = self.max_pool2(conv2)
x = self.LReLU3_1(self.conv3_1(x))
conv3 = self.LReLU3_2(self.conv3_2(x))
x = self.max_pool3(conv3)
x = self.LReLU4_1(self.conv4_1(x))
conv4 = self.LReLU4_2(self.conv4_2(x))
x = self.max_pool4(conv4)
x = self.LReLU5_1(self.conv5_1(x))
x = x * gray_5 if self.opt.self_attention else x
conv5 = self.LReLU5_2(self.conv5_2(x))
conv5 = F.upsample(conv5, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear')
conv4 = conv4 * gray_4 if self.opt.self_attention else conv4
up6 = torch.cat([self.deconv5(conv5), conv4], 1)
x = self.LReLU6_1(self.conv6_1(up6))
conv6 = self.LReLU6_2(self.conv6_2(x))
conv6 = F.upsample(conv6, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear')
conv3 = conv3 * gray_3 if self.opt.self_attention else conv3
up7 = torch.cat([self.deconv6(conv6), conv3], 1)
x = self.LReLU7_1(self.conv7_1(up7))
conv7 = self.LReLU7_2(self.conv7_2(x))
conv7 = F.upsample(conv7, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear')
conv2 = conv2 * gray_2 if self.opt.self_attention else conv2
up8 = torch.cat([self.deconv7(conv7), conv2], 1)
x = self.LReLU8_1(self.conv8_1(up8))
conv8 = self.LReLU8_2(self.conv8_2(x))
conv8 = F.upsample(conv8, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear')
conv1 = conv1 * gray if self.opt.self_attention else conv1
up9 = torch.cat([self.deconv8(conv8), conv1], 1)
x = self.LReLU9_1(self.conv9_1(up9))
conv9 = self.LReLU9_2(self.conv9_2(x))
latent = self.conv10(conv9)
if self.opt.times_residual:
latent = latent * gray
if self.opt.tanh:
latent = self.tanh(latent)
if self.skip:
if self.opt.linear_add:
if self.opt.latent_threshold:
latent = F.relu(latent)
elif self.opt.latent_norm:
latent = (latent - torch.min(latent)) / (torch.max(latent) - torch.min(latent))
input = (input - torch.min(input)) / (torch.max(input) - torch.min(input))
output = latent + input * self.opt.skip
output = output * 2 - 1
else:
if self.opt.latent_threshold:
latent = F.relu(latent)
elif self.opt.latent_norm:
latent = (latent - torch.min(latent)) / (torch.max(latent) - torch.min(latent))
output = latent + input * self.opt.skip
else:
output = latent
if self.opt.linear:
output = output / torch.max(torch.abs(output))
output = pad_tensor_back(output, pad_left, pad_right, pad_top, pad_bottom)
latent = pad_tensor_back(latent, pad_left, pad_right, pad_top, pad_bottom)
gray = pad_tensor_back(gray, pad_left, pad_right, pad_top, pad_bottom)
if flag == 1:
output = F.upsample(output, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear')
gray = F.upsample(gray, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear')
if self.skip:
return output, latent
else:
return output
这段代码主要作用是定义了一个Unet_resize_conv类,用于图像处理任务的深度学习模型,通常用于图像分割等任务。
代码的主要结构和功能:
-
初始化函数 (
__init__):
- 接受两个参数
opt和skip。 - 初始化模型的一些参数,包括选择是否使用自注意力机制(
opt.self_attention)、是否使用归一化(opt.use_norm)、是否使用平均池化(opt.use_avgpool)等。
-
前向传播函数 (
forward):
- 接受两个输入张量
input和gray。 - 根据输入的配置参数进行一系列卷积、激活函数、归一化等操作,构建了一个 U-Net 结构的神经网络。
- 根据模型配置选择是否使用自注意力机制。
- 最终输出图像结果。
-
深度到空间函数 (
depth_to_space):
- 用于将深度张量转换为空间张量。通常在图像处理任务中,将高分辨率图像转换为低分辨率图像时使用。
-
一些辅助函数:
- 例如,对输入进行填充(
pad_tensor)和反向填充(pad_tensor_back)等。
剩下非重点的就不再解读了~
🚀三、EnlightenGAN源码运行
在本文最上面已经放了项目地址,作者给出了源码,数据集等,这些都可以在里面下载到,ReadMe中也给出了详细的运行方法,对小白来说还是比较友好的。
我跑的过程没记录,哈哈~
这块网上有很多博主讲解的比较详细,大家可以参考一下:
EnlightenGAN训练复现记录_enlightengan代码复现-CSDN博客
代码调试记录EnlightenGAN 一_代码调试记录怎么写-CSDN博客
EnlightenGAN的运行环境搭建和训练自己的数据 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
EnlightenGAN的代码运行过程问题记录_enlightengan运行不了-CSDN博客
踩坑记录:
实现效果:

可以看到,增强效果还是不错滴~

本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 电子招标采购系统源码之从供应商管理到采购招投标、采购合同、采购执行的全过程数字化管理
- 常用命令-设置
- 大模型技术栈全览
- springboot集成tess4j
- 复杂网络传染动力学的深度学习
- 2018年认证杯SPSSPRO杯数学建模D题(第一阶段)投篮的最佳出手点全过程文档及程序
- 《SPSS统计学基础与实证研究应用精解》视频讲解:变量和样本观测值基本操作
- maui下sqlite演示增删改查
- 在使用springboot框架式的的script无法通过${}来获取值
- ChatGPT绘制全球植被类型分布图、生物量图、土壤概念图、处理遥感数据并绘图、病毒、植物、动物细胞结构图