1月12日&1月15日代码随想录路经总和&从中序和后序遍历构造二叉树
发布时间:2024年01月15日
112.路经总和
给你二叉树的根节点?root?和一个表示目标和的整数?targetSum?。判断该树中是否存在?根节点到叶子节点?的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和?targetSum?。如果存在,返回?true?;否则,返回?false?。
叶子节点?是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:

输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22 输出:true 解释:等于目标和的根节点到叶节点路径如上图所示。
示例 2:

输入:root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5 输出:false 解释:树中存在两条根节点到叶子节点的路径: (1 --> 2): 和为 3 (1 --> 3): 和为 4 不存在 sum = 5 的根节点到叶子节点的路径。
示例 3:
输入:root = [], targetSum = 0 输出:false 解释:由于树是空的,所以不存在根节点到叶子节点的路径。
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围?
[0, 5000]?内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
思路
深度优先搜索
递归思想就是每遍历到一个非叶子节点就把target值减去当前节点的值,递归的结束条件就是递归到叶子节点,若节点值等于target则返回true反之false,非常简单。
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root==null){
return false;
}
if(targetSum==root.val&&root.left==null&&root.right==null){
return true;
}
return hasPathSum(root.right,targetSum-root.val)||hasPathSum(root.left,targetSum-root.val);
}
}广度优先搜索
广搜的思路不是很好想,主要是这个再拿一个队列来存目前为止的路径和的想法比较难想,其他没什么变化。
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root==null){
return false;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queNode=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<Integer> queVal =new LinkedList<Integer>();
queNode.offer(root);
queVal.offer(root.val);
while(!queNode.isEmpty()){
TreeNode now=queNode.poll();
int temp=queVal.poll();
if(now.left==null&&now.right==null){
if(temp==targetSum){
return true;
}
continue;
}
if(now.left!=null){
queNode.offer(now.left);
queVal.offer(now.left.val+temp);
}
if (now.right != null) {
queNode.offer(now.right);
queVal.offer(now.right.val+temp);
}
}
return false;
}
}106.从中序和后序遍历序列构造二叉树
给定两个整数数组?inorder?和?postorder?,其中?inorder?是二叉树的中序遍历,?postorder?是同一棵树的后序遍历,请你构造并返回这颗?二叉树?。
示例 1:
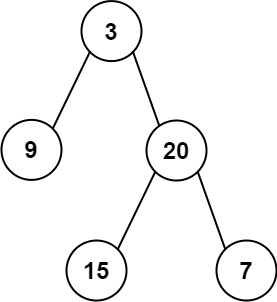
输入:inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder = [9,15,7,20,3] 输出:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
示例 2:
输入:inorder = [-1], postorder = [-1] 输出:[-1]
提示:
1 <= inorder.length <= 3000postorder.length == inorder.length-3000 <= inorder[i], postorder[i] <= 3000inorder?和?postorder?都由?不同?的值组成postorder?中每一个值都在?inorder?中inorder?保证是树的中序遍历postorder?保证是树的后序遍历
思路
递归法
直接投降,只记得408有相关内容,但早就忘完了
我们可以发现后序遍历的数组最后一个元素代表的即为根节点。知道这个性质后,我们可以利用已知的根节点信息在中序遍历的数组中找到根节点所在的下标,然后根据其将中序遍历的数组分成左右两部分,左边部分即左子树,右边部分为右子树,针对每个部分可以用同样的方法继续递归下去构造。
为了高效查找根节点元素在中序遍历数组中的下标,我们选择创建哈希表来存储中序序列,即建立一个(元素,下标)键值对的哈希表
思路就是从根节点开始构建,通过中序后序遍历数组找到左右子树,并继续递归。
class Solution {
int post_idx;
int[] postorder;
int[] inorder;
Map<Integer, Integer> idx_map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
public TreeNode helper(int in_left, int in_right) {
// 如果这里没有节点构造二叉树了,就结束
if (in_left > in_right) {
return null;
}
// 选择 post_idx 位置的元素作为当前子树根节点
int root_val = postorder[post_idx];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(root_val);
// 根据 root 所在位置分成左右两棵子树
int index = idx_map.get(root_val);
// 下标减一
post_idx--;
// 构造右子树
root.right = helper(index + 1, in_right);
// 构造左子树
root.left = helper(in_left, index - 1);
return root;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
this.postorder = postorder;
this.inorder = inorder;
// 从后序遍历的最后一个元素开始
post_idx = postorder.length - 1;
// 建立(元素,下标)键值对的哈希表
int idx = 0;
for (Integer val : inorder) {
idx_map.put(val, idx++);
}
return helper(0, inorder.length - 1);
}
}迭代法
明天更新,太难想了
总结
光是递归法就已经想不出来了,以后碰到这种题目还是要动笔找一找递归的切入角度,明天把这道递归法代码自己重新写一遍巩固一下。
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39911747/article/details/135611374
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 基于java的企业电子投票系统设计与实现
- 从0到1打造一款WebStyle串口调试工具【上篇】
- LTESniffer:一款功能强大的LTE上下行链路安全监控工具
- 鸿蒙原生应用再添新丁!中国移动 入局鸿蒙
- Selenium-java元素等待三种方式
- postgresql安装
- ModStart框架助力博客开发,全新视频教程助你轻松上手!
- 掌握 Python 异步编程:综合指南
- Python之安装和环境配置
- 能见度传感器有什么特点-交通安全的保障