c 实现jpeg中的ALI(可变长度整数转换)正反向转换
发布时间:2023年12月20日
用于DC的ALI表:DIFF 就是前后两个8X8块DC的差值,ssss就是DIFF值用二进制表示的位数
亮度,与色度的DC都是这种处理的。两个相邻的亮度与亮度比差,色度与色度比差产生DIFF,
扫描开始DIFF等于0。
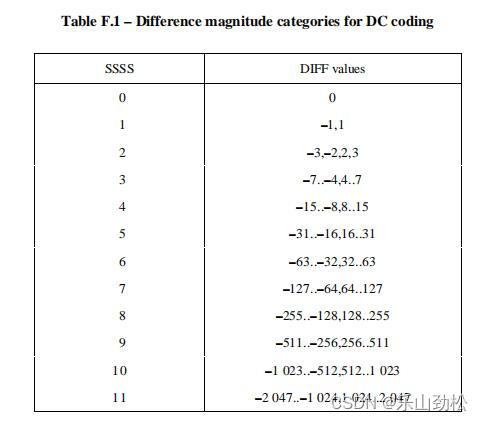
用于AC?ALI表:表中的AC 就是Z变换后(a,b)对中的b。ssss 是b值用2进制表示的位数
亮度与色度的AC都是这样处理的

对比,两者就是少了0的处理。因为AC中的0已经被(a,b)对中的a处理了。
1.把DC转换为 二进制位数加二进制的中间格式
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/videodev2.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <linux/fb.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(void) {
int i=-5;
int o=-1; //如果输出负数无意义
char len=-1; //如果输出负数无意义
if(i==0){
len=0;
}
if(i==-1){
len=1;
o=0;
}
if(i==1){
len=1;
o=1;
}
if((i>=2)&&(i<=32767)){ //二进制位数0-16位
for(int a=0;a<16;a++){
if((i>=pow(2,a))&&(i<pow(2,(a+1)))){
len=a+1;
o=i;
}
}
}
if((i>=-32767)&&(i<=-2)){
for(int a=0;a<16;a++){
if((i<=-pow(2,a))&&(i>-pow(2,(a+1)))){
len=a+1;
o=i+pow(2,(a+1))-1;
}
}
}
printf("len:%d o:%d\n",len,o);
return 0;
}2. ALI逆向转换
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/videodev2.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <linux/fb.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(void) {
int len = 4;
int i = 7;
int o;
if (len == 0) {
o = 0;
}
if ((len == 1) && (i == 0)) {
o = -1;
}
if ((len == 1) && (i == 1)) {
o = 1;
}
//--------------------------
if ((i >= pow(2, len - 1)) && (i <= pow(2, len))) {
o = i;
}
if ((i >= 0) && (i < pow(2, len - 1))) {
o = i - pow(2, len) + 1;
}
printf("o:%d ", o);
return 0;
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_59802969/article/details/135070901
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Python之PyCharm开发工具的安装与设置
- 基于梯度和频率域的深度超分辨率新方法笔记二
- 编程笔记 html5&css&js 055 CSS颜色表
- CMake入门教程【高级篇】创建自定义目标add_custom_target
- Unity 物体移动的方法
- SSM驾校预约管理系统----计算机毕业设计
- 【Python机器学习】基于随机森林全球经济危机预测
- arcEngine修改字段标注
- Spring Cloud Gateway + Nacos 灰度发布
- 了解JavaScript的执行环境及作用域