测试驱动开发:基于Jenkins+GoTest+HTML的持续化集成
目录
前言? ? ? ??
? ? ? ?目前我们的项目体系流程不够完善,我们针对这一现象引入了“测试驱动开发”观念,在开发测试部署阶段可以节省一部分工作量,对于比较复杂的场景,也可以编写一些测试工具。我们都知道如果仅靠传统的手工测试(偏功能)会存在很多的漏洞,为了提高迭代效率,引入自动化测试、CI/CD,在项目测试阶段、预上线、上线等各个阶段都能快速通过上述手段发现问题,保障产品质量。
? ? ?
一、项目框架
????????在日常测试过程中,需要验证测试环境&线上环境API接口,为了更方便,研究了通过Jenkins构建自动化项目并生成HTML报告。接下来会详细介绍项目构建步骤和遇到的问题。
1.项目迭代
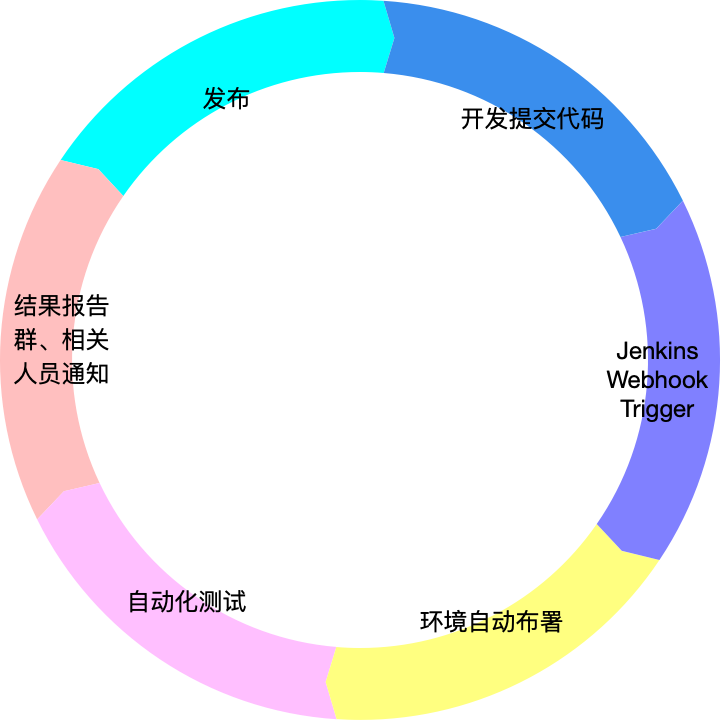
2.项目时序图

3.项目测试执行

二、项目具体实现
1.创建流水线
(1)新建任务

(2)选择流水线或者复制现有流水线任务

(3)配置流水线

(4)pipeline脚本的基本框架
#!groovy
pipeline {
????agent any
????environment {
????????GO_BINARY = "go"
????????TEST_REPORT_PATH = "test-report.xml"
????}
????stages {
????????stage('checkout') {
????????????steps {
????????????????sh"""
????????????????????echo "steps one"
????????????????"""
????????????}
????????}
????????stage('unit-test') {
????????????steps {
????????????????echo "step two"
????????????}
????????}
????????stage('api-test') {
????????????steps {
????????????????sh """
???????????????????ehco "step three"
???????????????????"""
????????????}
????????}
????}
????post {
????????always {
????????????echo "clean over..."
????????????echo "send email"
????????}
????????success {
????????????echo 'Build && Test Succeeded.'
????????}
????????failure {
????????????echo 'Build && Test Failured.'
????????}
????}
}对应在jenkins上的阶段视图:

2.拉取代码
repoURL = "git拉取代码地址"
rootPath = "/var/jenkins_work/workspace/pid-openapi-test-report"
repoPath = "${rootPath}/$BUILD_ID"
...
stages {
????stage('checkout') {
????????steps {
????????????sh"""
????????????????export PATH="${arcPath}:${goRoot}:${kubectlRoot}:${makeRoot}:$PATH"
????????????????git clone --depth 1 ${repoURL} ${repoPath}
????????????"""
????????}
????}
????...
}3.执行测试代码
利用go test命令执行代码。执行go test会进行全代码编译的,会拉取所有的依赖,所以需要提前配置go环境变量。
go test运行指定模块、指定优先级的测试用例,eg:
go test -v ./test/storage/... '-run=^Test+/TestP0' -json./test/storage/?storage在openapi-go项目中的代码目录
'-run=^Test+/TestP0'?^Test指定Test打头的suite,/TestP0指定该suite下的用例。这样可以将模块storage、用例名称TestP0参数化为MODULE_NAME、PRIORITY,并在jenkins上的参数化构建中进行赋值。
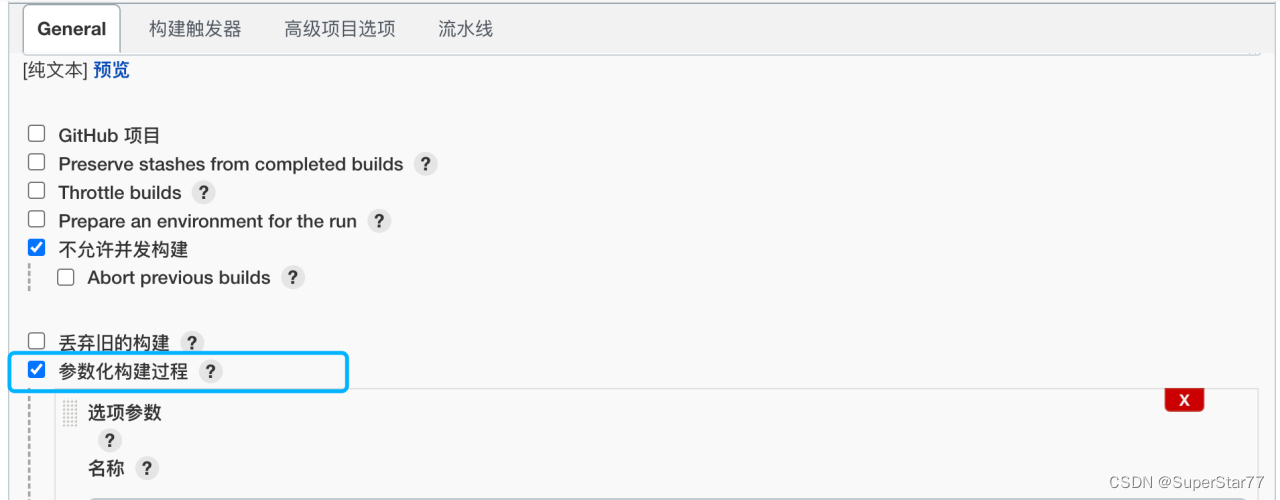

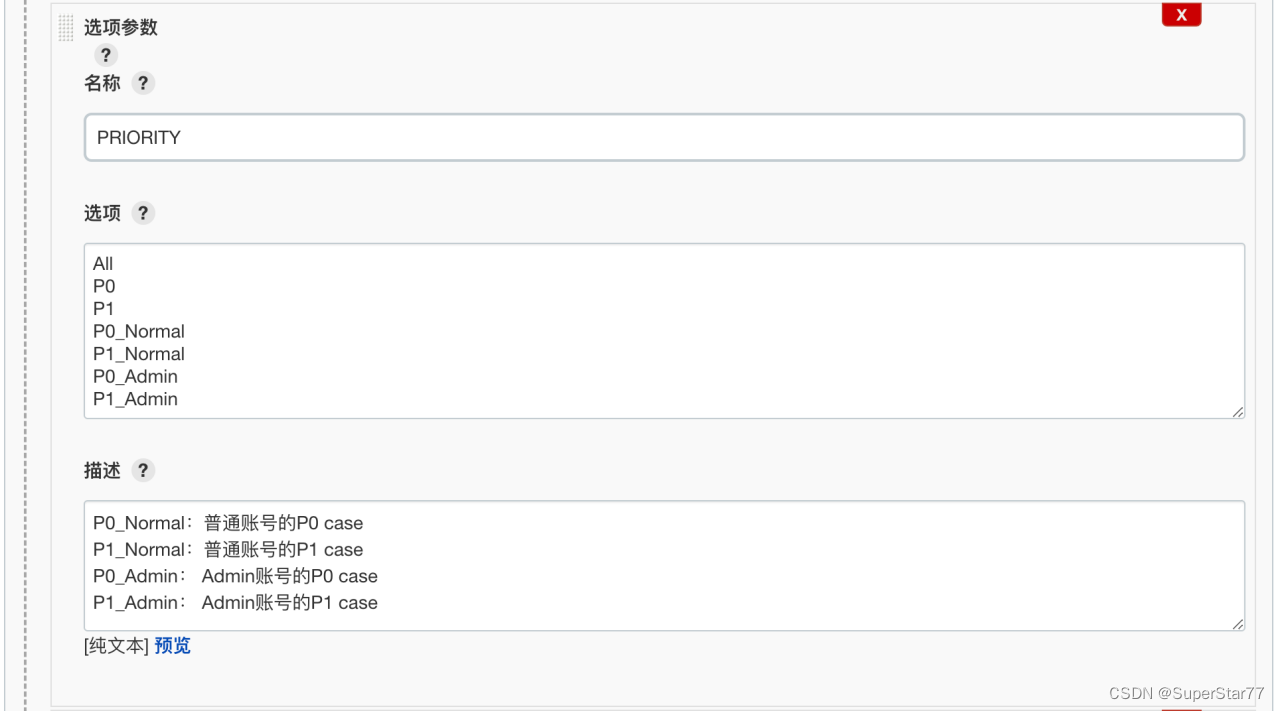
配置完成后go test可以写成这样了:
go test -v ./test/$MODULE_NAME/... ??-run="^Test"+"/Test"+$PRIORITY4.生成测试报告
安装go-test-report
go get github.com/vakenbolt/go-test-report/执行生成html格式测试报告的命令,会在当前目录生成一个test_report.html
go test -v ./test/$MODULE_NAME/... ??-run="^Test"+"/Test"+$PRIORITY ??-json | go-test-reportjenkins发布报告的pipeline script:
stage('Report') { ??????????
????????steps {
????????????echo "report"
????????????publishHTML (target: [
????????????allowMissing: false,
????????????alwaysLinkToLastBuild: false,
????????????keepAll: true,
????????????reportDir: '$BUILD_ID/test-output',
????????????reportFiles: 'test_report.html',
????????????reportName: "HTML Report"
????????])
????????}
????}然后就可以在jenkins查看该报告了

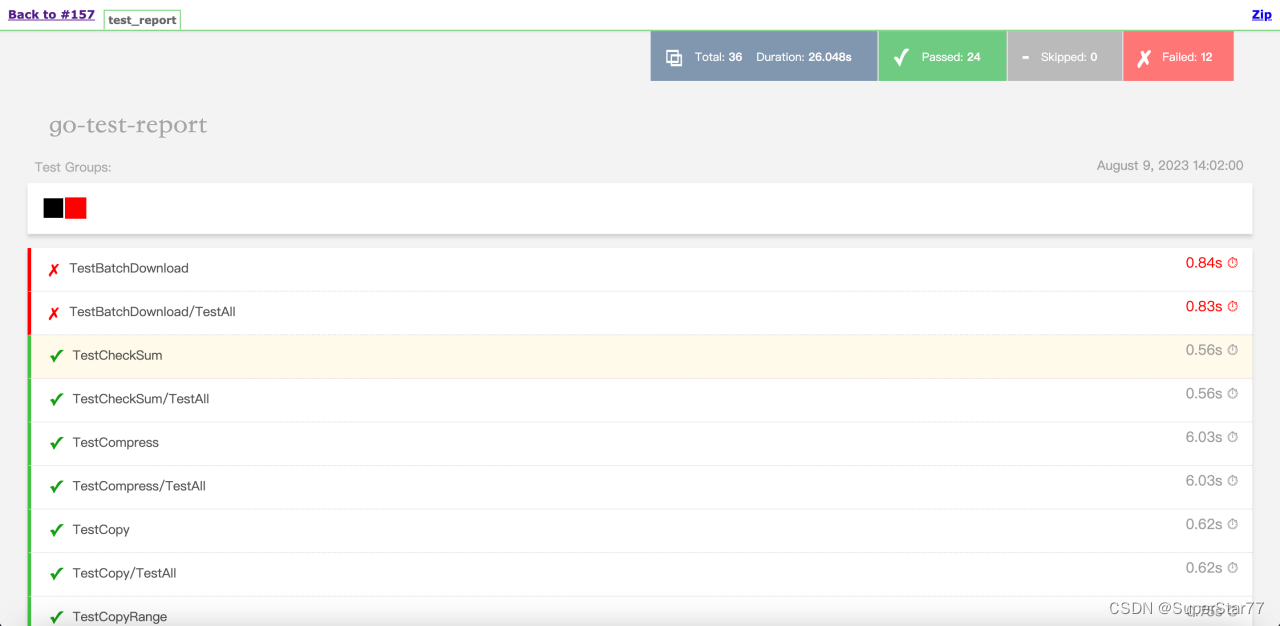
5.报告内容解读
失败的用例是红色,通过的用例是绿色。失败日志需要关注assert部分的日志,包括报错行数、期望值与实际值的比较结果。
6.数据统计
在测试代码执行结果及报告都有了之后就可以统计自已需要的数据,然后放在邮件内容里进行发送。
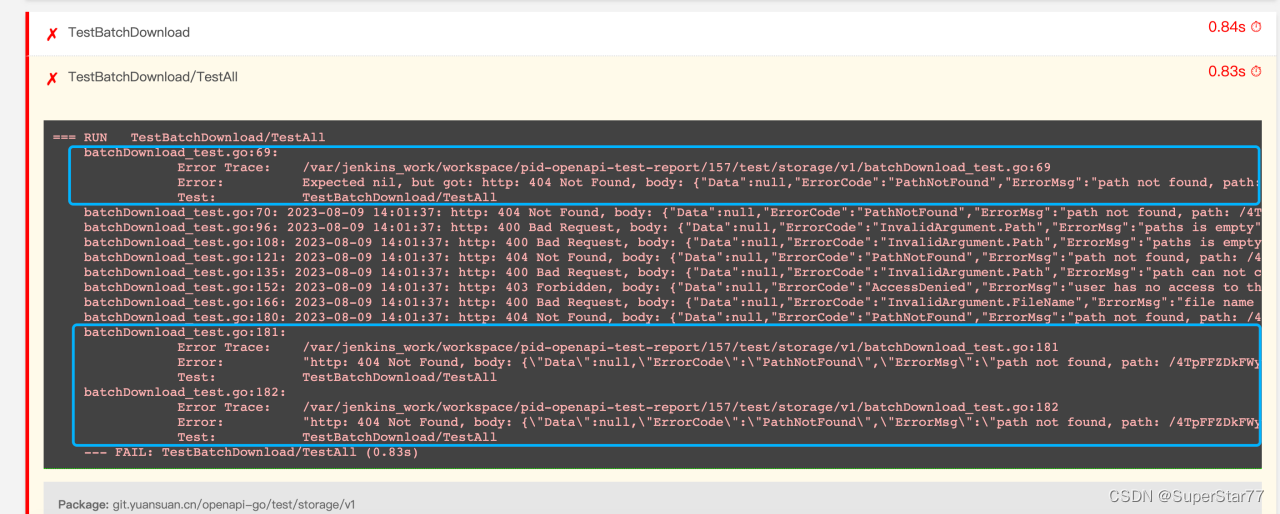
先分析下html源文件的内容,找到自已想要的数据。
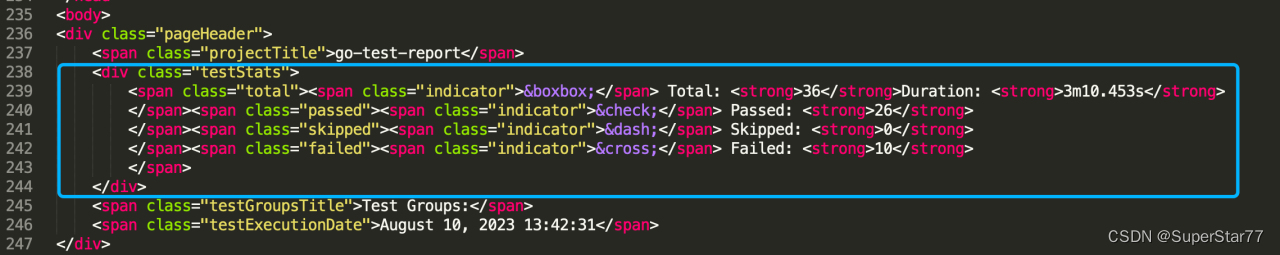
groovy自带解析html格式的库,但是不太好用。这里采用awk解析数据。
注:substr(s,p,n) 返回字符串s从p开始长度为n的部分
def genReportBody() {
// 生成测试报告内容
def testReport = readFile("$BUILD_ID/test-output/test_report.html")
// 获取执行时间
sh(script: 'pwd')
def duration = sh(script: 'grep "Duration:" '+"$BUILD_ID/test-output/test_report.html"+' | awk \'{print substr($6,9,length($6)-17)}\'', returnStdout: true).trim()
echo duration
def runtime = duration.split("\\.")[0].trim()
echo runtime
// 获取总数量
def total = sh(script: 'grep "Total:" '+"$BUILD_ID/test-output/test_report.html"+' | awk \'{print substr($5,9,length($5)-26)}\'', returnStdout: true).trim()
// 获取通过率
def passedCount = sh(script: 'grep "Passed:" '+"$BUILD_ID/test-output/test_report.html"+' | awk \'{print substr($5,9,length($5)-17)}\'', returnStdout: true).trim()
def skippedCount = sh(script: 'grep "Skipped:" '+"$BUILD_ID/test-output/test_report.html"+' | awk \'{print substr($5,9,length($5)-17)}\'', returnStdout: true).trim()
def failedCount = sh(script: 'grep "Failed:" '+"$BUILD_ID/test-output/test_report.html"+' | awk \'{print substr($5,9,length($5)-17)}\'', returnStdout: true).trim()
def passedRate = String.format("%.2f", passedCount.toInteger()/(total.toInteger()-skippedCount.toInteger()) * 100)
7.邮件通知
组装邮件中的内容
// 生成测试报告
def reportContent = """
<h2>OpenAPI Test Report (${MODULE_NAME})</h2>
<p>Environment: ${ENV}</p>
<p>Test Time: ${runtime}s</p>
<h3>Test Cases:</h3>
<ul>
<a href="https://jenkins地址/view/pid/job/${JOB_NAME}/$BUILD_ID/HTML_20Report/" target="_blank">https://jenkins地址/view/pid/job/${JOB_NAME}/$BUILD_ID/HTML_20Report/</a>
</ul>
<p>Pass Rate: ${passedRate}% </p>
<p>Test Range: ${PRIORITY}</p>
<h3>Failures: ${failedCount}</h3>
"""
发送邮件,在发送邮件前将无用的测试数据清除
post {
????????always {
????????????sh """
????????????????mv ${repoPath}/test-output ~/temp
????????????????rm -rf ${repoPath}/*
????????????????mv ~/temp/test-output ${repoPath}/
????????????"""
????????????echo "clean over..."
????????????emailext body: ?genReportBody(),
????????????????????subject: 'Test Report',
????????????????????// to: 'env.RECIPIENTS',
????????????????????to: '${RECIPIENT_LIST}',
????????????????????mimeType: 'text/html'
????????????// from: '邮件发送地址'
????????}
????????success {
????????????echo 'Build && Test Succeeded.'
????????}
????????failure {
????????????echo 'Build && Test Failured.'
????????}
}
8.企业微信通知


三、项目遇到的问题
1.go test -args?
利用该命令自定义参数时发现-args后面所有东西都当成agrs的值,且阻断后面所有指令的执行。后来在stackoverflow看见一个人发了同样的问题,我想到去看下官方说明
In addition to the build flags, the flags handled by 'go test' itself are:
-args
????Pass the remainder of the command line (everything after -args)
????to the test binary, uninterpreted and unchanged.
????Because this flag consumes the remainder of the command line,
????the package list (if present) must appear before this flag.上面的everything after -args和执行实际效果是一样。这样通过命令行方式来切换环境的做法是行不通,于是采用多个配置文件的方式,全部存放在jenkins机器的~/conf目录。

切换方式
if [ $ENV = "test" ]
then
????echo 'cp test .env'
????cp /home/jenkins/conf/.env ${repoPath}/test
????cp /home/jenkins/conf/.env.storage ${repoPath}/test/storage/v1/.env
elif [ $ENV = "dev" ]
then
????#statements
????echo 'cp dev .env'
????cp /home/jenkins/conf/.env.dev ${repoPath}/test/.env
????cp /home/jenkins/conf/.env.storage.dev ${repoPath}/test/storage/v1/.env
????
elif [ $ENV = "prod" ]
then
????echo 'cp prod .env'
????cp /home/jenkins/conf/.env.prod ${repoPath}/test/.env
????cp /home/jenkins/conf/.env.storage.prod ${repoPath}/test/storage/v1/.env
fi2.go test生成html格式的报告
最开始也是打算接入allure报告,但是发现go test并不支持,所以采用了go-test-report。发布的第一版的go?test report时并不是长这样的
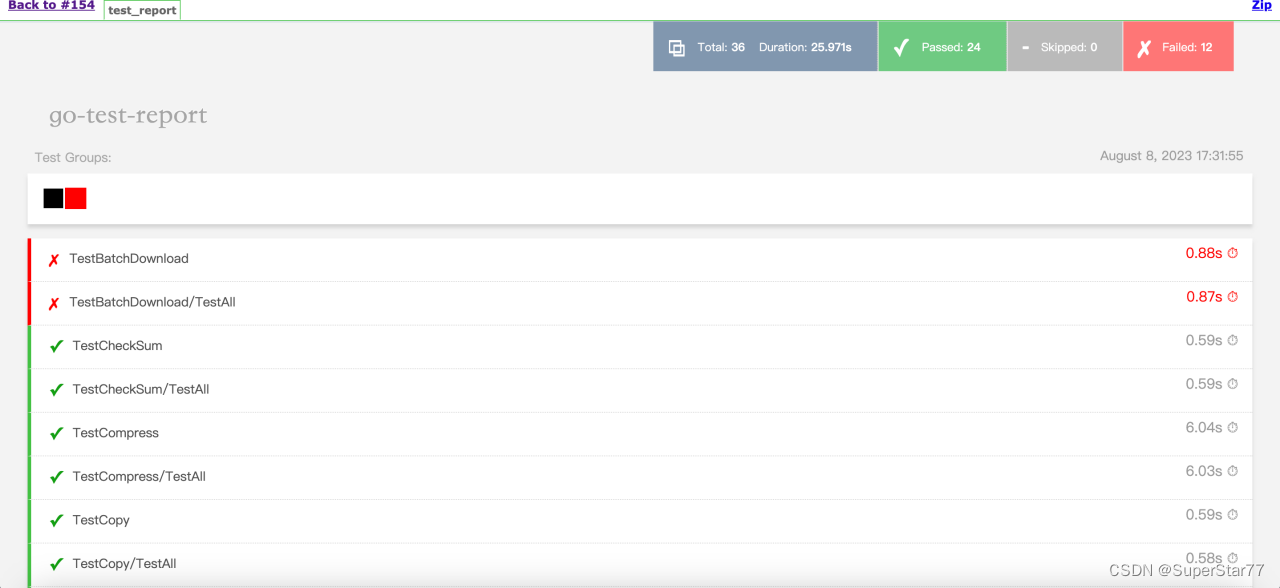
而是像下面这样不带css样式的

解决方法:在jenkins-->系统管理-->脚本命令行,输入以下命令
System.setProperty("hudson.model.DirectoryBrowserSupport.CSP", "")
3.数据统计问题
网上有很多groovy统计xml格式的文件,没找到能很好解析html格式的工具,想到awk这个工具。
def passedCount = sh(script: 'grep "Passed:" '+"$BUILD_ID/test-output/test_report.html"+' | awk \'{print substr($5,9,length($5)-17)}\'', returnStdout: true).trim()4.相对路径问题
我们用IDE编写用例时直接![]() 就可以执行了,这种情况下go会把该用例所在的目录当成pwd目录;而流水线中go?test是在项目根目录下执行的,这时go是把项目根目录当成pwd目录的。这样用例中使相对路径eg:.env、../.env等都会执行失败。
就可以执行了,这种情况下go会把该用例所在的目录当成pwd目录;而流水线中go?test是在项目根目录下执行的,这时go是把项目根目录当成pwd目录的。这样用例中使相对路径eg:.env、../.env等都会执行失败。
解决方法:利用runtime获取当前执行路径,然后代码中生成项目根目录,以该路径为基点再去拼接文件的路径,尽量不要使相对路径。
5.错误排查问题
后面发现现有的脚本case编写如果有一个报错,全部都是红色,找到报错点不是很方便,修改脚本case为:
func (s *JobBatchGetSuite) TestP0_Normal() {
s.Run("TestSuccessJobBatchGet", func() {
s.TestSuccessJobBatchGet()
})
}
func (s *JobBatchGetSuite) TestP1_Normal() {
s.Run("TestJobBatchGetJobIdsTooMuch", func() {
s.TestJobBatchGetJobIdsTooMuch()
})
}在jenkins上执行后,报告展示更为直观。


今天的分享就到此结束喽~

本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!