DiffUtil + RecyclerView 在 Kotlin中的使用
很惭愧, 做了多年的Android开发还没有使用过DiffUtil这样解放双手的工具。
1 DiffUtil 用来解决什么问题?
先举几个实际开发中的例子帮助我们感受下:
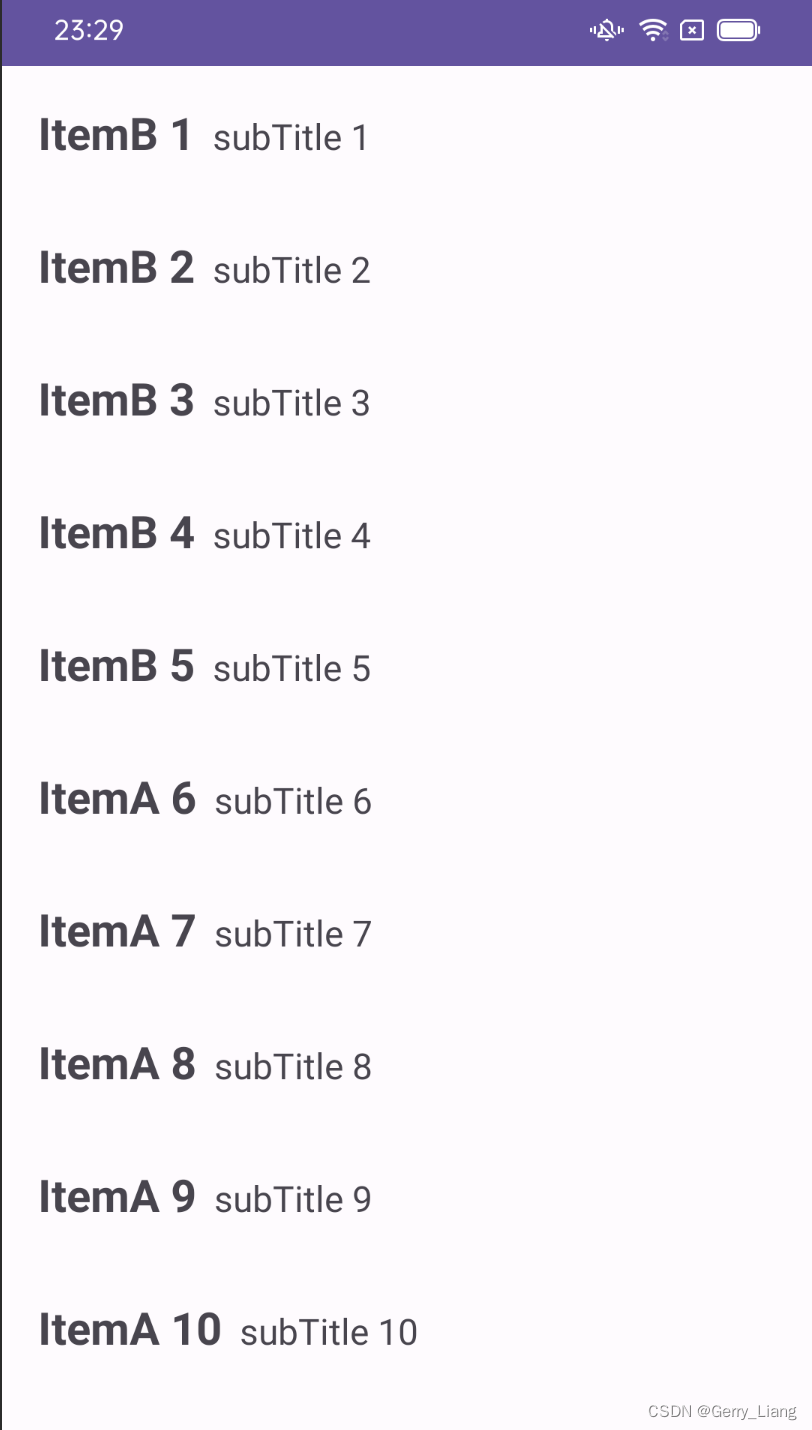
- 加载内容流时,第一次加载了ABC,第二次加载了BCD,如何让用户能看到不重复的内容?
- 网络数据和本地数据不一致, 如何能够找出不一致的内容?
我们可以采用最笨的方法, 自己比较两个集合的差异,但是效率较低,每个开发者都要重复做这样的事情, 是谷歌不愿意看到的。
2 DiffUtil 是什么?
DiffUtil is a utility class that calculates the difference between two lists and outputs a list of update operations that converts the first list into the second one.
It can be used to calculate updates for a RecyclerView Adapter. See ListAdapter and AsyncListDiffer which can simplify the use of DiffUtil on a background thread.
DiffUtil uses Eugene W. Myers’s difference algorithm to calculate the minimal number of updates to convert one list into another. Myers’s algorithm does not handle items that are moved so DiffUtil runs a second pass on the result to detect items that were moved.
DiffUtil 是一个实用程序类,它计算两个列表之间的差异并输出将第一个列表转换为第二个列表的更新操作列表。
它可用于计算 RecyclerView 适配器的更新。请参阅 ListAdapter 和 AsyncListDiffer,它们可以简化后台线程上 DiffUtil 的使用。
DiffUtil 使用 Eugene W. Myers 的差分算法来计算将一个列表转换为另一列表所需的最小更新次数。 Myers 的算法不处理已移动的项目,因此 DiffUtil 对结果运行第二遍以检测已移动的项目。
3 DiffUtil的使用
item_song_info.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:padding="16dp">
<!-- Title TextView -->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_title"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Title"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textStyle="bold" />
<!-- Spacer View to add space between title and subtitle -->
<View
android:layout_width="8dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
<!-- Subtitle TextView -->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_sub_title"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Subtitle"
android:textSize="16sp" />
</LinearLayout>
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/recyclerView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
MusicBean.kt
data class MusicBean(var type: Int, var title: String, val subTitle: String)
MainActivity.kt
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val recyclerView: RecyclerView = findViewById(R.id.recyclerView)
recyclerView.layoutManager = LinearLayoutManager(this)
val adapter = MyAdapter()
recyclerView.adapter = adapter
adapter.data = getSampleDataA()
Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()).postDelayed({
adapter.data = getSampleDataB()
}, 2000)
}
// 用于生成初始数据
private fun getSampleDataA(): List<MusicBean> {
val data = mutableListOf<MusicBean>()
for (i in 1..10) {
MusicBean(type = i, title = "ItemA $i", subTitle = "subTitle $i").let {
data.add(it)
}
}
return data
}
// 用于生成变化后的数据
private fun getSampleDataB(): List<MusicBean> {
val data = mutableListOf<MusicBean>()
for (i in 1..10) {
val tag = if (i <= 5) {
"B"
} else "A"
MusicBean(type = i, title = "Item$tag $i", subTitle = "subTitle $i").let {
data.add(it)
}
}
return data
}
class MyAdapter : RecyclerView.Adapter<MyAdapter.MyViewHolder>() {
var data: List<MusicBean> = emptyList()
set(value) {
// 如果比较的集合较多(比如超过1000个), 建议使用子线程去比较
val diffResult = DiffUtil.calculateDiff(MyDiffCallback(field, value))
// 旧值赋新值
field = value
// 这里一定要保证在主线程调用
diffResult.dispatchUpdatesTo(this)
}
class MyDiffCallback(
private val oldList: List<MusicBean>, private val newList: List<MusicBean>
) : DiffUtil.Callback() {
override fun getOldListSize(): Int = oldList.size
override fun getNewListSize(): Int = newList.size
override fun areItemsTheSame(oldItemPosition: Int, newItemPosition: Int): Boolean {
// 把这里想成是比较holder的类型, 比如纯文本的holder和纯图片的holder的type肯定不同
return oldList[oldItemPosition].type == newList[newItemPosition].type
}
override fun areContentsTheSame(oldItemPosition: Int, newItemPosition: Int): Boolean {
// 把这里想成是同一种holder的比较,比如都是纯文本holder,但是title不一致
return oldList[oldItemPosition].title == newList[newItemPosition].title
}
}
override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int): MyViewHolder {
val view =
LayoutInflater.from(parent.context).inflate(R.layout.item_song_info, parent, false)
return MyViewHolder(view)
}
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: MyViewHolder, position: Int) {
val item = data[position]
holder.bind(item)
}
override fun getItemCount(): Int {
return data.size
}
class MyViewHolder(itemView: View) : RecyclerView.ViewHolder(itemView) {
fun bind(item: MusicBean) {
val tvTitle: TextView = itemView.findViewById(R.id.tv_title)
val tvSubTitle: TextView = itemView.findViewById(R.id.tv_sub_title)
tvTitle.text = item.title
tvSubTitle.text = item.subTitle
}
}
}
}
4 参考文章
DiffUtil 官方介绍
将 DiffUtil 和数据绑定与 RecyclerView 结合使用
DiffUtil和它的差量算法
DiffUtils 遇到 Kotlin,榨干视图局部刷新的最后一滴性能
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 解析用GraalVm编译的class文件
- 打造高效接口测试:Python自动化框架设计与实现
- 塑料检查井配套开发了注塑成型的井盖、井筒、井座
- 学习Java第66天,路径问题
- 【华为OD机试真题2023C&D卷 JAVA&JS】项目排期
- 书接上文,Java里的Map接口和泛型
- ROS第 11 课 参数的使用与编程方法
- Ultra Mobile PayGO购买充值激活
- MDT的驱动管理和自动匹配
- 【Spark精讲】Spark内存管理