编写一个Java程序,其中包含三个线程: 厨师(Chef)、服务员(Waiter)和顾客(Customer)
发布时间:2023年12月24日
编写一个Java程序,其中包含三个线程: 厨师(Chef)、服务员(Waiter)和顾客(Customer)。他们的行动如下:
- 厨师准备菜肴,每次准备一个。
- 服务员等待菜肴准备好,然后将其送到顾客那里。
- 顾客等待服务员送来菜看后才开始吃。
- 所有三个角色应该循环进行他们的行为,直到指定数量的菜肴被制作和消费完。
- 使用wait()和notify0)确保线程间正确的通信和同步。
package com;
/**
* @program: RestaurantDemo
* @description: 餐厅类
* @author: Casey Hu
* @create: 2023-12-18 16:13
**/
public class Restaurant {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Chef chef = new Chef();
Waiter waiter = new Waiter(chef);
Customer customer = new Customer(waiter);
chef.start();
waiter.start();
customer.start();
chef.join();
waiter.join();
customer.join();
System.out.println("餐厅关闭.");
}
static class Chef extends Thread {
private final int MAX_FOOD = 10;
private int foodCount = 0;
private boolean isFinished = false;
@Override
public void run() {
while (!isFinished) {
try {
// 厨师准备菜肴
System.out.println("厨师准备菜肴...");
Thread.sleep(1000);
// 菜肴准备好后唤醒服务员
foodCount++;
synchronized (this) {
this.notify();
}
if (foodCount >= MAX_FOOD) {
isFinished = true;
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
static class Waiter extends Thread {
private Chef chef;
public Waiter(Chef chef) {
this.chef = chef;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (!chef.isFinished) {
try {
synchronized (chef) {
// 等待厨师准备菜肴
chef.wait();
}
// 将菜肴送到顾客那里
System.out.println("服务员将菜肴送到顾客那里...");
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
static class Customer extends Thread {
private Waiter waiter;
public Customer(Waiter waiter) {
this.waiter = waiter;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (!waiter.chef.isFinished) {
try {
// 等待服务员送来菜肴
Thread.sleep(1000);
// 开始吃菜肴
System.out.println("顾客开始吃菜肴...");
// 通知服务员可以送下一道菜了
synchronized (waiter.chef) {
waiter.chef.notify();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
上述代码中启动了三个子线程:厨师线程、服务员线程和顾客线程。厨师线程使用foodCount计数器来记录制作的菜肴数量,并使用synchronized关键字确保线程安全。每当它制作好一道菜肴后,它唤醒等待的服务员线程。
服务员线程使用synchronized和wait()方法等待厨师线程准备好菜肴。一旦收到通知,它将菜肴送到顾客那里。
顾客线程使用synchronized关键字和notify()方法通知服务员准备下一道菜肴,并在接收到菜肴后开始吃。
主线程使用join()方法等待所有子线程完成。
这个示例使用了Java中的核心多线程机制(Thread、Runnable、synchronized、wait()和notify()等)来模拟餐厅的运作。
运行结果:
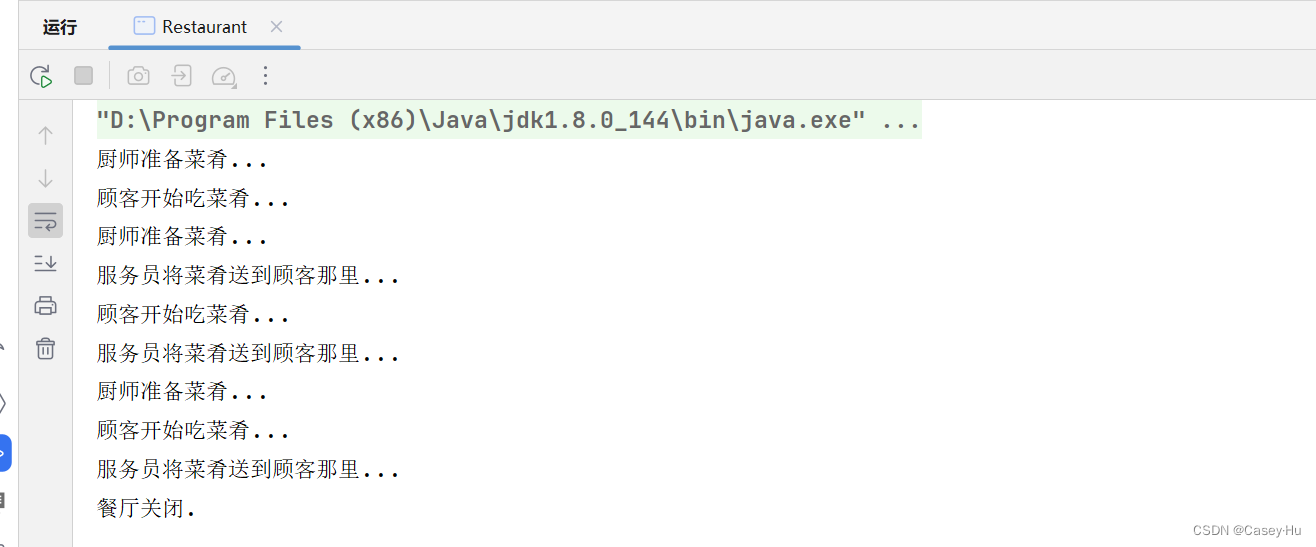
但是有一段代码
public class Restaurant {
private static final int MAX_FOOD = 10;
private static final Object lock = new Object();
private static int foodCount = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Chef chef = new Chef();
Waiter waiter = new Waiter();
Customer customer = new Customer();
chef.start();
waiter.start();
customer.start();
}
static class Chef extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
while (foodCount < MAX_FOOD) {
try {
// 厨师准备菜肴
System.out.println("厨师准备菜肴...");
Thread.sleep(1000);
// 菜肴准备好后唤醒服务员
foodCount++;
lock.notify();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
static class Waiter extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
while (foodCount < MAX_FOOD) {
try {
// 等待菜肴准备好
lock.wait();
// 将菜肴送到顾客那里
System.out.println("服务员将菜肴送到顾客那里...");
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
static class Customer extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
while (foodCount < MAX_FOOD) {
try {
// 等待菜肴送来
lock.wait();
// 开始吃菜肴
System.out.println("顾客开始吃菜肴...");
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
运行结果:
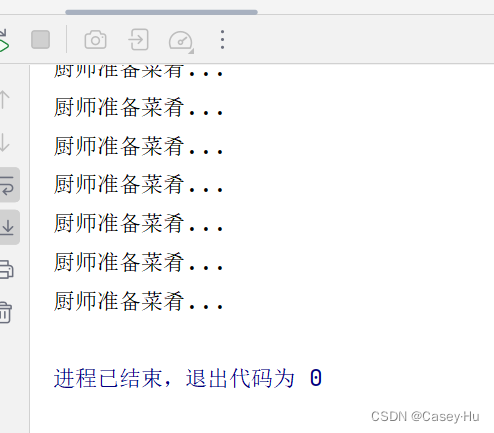
就是厨师准备好菜肴之后,main线程结束
所以才会选择子线程的方式,有大佬知道为啥会出现这样的结果吗?评论区聊聊
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43658218/article/details/135068606
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- go从0到1项目实战体系二十九:演示案列实例一
- Java集合
- 最小化数组中的最大值
- RLHF几大常用框架实践对比(trlx、deepspeedchat、colossalaichat)
- nginx 优化和安装防盗链以及实验举例
- 第二百八十回
- MySQL语法及IDEA使用MySQL大全
- 绘制一个可以移动的矩形,当矩形碰到屏幕边界时,矩形都将会改变颜色
- FPC柔性化机器视觉缺陷检测
- Python: Spire.PDF-for-Python