C2-4.2.2 决策树-纯度+信息熵+信息增益
C2-4.2.2 决策树-纯度+信息熵+信息增益
1、首先了解他的应用背景——决策树

其实说白了,就是一个二叉树
2、纯度
我们举一个买黄金的例子吧!黄金有999 和 9999 。 他们是有区别的,代表着黄金的纯度(相对杂质而言),那在决策树中——我们也引入了“纯度”这一概念。如果结果集中,全是这一类的,那么我们说“vary pure”。如果结果集中有6个,但是3个是一个类别,那么我们说"not pure",把除这三个外的东西叫做“杂质”
2.1 纯度简述
-
如果一个结果集(经过 一次 或多次 二叉树判别),都是猫 / 都是非猫,那么就说这个结果集 very pure。
-
如果一个结果集 既有 猫 又有 非猫,那么就是not pure。但是not pure 也分级别。——引出我们计算的公式
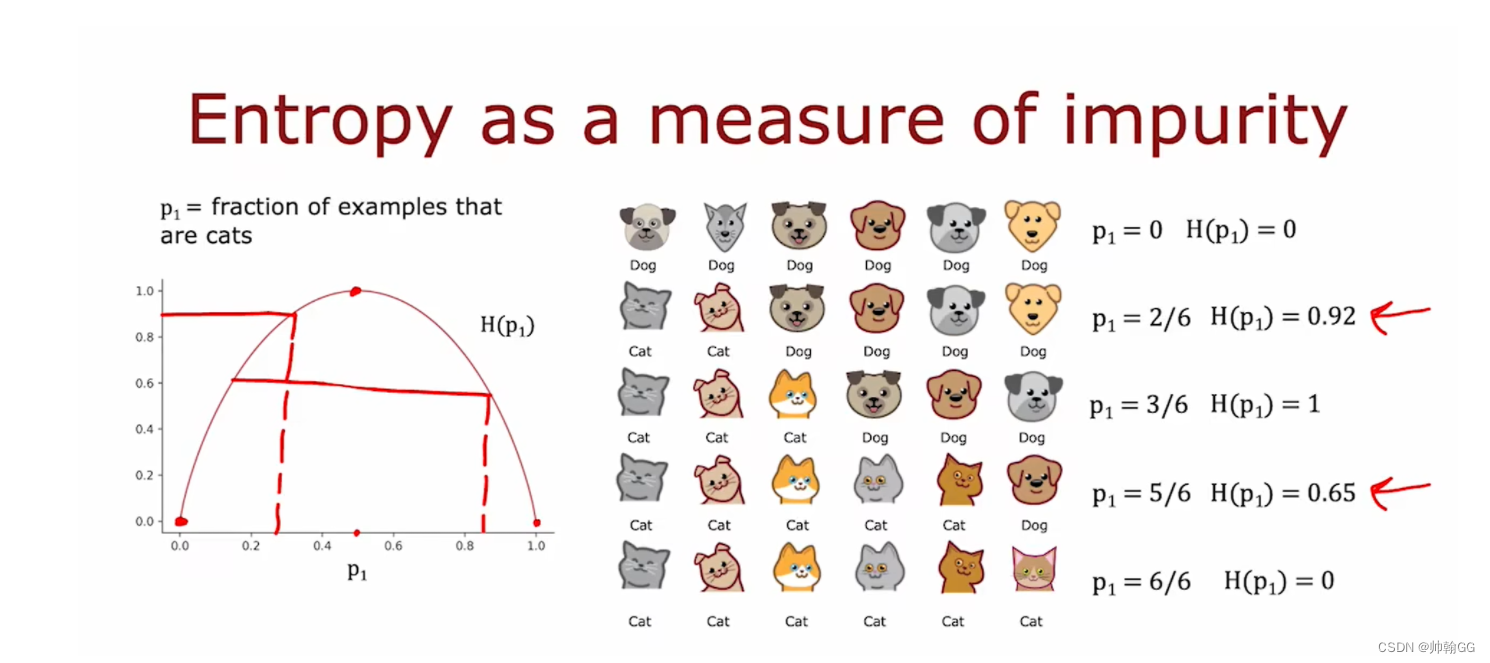
-
P1:是 猫的纯度。
-
当一组数据有6个,猫有0个时,熵为0,纯度最高
-
当一组数据有6个,猫有3个时,熵为0.92,纯度不好
…
-
3、信息熵(entropy )
那买黄金,有专业的机器来判别我们的黄金的纯度,那在决策树中的结果集中,如何判别纯度呢 / 判别纯度的标准??——这就引出了**“信息熵”** 的定义。
3.1 信息熵的定义
In Machine Learning, entropy ※※measures the level of disorder or uncertainty in a given dataset or system. It is a metric that quantifies the amount of information in a dataset, and it is commonly used to evaluate the quality of a model and its ability to make accurate predictions.
※A higher entropy value indicates a more heterogeneous dataset with diverse classes, while a lower entropy signifies a more pure and homogeneous subset of data. Decision tree models can use entropy to determine the best splits to make informed decisions and build accurate predictive models.
- 【※※※总结】:
- 信息熵是用来衡量 给出的数据集中 数据的纯度的
- 信息熵越小,数据就越纯。
- 通常用在机器学习分类的情况下
3.2 信息熵公式
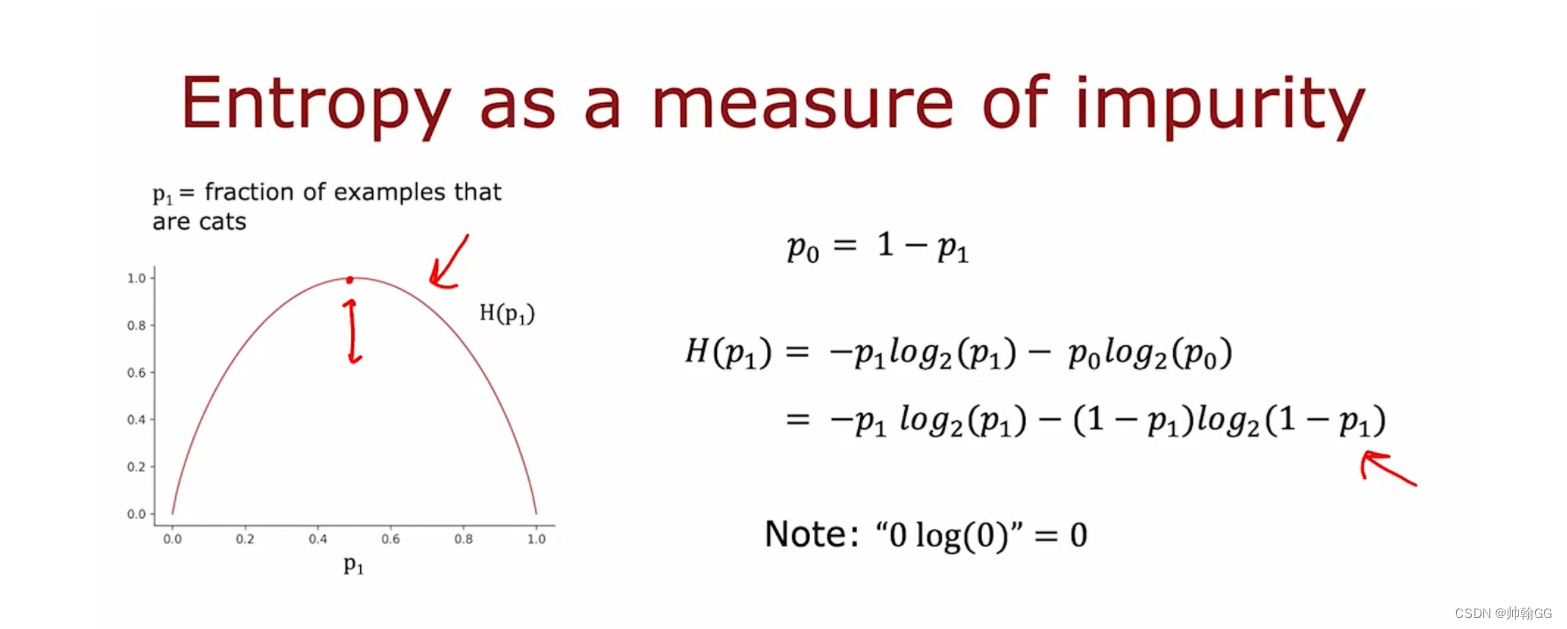
4、信息增益(Information Gain)
4.1、信息增益概念:
Information gain calculates the reduction in entropy or surprise from transforming a dataset in some way.
It is commonly used in the construction of decision trees from a training dataset, by evaluating the information gain for each variable, and selecting the variable that maximizes the information gain, which in turn minimizes the entropy and best splits the dataset into groups for effective classification.
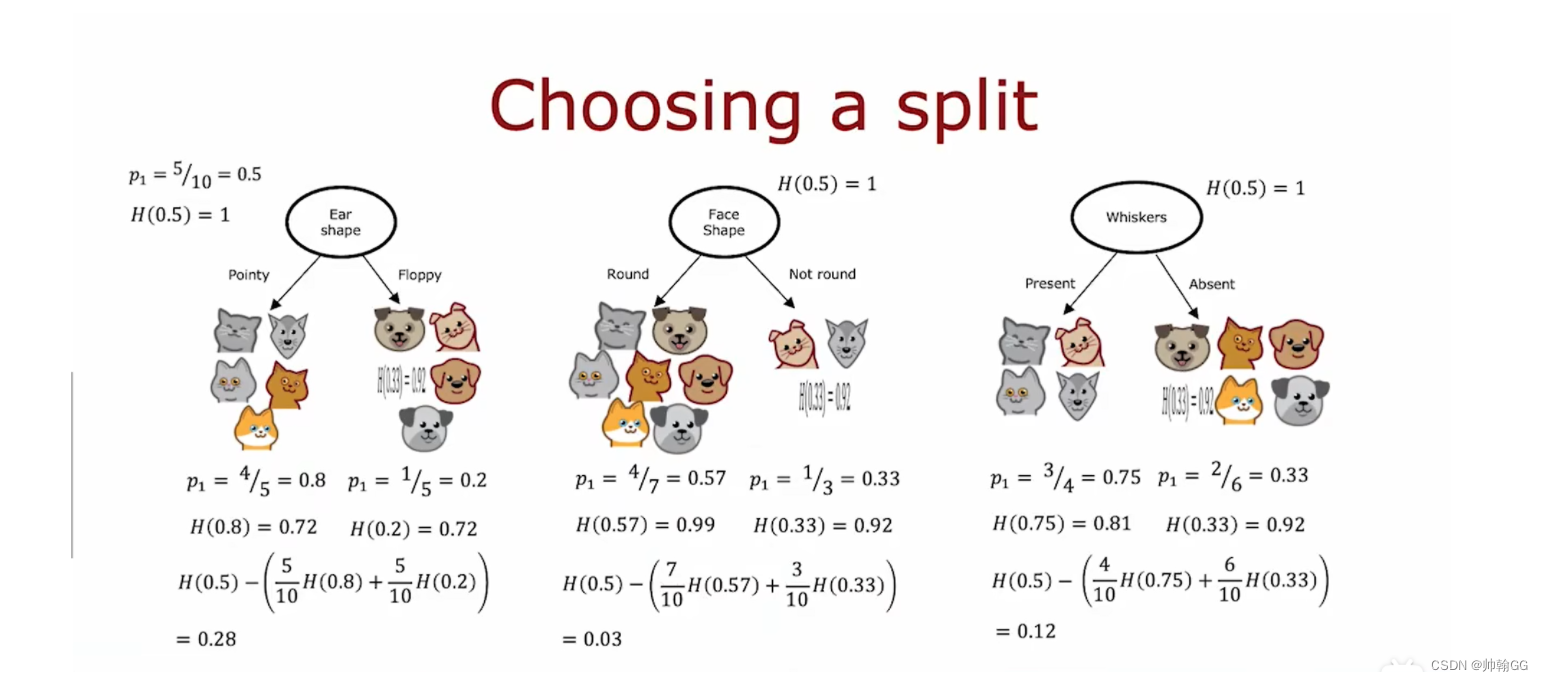
【※※※总结】:
- 信息增益:是计算信息熵的减少量/看做减少速率的
- 被广泛用在 决策树的节点选择上:对每一个可选的节点 进行信息增益判断,选择结果最大的作为节点——才能产生最小的信息熵结果
- 信息增益代表了在一个条件下,信息复杂度(不确定性)减少的程度。
4.2 信息增益公式:
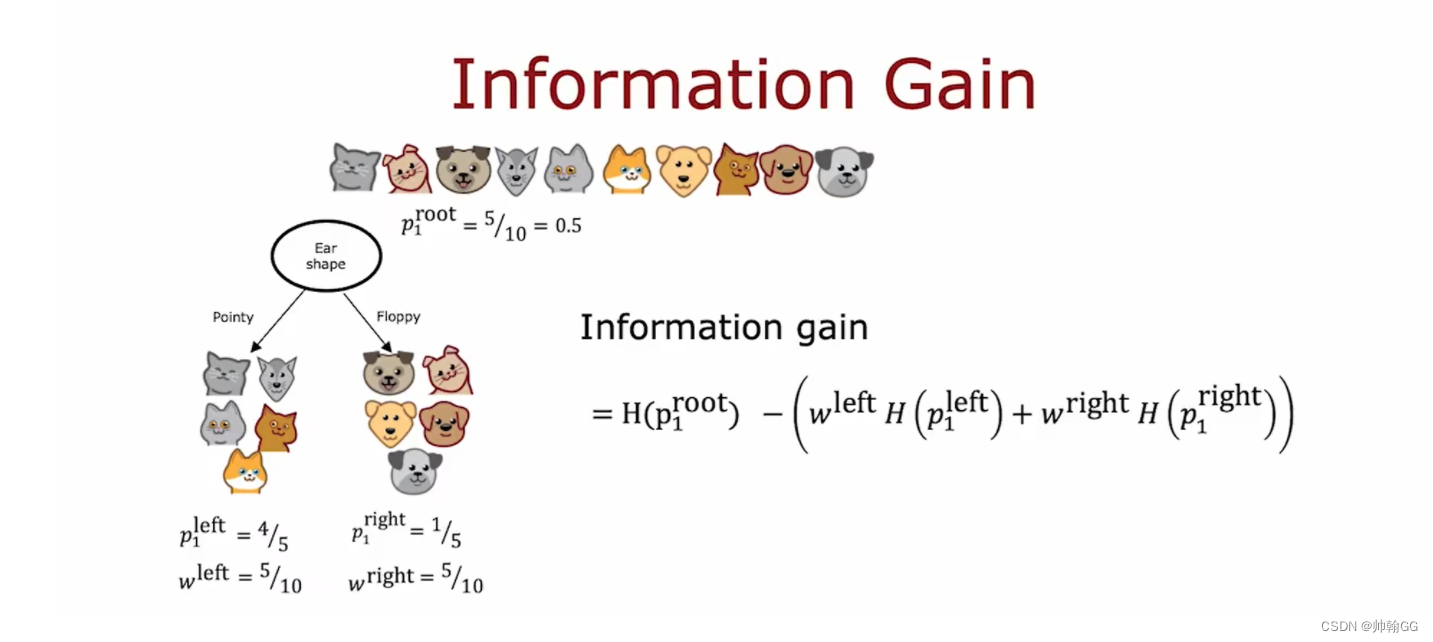
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Vue学习笔记8--插槽<slot></slot>
- random模块
- Java实现简单的Redis
- Springboot启动后自动退出解决办法
- 第29节: Vue3 列表渲染
- 抖店商品卡不出单做不起来?抖店玩法解读+经验分享,建议收藏
- 延迟减少10倍!OCD:基于以目标为中心Diffusion的高效视频编辑方法
- 深度学习论文解读分享之diffGrad:一种卷积神经网络优化方法
- S32K312软件看门狗之Software Watchdog Timer (SWT)
- day 25回溯(二)