[java数据结构] ArrayList和LinkedList介绍与使用
目录

(一) 线性表
线性表(linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使用的数据结 构,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列...
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的,线性表在物 理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。如下图:
(二) ArrayList
1. ArrayList的介绍
ArrayList是Java中的一个动态数组类, 即顺序表,可以动态地增加或减少数组的大小。它是一个可以动态改变大小的数组,可以根据需要自动地增加或减少数组的大小。ArrayList可以存储任意类型的对象,包括基本数据类型和引用类型, 它实现了List接口, 具体框架图如下:
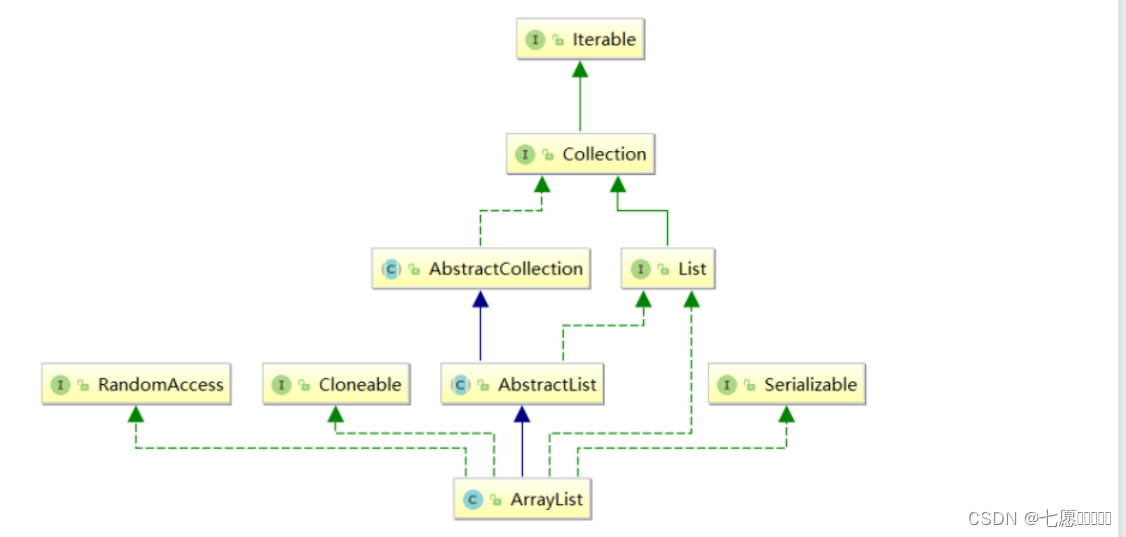
[说明]
1. ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口,表明ArrayList支持随机访问
2. ArrayList实现了Cloneable接口,表明ArrayList是可以clone的
3. ArrayList实现了Serializable接口,表明ArrayList是支持序列化的
4. 和Vector不同,ArrayList不是线程安全的,在单线程下可以使用,在多线程中可以选择Vector或者 CopyOnWriteArrayList
5. ArrayList底层是一段连续的空间,并且可以动态扩容,是一个动态类型的顺序表
2. ArrayList的常见方法和使用
使用ArrayList可以方便地进行元素的添加、删除和查找操作,是Java中常用的集合类之一。
ArrayList类包含许多常用的方法,以下是一些常见的方法和它们的使用:
常见的方法
- boolean add(E e):向ArrayList中尾插 一个元素e。
- void add(int index, E element): 将 e 插入到 index 位置
- E remove(int index):移除指定索引位置的元素。
- E get(int index):获取指定索引位置的元素。
- size():获取ArrayList的大小
- E set(int index, E element): 将下标 index 位置元素设置为 element
- void clear(): 清空
- boolean contains(Object o):判断ArrayList是否包含指定的元素。
- int indexOf(Object o):返回指定元素在ArrayList中第一次出现的索引。
- int lastIndexOf(Object o):?返回指定元素在ArrayList中最后一次出现的索引。
? 使用:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个ArrayList
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 向ArrayList中尾插元素
list.add("apple");
list.add("banana");
list.add("orange");
// 将元素插入到指定索引位置
list.add(1, "grape");
//遍历ArrayList
System.out.print("打印1: ");
for (String ret: list) {
System.out.print(ret+" ");
}
System.out.println();
// 移除指定索引位置的元素
list.remove(2);
//遍历ArrayList
System.out.print("打印2: ");
for (String ret: list) {
System.out.print(ret+" ");
}
System.out.println();
// 获取指定索引位置的元素
String fruit = list.get(0);
System.out.println("索引0处的水果: " + fruit);
// 获取ArrayList的大小
int size = list.size();
System.out.println("ArrayList的大小: " + size);
// 将指定索引位置的元素设置为新元素
list.set(2, "cherry");
// 判断ArrayList是否包含指定的元素
boolean contains = list.contains("apple");
System.out.println("是否包含'apple': " + contains);
// 返回指定元素在ArrayList中第一次出现的索引
int index = list.indexOf("banana");
System.out.println("'banana'第一次出现的索引: " + index);
// 返回指定元素在ArrayList中最后一次出现的索引
int lastIndex = list.lastIndexOf("apple");
System.out.println("'apple'最后一次出现的索引: " + lastIndex);
// 清空ArrayList
list.clear();
//遍历ArrayList
System.out.print("打印3: ");
for (String ret: list) {
System.out.print(ret+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}

3. ArrayList的遍历
ArrayList可以使用三种方式遍历:for循环+下标、foreach、使用迭代器, 代码如下:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个ArrayList对象,它是List接口的实现类
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 将指定的元素添加到列表的末尾
list.add("apple");
list.add("banana");
list.add("cherry");
//for循环+下标
System.out.print("for循环+下标: ");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(list.get(i)+" ");
}
System.out.println();
//foreach遍历
System.out.print("foreach遍历: ");
for (String ret : list) {
System.out.print(ret+" ");
}
System.out.println();
//使用迭代器
System.out.print("迭代器遍历: ");
Iterator<String> iter = list.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()){
String ret = iter.next();
System.out.print(ret+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
4. ArrayList的模拟实现
package List;
import java.util.Arrays;
// 自定义的ArrayList类
public class MyArrayList {
public int[] arr; // 用于存储元素的数组
public int size; // 记录当前数组中的元素个数
public static final int Max = 10; // 默认最大容量
// 构造方法,初始化数组
public MyArrayList() {
this.arr = new int[10];
}
// 打印元素
public void display() {
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// 增加元素
public void add(int data) {
if (isFull()) {
arr = Arrays.copyOf(arr, arr.length * 2); // 如果数组已满,扩容为原来的两倍
}
arr[size++] = data;
}
// 判断数组是否已满
public boolean isFull() {
if (size == Max) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 检查插入位置是否合法
private void checkAddPos(int pos) {
if (pos < 0 || pos > size) {
throw new PosIndexNotLegalException("pos位置不合法");
}
}
// 在指定位置插入元素
public void add(int pos, int data) {
try {
checkAddPos(pos);
if (isFull()) {
arr = Arrays.copyOf(arr, 2 * arr.length); // 如果数组已满,扩容为原来的两倍
}
for (int i = size - 1; i >= pos; i--) {
arr[i + 1] = arr[i]; // 元素后移
}
arr[pos] = data; // 在指定位置插入新元素
size++;
} catch (PosIndexNotLegalException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 判断是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (arr[i] == toFind) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// 查找某个元素对应的位置
public int indexOf(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (arr[i] == toFind) {
return i;
}
}
return -1; // 如果找不到返回-1
}
// 获取指定位置的元素
public int get(int pos) {
checkAddPos(pos);
return arr[pos];
}
// 给指定位置的元素赋值
public void set(int pos, int value) {
checkAddPos(pos);
arr[pos] = value;
}
// 删除第一次出现的指定元素
public void remove(int toRemove) {
int index = indexOf(toRemove);
if (index == -1) {
System.out.println("没有你要删除的数字!");
return;
}
for (int j = index; j < size; j++) {
arr[j] = arr[j + 1]; // 元素前移
}
size--;
}
// 获取顺序表长度
public int size() {
int ret = size;
return ret;
}
// 清空顺序表
public void clear() {
size = 0; // 将元素个数置为0,实现清空操作
}
}
5. ArrayList的优缺点
优点:
- 随机访问:由于 ArrayList 使用数组来存储元素,可以通过索引快速访问元素,性能较好,时间复杂度为 O(1)。
- 灵活的大小:ArrayList 的大小可以动态调整,不需要预先指定数组大小,可以根据需求动态增加或减少元素。
缺点:
- 插入和删除效率低:在 ArrayList 中间或开头插入或删除元素时,需要移动后续元素,时间复杂度为 O(n),性能较差。
- 内存开销:ArrayList 在动态扩容时需要重新分配内存并拷贝元素,可能会产生额外的内存开销。
总结
ArrayList 适合需要频繁随机访问元素、对大小变化较为频繁的场景,但在大量插入和删除操作时性能较差。
(三)?LinkedList
1. LinkedList的介绍
在前面ArrayList我们知道,当在ArrayList任意位置插入或者删除元素时,就需要将后序元素整体往前或者往后搬移,时间复杂度为O(n),效率比较低,因此ArrayList不适合做任意位置插入和删除比较多的场景。因此:java 集合中又引入了LinkedList,即链表结构。
LinkedList 是 Java 中的一个无头双向链表。实现,实现了 List 和 Deque 接口,LinkedList 内部是使用无头双向循环链表。表来存储元素,每个节点包含对前一个节点和后一个节点的引用。LinkedList 支持在任意位置进行高效的插入和删除操作,时间复杂度为 O(1)。无头双向链表结构图:
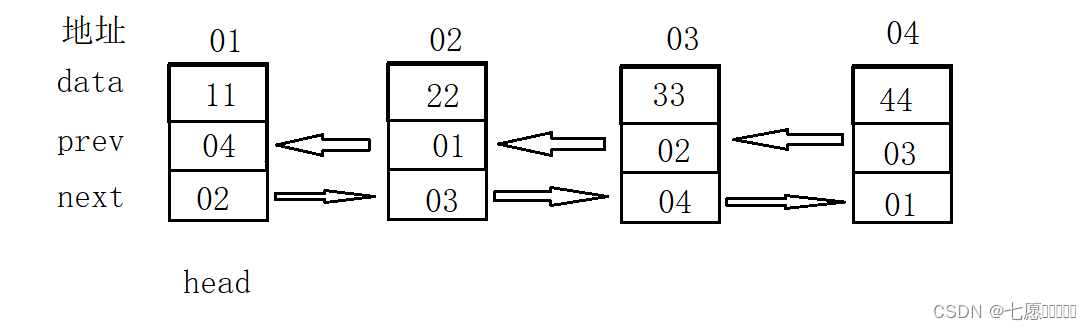
双向链表的每个节点都有 3 个属性:
-
data : 实际存放的内容;
-
prev : 指向前一节点的指针;
-
next : 指向后一节点的指针。
实际中链表的结构非常多样,单向或者双向, 带头或者不带头, 循环或者非循环
虽然有这么多的链表的结构,但是我们重点掌握两种:
无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如 哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。另外这种结构在笔试面试中出现很多。
无头双向链表:在Java的集合框架库中LinkedList底层实现就是无头双向循环链表。
2. LinkedList的常见方法和使用
LinkedList 类实现了 List 接口,因此它包含了 List 接口定义的所有方法,例如 add、remove、get、set 等。此外,LinkedList 还包含了一些特有的方法,如 addFirst、addLast等,用于在链表的开头或结尾进行操作
常见方法
- boolean add(E e): 在链表的末尾添加元素。
- void addFirst(E e): 在链表的开头添加元素。
- void addLast(E e): 在链表的末尾添加元素。
- E get(int index): 获取指定位置的元素。
- E set(int index, E element) 将下标 index 位置元素设置为 element
- boolean remove(): 删除并返回链表的第一个元素。
- String removeFirst(): 删除并返回链表的第一个元素。
- String removeLast(): 删除并返回链表的最后一个元素。
- int size(): 获取链表的大小。
- boolean contains(Object o): 判断链表是否包含指定的元素。
- int indexOf(Object o): 返回指定元素在链表中第一次出现的位置。
- int lastIndexOf(Object o) 返回最后一个 o 的下标
- void clear() 清空
import java.util.LinkedList;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
// 添加元素
linkedList.add("A");
System.out.println("添加 'A' 后的链表: " + linkedList);
linkedList.addFirst("B");
System.out.println("在链表开头添加 'B' 后的链表: " + linkedList);
linkedList.addLast("C");
System.out.println("在链表末尾添加 'C' 后的链表: " + linkedList);
// 获取元素
String elementAtIndex1 = linkedList.get(1);
System.out.println("索引为 1 的元素: " + elementAtIndex1);
// 设置元素
linkedList.set(0, "D");
System.out.println("将索引为 0 的元素设置为 'D' 后的链表: " + linkedList);
// 删除元素
String removedElement = linkedList.remove();
System.out.println("删除的元素: " + removedElement);
String removedFirst = linkedList.removeFirst();
System.out.println("删除的第一个元素: " + removedFirst);
String removedLast = linkedList.removeLast();
System.out.println("删除的最后一个元素: " + removedLast);
// 获取链表大小
int size = linkedList.size();
System.out.println("链表的大小: " + size);
// 判断是否包含元素
boolean contains = linkedList.contains("A");
System.out.println("链表是否包含 'A': " + contains);
// 获取元素的索引
int index = linkedList.indexOf("B");
System.out.println("'B' 在链表中的索引: " + index);
// 清空链表
linkedList.clear();
System.out.println("清空链表后的结果: " + linkedList);
}
}

3. LinkedList的遍历
可以使用foreach、迭代器来访问链表中的每个元素。?代码如下:
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
linkedList.add("A");
linkedList.add("B");
linkedList.add("C");
// 使用迭代器遍历
Iterator<String> iterator = linkedList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
String element = iterator.next();
System.out.println("Element: " + element);
}
// 使用foreach遍历
for (String element : linkedList) {
System.out.println("Element: " + element);
}
}
}
4. LinkedList的模拟实现
无头单向非循环链表代码如下:
public class SingleLinkedList {
// 定义节点类
static class Node {
public int val;
public Node next;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public Node head; // 链表头节点
// 头插法
public void addFirst(int data) {
Node node = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = node;
} else {
node.next = head;
head = node;
}
}
// 尾插法
public void addLast(int data) {
Node node = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = node;
return;
} else {
Node cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}
}
// 任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
checkIndex(index);
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index == size()) {
addLast(data);
return;
}
Node node = new Node(data);
// 找到要插入的前一个位置
Node cur = prevIndex(index - 1);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
private void checkIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size()) {
throw new IndexNotLegalException("index位置不合法!");
}
}
private Node prevIndex(int index) {
Node cur = head;
while (index > 0) {
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}
// 查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key) {
if (head == null) return false;
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
// 删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key) {
if (head == null) return;
if (head.val == key) {
head = head.next;
return;
}
Node cur = head.next;
Node prev = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
prev.next = cur.next;
return;
} else {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
// 删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
if (head == null) return;
Node cur = head.next;
Node prev = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
} else {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if (head.val == key) {
head = head.next;
}
}
// 得到单链表的长度
public int size() {
Node cur = head;
int count = 0;
while (cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
// 打印链表
public void display() {
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// 清空链表
public void clear() {
if (head == null) return;
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
Node curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
cur = curNext;
}
head = null;
}
// 一道练习题 -- 单链表的逆置
// 递归.单链表的逆置
public Node reverseList(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
if (head.next == null) {
return head;
}
Node newHead = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
// 要注意的是的下一个节点必须指向?。如果忽略了这一点,链表中会产生环,所以每反转一个,要把原来下个结点置null;
head.next = null;
return newHead;
}
// 非递归.单链表的逆置
public Node reverseList1() {
Node cur = head;
Node prev = null;
while (cur != null) {
Node nextCur = cur.next;
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = nextCur;
}
return prev;
}
}
无头双向循环链表的实现如下:
package MyLinkedList;
// 无头双向链表实现
public class MyTwoLinkedList {
// 定义节点类
static class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode next; //指向下一个节点
public ListNode prev; //指向上一个节点
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public ListNode head; // 表示存储当前链表的头节点的引用
public ListNode last; // 尾节点
// 打印链表
public void display() {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// 头插法
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (head == null) {
head = node;
last = node;
} else {
node.next = head;
head.prev = node;
head = node;
}
}
// 尾插法
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (head == null) {
head = node;
last = node;
return;
}
last.next = node;
node.prev = last;
last = last.next;
}
// 根据索引查找节点
private ListNode findIndex(int index) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (index > 0) {
index--;
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur;
}
// 任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (index < 0 || index > this.size()) {
throw new IndexNotLegalException("双向链表index不合法!");
}
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index == size()) {
addLast(data);
return;
}
// 获取到当前的index位置的节点的地址
ListNode cur = findIndex(index);
node.next = cur;
cur.prev.next = node;
node.prev = cur.prev;
cur.prev = node;
}
// 查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
// 删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
if (cur == head) {
head = head.next;
if (head != null) { // 防止只有一个节点
head.prev = null;
}
} else {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
// 删除的不是尾巴节点
if (last.val != key) {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
} else {
last = cur.prev;
}
}
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
// 删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
if (cur == head) {
head = head.next;
if (head != null) { // 防止只有一个节点
head.prev = null;
}
} else {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
// 删除的不是尾巴节点
if (cur.next != null) {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
} else {
// 删除的是尾结点
last = cur.prev;
}
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
// 得到单链表的长度
public int size() {
ListNode cur = head;
int len = 0;
while (cur != null) {
len++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return len;
}
// 清空链表
public void clear() {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode nextCur = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
cur.prev = null;
cur = nextCur;
}
head = null;
last = null;
}
}
5. LinkedList的优缺点
优点:
- 插入和删除操作效率高:在链表中插入和删除元素的效率很高,只需要修改节点的指针,不需要移动其他元素。
- 灵活性:链表可以动态地分配内存空间,可以根据需要动态地添加或删除节点。
缺点:
- 随机访问效率低:链表中要想访问第k个元素,需要从头节点开始顺序遍历,时间复杂度为O(n)。
- 占用空间多:链表中每个节点都需要额外的空间来存储指针,占用的空间比数组大。
- 不支持随机访问:链表不支持通过下标直接访问元素,只能通过指针进行遍历访问。
总结
LinkedList 适合需要频繁插入和删除操作、对随机访问要求不高的场景,但在需要频繁随机访问元素时性能较差。
(四) ArrayList和LinkedList的区别
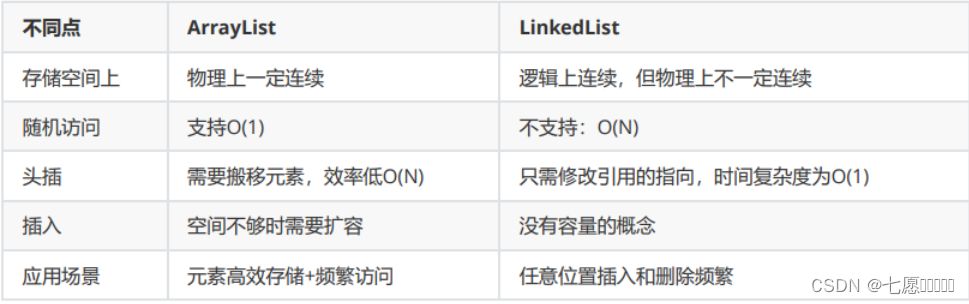
ArrayList 和 LinkedList 都是 Java 中的集合类,用于存储一组元素。它们之间的主要区别在于底层的数据结构和对元素的访问方式。
ArrayList 是基于数组实现的动态数组,它提供了快速的随机访问和遍历。在 ArrayList 中,每个元素都有一个索引,可以通过索引快速访问元素,但在插入和删除元素时需要移动其他元素,因此插入和删除操作的效率较低。
LinkedList 是基于链表实现的双向链表,它提供了快速的插入和删除操作。在 LinkedList 中,每个元素都包含对前一个元素和后一个元素的引用,因此插入和删除操作的效率比较高。但是在访问元素时需要从头或尾开始遍历,因此随机访问的效率较低。
总结
如果需要频繁进行插入和删除操作,可以选择 LinkedList;如果需要频繁进行随机访问和遍历操作,可以选择 ArrayList。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 园艺伴侣应用程序Plant-it
- idea中使用Lombok 失效,@Slf4j 找不到符号的解决办法
- This error originates from a subprocess, and is likely not a problem with pip
- 全国(山东、安徽)职业技能大赛--信息安全管理与评估大赛题目+答案讲解——windows应急响应篇
- 预处理详解(#和##运算符、命名约定、#undef??、命令行定义?、条件编译、头文件的包含?)
- 【上分日记】第381场周赛(差分 + 分类讨论)
- 在 Go 语言中使用 regexp 包处理正则表达式
- 云风网(www.niech.cn)个人网站搭建(一)基础准备
- Jmeter接口自动化03-JMeter的常用核心组件
- Redis 和 memcache 有什么区别?