@Scheduled任务调度/定时任务-非分布式
1、功能概述
任务调度就是在规定的时间内执行的任务或者按照固定的频率执行的任务。是非常常见的功能之一。常见的有JDK原生的Timer, ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor以及springboot提供的@Schduled。分布式调度框架如QuartZ、Elasticjob、XXL-JOB、SchedulerX、PowerJob等。
本文主要讲解非分布式环境下的@Scheduled任务调度讲解,以及@Scheduled结合多线程和@Async异步任务的使用。
当然在任务不是很多的情况下@Scheduled也可以结合如Redis的锁机制实现分布式的任务调度,但是还是建议在分布式环境下,使用分布式调度框架如:QuartZ、Elasticjob、XXL-JOB、SchedulerX、PowerJob等。
2、@Scheduled基本使用
2.1、创建springboot工程引入包信息
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.1.6</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.txc</groupId>
<artifactId>scheduleddemo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>scheduleddemo</name>
<description>scheduleddemo</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<image>
<builder>paketobuildpacks/builder-jammy-base:latest</builder>
</image>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
2.2、按照固定间隔执行
fixedDelay:按照固定间隔执行,上一个任务的结束到下一个任务的开始间隔。
initialDealay:延迟启动,启动之后指定时间再执行调度任务
@EnableScheduling:开启任务调度,写在类上只开启当前类中的任务调度,如果写在启动类上则开启项目中的所有任务调度。
@Slf4j
//加载类型开启类中,加载启动类上,开启整个项目
@EnableScheduling //是否开启
@Component
public class MyScheduled {
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 3000,initialDelay = 3000)
public void process(){
log.info("=====process执行========"+ LocalDateTime.now());
}
}
结果分析:
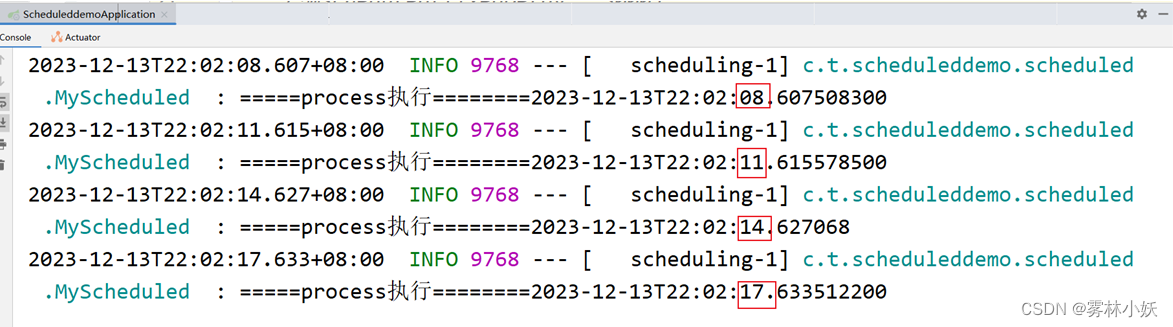
从输出结果中可以看出,程序每隔3s执行一次
2.3、按照固定频率执行任务
说明1:fixedRate:按照固定频率执行任务,如每三秒执行一次,上一个任务下次任务的开始,由于此时是单线程,下一个任务开始需要等上一个任务结束。
说明2:我们通过Thread.sleep(5000)设置任务执行需要2s时间
@Slf4j
//加载类型开启类中,加载启动类上,开启整个项目
@EnableScheduling //是否开启
@Component
public class MyScheduled {
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 3000,initialDelay = 3000)
public void process() throws InterruptedException {
log.info("=====process执行fixedRate开始========"+ LocalDateTime.now());
Thread.sleep(2000);
log.info("=====process执行fixedRate结束========"+ LocalDateTime.now());
}
}
结果分析:
从结果中可以看出由于设置process执行的时间为2s钟,process按照固定的频率(3s)每3s执行一次,第一次开始是22:19:22,第二次开始是22:19:25
2.4、按照固定频率执行任务
说明1:fixedRate:按照固定频率执行任务,如每三秒执行一次,上一个任务下次任务的开始,由于此时是单线程,下一个任务开始需要等上一个任务结束。
说明2:我们通过Thread.sleep(5000)设置任务执行需要5s时间
@Slf4j
//加载类型开启类中,加载启动类上,开启整个项目
@EnableScheduling //是否开启
@Component
public class MyScheduled {
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 3000,initialDelay = 3000)
public void process() throws InterruptedException {
log.info("=====process执行fixedRate开始========"+ LocalDateTime.now());
Thread.sleep(5000);
log.info("=====process执行fixedRate结束========"+ LocalDateTime.now());
}
}
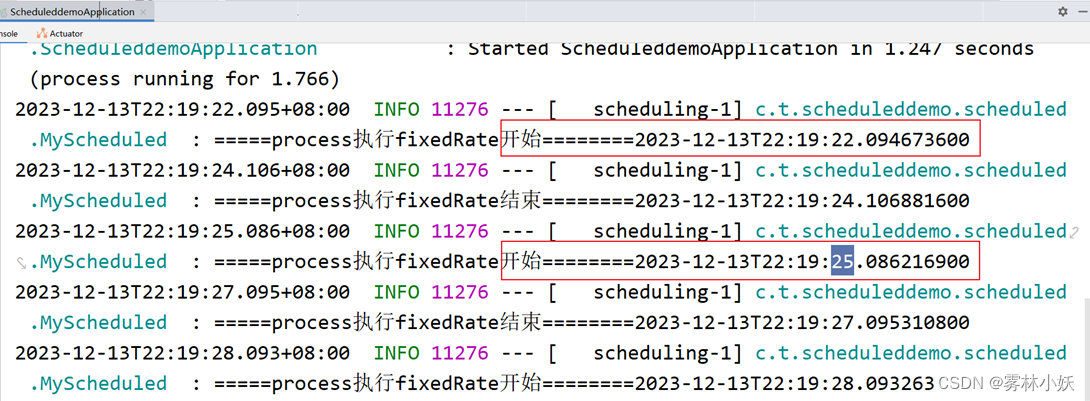
结果分析:
从结果可以看出:虽然设置固定的频率是3s,但是由于在单线程情况下下次任务的开启需要等待上一个任务的结束,第一次任务开始时间为22:17:43,第二次任务开启时间为22:17:48中间间隔了5s钟。

2.5、通过公式设置定时任务
cron:可以通过特性的公式设定定时任务,任务生成网站https://cron.qqe2.com/
如:可以设置每周三下午五点执行,每月的月尾执行一次等。
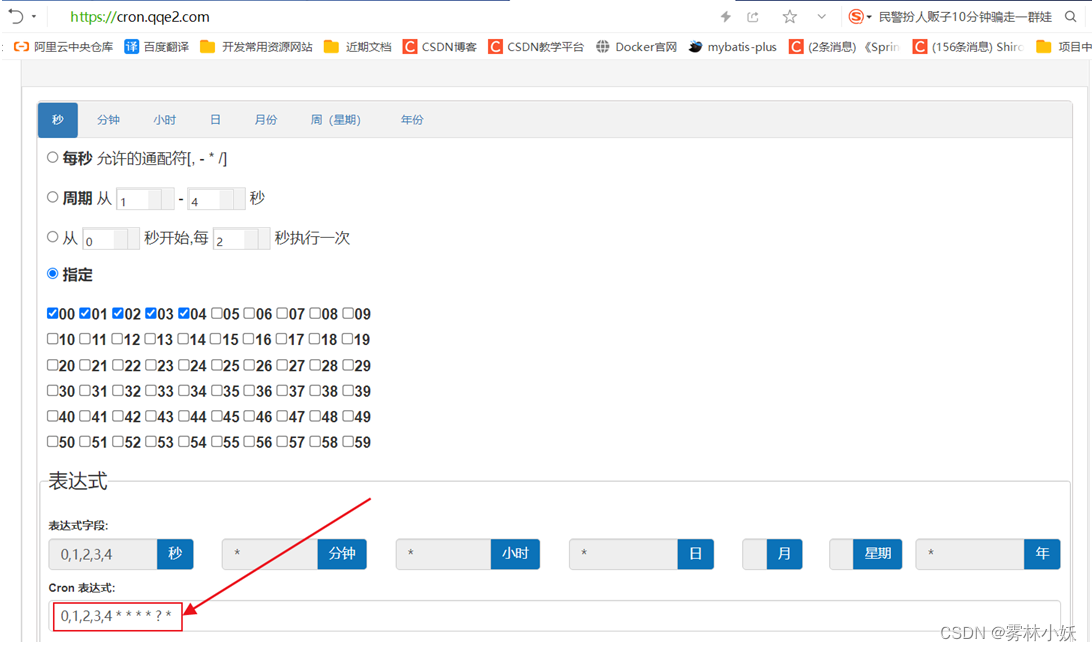
如上图生成的语法表示:每分钟的前五秒执行process
@Slf4j
//加载类型开启类中,加载启动类上,开启整个项目
@EnableScheduling //是否开启
@Component
public class MyScheduled {
@Scheduled(cron ="0,1,2,3,4 * * * * ? ")
public void process() throws InterruptedException {
log.info("=====process执行fixedRate开始========"+ LocalDateTime.now());
Thread.sleep(5000);
log.info("=====process执行fixedRate结束========"+ LocalDateTime.now());
}
}
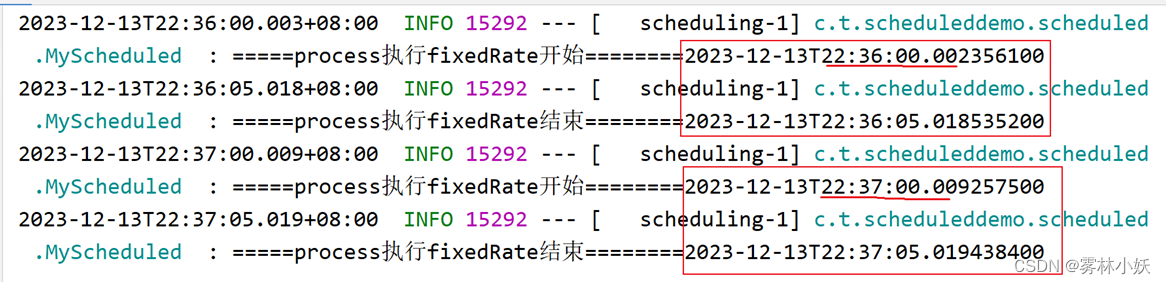
结果分析:
从图中可以看出每每分钟开始的时候执行,五秒后结束。
3、@Scheduled与多线程
加入多线程的目的是为了程序执行的效率能够提高。但是在设置多线程的时候,不能开辟过多的线程,因为线程资源非常的消耗cpu资源,必要的时候需要使用分布式任务调度。
3.1、非多线程的情况
理论上当process1结束的时候,下次process1启动的时候需要等待process2执行结束,否则1不能启动,应该这个时候依旧是单线程。
@Slf4j
//加载类型开启类中,加载启动类上,开启整个项目
@EnableScheduling //是否开启
@Component
public class MyScheduled {
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 3000)
public void process1() throws InterruptedException {
log.info("=====process1执行开始========"+ LocalDateTime.now());
Thread.sleep(5000);
log.info("=====process1执行结束========"+ LocalDateTime.now());
}
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 3000)
public void process2() throws InterruptedException {
log.info("=====process2执行开始========"+ LocalDateTime.now());
Thread.sleep(5000);
log.info("=====process2执行结束========"+ LocalDateTime.now());
}
}
结果分析:
从输出结果可以看出process2的开始是等到process1结束后才执行的。
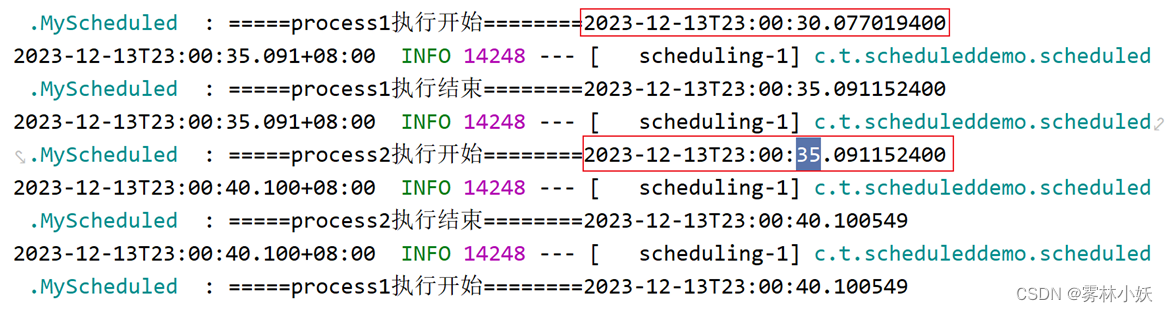
3.2、多线程的情况
在启动类中定义线程池。值不需要设置太大,现成对cpu资源消耗大,搞不好容易让系统宕机。
设置多线程后直接启动程序,继续观看process1和process2的输出情况。
package com.txc.scheduleddemo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.scheduling.TaskScheduler;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskScheduler;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ScheduleddemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ScheduleddemoApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public TaskScheduler taskScheduler(){
ThreadPoolTaskScheduler taskScheduler=new ThreadPoolTaskScheduler();
//设置线程池中线程的数量
//多线程对cpu资源消耗较大,值不能太大。
taskScheduler.setPoolSize(5);
return taskScheduler;
}
}
结果分析:
process1和process2使用的是不同的线程,一个线程为taskSheduler-1,一个线程为taskSheduler-2。
而且process1和process2是同时启动的,没有出现相互等待的情况,因为现在使用的是多线程的情况。
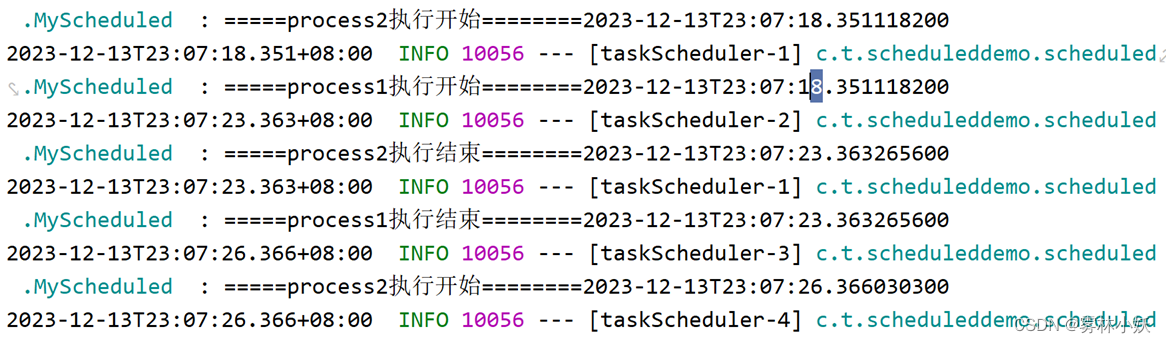
4、@Scheduled与@ Async异步任务
在上面的案例中虽然process1和process2同时执行了,没有出现相互等待的情况。但是第二次process1和process2执行依旧是等待程序5s结束后再等待3是执行。
name如何能够实现即使process1执行时间为5s,但是下一次process1的启动依旧是3s后。而不是当前的8是后。这就可以使用异步任务@Async。当然复杂的异步任务还是建议使用如MQ技术。
注意点:@Async的使用需要写在单独的一个类中,不能与当前调用业务写在一起,否则不生效。
完全不会使用@Async看如下博客:
https://blog.csdn.net/tangshiyilang/article/details/129440283
4.1、创建异步任务类及异步方法
@Component
public class AsyncTaskScheduled {
@Async//那个方法需要使用异步调用,就使用该注解
public void asyncMethod() {
try{
Thread.sleep(6000);//模拟异步执行业务的时间
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getStackTrace());
}
}
}
4.2、需要再启动类上开启异步任务
@EnableAsync:开启异步任务调度
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAsync
public class ScheduleddemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ScheduleddemoApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public TaskScheduler taskScheduler(){
ThreadPoolTaskScheduler taskScheduler=new ThreadPoolTaskScheduler();
//设置线程池中线程的数量
//多线程对cpu资源消耗较大,值不能太大。
taskScheduler.setPoolSize(10);
return taskScheduler;
}
}
4.3、创建process3和process4方法
process3和process3与之前的process1和process2方法一样都是基于多线程操作。
@Slf4j
//加载类型开启类中,加载启动类上,开启整个项目
@EnableScheduling //是否开启
@Component
public class MyScheduled {
@Autowired
AsyncTaskScheduled asyncTaskScheduled;
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 3000)
public void process3() throws InterruptedException {
log.info("=====process3执行开始========"+ LocalDateTime.now());
asyncTaskScheduled.asyncMethod();
log.info("=====process3执行结束========"+ LocalDateTime.now());
}
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 3000)
public void process4() throws InterruptedException {
log.info("=====process4执行开始========"+ LocalDateTime.now());
asyncTaskScheduled.asyncMethod();
log.info("=====process4执行结束========"+ LocalDateTime.now());
}
}
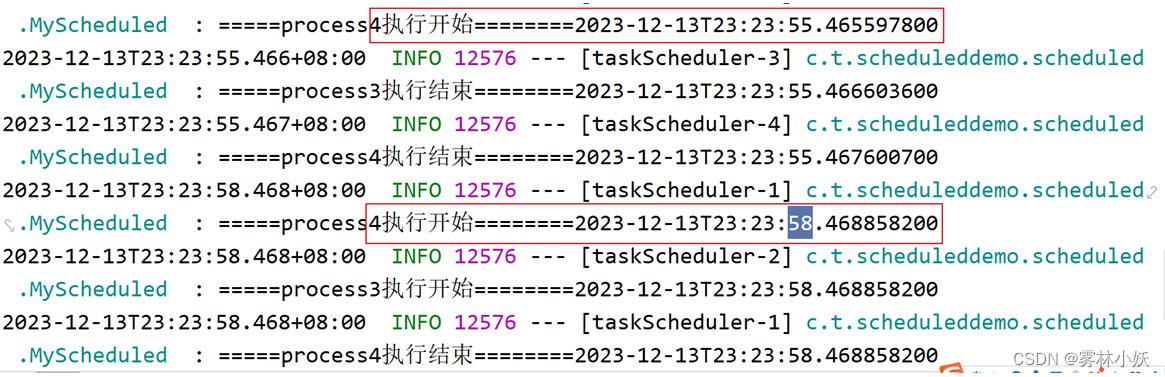
结果分析:
从结果可以看出,虽然异步任务执行的时间为6s,但是process4第一次开始和第二次开始的时间间隔为3s.
5、源码下载
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 软件工程复习自用---第三章
- Unity inspector绘制按钮与Editor下生成与销毁物体的方法 反射 协程 Editor
- 深入理解 Flink(八)Flink Task 部署初始化和启动详解
- 华为HCIP认证H12-831题库
- Java---IO流讲解(2)
- LINUX基础培训六之磁盘和文件系统管理
- SVN管理-备份还原篇
- 深度学习与大数据在自然语言处理中的应用与进展
- 一分钟教你搭建《幻兽帕鲁》服务器
- 2024免费的数据恢复软件EasyRecovery14自己操作就能恢复的方法