BFS basic_practice
发布时间:2024年01月09日
AcWing 844. 走迷宫
模版bfs
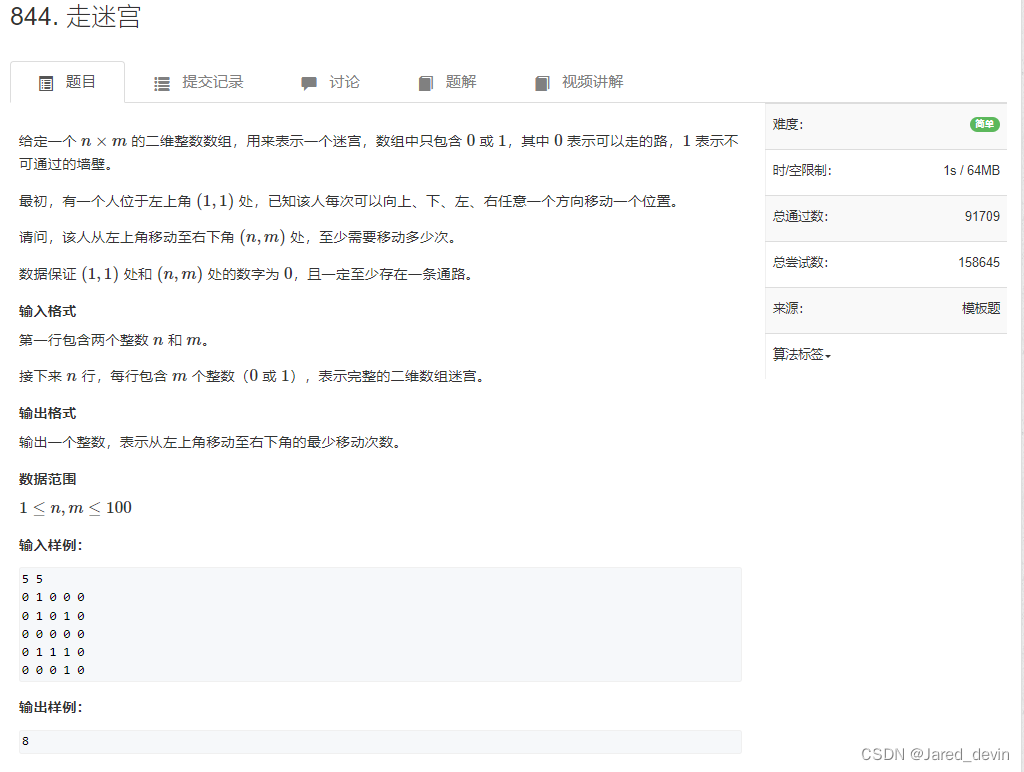
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 105;
int g[N][N];
int dist[N][N];
int dx[4] = { 1,0,-1,0 };
int dy[4] = { 0,-1,0,1 };
int n, m;
void bfs()
{
queue<PII> q;
q.push({ 0,0 });
while (!q.empty())
{
PII t = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int nex = t.first + dx[i];
int ney = t.second + dy[i];
//没有越界 && 不是墙 && 没有被更新(bfs可以保证每个合法点只更新一次)
if (nex >= 0 && nex < n && ney >= 0 && ney < m && dist[nex][ney] == 0 && g[nex][ney] == 0)
{
dist[nex][ney] = dist[t.first][t.second] + 1;
q.push({ nex,ney });
}
}
}
cout << dist[n - 1][m - 1];
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
memset(dist, 0, sizeof(dist));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
cin >> g[i][j];
}
}
bfs();
return 0;
}
AcWing 845. 八数码
此题时用字符串作为载体,并且用到字符串和矩阵的坐标转化
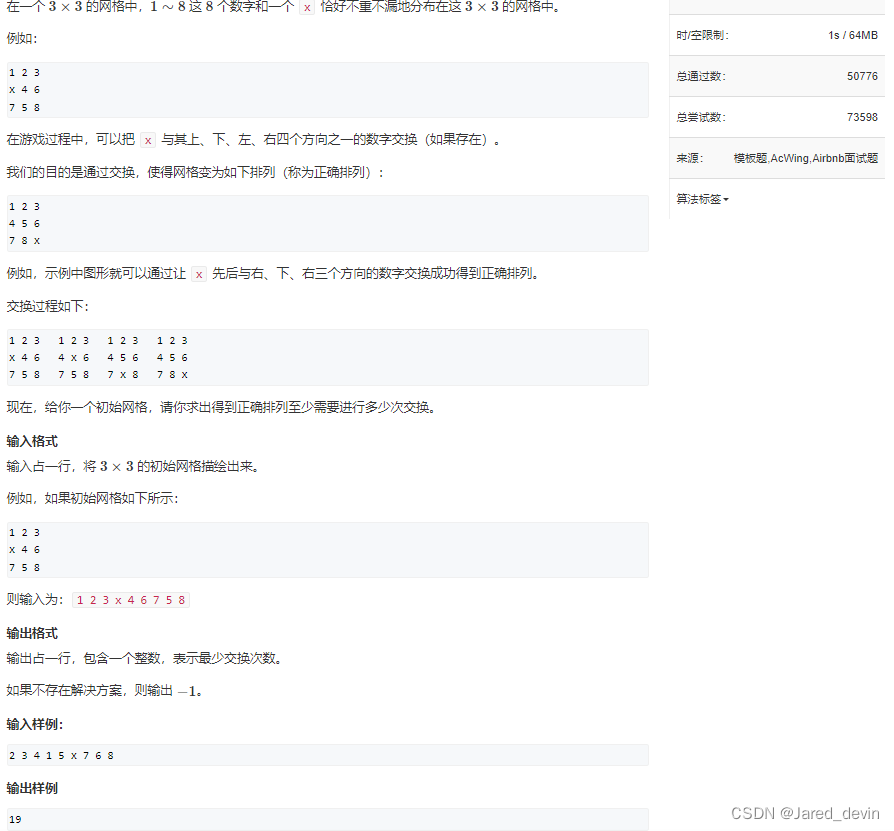
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
int dx[4] = { 1,0,-1,0 };
int dy[4] = { 0,-1,0,1 };
int n, m;
int bfs(string s)
{
string end = "12345678x";
queue<string> q;
map<string, int> dist;
q.push(s);
dist[s] = 0;
while (!q.empty())
{
string t = q.front();
q.pop();
int distance = dist[t];//用变量保存此状态字符串的距离,以便后续更新
if (t == end)return distance;
int k = t.find('x');//字符串中x的下标
int x = k / 3, y = k % 3;//矩阵中x的坐标
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int nex = x + dx[i];
int ney = y + dy[i];
if (nex >= 0 && nex < 3 && ney >= 0 && ney < 3)
{
//更新字符串中x的位置
swap(t[k],t[nex*3+ney]);
if (dist.find(t) == dist.end())//头一次遍历才更新距离
{
dist[t] = distance + 1;//等于上一次状态的字符串dist距离+1
q.push(t);
}
swap(t[k], t[nex * 3 + ney]);//还原现场
}
}
}
return -1;//无法转化为end
}
int main()
{
string s,c;
for(int i=1;i<=9;i++)
{
cin>>c;
s+=c;
}
cout<<bfs(s);
return 0;
}
坐标转化

文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_79227549/article/details/135453079
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 基于Scrapy的IP代理池搭建
- 这个被禁售的黑客小工具,曾让苹果用户崩溃
- python------Pymysql模块
- 设计模式-简单工厂
- YOLOv5改进 | 损失函数篇 | InnerIoU、InnerSIoU、InnerWIoU、FocusIoU等损失函数
- 鸿蒙原生应用/元服务实战-AGC团队账户
- TMC2208-LA单轴步进驱动器可替代A4988
- 【Linux系统编程二十九】基于信号量的环形队列生产消费模型
- 关于程序员的未来的这件事情,我是这么看的!
- 算法训练营第五十三天|1143.最长公共子序列 1035.不相交的线 53. 最大子序和