Spring学习之——事务控制
Spring中的事务控制
说明:
-
JavaEE体系进行分层开发,事务处理位于业务层,Spring提供了分层设计业务层的事务处理解决方案。
-
Spring框架为我们提供了一组事务控制的接口。具体在后面的小节介绍。这组接口是在spring-tx.RELEASE.jar中。
-
spring的事务控制都是基于AOP的,它既可以使用编程的方式实现,也可以使用配置的方式实现。我们学习的重点是使用配置的方式实现。
PlatformTransactionManager
- 此接口是spring的事务管理器,它里面提供了我们常用的操作事务的方法,源代码如下:
public interface PlatformTransactionManager {
//开启事务
TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition)
throws TransactionException;
//提交事务
void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
//回滚事务
void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
}
-
真正管理事务的对象
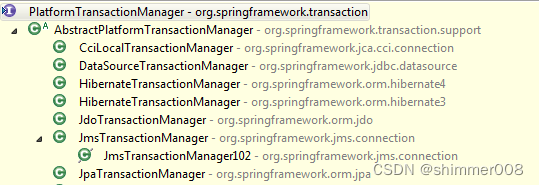
Spring为不同的orm框架提供了不同的PlatformTransactionManager接口实现类:
- DataSourceTransactionManager:使用Spring JDBC或iBatis 进行持久化数据时使用
- HibernateTransactionManager:使用Hibernate版本进行持久化数据时使用
TransactionDefinition
- TransactionDefinition接口包含与事务属性相关的方法,源代码如下:
public interface TransactionDefinition {
int PROPAGATION_REQUIRED = 0;
int PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS = 1;
int PROPAGATION_MANDATORY = 2;
int PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW = 3;
int PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED = 4;
int PROPAGATION_NEVER = 5;
int PROPAGATION_NESTED = 6;
int ISOLATION_DEFAULT = -1;
int ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED = 1;
int ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED = 2;
int ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ = 4;
int ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE = 8;
int TIMEOUT_DEFAULT = -1;
//传播行为
int getPropagationBehavior();
//隔离级别
int getIsolationLevel();
int getTimeout();
boolean isReadOnly();
}
TransactionDefinition 接口定义的事务规则包括:事务隔离级别、事务传播行为、事务超时、事务的只读、回滚规则属性,同时,Spring 还为我们提供了一个默认的实现类:DefaultTransactionDefinition,该类适用于大多数情况。如果该类不能满足需求,可以通过实现 TransactionDefinition 接口来实现自己的事务定义。
1.事务隔离级别
-
事务并发时的安全问题
问题 描述 隔离级别 脏读 一个事务读取到另一个事务还未提交的数据 read-commited 不可重复读 一个事务内多次读取一行数据的内容,其结果不一致 repeatable-read 幻读 一个事务内多次读取一张表中的内容,其结果不一致 serialized-read -
Spring事务隔离级别(比数据库事务隔离级别多一个default)由低到高为:
隔离级别 ISOLATION_DEFAULT 这是一个platfromtransactionmanager默认的隔离级别,使用数据库默认的事务隔离级别。 ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED 这是事务最低的隔离级别,会产生脏读,不可重复读和幻像读。 ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED 这种事务隔离级别可以避免脏读出现,但是可能会出现不可重复读和幻像读。 Oracle数据库默认的隔离级别。 ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ 这种事务隔离级别可以防止脏读、不可重复读,但是可能出现幻像读。MySQL数据库默认的隔离级别。 ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE 这是花费最高代价但是最可靠的事务隔离级别,事务被处理为顺序执行。除了防止脏读、不可重复读外,还避免了幻像读。
2.事务的传播行为
-
什么是事务传播行为?
事务传播行为(propagation behavior)指的就是当一个事务方法被另一个事务方法调用时,这个事务方法应该如何进行。
例如:methodA事务方法调用methodB事务方法时,methodB是继续在调用者methodA的事务中运行呢,还是为自己开启一个新事务运行,这就是由methodB的事务传播行为决定的。 -
Spring定义了七种传播行为:
事务传播行为类型 说明 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED 如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务,如果已经存在一个事务中,加入到这个事务中。这是最常见的选择。 PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行。 PROPAGATION_MANDATORY 使用当前的事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常。 PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW 新建事务,如果当前存在事务,把当前事务挂起。 PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED 以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起。 PROPAGATION_NEVER 以非事务方式执行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。 PROPAGATION_NESTED 如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行与REQUIRED类似的操作。
3.事务超时
timeout事务超时时间: 当前事务所需操作的数据被其他事务占用,则等待。- 100:自定义等待时间100(秒)。
- -1:由数据库指定等待时间,默认值。(建议)
4.读写性
readonly读写性-
true:只读,可提高查询效率,适合查询
-
false:可读可写,适合增删改
-
5.回滚规则
-
TransactionAttribute
TransactionAttribute 的默认实现类是DefaultTransactionAttribute ,它同时继承了DefaultTransactionDefinition。在DefaultTransactionDefinition 的基础上增加了rollbackOn的实现,DefaultTransactionAttribute的实现指定了,当异常类型为unchecked exception 的情况下将回滚事务。
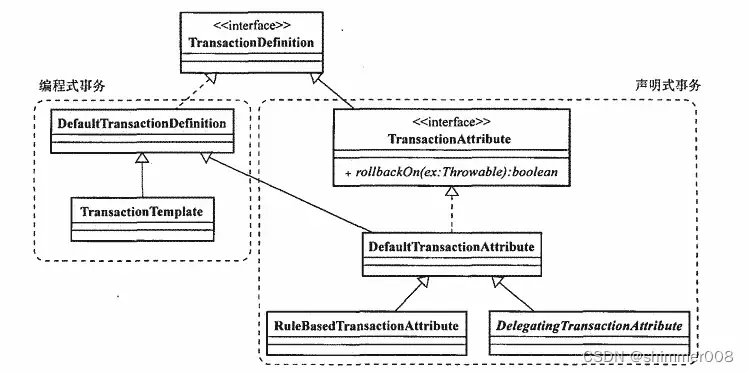
-
rollbackOn回滚规则,可省略或设置 rollbackOn=“Exception”-
如果事务中抛出 RuntimeException,则自动回滚
-
如果事务中抛出 CheckException,不会自动回滚
-
TransactionStatus
- PlatformTransactionManager.getTransaction(…) 方法返回一个 TransactionStatus 对象,该对象代表一个新的或已经存在的事务,源代码如下:
public interface TransactionStatus{
boolean isNewTransaction();
void setRollbackOnly();
boolean isRollbackOnly();
}
配置事务applicationContext.xml
<!--配置事物管理器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--配置事物属性-->
<bean class="org.springframework.transaction.support.DefaultTransactionDefinition">
<property name="propagationBehaviorName" value="PROPAGATION_REQUIRED"/>
<property name="readOnly" value="false"></property>
</bean>
Spring AOP控制事务
1.导入schema约束
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--配置事物属性
<bean class="org.springframework.transaction.support.DefaultTransactionDefinition">
<property name="propagationBehaviorName" value="PROPAGATION_REQUIRED"/>
<property name="readOnly" value="false"></property>
</bean>
配置service代理对象
<bean id="proxyService" factory-bean="beanFactory" factory-method="getUserService">
</bean>-->
</beans>
2.配置增强
<!-- 1、增强 -->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<!--事务属性-->
<tx:attributes>
<!-- 指定方法名称:是业务核心方法
read-only:是否是只读事务。默认false,不只读。
isolation:指定事务的隔离级别。默认值是使用数据库的默认隔离级别。
propagation:指定事务的传播行为。
timeout:指定超时时间。默认值为:-1。永不超时。
rollback-for:用于指定一个异常,当执行产生该异常时,事务回滚。产生其他异常,事务不回滚。
省略时任何异常都回滚。
-->
<tx:method name="*" read-only="false" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="select*" read-only="true" propagation="SUPPORTS"/>
<tx:method name="get*" read-only="true" propagation="SUPPORTS"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
3.配置切点
<aop:config>
<!--2、切点-->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.by.service.*.*(..))" id="pointcut"/>
</aop:config>
4.配置切面
<aop:config>
<!--3、切面-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pointcut"></aop:advisor>
</aop:config>
5.测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")//加载配置文件
public class ServiceTest {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
/**
* 转账业务
*/
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
userService.updateUser("张三丰","宋远桥",1F);
}
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Vue实现JSON字符串格式化编辑器组件
- 《GreenPlum系列》GreenPlum初级教程-03GreenPlum系统管理
- UI自动化测试框架搭建
- 电子公章软件,怎么实现批量自动盖章?
- Apollo Planning——PathLaneBorrowDecider
- 私有部署ELK,搭建自己的日志中心(二)-- filebeat的介绍与安装
- 1.15 freertos 计数器生产和消费模型
- 03.MySQL的体系架构
- odoo 一日一技 系统参数 config_parameter
- 1.4 Unity协程