linux多进程-fork和vfork
发布时间:2024年01月02日
参考文章:
Linux——进程(fork与vfork)
多进程编程学习笔记-1-进程基础
演示demo1
fork()和wait()
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
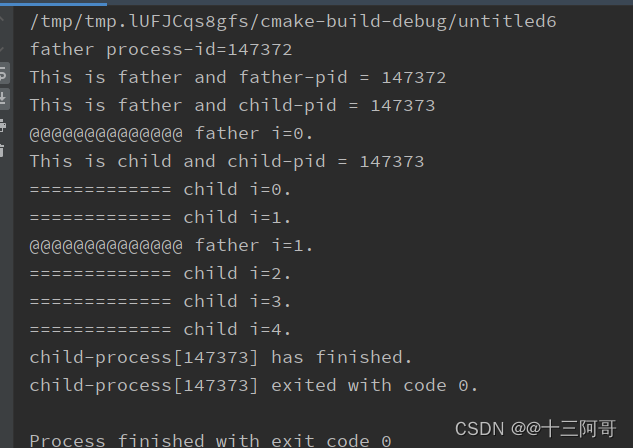
printf("father process-id=%d\n", getpid());
pid_t pid_fork = fork(); // if success, the pid_fork is child-process-id
if(pid_fork > 0) {
printf("This is father and father-pid = %d\n", getpid());
printf("This is father and child-pid = %d\n", pid_fork);
//
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
printf("@@@@@@@@@@@@@@ father i=%d.\n", i);
sleep(1);
}
// wait child-process finished
int stat_val ;
pid_t child_pid;
child_pid = wait(&stat_val);
printf("child-process[%d] has finished.\n", child_pid);
if(WIFEXITED(stat_val)) {
printf("child-process[%d] exited with code %d.\n", child_pid, WEXITSTATUS(stat_val));
} else {
printf("child-process[%d] terminated abnormally.\n", child_pid);
}
} else if(pid_fork == 0) {
printf("This is child and child-pid = %d\n", getpid());
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("============= child i=%d.\n", i);
sleep(1);
}
} else {
printf("fork error and error is %d[%s].", errno, strerror(errno));
perror("fork error.");
exit(1);
}
return 0;
}
演示demo2
fork()和vfork()的区别:
1)fork(): 父子进程的执行次序不确定。
?????vfork():保证子进程先运行,在它调用 exec(进程替换) 或 exit(退出进程)之后父进程才可能被调度运行。
2)fork(): 子进程拷贝父进程的地址空间,子进程是父进程的一个复制品。
?????vfork():子进程共享父进程的地址空间(准确来说,在调用 exec(进程替换) 或 exit(退出进程) 之前与父进程数据是共享的。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// vfork()
int main()
{
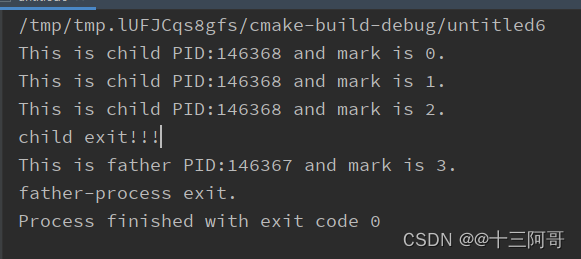
int mark = 0;
pid_t pid = vfork();
while(1) {
if(pid > 0) {
printf("This is father PID:%d and mark is %d.\n", getpid(), mark);
sleep(2);
printf("father-process exit.");
break;
} else if(pid == 0) {
printf("This is child PID:%d and mark is %d.\n", getpid(), mark++);
sleep(2);
if(mark > 2) {
printf("child exit!!!\n");
exit(-1);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/TianYanRen111/article/details/135348238
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- DAY4 --English learning
- 【Python 数据分析】描述性统计:平均数(均值)、方差、标准差、极大值、极小值、中位数、百分位数、用箱型图表示分位数
- 智能线上教育(开题+源码)
- java中反射的实际应用
- k8s的二进制部署(源码包部署)
- 2023.12.18Linux部署项目
- 晋江IP影视化频频折戟,网文陷入工业化困境
- 36个校招网络原理面试题
- prometheus node-exporter 全部指标说明
- python 1200例——【5】奇数求和