【Win11 搭建miniconda 的pytorch1.12环境】
请不要质疑我一直在水文章,因为我电脑被格式化了,需求又变了,这不得多多与时代接轨哦!
为我的GRCNN抓取打基础,之前是在Ubuntu上跑:【机械臂视觉抓取从理论到实战】,没错现在就是在WIN11上跑🤣🤣🤣,后面还会有对应演示视频哦💕💕💕
1. 下载miniconda
官网地址:https://docs.conda.io/projects/miniconda/en/latest/
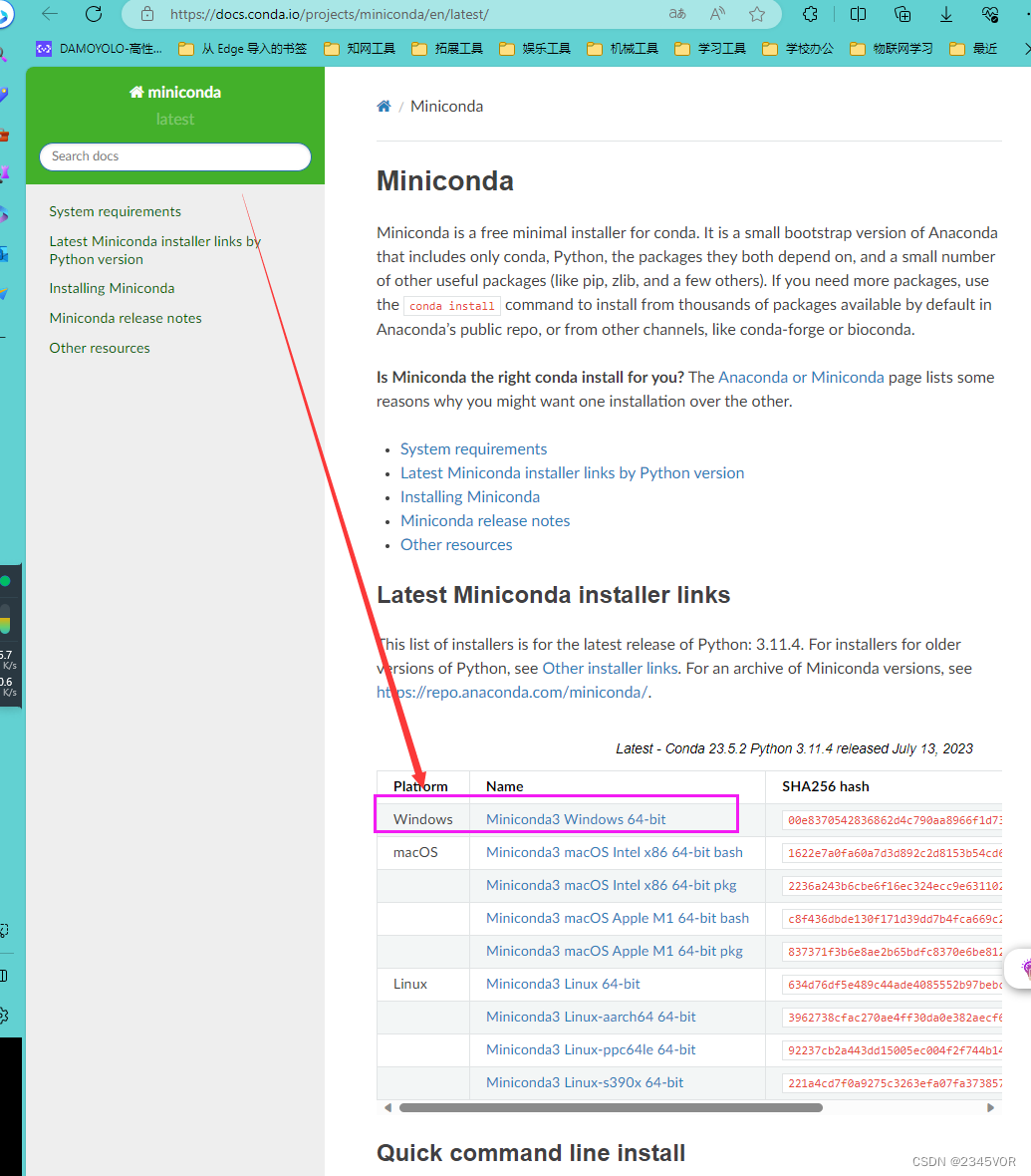
点击Miniconda3 Windows 64-bit下载
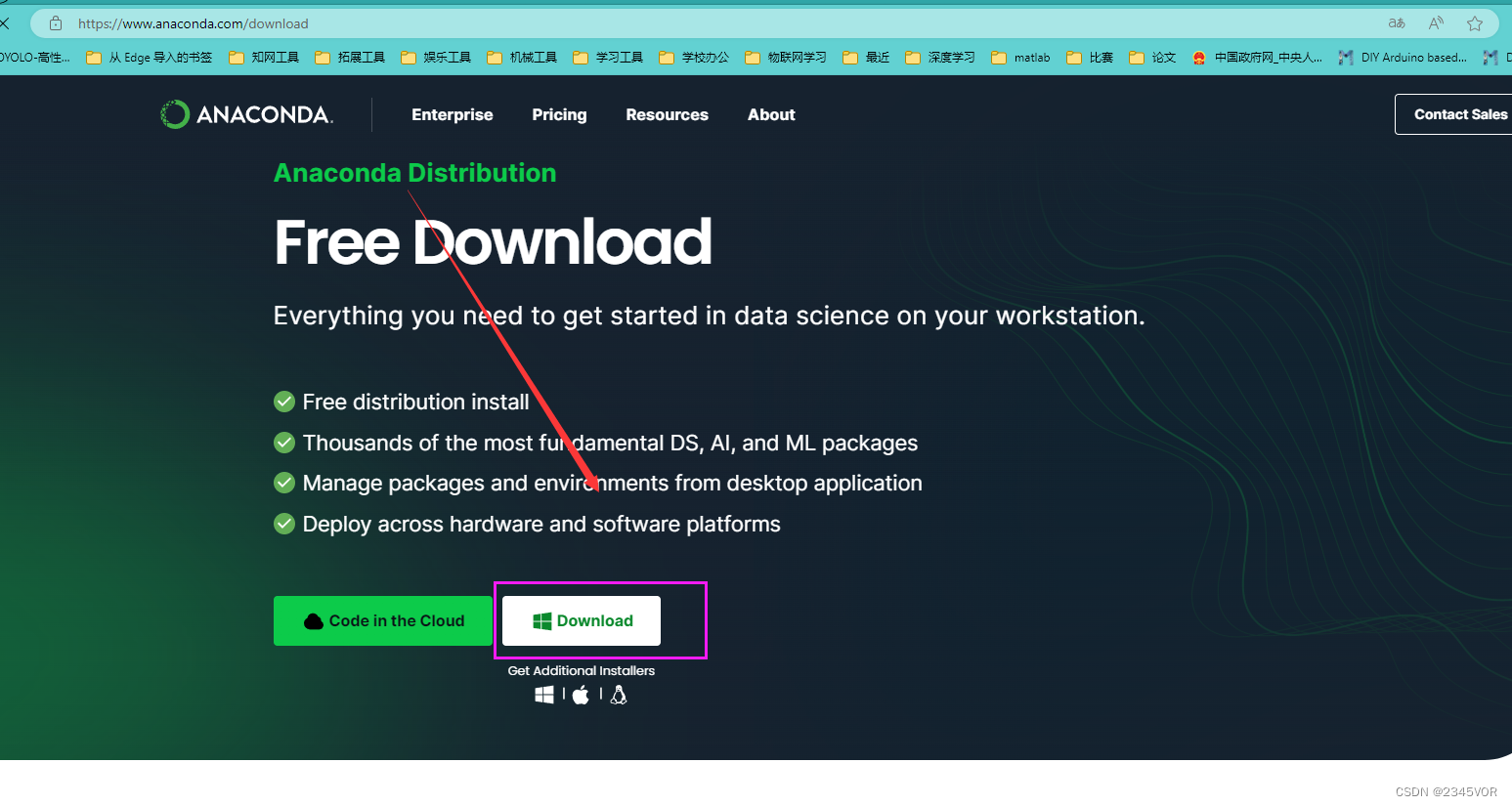
如果想体验全面的功能可下载完整版:https://www.anaconda.com/download
2. 安装miniconda
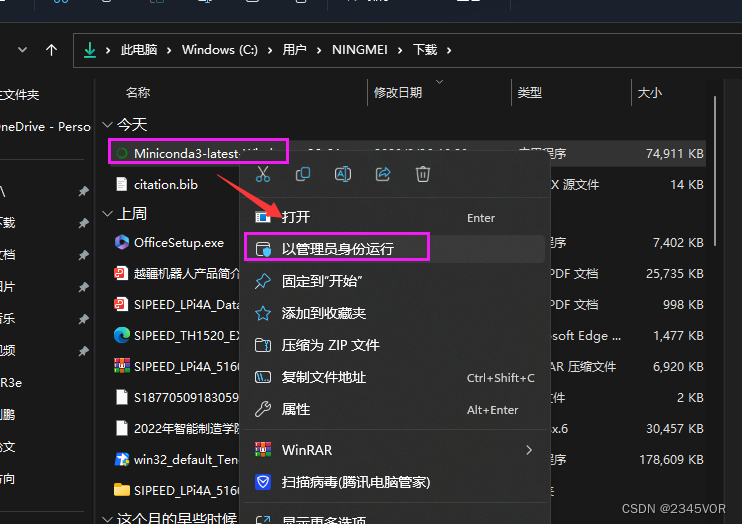
以管理员方式运行
点击下一步
点击我同意
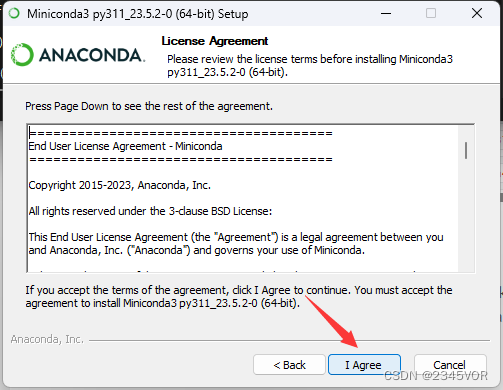
点击下一步
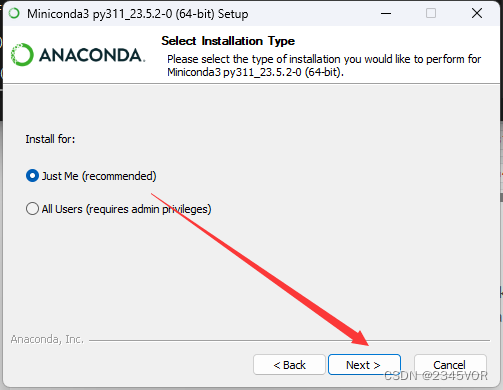
选择合适的安装路径,点击下一步
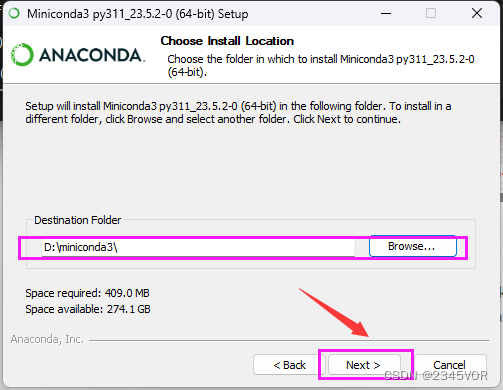
点击全选,第二项一定需要勾选,此处是添加环境变量,方便后期Vscode找到,点击安装
点击完成
在菜单中选择应用,搜索miniconda,打开miniconda终端
# 查看有那些虚拟环境
conda env list
# 查看有某个虚拟环境有那些包
conda list
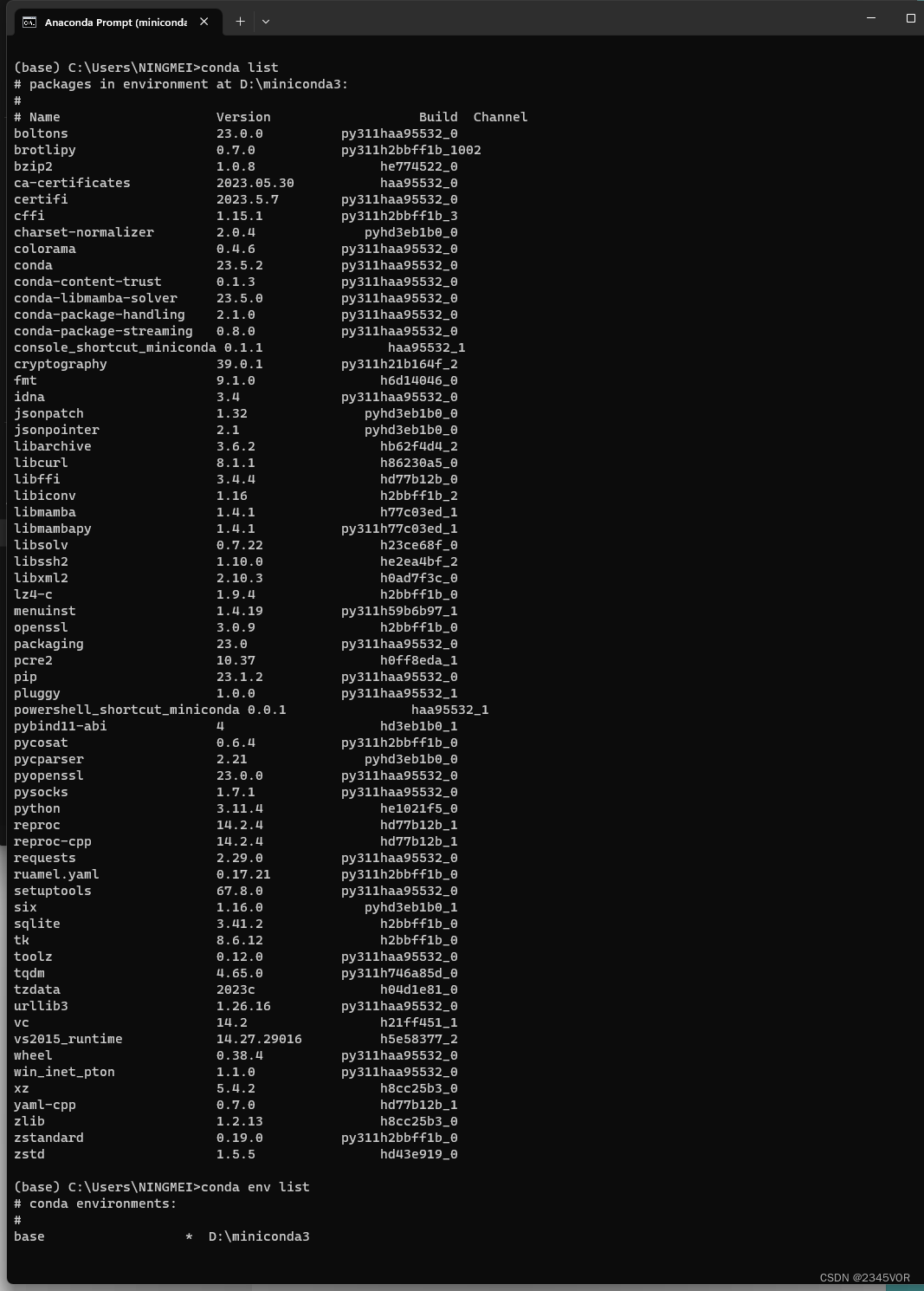
值得注意的是。若采用conda环境配置后续环境,需要注意python版本与Pytorch、Tensorflow等的版本对应关系!接下来的安装与配置均建立在系统环境基础上,不建立在conda环境基础上
3. miniconda换源
windows环境下conda更换为国内清华镜像源
或者
step1 Anaconda Prompt下输入以下命令 生成.condarc文件
conda config --set show_channel_urls yes
step2 找到.condarc文件,一般该文件在目录C:\Users\用户名 路径下
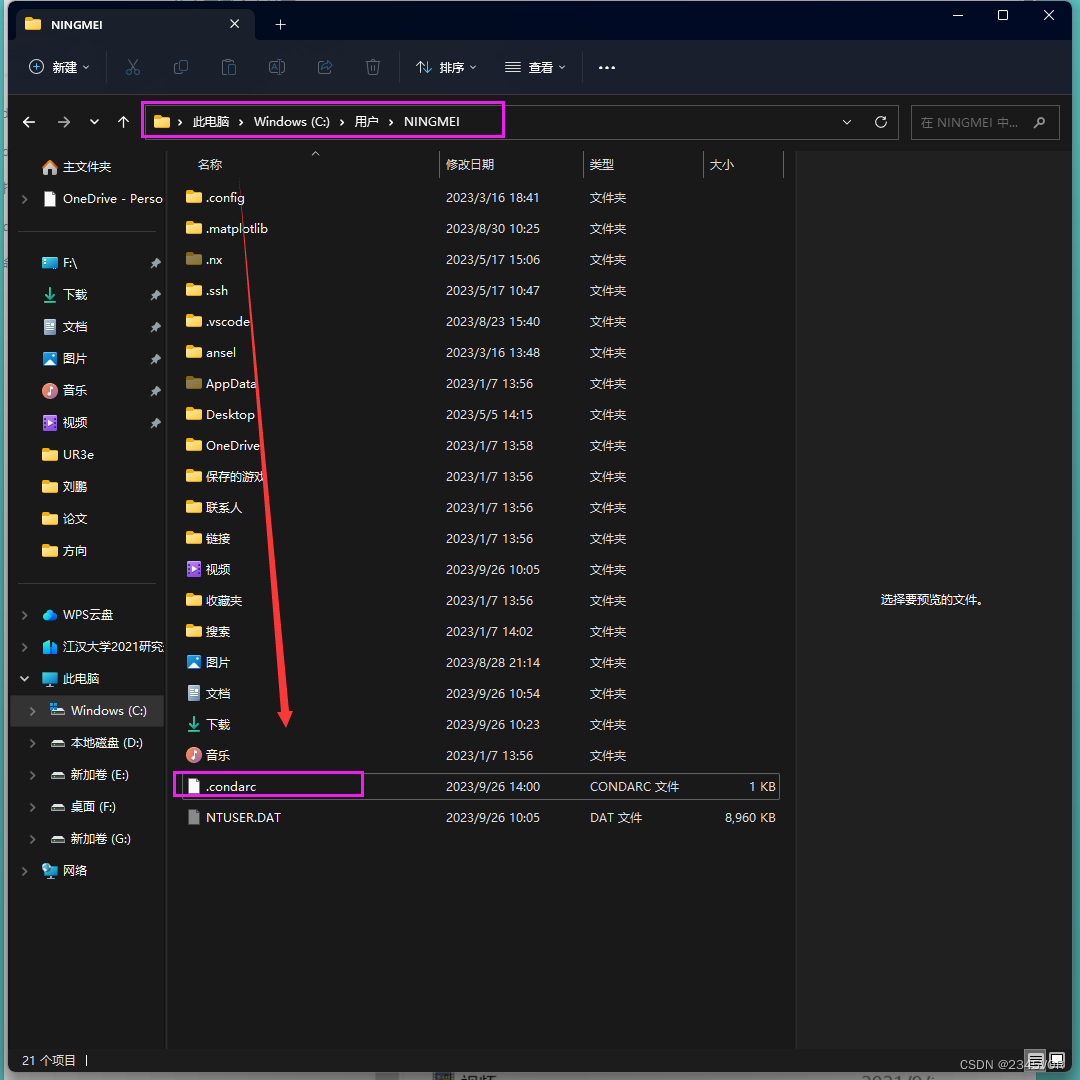
step3 以记事本打开.condarc,修改内容为:
channels:
- defaults
show_channel_urls: true
default_channels:
- https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main
- https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/r
- https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/msys2
custom_channels:
conda-forge: https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud
msys2: https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud
bioconda: https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud
menpo: https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud
pytorch: https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud
pytorch-lts: https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud
simpleitk: https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud
deepmodeling: https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud/
step4 运行 conda clean -i 清除索引缓存,保证用的是镜像站提供的索引。
conda clean -i
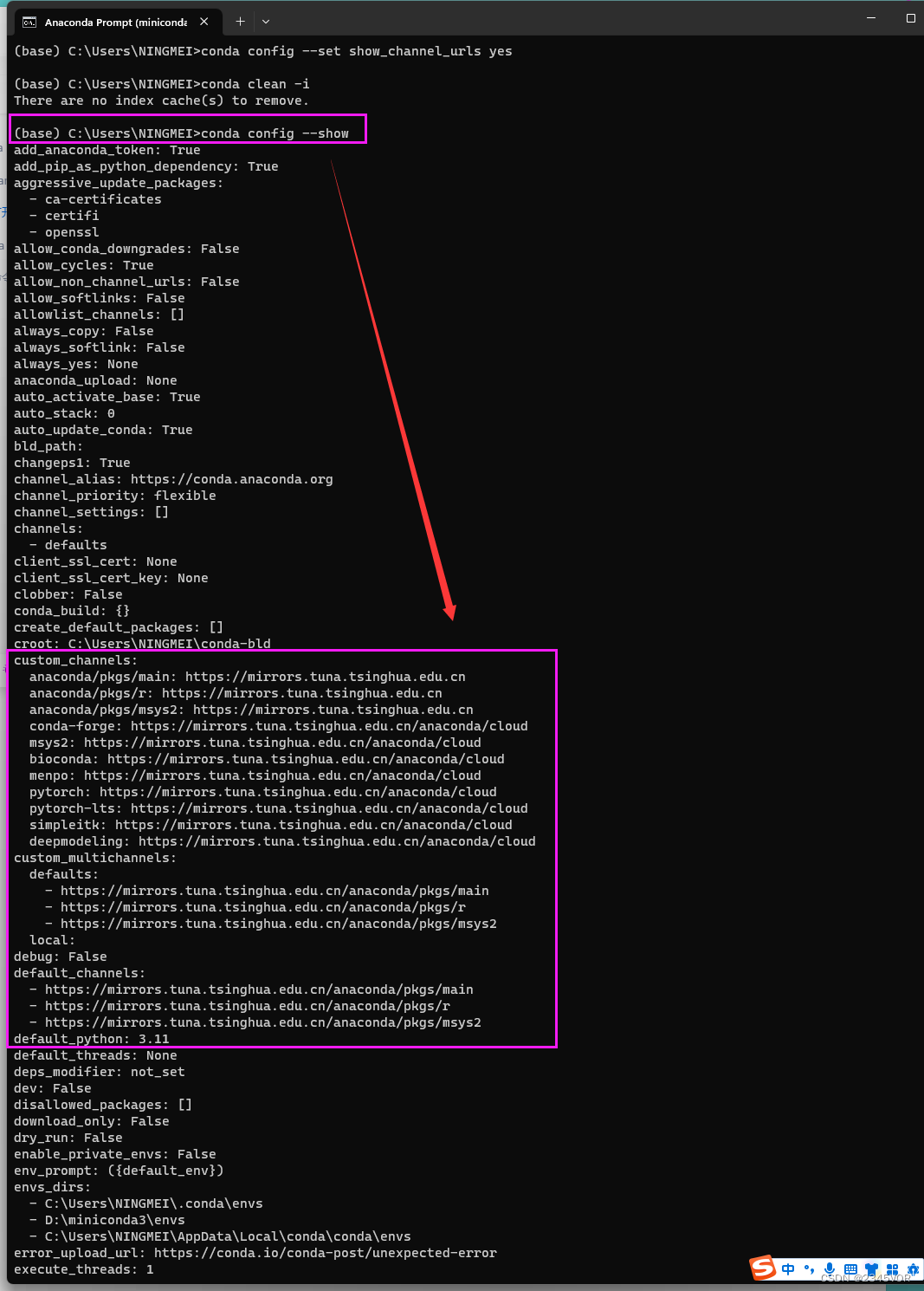
step5 输入以下命令将会显示conda的配置信息, 换源成功!!
conda config --show
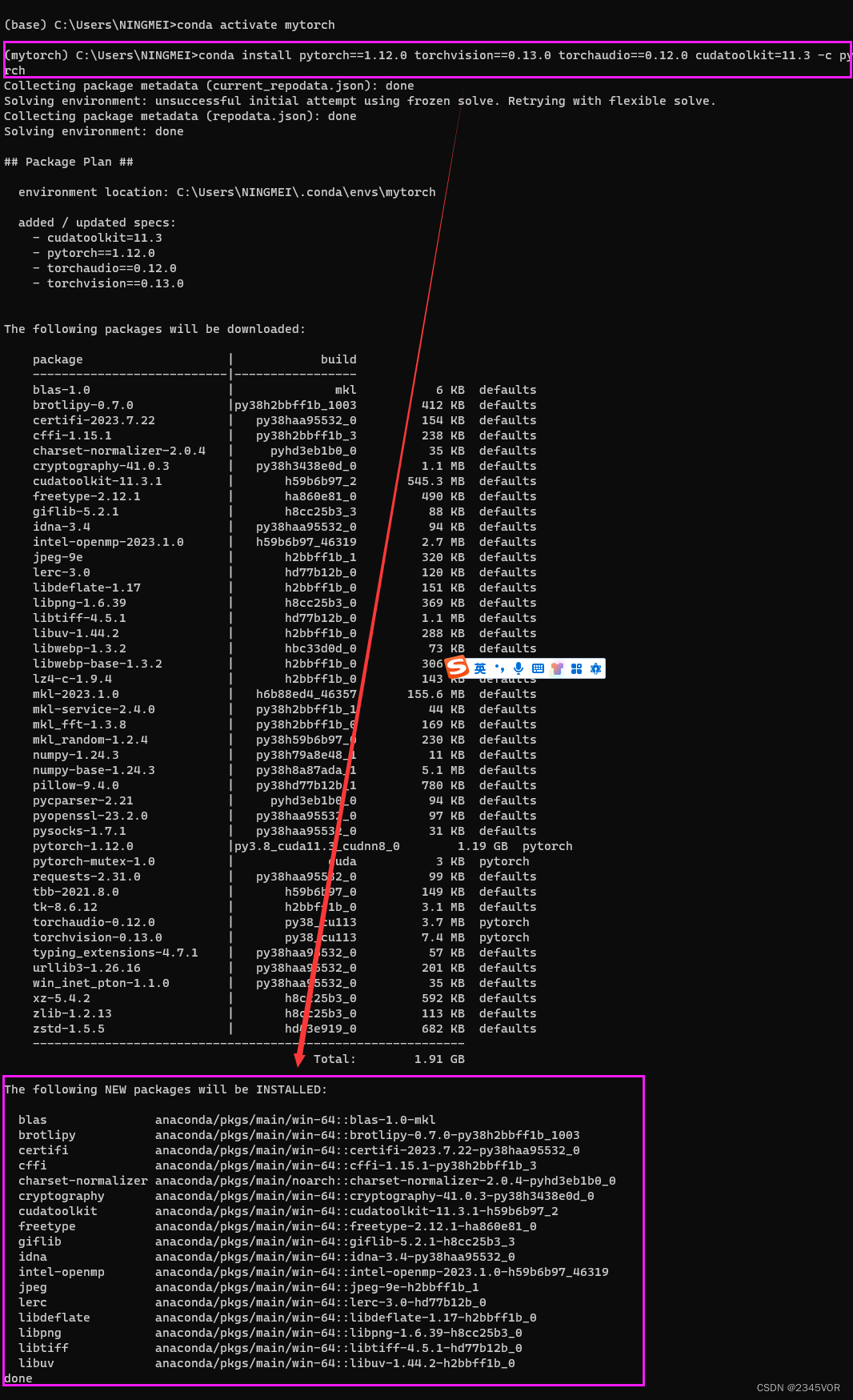
4. 安装pytorch
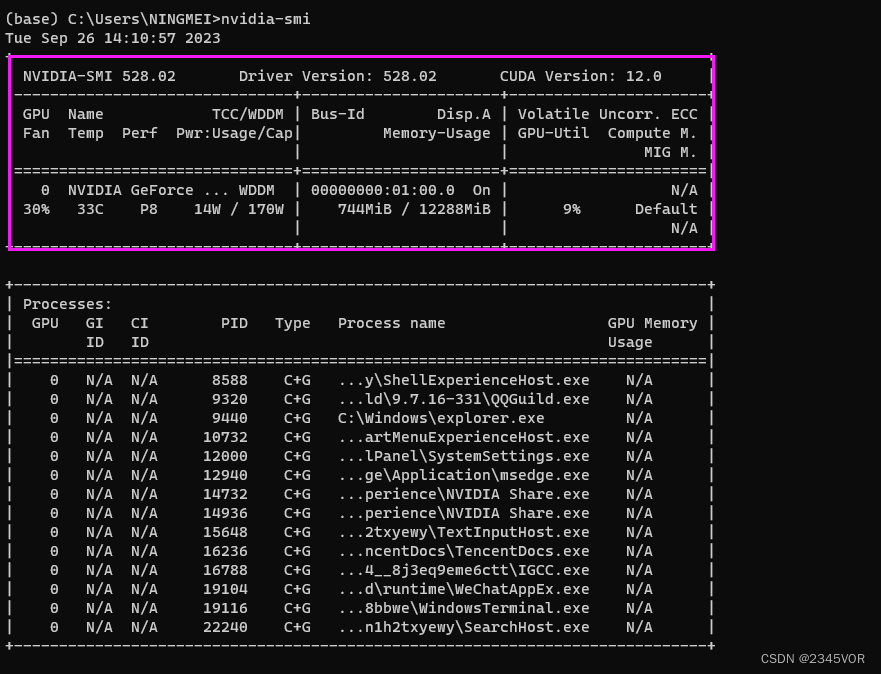
输入如下的命令。
nvidia-smi
得到如下图的信息图,可以看到驱动的版本是528.02;最高支持的CUDA版本是12.0版本。得到显卡的最高支持的CUDA版本,我们就可以根据这个信息来安装环境了。
大家需要根据自己开发环境选择合适版本,可参考:https://github.com/pytorch/vision
The following is the corresponding torchvision versions and supported Python
versions.
torch | torchvision | Python |
|---|---|---|
main / nightly | main / nightly | >=3.8, <=3.11 |
2.1 | 0.16 | >=3.8, <=3.11 |
2.0 | 0.15 | >=3.8, <=3.11 |
1.13 | 0.14 | >=3.7.2, <=3.10 |
torch | torchvision | Python |
|---|---|---|
1.12 | 0.13 | >=3.7, <=3.10 |
1.11 | 0.12 | >=3.7, <=3.10 |
1.10 | 0.11 | >=3.6, <=3.9 |
1.9 | 0.10 | >=3.6, <=3.9 |
1.8 | 0.9 | >=3.6, <=3.9 |
1.7 | 0.8 | >=3.6, <=3.9 |
1.6 | 0.7 | >=3.6, <=3.8 |
1.5 | 0.6 | >=3.5, <=3.8 |
1.4 | 0.5 | ==2.7, >=3.5, <=3.8 |
1.3 | 0.4.2 / 0.4.3 | ==2.7, >=3.5, <=3.7 |
1.2 | 0.4.1 | ==2.7, >=3.5, <=3.7 |
1.1 | 0.3 | ==2.7, >=3.5, <=3.7 |
<=1.0 | 0.2 | ==2.7, >=3.5, <=3.7 |
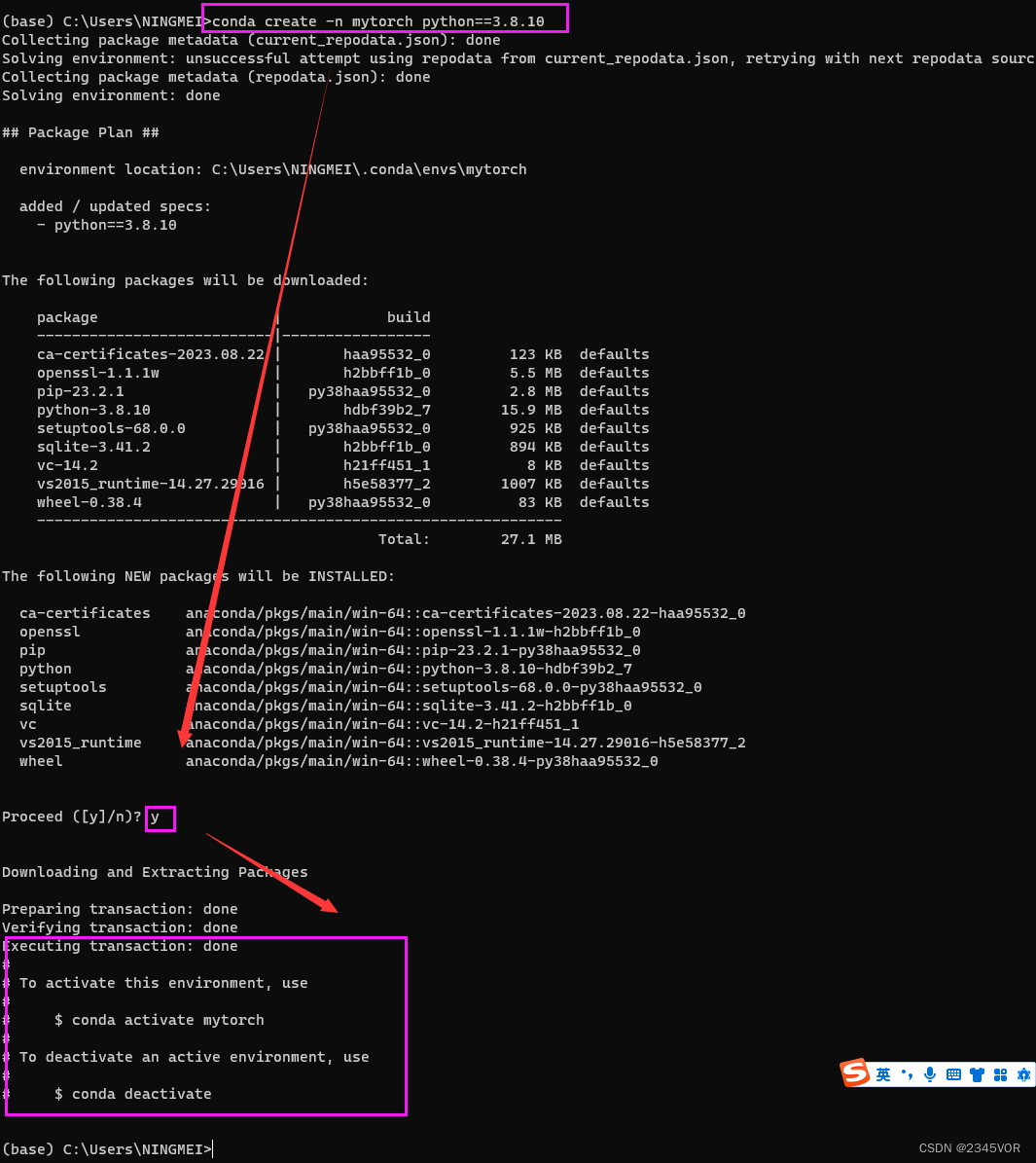
# 创建新的环境
conda create -n mytorch python==3.8.10
# 激活环境
conda activate mytorch
# 删除环境
conda remove -n mytorch --all
# 退出当前环境
conda deactivate
输入y
进入mytorch环境
# 激活环境
conda activate mytorch
根据官网提供的一键安装
#3.安装cuda,注意30系需要cudatoolkit11以上
# CUDA 10.2
conda install pytorch==1.12.0 torchvision==0.13.0 torchaudio==0.12.0 cudatoolkit=10.2 -c pytorch
# CUDA 11.3
conda install pytorch==1.12.0 torchvision==0.13.0 torchaudio==0.12.0 cudatoolkit=11.3 -c pytorch
# CUDA 11.6
conda install pytorch==1.12.0 torchvision==0.13.0 torchaudio==0.12.0 cudatoolkit=11.6 -c pytorch -c conda-forge
# CPU Only
conda install pytorch==1.12.0 torchvision==0.13.0 torchaudio==0.12.0 cpuonly -c pytorch
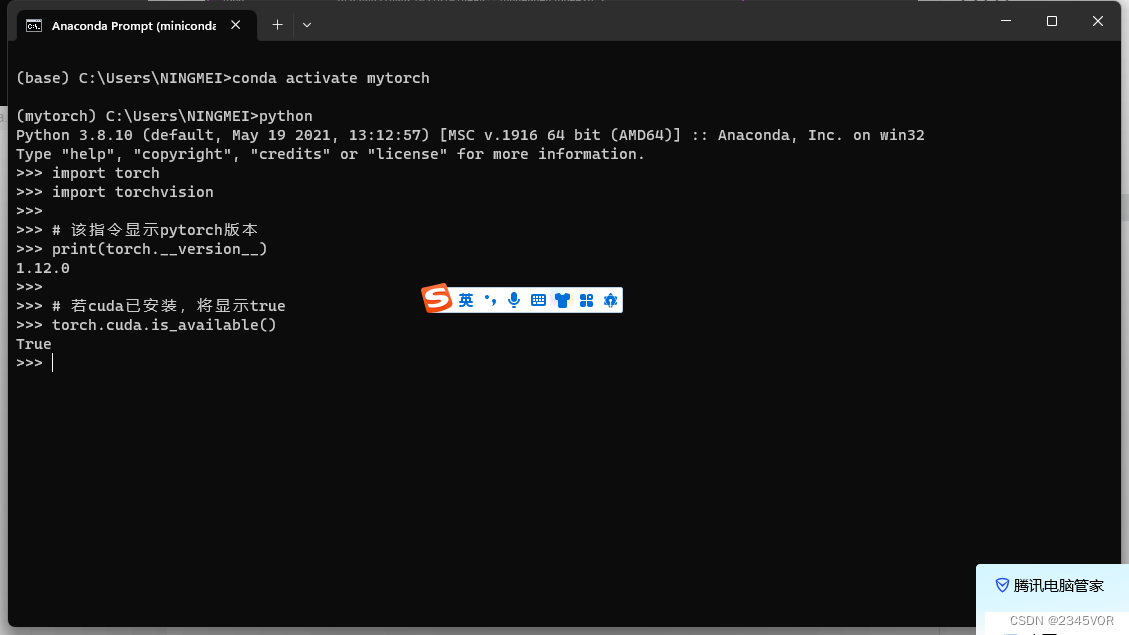
5. 测试是否安装成功
在终端激活环境后,输入python,输入下列指令:
import torch
import torchvision
# 该指令显示pytorch版本
print(torch.__version__)
# 若cuda已安装,将显示true
torch.cuda.is_available()
返回
有时可用使用pip临时更换镜像源
国内使用 pip命令安装包时,有时候会因为国外服务器的原因,安装速度过慢,使用国内镜像源安装包,速度会灰常快滴。以下是国内镜像源:
清华:https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
阿里云:http://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/
豆瓣:http://pypi.douban.com/simple/
pip 后面 加上 -i参数,再加上面的镜像源即可,示例如下:
pip install requests -i http://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/
6. 问题:
如果anaconda无法使用,可以考虑是否添加环境变量
说明
在Win11系统上正常安装完Anaconda之后,在cmd命令行窗口:
设置环境变量
1.此电脑-》属性-》高级系统设置-》环境变量
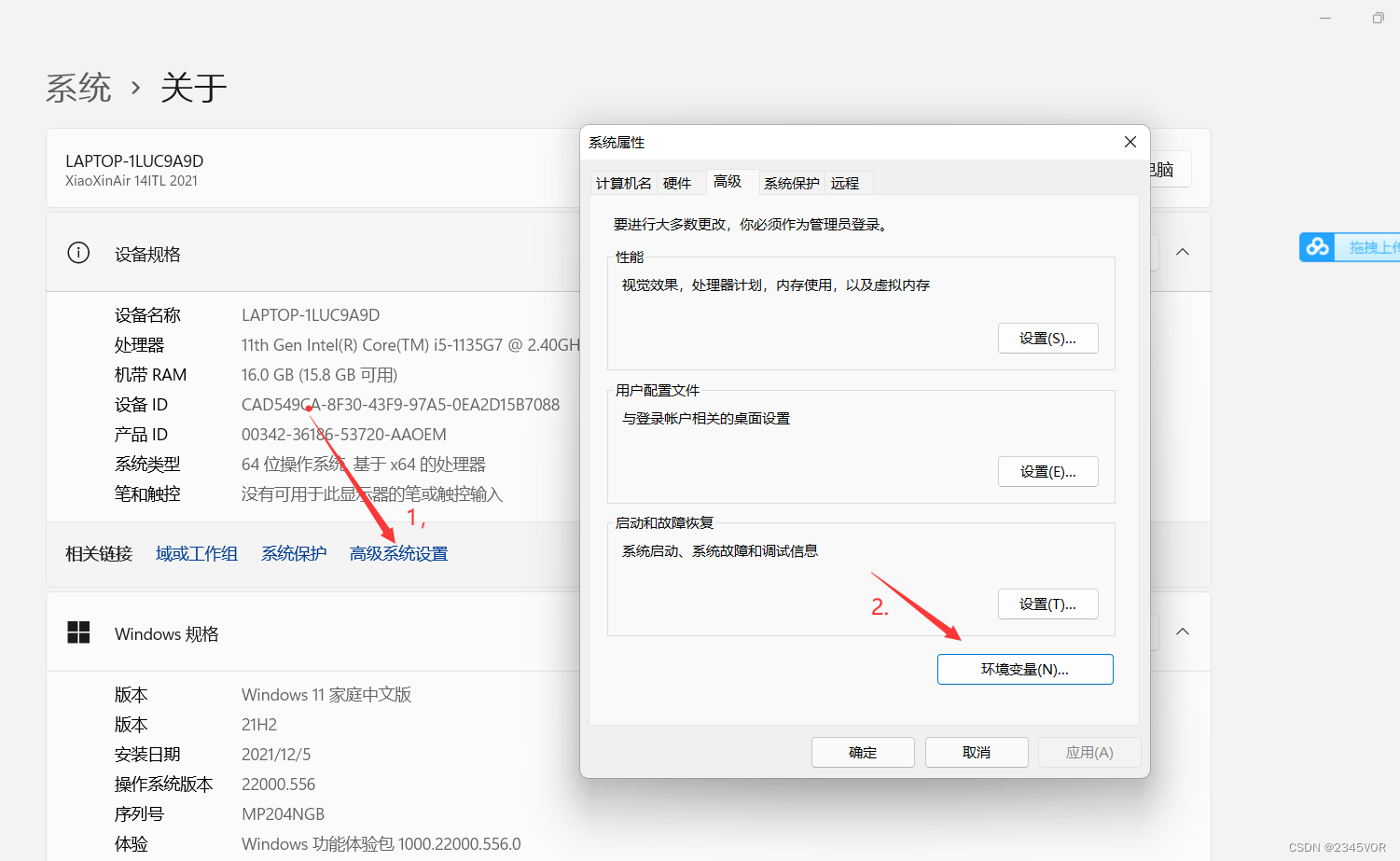
2.系统变量找到Path,在Path中添加如下两个变量
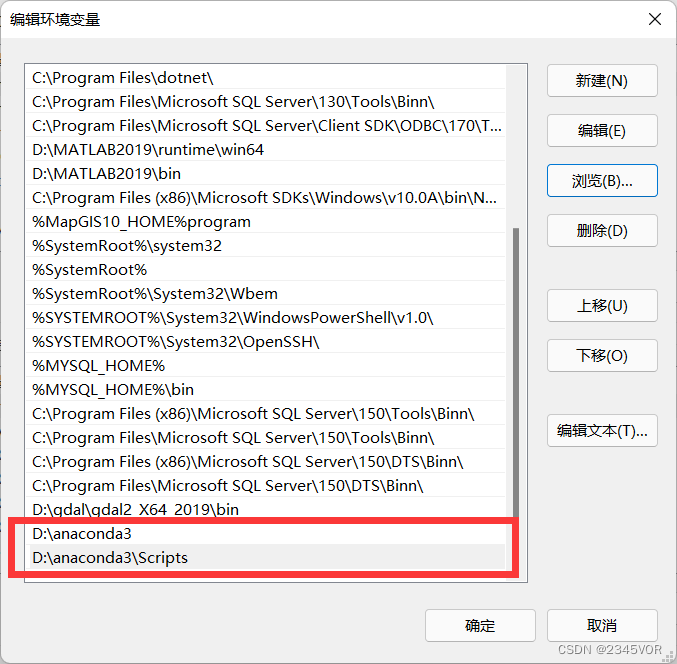
3.测试

至此,OK!!!
7. 总结
不管环境怎么更新,只要掌握其精髓,自然水到渠成。🎉🎉🎉🤣🤣🤣
import os
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import torch
from UR_Robot_real import UR_Robot_real
from inference.post_process import post_process_output
from utils.data.camera_data import CameraData
from utils.dataset_processing.grasp import detect_grasps
from utils.visualisation.plot import plot_grasp
import cv2
from PIL import Image
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import yaml
import pyrealsense2 as rs
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.torch_utils import select_device, time_sync
# from utils.general import (
# check_img_size, non_max_suppression, apply_classifier, scale_coords,
# xyxy2xywh, strip_optimizer, set_logging)
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.checks import check_imgsz
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.ops import non_max_suppression, scale_coords
from ultralytics.yolo.utils import LOGGER
from ultralytics import YOLO
from ultralytics.yolo.data.dataloaders.v5loader import LoadStreams, LoadImages, letterbox
# from models.experimental import attempt_load,
from ultralytics.nn.tasks import attempt_load_weights, attempt_load_one_weight
from ultralytics import YOLO
tool_xyz = np.asarray([-0.1, 0.25, 0.34])
tool_orientation = np.asarray([-np.pi,0,0])
hole_xyz = np.asarray([-0.105, -0.305, 0.345])
hole_orientation = np.asarray([np.pi/2,np.pi,0])
camera_target_position = np.asarray([[0],[0],[0],[1]])
target_position = np.asarray([-0.105, -0.305, 0.345])
image_wide_size = 640
image_high_size = 480
# PyTorch
# YoloV5-PyTorch
BH_yaml_path = 'weights/yolov8n.yaml'
with open(BH_yaml_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
yolov8 = yaml.load(f.read(), Loader=yaml.SafeLoader)
color_dict = {} # 创建一个空的字典来存储数字与颜色的对应关系
# 生成每个类别的颜色
for class_id in range(yolov8['nc']):
color = [np.random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)] # 生成一个随机颜色
color_dict[class_id] = color # 将数字和颜色添加到字典中
class PlaneGraspClass:
def __init__(self, saved_model_path=None,use_cuda=True,visualize=False,include_rgb=True,include_depth=True,output_size=300):
if saved_model_path==None:
saved_model_path = 'logs\\230802_1421_training_jacquard\epoch_30_iou_1.00'
# saved_model_path = 'trained-models/jacquard-rgbd-grconvnet3-drop0-ch32/epoch_48_iou_0.93'
self.model = torch.load(saved_model_path)
# YOLOV5模型配置文件(YAML格式)的路径 yolov5_yaml_path
self.model1 = YOLO("weights/best1.pt")
# model = YoloV8(yolov8_yaml_path='ultralytics/models/v8/yolov8.yaml')
print("[INFO] 完成YoloV8模型加载")
self.device = "cuda:0" if use_cuda else "cpu"
self.visualize = visualize
self.cam_data = CameraData(include_rgb=include_rgb,include_depth=include_depth,output_size=output_size)
# Load camera pose and depth scale (from running calibration)
self.ur_robot = UR_Robot_real(tcp_host_ip="192.168.56.10", tcp_port=30003, workspace_limits=None, is_use_robotiq85=True,
is_use_camera=True)
self.cam_pose = self.ur_robot.cam_pose
self.cam_depth_scale = self.ur_robot.cam_depth_scale
self.intrinsic = self.ur_robot.cam_intrinsics
if self.visualize:
self.fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
else:
self.fig = None
def get_aligned_images(self):
# frames = pipeline.wait_for_frames() # 等待获取图像帧
# aligned_frames = align.process(frames) # 获取对齐帧
# aligned_depth_frame = aligned_frames.get_depth_frame() # 获取对齐帧中的depth帧
# color_frame = aligned_frames.get_color_frame() # 获取对齐帧中的color帧
aligned_depth_frame, color_frame= self.ur_robot.get_camera_data1() # meter
############### 相机参数的获取 #######################
intr = color_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile().intrinsics # 获取相机内参
depth_intrin = aligned_depth_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile(
).intrinsics # 获取深度参数(像素坐标系转相机坐标系会用到)
'''camera_parameters = {'fx': intr.fx, 'fy': intr.fy,
'ppx': intr.ppx, 'ppy': intr.ppy,
'height': intr.height, 'width': intr.width,
'depth_scale': profile.get_device().first_depth_sensor().get_depth_scale()
}'''
# 保存内参到本地
# with open('./intrinsics.json', 'w') as fp:
# json.dump(camera_parameters, fp)
#######################################################
depth_image = np.asanyarray(aligned_depth_frame.get_data()) # 深度图(默认16位)
depth_image_8bit = cv2.convertScaleAbs(depth_image, alpha=0.03) # 深度图(8位)
depth_image_3d = np.dstack(
(depth_image_8bit, depth_image_8bit, depth_image_8bit)) # 3通道深度图
color_image = np.asanyarray(color_frame.get_data()) # RGB图
# 返回相机内参、深度参数、彩色图、深度图、齐帧中的depth帧
return intr, depth_intrin, color_image, depth_image, aligned_depth_frame
def camera_xyz_list_function(self):
# Wait for a coherent pair of frames: depth and color
intr, depth_intrin, color_image, depth_image, aligned_depth_frame = self.get_aligned_images() # 获取对齐的图像与相机内参
time.sleep(4)
intr, depth_intrin, color_image, depth_image, aligned_depth_frame = self.get_aligned_images() # 获取对齐的图像与相机内参
# Convert images to numpy arrays
# Apply colormap on depth image (image must be converted to 8-bit per pixel first)
depth_colormap = cv2.applyColorMap(cv2.convertScaleAbs(
depth_image, alpha=0.03), cv2.COLORMAP_JET)
# Stack both images horizontally
images = np.hstack((color_image, depth_colormap))
# Show images
camera_xyz_list = []
t_start = time.time() # 开始计时
# YoloV8 目标检测
results = self.model1.predict(color_image)
xyxy_list = results[0].boxes.xyxy
conf_list = results[0].boxes.conf
class_id_list = results[0].boxes.cls
canvas = np.copy(color_image)
t_end = time.time() # 结束计时
for i in range(len(xyxy_list)):
if conf_list[i] > 0.6:
x_min = int(xyxy_list[i][0])
y_min = int(xyxy_list[i][1])
x_max = int(xyxy_list[i][2])
y_max = int(xyxy_list[i][3])
if x_min < image_wide_size and y_min < image_high_size and x_max < image_wide_size and y_max < image_high_size:
dis_min = aligned_depth_frame.get_distance(x_min, y_min)
dis_max = aligned_depth_frame.get_distance(x_max, y_max)
dis = (dis_min + dis_max) / 2
ux = int((x_min + x_max) / 2)
uy = int((y_min + y_max) / 2)
camera_xyz = rs.rs2_deproject_pixel_to_point(
depth_intrin, (ux, uy), dis) # 计算相机坐标系的xyz
camera_xyz = np.round(np.array(camera_xyz), 3) # 转成3位小数
camera_xyz = camera_xyz.tolist()
camera_xyz_list.append(camera_xyz)
num_cls = int(class_id_list[i].item())
label = '%s ' % (yolov8['class_name'][num_cls])
color = color_dict[num_cls]
cv2.putText(canvas, label + str(round(conf_list[i].item(), 2)),
(int(xyxy_list[i][0]), int(xyxy_list[i][1])), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1,
(255, 255, 255),
2)
cv2.rectangle(canvas, (int(xyxy_list[i][0]), int(xyxy_list[i][1])),
(int(xyxy_list[i][2]), int(xyxy_list[i][3])), color, 2)
cv2.circle(canvas, (ux, uy), 4, (255, 255, 255), 5) # 标出中心点
cv2.putText(canvas, str(camera_xyz), (ux + 20, uy + 10), 0, 1,
[225, 255, 255], thickness=2, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA) # 标出坐标
fps = int(1.0 / (t_end - t_start))
cv2.putText(canvas, text="FPS: {}".format(fps), org=(50, 50),
fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, fontScale=1, thickness=2,
lineType=cv2.LINE_AA, color=(0, 0, 0))
cv2.namedWindow('detection', flags=cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL |
cv2.WINDOW_KEEPRATIO | cv2.WINDOW_GUI_EXPANDED)
cv2.imshow('detection', canvas)
return camera_xyz_list, t_end, t_start, canvas
def generate(self):
target1_position= [0,0,0]
destination1=np.append(hole_xyz,hole_orientation)
self.ur_robot.move_j_p(destination1)
xyz_list, t_end, t_start, canvas = self.camera_xyz_list_function()
xyz_list = np.asarray(xyz_list)
index=xyz_list.shape[0]
print(xyz_list)
# target1_position[0] = hole_xyz[0]+xyz_list[0,0]-0.043
# target1_position[1] = hole_xyz[1]- xyz_list[0,2]+0.28
# target1_position[2] = hole_xyz[2]+xyz_list[0,1]+0.075
# target1_position= np.asarray(target1_position)
# target1_position = np.append(target1_position,hole_orientation)
# print(target1_position)
# self.ur_robot.move_j_p(target1_position)
for i in range(index):
# time.sleep(1.5)
# # 添加fps显示
self.ur_robot.move_j([-(0 / 360.0) * 2 * np.pi, -(90 / 360.0) * 2 * np.pi,
(0 / 360.0) * 2 * np.pi, -(90 / 360.0) * 2 * np.pi,
-(0 / 360.0) * 2 * np.pi, 0.0])# return home
# time.sleep(1.5)
## if you want to use RGBD from camera,use me
# Get RGB-D image from camera
grasp_home = np.append(tool_xyz,tool_orientation)
self.ur_robot.move_j_p(grasp_home)
time.sleep(1.5)
rgb, depth= self.ur_robot.get_camera_data() # meter
depth = depth *self.cam_depth_scale
depth[depth >1]=0 # distance > 1.2m ,remove it
## if you don't have realsense camera, use me
# num =2 # change me num=[1:6],and you can see the result in '/result' file
# rgb_path = f"./cmp{num}.png"
# depth_path = f"./hmp{num}.png"
# rgb = np.array(Image.open(rgb_path))
# depth = np.array(Image.open(depth_path)).astype(np.float32)
# depth = depth * self.cam_depth_scale
# depth[depth > 1.2] = 0 # distance > 1.2m ,remove it
depth= np.expand_dims(depth, axis=2)
x, depth_img, rgb_img = self.cam_data.get_data(rgb=rgb, depth=depth)
time.sleep(1.5)
x, depth_img, rgb_img = self.cam_data.get_data(rgb=rgb, depth=depth)
rgb = cv2.cvtColor(rgb,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
with torch.no_grad():
xc = x.to(self.device)
pred = self.model.predict(xc)
q_img, ang_img, width_img = post_process_output(pred['pos'], pred['cos'], pred['sin'], pred['width'])
grasps = detect_grasps(q_img, ang_img, width_img)
# np.save(self.grasp_pose, grasp_pose)
if self.visualize:
plot_grasp(fig=self.fig, rgb_img=self.cam_data.get_rgb(rgb, False), grasps=grasps, save=True)
if len(grasps) ==0:
print("Detect 0 grasp pose!")
if self.visualize:
plot_grasp(fig=self.fig, rgb_img=self.cam_data.get_rgb(rgb, False), grasps=grasps, save=True)
return False
## For real UR robot
# Get grasp position from model output
pos_z = depth[grasps[0].center[0] + self.cam_data.top_left[0], grasps[0].center[1] + self.cam_data.top_left[1]]
pos_x = np.multiply(grasps[0].center[1] + self.cam_data.top_left[1] - self.intrinsic[0][2],
pos_z / self.intrinsic[0][0])
pos_y = np.multiply(grasps[0].center[0] + self.cam_data.top_left[0] - self.intrinsic[1][2],
pos_z / self.intrinsic[1][1])
if pos_z == 0:
return False
target = np.asarray([pos_x, pos_y, pos_z])
target.shape = (3, 1)
# Convert camera to robot coordinates
camera2tool = self.cam_pose
target_position = self.ur_robot.target1_position(camera2tool, tool_orientation, tool_xyz, target)
# print(target_position)
# Convert camera to robot angle
angle = np.asarray([0, 0, grasps[0].angle])
angle.shape = (3, 1)
target_angle = self.ur_robot.target1_angle(camera2tool, tool_orientation, angle)
angle.shape = (1,3)
# print(target_angle)
# target_angle = np.dot(camera2robot[0:3, 0:3], angle)
# compute gripper width
width = grasps[0].length # mm
if width < 25: # detect error
width = 70
elif width <40:
width =45
elif width > 85:
width = 85
# Concatenate grasp pose with grasp angle
grasp_pose = np.append(target_position, target_angle[2])
print('grasp_pose: ', grasp_pose)
print('grasp_width: ',grasps[0].length)
destination=np.append([grasp_pose[0],grasp_pose[1],grasp_pose[2]],tool_orientation)
print(destination)
# self.ur_robot.move_j_p(destination)
# hole targrt destination
target1_position[0] = hole_xyz[0]+xyz_list[i,0]-0.037
target1_position[1] = hole_xyz[1]- xyz_list[i,2]+0.18
target1_position[2] = hole_xyz[2]+xyz_list[i,1]+0.066
target1_position= np.asarray(target1_position)
target1_position = np.append(target1_position,hole_orientation)
print(target1_position)
# self.ur_robot.move_j_p(target1_position)
# target_position[0] = hole_xyz[0]+xyz_list[i,0]
# target_position[1] = hole_xyz[1]- xyz_list[i,2]+0.25
# target_position[2] = hole_xyz[2]+xyz_list[i,1]
# target_position = np.append(target_position,hole_orientation)
# self.ur_robot.move_j_p(target_position)
success = self.ur_robot.plane_grasp_hole([grasp_pose[0],grasp_pose[1],grasp_pose[2]],target1_position, yaw=grasp_pose[3], open_size=width/100)
if success==True:
print("success:",i+1)
elif success==False:
print("unsuccess")
break
print("Grasp and full success:",i+1)
self.ur_robot.move_j([-(0 / 360.0) * 2 * np.pi, -(90 / 360.0) * 2 * np.pi,
(0 / 360.0) * 2 * np.pi, -(90 / 360.0) * 2 * np.pi,
-(0 / 360.0) * 2 * np.pi, 0.0])# return home
## For having not real robot
# if self.visualize:
# plot_grasp(fig=self.fig, rgb_img=self.cam_data.get_rgb(rgb, False), grasps=grasps, save=True)
# return True
if __name__ == '__main__':
g = PlaneGraspClass(
# saved_model_path='/home/robot/UR_grasping_net/robotic-grasping-explosives/logs/230801_0934_training_jacquard/epoch_34_iou_1.00',
# saved_model_path='/home/robot/UR_grasping_net/robotic-grasping-explosives/logs/230801_2225_training_jacquard/epoch_44_iou_1.00',
saved_model_path = 'logs/230802_0918_training_jacquard/epoch_31_iou_1.00',
# saved_model_path='/home/robot/UR_grasping_net/robotic-grasping-explosives/logs/230802_1421_training_jacquard/epoch_20_iou_1.00',
visualize=True,
include_rgb=True
)
g.generate()
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Mongodb基础介绍与应用场景
- 如何无公网ip实现SSH远程访问本地局域网openEuler系统?
- 附下载|200页幻灯片图解医疗数据安全
- PCL 大地坐标转空间直角坐标(C++详细过程版)
- 【AI视野·今日NLP 自然语言处理论文速览 第六十八期】Tue, 2 Jan 2024
- Pinia与Vuex:Vue状态管理库的比较与选择
- redisson分布式锁实现方式
- 【算法集训】基础数据结构:十一、邻接矩阵
- git运用之.gitignore 配置文件的常用写法及案例
- 基于SpringBoot的校园生活服务平台