代码训练营Day.20 | 654. 最大二叉树, 617. 合并二叉树,700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索,98. 验证二叉搜索树
发布时间:2024年01月02日
654. 最大二叉树
1. LeetCode链接
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
2. 题目描述



3. 解法
与知道中序和后序数列的情况下啊构造树一样,将左右区间标出更省空间。
class Solution {
public:
int maxe(vector<int>& nums, int left, int right) {
int max = left;
for (int i = left; i < right; i++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[max]) max = i;
}
return max;
}
TreeNode* construct(vector<int>& nums, int left, int right) {
if (left >= right) return NULL;
int max = maxe(nums, left, right);
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nums[max]);
root->left = construct(nums, left, max);
root->right = construct(nums, max + 1, right);
return root;
}
TreeNode* constructMaximumBinaryTree(vector<int>& nums) {
return construct(nums, 0, nums.size());
}
};不太省的
class Solution {
public:
int maxe(vector<int>& nums) {
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[max]) max = i;
}
return max;
}
TreeNode* constructMaximumBinaryTree(vector<int>& nums) {
if (nums.empty()) return NULL;
int max = maxe(nums);
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nums[max]);
vector<int> left(nums.begin(), nums.begin() + max);
vector<int> right(nums.end() - nums.size() + max + 1, nums.end());
root->left = constructMaximumBinaryTree(left);
root->right = constructMaximumBinaryTree(right);
return root;
}
};617. 合并二叉树
1. LeetCode链接
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
2. 题目描述

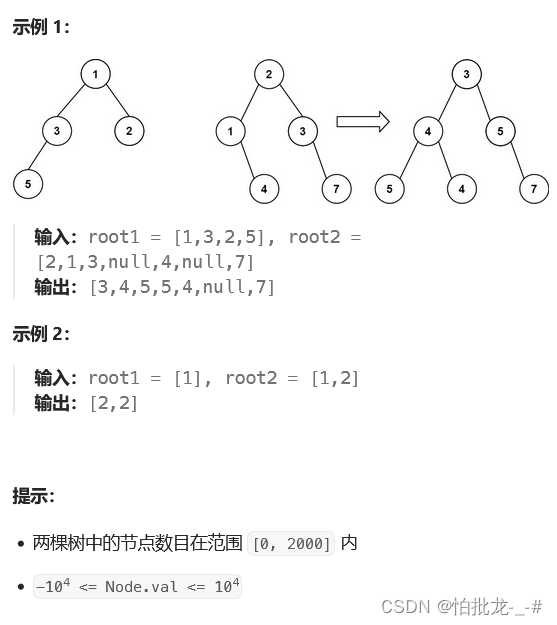
3. 解法
递归,如代码所示。让root1最终承载最后的树。
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* mergeTrees(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {
if (root1 == NULL) return root2;
if (root2 == NULL) return root1;
root1->val += root2->val;
root1->left = mergeTrees(root1->left, root2->left);
root1->right = mergeTrees(root1->right, root2->right);
return root1;
}
};迭代法,与判断二叉树是否对称相似,两个两个走,注意,先判断是否两个都不是NULL而可以push,再考虑root1子树是NULL的情况而替换成root2子树。for循环注意stride。
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* mergeTrees(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {
if (root1 == NULL) return root2;
if (root2 == NULL) return root1;
queue<TreeNode*> qu;
qu.push(root1);
qu.push(root2);
while (!qu.empty()) {
int size = qu.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i+=2) {
TreeNode* cur1 = qu.front();
qu.pop();
TreeNode* cur2 = qu.front();
qu.pop();
cur1->val += cur2->val;
if (cur1->left != NULL && cur2->left != NULL) {
qu.push(cur1->left);
qu.push(cur2->left);
}
if (cur1->right != NULL && cur2->right != NULL) {
qu.push(cur1->right);
qu.push(cur2->right);
}
if (cur1->left == NULL) cur1->left = cur2->left;
if (cur1->right == NULL) cur1->right = cur2->right;
}
}
return root1;
}
};700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索
1. LeetCode链接
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
2. 题目描述
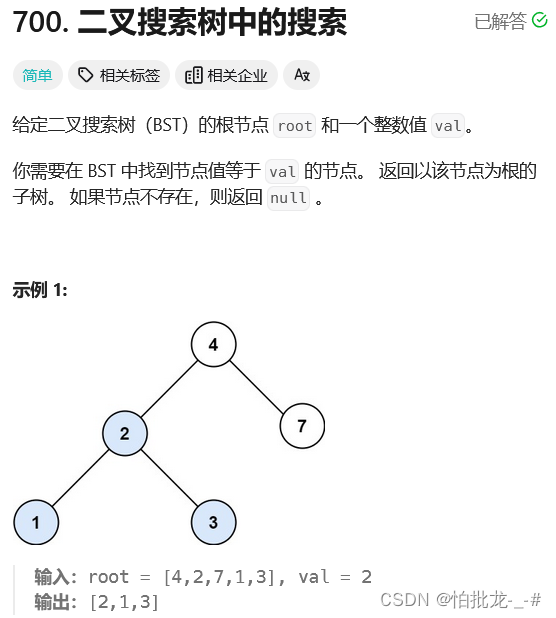
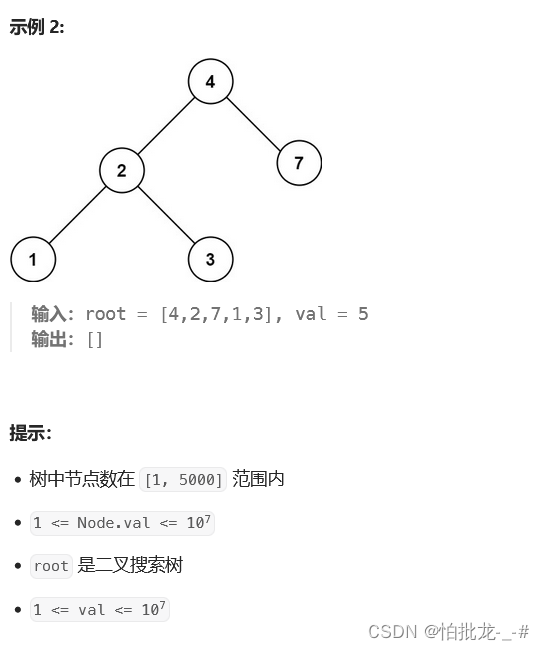
3. 解法
1. 普通树
迭代,普普通通遍历。
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* searchBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
queue<TreeNode*> qu;
qu.push(root);
while (!qu.empty()) {
int size = qu.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* cur = qu.front();
qu.pop();
if (cur->val == val) return cur;
if (cur->left) qu.push(cur->left);
if (cur->right) qu.push(cur->right);
}
}
return NULL;
}
};递归,在判断root->val之前,一定要确保root != NULL。
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* searchBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if (root == NULL) return NULL;
if (root->val == val) return root;
TreeNode* left = searchBST(root->left, val);
TreeNode* right = searchBST(root->right, val);
if (left != NULL && left->val == val) return left;
if (right != NULL && right->val == val) return right;
return NULL;
}
};2. 二叉搜索树
二叉搜索树是一个有序树:
- 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
- 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
- 它的左、右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
递归:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* searchBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if (root == NULL) return NULL;
if (root->val == val) return root;
else if (root->val < val) return searchBST(root->right, val);
else return searchBST(root->left, val);
}
};迭代:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* searchBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
queue<TreeNode*> qu;
qu.push(root);
while (!qu.empty()) {
int size = qu.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* cur = qu.front();
qu.pop();
if (cur->val == val) return cur;
else if (cur->val > val && cur->left != NULL) qu.push(cur->left);
else if (cur->val < val && cur->right != NULL) qu.push(cur->right);
}
}
return NULL;
}
};98. 验证二叉搜索树
1. LeetCode链接
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
2. 题目描述

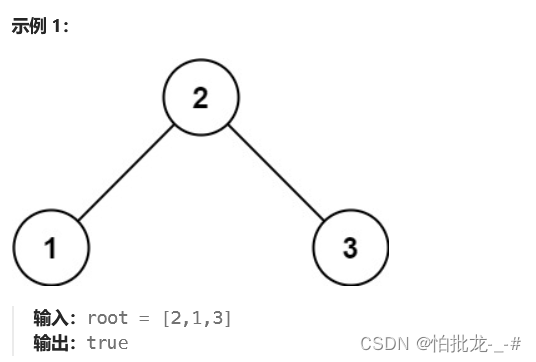

3. 解法
1)递归,一棵树是否为有效二叉搜索树,取决于两个条件:1. 两棵子树都是二叉搜索树;2. 左子树的最大值小于root->val,右子树的最小值大于root->val。
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return true;
TreeNode* left = root->left;
TreeNode* right = root->right;
while (left != NULL && left->right != NULL) left = left->right;
if (left != NULL && left->val >= root->val) return false;
while (right != NULL && right->left != NULL) right = right->left;
if (right != NULL && right->val <= root->val) return false;
return isValidBST(root->left) && isValidBST(root->right);
}
};2)中序遍历后的数组是否单调递增!可以构造数组,也有不构造数组的方法。记录最大值或者上一个结点,及在中序递归时,如果是二叉搜索树,下一个要遍历的结点值必大于当前值。否则就不是二叉搜索树。
## 记录最大值。
class Solution {
public:
long long maxVal = LONG_MIN; // 因为后台测试数据中有int最小值
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return true;
bool left = isValidBST(root->left);
// 中序遍历,验证遍历的元素是不是从小到大
if (maxVal < root->val) maxVal = root->val;
else return false;
bool right = isValidBST(root->right);
return left && right;
}
};
?
## 记录结点。
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* pre = NULL; // 用来记录前一个节点
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return true;
bool left = isValidBST(root->left);
if (pre != NULL && pre->val >= root->val) return false;
pre = root; // 记录前一个节点
bool right = isValidBST(root->right);
return left && right;
}
};
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/papilon_/article/details/135325181
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Linux实验——页面置换算法模拟
- 零售的数字化转型,利用AWS云服务资源如何操作?
- 应用案例——音箱系统的芯片组成
- 读书笔记-《数据结构与算法》-摘要8[桶排序]
- VMnet1、VMnet8到底是什么?
- 【星海记录】文献记录
- 抖音详情API:从零开始构建抖音应用
- C++的面向对象学习(9):文件操作
- c++ websocket 协议分析与实现
- Xgboost: bst.best_iteration 和 bst.best_ntree_limit 有什么区别?