how2heap-2.23-01-fastbin_dup
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
int main()
{
fprintf(stderr, "This file demonstrates a simple double-free attack with fastbins.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "Allocating 3 buffers.\n");
int *a = malloc(8);
int *b = malloc(8);
int *c = malloc(8);
fprintf(stderr, "1st malloc(8): %p\n", a);
fprintf(stderr, "2nd malloc(8): %p\n", b);
fprintf(stderr, "3rd malloc(8): %p\n", c);
fprintf(stderr, "Freeing the first one...\n");
free(a);
fprintf(stderr, "If we free %p again, things will crash because %p is at the top of the free list.\n", a, a);
// free(a);
fprintf(stderr, "So, instead, we'll free %p.\n", b);
free(b);
fprintf(stderr, "Now, we can free %p again, since it's not the head of the free list.\n", a);
free(a);
fprintf(stderr, "Now the free list has [ %p, %p, %p ]. If we malloc 3 times, we'll get %p twice!\n", a, b, a, a);
a = malloc(8);
b = malloc(8);
c = malloc(8);
fprintf(stderr, "1st malloc(8): %p\n", a);
fprintf(stderr, "2nd malloc(8): %p\n", b);
fprintf(stderr, "3rd malloc(8): %p\n", c);
assert(a == c);
}
fastbin支持的chunk大小
默认情况下,哪些大小的chunk释放可以放进fastbin
- 32位系统:最大80字节
- 64位系统:最大128字节(按照chunk 的size来说的,实际最大的是malloc(0x78))
#ifndef DEFAULT_MXFAST
#define DEFAULT_MXFAST (64 * SIZE_SZ / 4)
可以支持的fastbin最大大小
#define MAX_FAST_SIZE (80 * SIZE_SZ / 4)
通过mallopt设置fastbin支持的大小
int mallopt(int param,int value)
https://baike.baidu.com/item/mallopt/1731899
https://blog.csdn.net/u013920085/article/details/52847464
https://www.cnblogs.com/ho966/p/17671723.html
还可以通过漏洞修改glibc中的全局变量global_max_fast,使fastbin支持的大小,超过MAX_FAST_SIZE
分配3个chunk malloc(8)
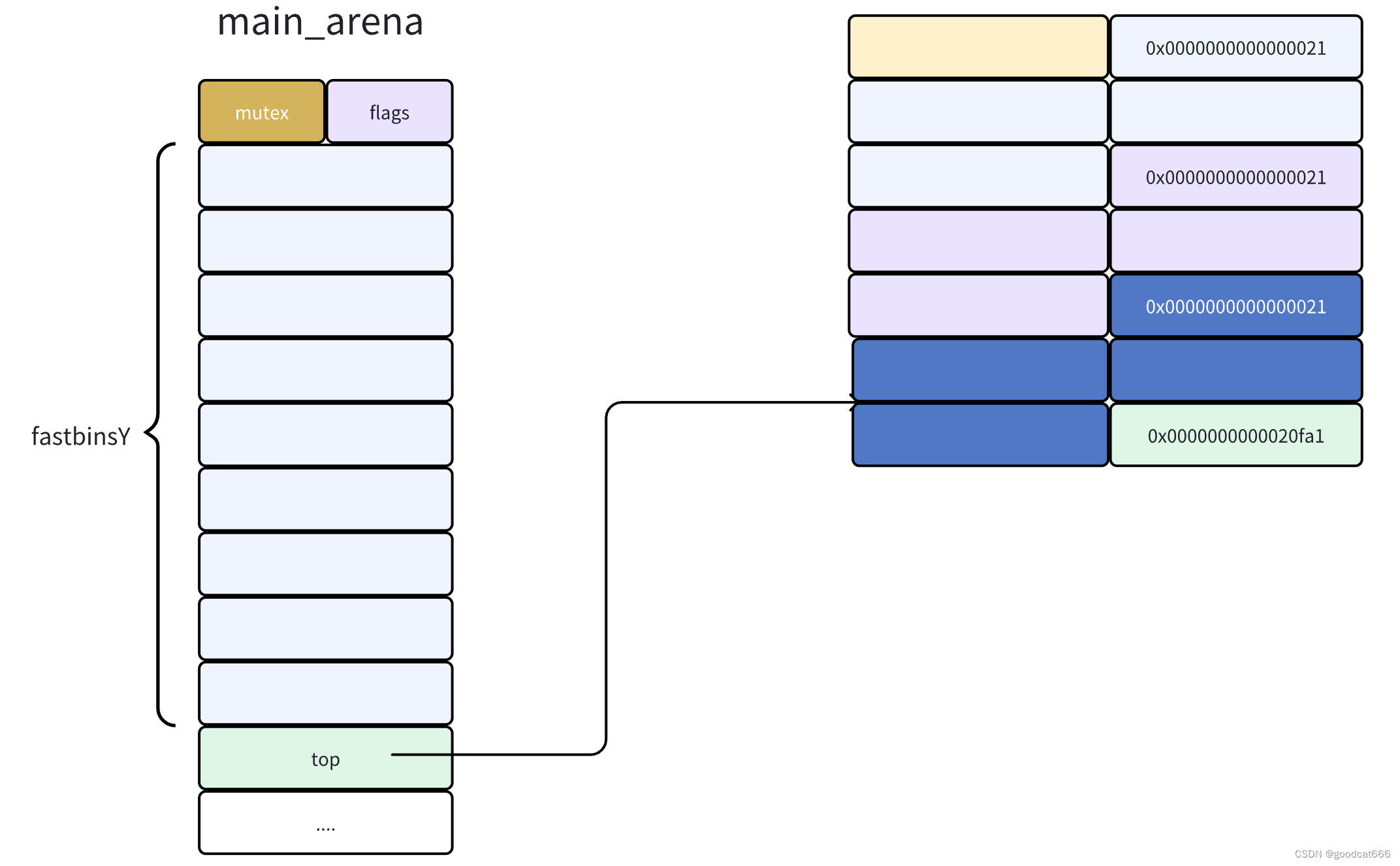
释放chunk a
会在fastbinY[0]记录chunk a的地址
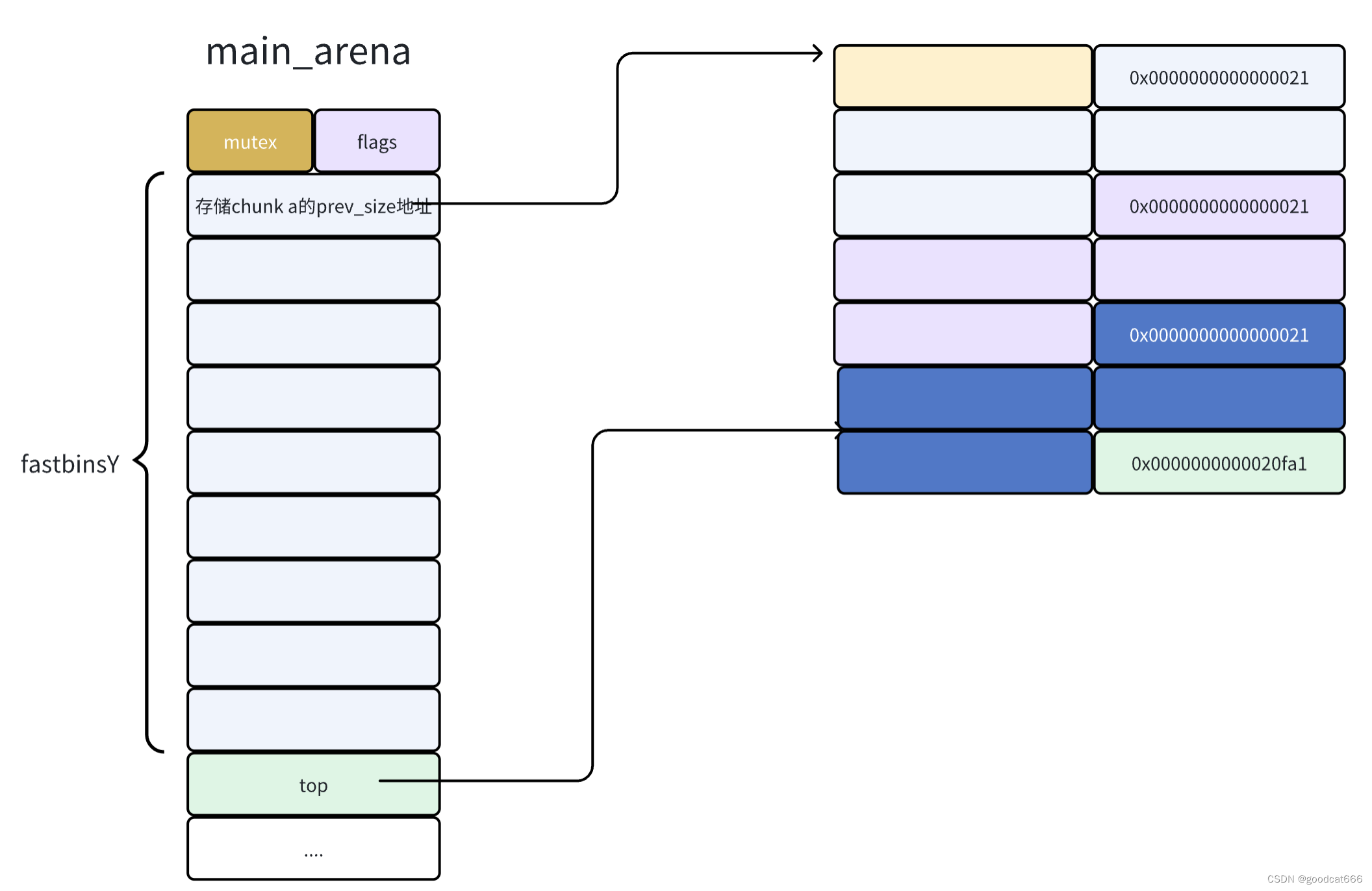
分配chunk b
fastbin是先进后出的
- 最近释放的chunk的地址,会被放到fastbinY中
- 原先的存储在fastbinY的地址,会被放在最新释放chunk的fd处
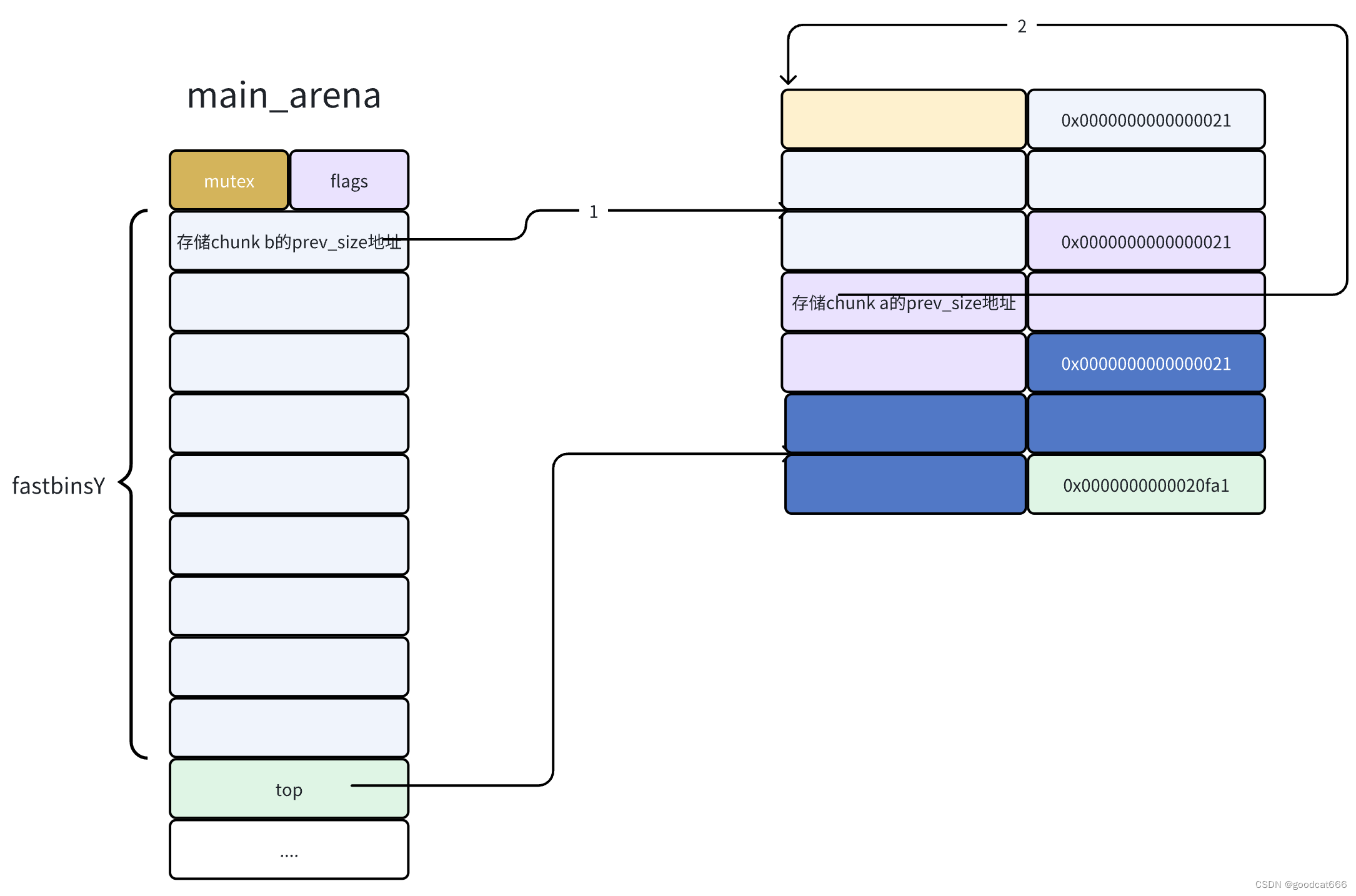
为什么直接释放chunk a(为什么不能连续释放chunk a)
因为会对fastbinY中之前释放的chunk与刚刚释放的chunk进行检查
if (__builtin_expect(old == p, 0)) {
errstr = "double free or corruption (fasttop)";
goto errout;
}
再次释放chunk a
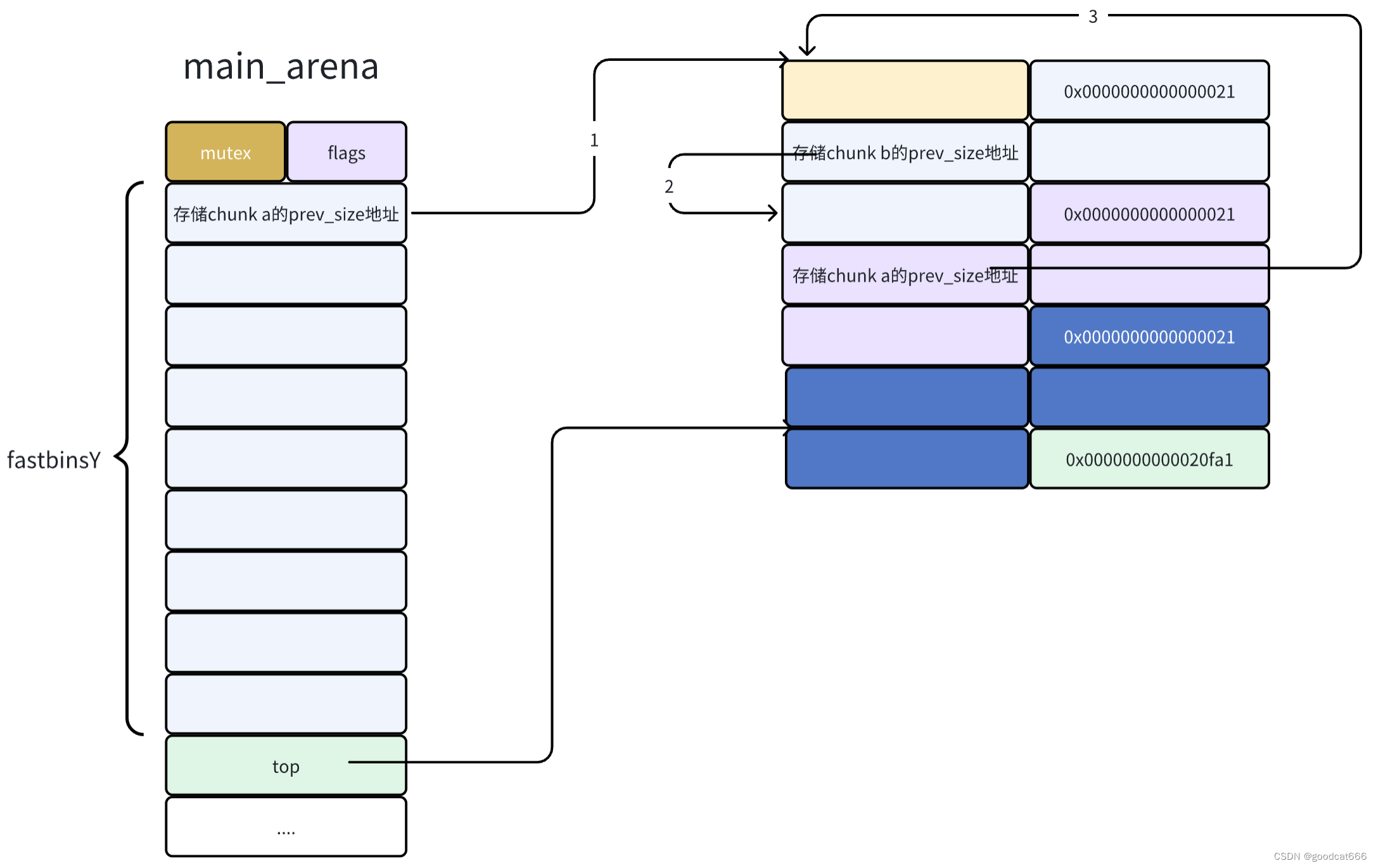
现在chunk a被释放了两次,这就是所谓的double-free
同时被释放的chunk,在fastbinY链中形成了一个循环链
从fastbin中申请chunk a
将fastbinY中存储的chunk申请出来,并将该chunk->fd中存储的地址放到fastbinY中
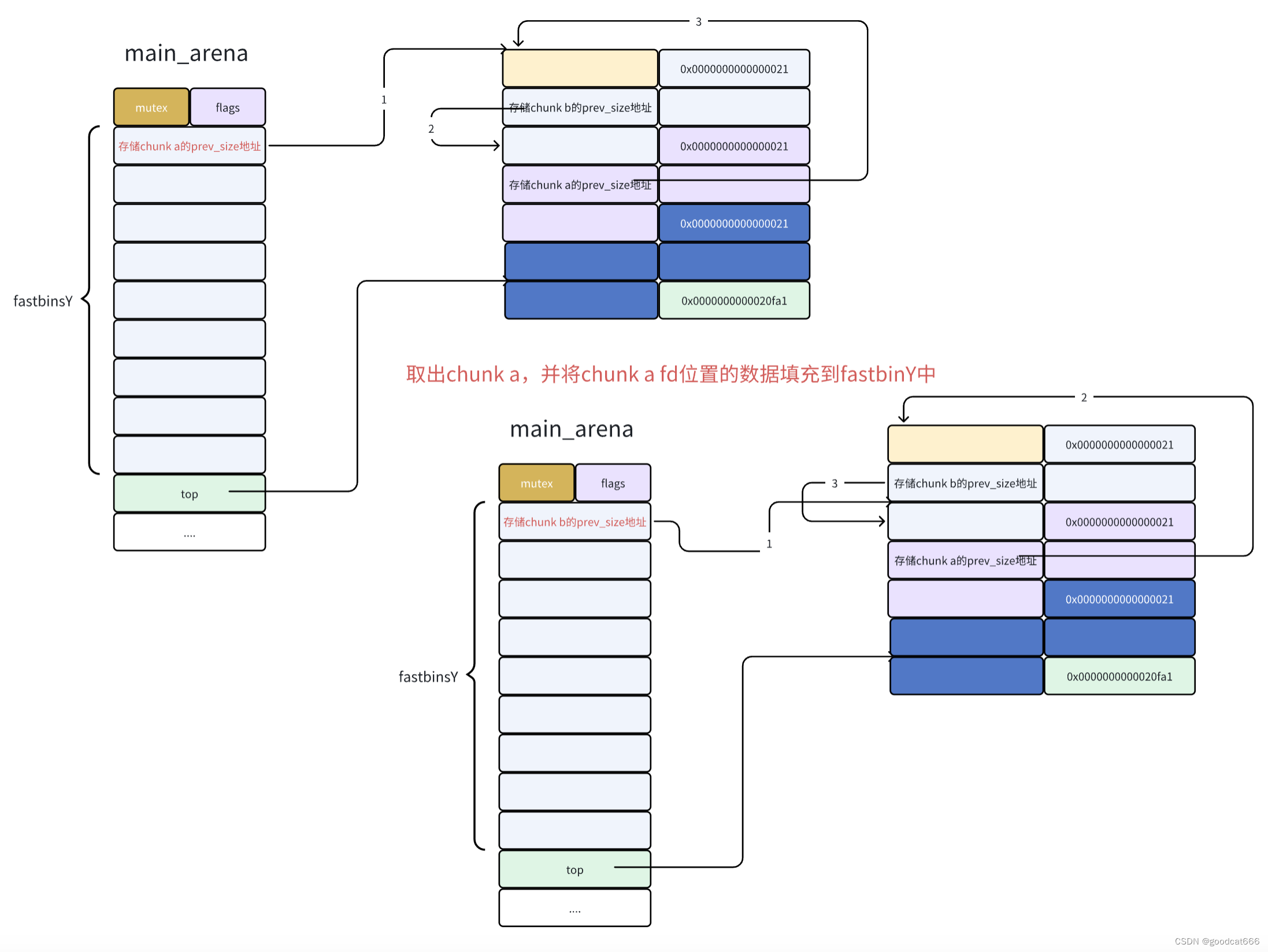
fastbin 的利用方式
在上面,已经将chunk a给申请出来了,可以在chunk a的fd处写入想修改位置的地址-SIZE_SZ*2
再申请几次
- malloc ,申请出chunk b
- malloc,申请出chunk b中记录的chunk a
- malloc,申请出chunk a中记录的欲修改的位置
然后就可以对期望的位置进行修改了
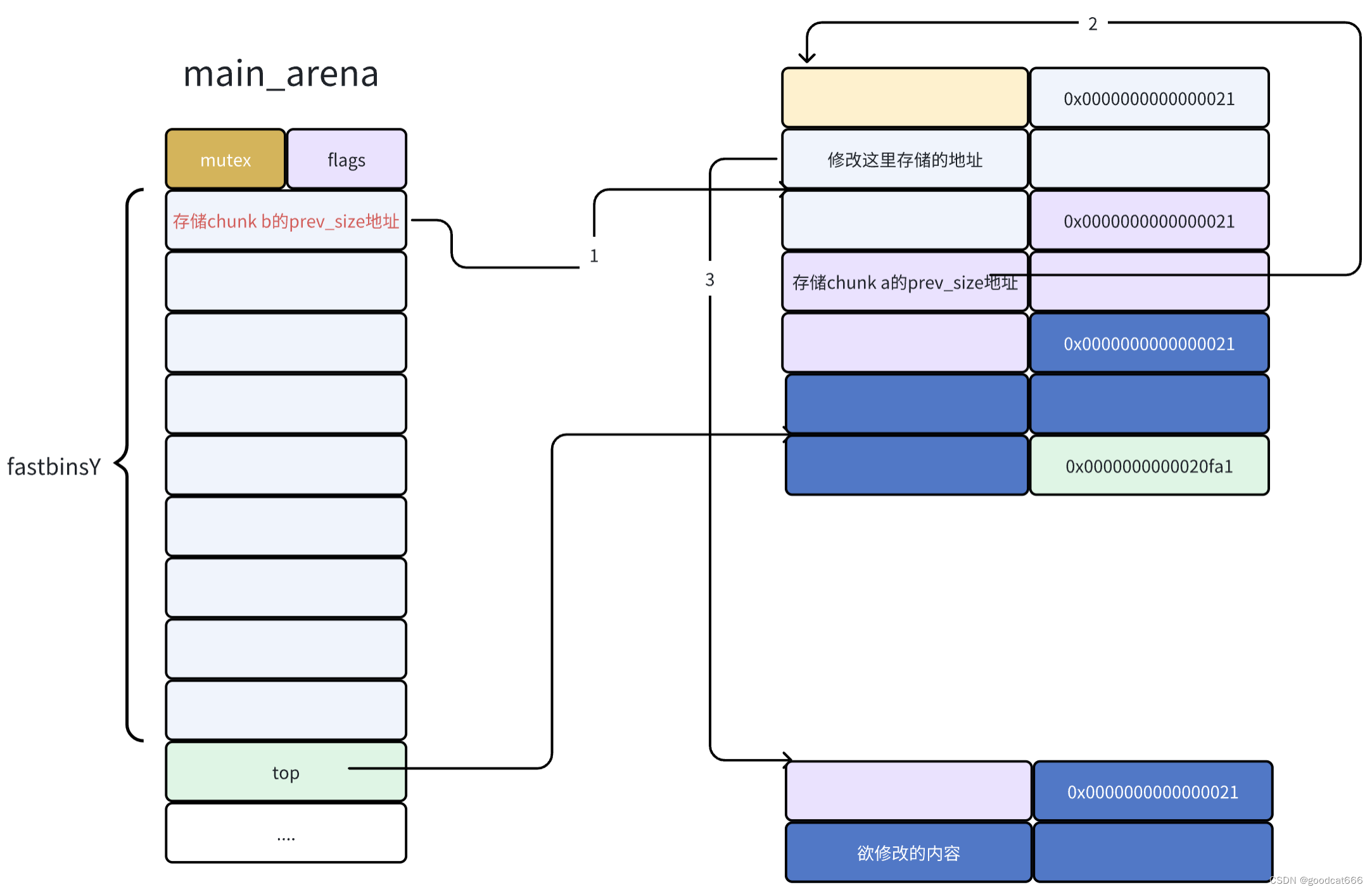
需要注意的点
fastbinY中最大可以存放10个fastbin链,默认情况下仅使用了前7个。在从fastbin中申请chunk的时候,会检查该链中chunk的是否确实属于该fastbin链,检查的是在fastbin中的下标,实际检查的是该chunk的size
if (__builtin_expect(fastbin_index(chunksize(victim)) != idx, 0))
{
errstr = "malloc(): memory corruption (fast)";
errout:
malloc_printerr(check_action, errstr, chunk2mem(victim), av);
return NULL;
}
所以欲修改的位置之前需要有一个正确的fastbin的size(这个位置不一定必须是前8个字节)。
只要这个size和欲修改的位置,包含在一个允许的fastbin大小中就行。
然后为了适应这个欲修改位置的fastbin,需要自己申请malloc合适该chunk的大小,再释放到fastbin,并将欲修改的位置链进去。
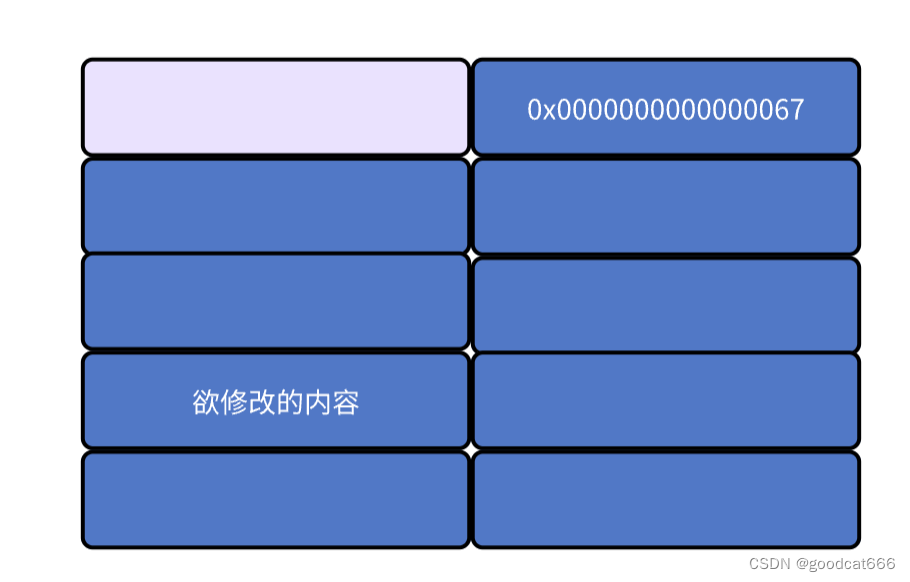
在pwndbg中存在find_fake_fast命令,用于在欲修改的地址周围,搜索符合fastbin要求的地址
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 音频编辑软件:Studio One 6 中文
- Java 创建事件(Event)、事件监听器(EventListener)、事件发布(publishEvent)详解
- 寻路迷宫,Android休闲益智小游戏开发
- 若依如何集成websocket实现实时通信?
- TikTok真题第1天 | 666.路径和IV、 207.课程安排、210.课程安排
- 浏览器常用基本操作之python3+selenium4自动化测试
- vue 本地中导入 maptalks
- 3分钟部署自己独享的Gemini
- 林浩然的Java奇幻之旅:编码舞蹈、编程精灵与IDE仙境
- 机器学习 | 掌握Matplotlib的可视化图表操作