异步通知
一、异步通知
1、应用场景
当应用程序不想休眠时,可以使用异步通知的方式;当驱动程序有数据时主动通知应用程序,应用程序收到信号后执行信息处理函数。
2、执行流程(基于读取按键值的情景)
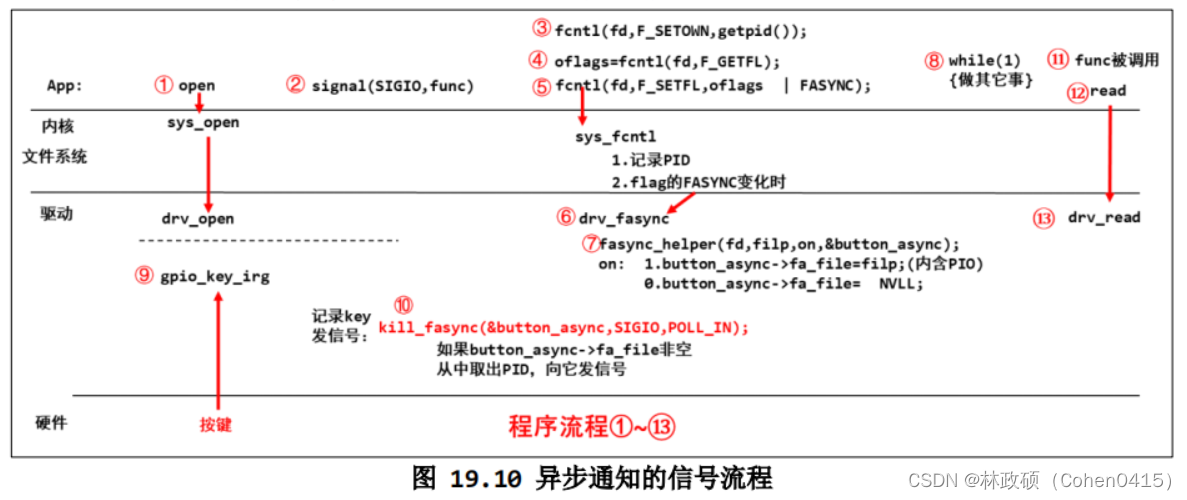
大致思想:驱动程序会发送信号给应用程序,应用程序收到信号会执行指定函数;
应用程序使用的关键函数:
- sighandler_t signal(int signum, sighandler_t handler)
- int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, … /* arg */ )
驱动程序使用的关键函数:
- int fasync_helper(int fd, struct file * filp, int on, struct fasync_struct **fapp)
- void kill_fasync(struct fasync_struct **fp, int sig, int band)
2.1、应用程序具体做什么?
以下涉及的函数并不是函数原型,而是从实际程序里复制出来的;以下步骤序号和上图序号无关联;
①、应用程序需要使用 signal(SIGIO, func) 函数绑定信号与函数,这样收到驱动程序发送的信号后func()函数会自动执行,读按键操作就在func()函数里完成;
②、那驱动程序到底发送信号给谁是由 fcntl(fd, F_SETOWN, getpid()) 函数决定,这个函数是把应用程序的pid告诉驱动程序;
③、随后使用 flags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL) 来获取标志位;再通过 fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flags | FASYNC) 启动fasync功能,启用fasync功能实际上就会调用驱动层的drv_fasync()函数,下面介绍drv_fasync();
2.2、驱动程序具体做什么?
以下涉及的函数并不是函数原型,而是从实际程序里复制出来的;以下步骤序号和上图序号无关联;
①、驱动程序里需要实现drv_fasync()函数,而该函数里只需要调用 fasync_helper(fd, file, on, &button_fasync) 函数,button_fasync是一个fasync_struct类型的结构体,里面会存放应用程序的pid,后续发送信号时也会用到button_fasync;
②、信号的发送在按键中断程序里,调用 kill_fasync(&button_fasync, SIGIO, POLL_IN) 发送信号;
三、程序
1、驱动程序
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/major.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/stat.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/kmod.h>
#include <linux/gfp.h>
#include <linux/gpio/consumer.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/of_irq.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
struct gpio_key{
int gpio;
struct gpio_desc *gpiod;
int flag;
int irq;
};
static struct gpio_key *gpio_keys_f1c100s;
static int major = 0;
static struct class *key_class;
static int g_key = 0;
struct fasync_struct *button_fasync;
static DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(gpio_key_wait);
static ssize_t key_drv_read (struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
int err;
wait_event_interruptible(gpio_key_wait, g_key);
err = copy_to_user(buf, &g_key, 4);
g_key = 0;
return 4;
}
static int key_drv_fasync(int fd, struct file *file, int on)
{
if (fasync_helper(fd, file, on, &button_fasync) >= 0)
return 0;
else
return -EIO;
}
static struct file_operations key_drv = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = key_drv_read,
.fasync = key_drv_fasync,
};
static irqreturn_t gpio_key_isr(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = dev_id;
int val;
val = gpiod_get_value(gpio_key->gpiod);
printk("key %d %d\n", gpio_key->gpio, val);
g_key = (gpio_key->gpio << 8) | val;
wake_up_interruptible(&gpio_key_wait);
kill_fasync(&button_fasync, SIGIO, POLL_IN); //发送信号
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
static int f1c100s_key_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct device_node *node = pdev->dev.of_node;
int err;
int i;
int count;
enum of_gpio_flags flag;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
count = of_gpio_count(node); //获取GPIO数量
if(!count)
{
printk("%s %s line %d, there isn't any gpio available\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
gpio_keys_f1c100s = kzalloc(sizeof(struct gpio_key) * count, GFP_KERNEL);
if(gpio_keys_f1c100s == NULL)
{
printk("%s %s line %d, kzalloc fail\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
for(i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
gpio_keys_f1c100s[i].gpio = of_get_gpio_flags(node, i, &flag);
if (gpio_keys_f1c100s[i].gpio < 0)
{
printk("%s %s line %d, of_get_gpio_flags fail\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
gpio_keys_f1c100s[i].gpiod = gpio_to_desc(gpio_keys_f1c100s[i].gpio);
gpio_keys_f1c100s[i].flag = flag & OF_GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW;
gpio_keys_f1c100s[i].irq = gpio_to_irq(gpio_keys_f1c100s[i].gpio); //获取中断号
}
for(i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
err = request_irq(gpio_keys_f1c100s[i].irq, gpio_key_isr, IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING, "f1c100s_gpio_key", &gpio_keys_f1c100s[i]); //申请中断
}
major = register_chrdev(0, "f1c100s_key", &key_drv);
key_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "f1c100s_key_class");
if (IS_ERR(key_class)) {
unregister_chrdev(major, "f1c100s_key");
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return PTR_ERR(key_class);
}
device_create(key_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "keys-key");
return 0;
}
static int f1c100s_key_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct device_node *node = pdev->dev.of_node;
int count;
int i;
device_destroy(key_class, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_destroy(key_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, "f1c100s_key");
count = of_gpio_count(node);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
free_irq(gpio_keys_f1c100s[i].irq, &gpio_keys_f1c100s[i]);
}
kfree(gpio_keys_f1c100s);
return 0;
}
static const struct of_device_id f1c100s_key_table[] = {
{ .compatible = "f1c100s,keysdrv" },
{ },
};
static struct platform_driver f1c100s_key_driver = {
.probe = f1c100s_key_probe,
.remove = f1c100s_key_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "f1c100s_keys",
.of_match_table = f1c100s_key_table,
},
};
static int __init f1c100s_key_init(void)
{
int err;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
err = platform_driver_register(&f1c100s_key_driver);
return err;
}
static void __exit f1c100s_key_exit(void)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
platform_driver_unregister(&f1c100s_key_driver);
}
module_init(f1c100s_key_init);
module_exit(f1c100s_key_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
2、测试应用程序
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <poll.h>
#include <signal.h>
static int fd;
static void sig_func(int sig)
{
int bit = 1;
int val;
read(fd, &val, 4);
bit &= val;
val >>= 8;
printf("get %d button : %d\n", val, bit);
bit = 1;
}
/*
* ./button_test /dev/keys-key
*
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int flags;
/* 1. 判断参数 */
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("Usage: %s <dev>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
signal(SIGIO, sig_func); //绑定信号与函数
/* 2. 打开文件 */
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
if (fd == -1)
{
printf("can not open file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
fcntl(fd, F_SETOWN, getpid()); //传入应用程序pid
flags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL); //获取flags
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flags | FASYNC); //启动fasync功能,驱动程序的key_drv_fasync()会被调用
/* 3. 写文件 */
while(1)
{
printf("asyn button test\n");
sleep(2);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
三、总结
1、以上专业术语或名词解释有个人理解,感谢指点纠错!
2、视频学习B站韦东山:【第5篇】嵌入式Linux驱动开发基础知识 - 异步通知
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- C++ //习题 7.10 将以上4个函数组成一个程序,由主程序先后调用这些函数,实现链表的建立、输出、删除和插入,在主程序中指定需要删除和插入的结点。
- 图像融合论文阅读:CS2Fusion: 通过估计特征补偿图谱实现自监督红外和可见光图像融合的对比学习
- Verilog HDL数据类型
- 思迈特2023 年度回顾:这一年,在不确定的时代里做好正确的事
- css 边框渐变
- 表格实现高级搜索,并封装高级搜索组件
- thingsboard前端缓存--nginx
- 计算机毕业设计-----SSM学生成绩信息管理系统
- LeetCode 21 合并两个有序链表
- PHP Web应用程序中常见漏洞