PaddleDetection学习2——使用Paddle-Lite在 Android 上实现行人检测
发布时间:2024年01月19日
使用Paddle-Lite在 Android 上实现行人检测
1. 环境准备
参考前一篇在 Android 上使用Paddle-Lite实现实时的目标检测功能
2. 准备模型
2.1 下载模型
官网下载行人检测模型,解压下载的mot_ppyoloe_s_36e_pipeline.zip

2.2 模型优化
使用Paddle-Lite的opt工具可以自动对inference模型进行优化。
安装paddle_lite_opt工具:
pip install paddlelite
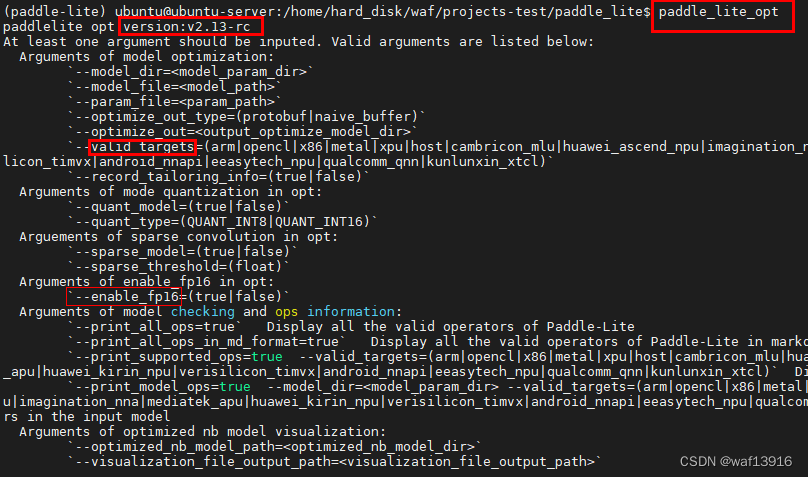
使用paddle_lite_opt工具可以进行inference模型的转换:
paddle_lite_opt --valid_targets=arm \
--model_file=mot_ppyoloe_s_36e_pipeline/model.pdmodel \
--param_file=mot_ppyoloe_s_36e_pipeline/model.pdiparams \
--optimize_out=output_inference/mot_ppyoloe_s_36e_pphuman/model \
#--enable_fp16=true 转化fp16测试报错:paddle-lite提示不支持swish算子
paddle_lite_opt的部分参数如下:

更详细的paddle_lite_opt工具使用说明请参考使用opt转化模型文档
–model_file表示inference模型的model文件地址,
–param_file表示inference模型的param文件地址;
–optimize_out用于指定输出文件的名称(不需要.nb的后缀)。
直接在命令行中运行paddle_lite_opt,也可以查看所有参数及其说明。
3. 部署模型
3.1 目标检测C++代码
修改yolo_detection_demo中的C++预测代码:
Pipeline.h
class Detector {
public: // NOLINT
explicit Detector(const std::string &modelDir, const std::string &labelPath,
const int cpuThreadNum, const std::string &cpuPowerMode,
int inputWidth, int inputHeight,
const std::vector<float> &inputMean,
const std::vector<float> &inputStd, float scoreThreshold);
void Predict(const cv::Mat &rgbImage, std::vector<RESULT> *results,
double *preprocessTime, double *predictTime,
double *postprocessTime);
void Predict_for_human(const cv::Mat &rgbImage, std::vector<RESULT> *results,
double *preprocessTime, double *predictTime,
double *postprocessTime);
private: // NOLINT
std::vector<std::string> LoadLabelList(const std::string &path);
std::vector<cv::Scalar> GenerateColorMap(int numOfClasses);
void Preprocess(const cv::Mat &rgbaImage);
void Preprocess_for_human(const cv::Mat &rgbaImage);
void Postprocess(std::vector<RESULT> *results);
void Postprocess_for_human(std::vector<RESULT> *results,std::vector<int>out_bbox_num);
private: // NOLINT
int inputWidth_;
int inputHeight_;
std::vector<float> inputMean_;
std::vector<float> inputStd_;
float scoreThreshold_;
std::vector<std::string> labelList_;
std::vector<cv::Scalar> colorMap_;
std::shared_ptr<paddle::lite_api::PaddlePredictor> predictor_;
//for human
PaddleDetection::Preprocessor preprocessor_;
PaddleDetection::ImageBlob inputs_;
std::vector<float> output_data_;
std::vector<int> out_bbox_num_data_;
};
Pipeline.cpp
oid Detector::Preprocess_for_human(const cv::Mat &rgbaImage) {
// Set the data of input image
// Clone the image : keep the original mat for postprocess
cv::Mat im = rgbaImage.clone();
cv::cvtColor(im, im, cv::COLOR_BGR2RGB);
preprocessor_.Run(&im, &inputs_);
}
void Detector::Postprocess_for_human(std::vector<RESULT> *results, std::vector<int> bbox_num) {
for (int j = 0; j < bbox_num[0/*im_id*/]; j++) {
// Class id
int class_id = static_cast<int>(round(output_data_[0 + j * 6]));
// Confidence score
float score = output_data_[1 + j * 6];
int xmin = (output_data_[2 + j * 6]);
int ymin = (output_data_[3 + j * 6]);
int xmax = (output_data_[4 + j * 6]);
int ymax = (output_data_[5 + j * 6]);
int wd = xmax - xmin;
int hd = ymax - ymin;
if (score < scoreThreshold_)
continue;
RESULT object;
object.class_name = class_id >= 0 && class_id < labelList_.size()
? labelList_[class_id]
: "Unknow";
object.fill_color = class_id >= 0 && class_id < colorMap_.size()
? colorMap_[class_id]
: cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0);
object.score = score;
object.x = xmin*1.0;
object.y = ymin*1.0;
object.w = wd*1.0;
object.h = hd*1.0;
results->push_back(object);
}
}
preprocess_op.h
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <utility>
#include <vector>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
namespace PaddleDetection {
// Object for storing all preprocessed data
class ImageBlob {
public:
// image width and height
std::vector<float> im_shape_;
// Buffer for image data after preprocessing
std::vector<float> im_data_;
// in net data shape(after pad)
std::vector<float> in_net_shape_;
// Evaluation image width and height
// std::vector<float> eval_im_size_f_;
// Scale factor for image size to origin image size
std::vector<float> scale_factor_;
};
// Abstraction of preprocessing opration class
class PreprocessOp {
public:
virtual void Init() = 0;
virtual void Run(cv::Mat* im, ImageBlob* data) = 0;
};
class InitInfo : public PreprocessOp {
public:
virtual void Init(){};
virtual void Run(cv::Mat* im, ImageBlob* data);
};
class Permute : public PreprocessOp {
public:
virtual void Init(){};
virtual void Run(cv::Mat* im, ImageBlob* data);
};
class Resize : public PreprocessOp {
public:
virtual void Init() {
interp_ = 2;
keep_ratio_ = false;
target_size_.clear();
target_size_.emplace_back(640);
target_size_.emplace_back(640);
}
// Compute best resize scale for x-dimension, y-dimension
std::pair<float, float> GenerateScale(const cv::Mat& im);
virtual void Run(cv::Mat* im, ImageBlob* data);
private:
int interp_;
bool keep_ratio_;
std::vector<int> target_size_;
std::vector<int> in_net_shape_;
};
class Preprocessor {
public:
void Init() {
// initialize image info at first
ops_["InitInfo"] = std::make_shared<InitInfo>();
// ops_["InitInfo"] = CreateOp("InitInfo");
ops_["Resize"] = CreateOp("Resize");
ops_["Resize"]->Init();
ops_["Permute"] = CreateOp("Permute");
ops_["Permute"]->Init();
}
std::shared_ptr<PreprocessOp> CreateOp(const std::string& name) {
if (name == "Resize") {
return std::make_shared<Resize>();
} else if (name == "Permute") {
return std::make_shared<Permute>();
}
std::cerr << "can not find function of OP: " << name
<< " and return: nullptr" << std::endl;
return nullptr;
}
void Run(cv::Mat* im, ImageBlob* data);
public:
static const std::vector<std::string> RUN_ORDER;
private:
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::shared_ptr<PreprocessOp>> ops_;
};
} // namespace PaddleDetection
preprocess_op.cc
#include <string>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>
#include "preprocess_op.h"
namespace PaddleDetection {
void InitInfo::Run(cv::Mat* im, ImageBlob* data) {
data->im_shape_ = {static_cast<float>(im->rows),
static_cast<float>(im->cols)};
data->scale_factor_ = {1., 1.};
data->in_net_shape_ = {static_cast<float>(im->rows),
static_cast<float>(im->cols)};
}
void Permute::Run(cv::Mat* im, ImageBlob* data) {
(*im).convertTo(*im, CV_32FC3);
int rh = im->rows;
int rw = im->cols;
int rc = im->channels();
(data->im_data_).resize(rc * rh * rw);
float* base = (data->im_data_).data();
for (int i = 0; i < rc; ++i) {
cv::extractChannel(*im, cv::Mat(rh, rw, CV_32FC1, base + i * rh * rw), i);
}
}
void Resize::Run(cv::Mat* im, ImageBlob* data) {
auto resize_scale = GenerateScale(*im);
data->im_shape_ = {static_cast<float>(im->cols * resize_scale.first),
static_cast<float>(im->rows * resize_scale.second)};
data->in_net_shape_ = {static_cast<float>(im->cols * resize_scale.first),
static_cast<float>(im->rows * resize_scale.second)};
cv::resize(
*im, *im, cv::Size(), resize_scale.first, resize_scale.second, interp_);
data->im_shape_ = {
static_cast<float>(im->rows), static_cast<float>(im->cols),
};
data->scale_factor_ = {
resize_scale.second, resize_scale.first,
};
}
std::pair<float, float> Resize::GenerateScale(const cv::Mat& im) {
std::pair<float, float> resize_scale;
int origin_w = im.cols;
int origin_h = im.rows;
if (keep_ratio_) {
int im_size_max = std::max(origin_w, origin_h);
int im_size_min = std::min(origin_w, origin_h);
int target_size_max =
*std::max_element(target_size_.begin(), target_size_.end());
int target_size_min =
*std::min_element(target_size_.begin(), target_size_.end());
float scale_min =
static_cast<float>(target_size_min) / static_cast<float>(im_size_min);
float scale_max =
static_cast<float>(target_size_max) / static_cast<float>(im_size_max);
float scale_ratio = std::min(scale_min, scale_max);
resize_scale = {scale_ratio, scale_ratio};
} else {
resize_scale.first =
static_cast<float>(target_size_[1]) / static_cast<float>(origin_w);
resize_scale.second =
static_cast<float>(target_size_[0]) / static_cast<float>(origin_h);
}
return resize_scale;
}
// Preprocessor op running order
const std::vector<std::string> Preprocessor::RUN_ORDER = {"InitInfo",
"TopDownEvalAffine",
"Resize",
"NormalizeImage",
"PadStride",
"Permute"};
void Preprocessor::Run(cv::Mat* im, ImageBlob* data) {
ops_["InitInfo"]->Run(im, data);
ops_["Resize"]->Run(im, data);
ops_["Permute"]->Run(im, data);
}
void CropImg(cv::Mat& img,
cv::Mat& crop_img,
std::vector<int>& area,
std::vector<float>& center,
std::vector<float>& scale,
float expandratio) {
int crop_x1 = std::max(0, area[0]);
int crop_y1 = std::max(0, area[1]);
int crop_x2 = std::min(img.cols - 1, area[2]);
int crop_y2 = std::min(img.rows - 1, area[3]);
int center_x = (crop_x1 + crop_x2) / 2.;
int center_y = (crop_y1 + crop_y2) / 2.;
int half_h = (crop_y2 - crop_y1) / 2.;
int half_w = (crop_x2 - crop_x1) / 2.;
if (half_h * 3 > half_w * 4) {
half_w = static_cast<int>(half_h * 0.75);
} else {
half_h = static_cast<int>(half_w * 4 / 3);
}
crop_x1 =
std::max(0, center_x - static_cast<int>(half_w * (1 + expandratio)));
crop_y1 =
std::max(0, center_y - static_cast<int>(half_h * (1 + expandratio)));
crop_x2 = std::min(img.cols - 1,
static_cast<int>(center_x + half_w * (1 + expandratio)));
crop_y2 = std::min(img.rows - 1,
static_cast<int>(center_y + half_h * (1 + expandratio)));
crop_img =
img(cv::Range(crop_y1, crop_y2 + 1), cv::Range(crop_x1, crop_x2 + 1));
center.clear();
center.emplace_back((crop_x1 + crop_x2) / 2);
center.emplace_back((crop_y1 + crop_y2) / 2);
scale.clear();
scale.emplace_back((crop_x2 - crop_x1));
scale.emplace_back((crop_y2 - crop_y1));
}
} // namespace PaddleDetection
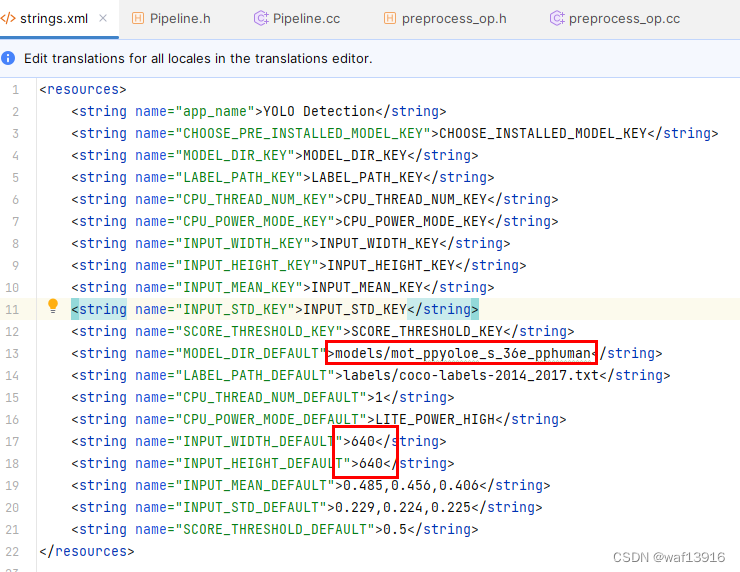
3.2 修改配置文件
将app/src/main/res/values/strings.xml中的模型路径、模型输入宽高设置为对应值。
3.4 部署模型到移动端
手机连接电脑,打开 USB 调试和文件传输模式,并在 Android Studio 上连接自己的手机设备(手机需要开启允许从 USB 安装软件权限)
 点击 Run 按钮,自动编译 APP 并安装到手机。图一:APP 安装到手机 图二: APP 打开后的效果,会自动识别图片中的物体并标记。
点击 Run 按钮,自动编译 APP 并安装到手机。图一:APP 安装到手机 图二: APP 打开后的效果,会自动识别图片中的物体并标记。

文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/u014377655/article/details/135678220
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!