二分&半平面求交 - 洛谷 - P3222 [HNOI2012] 射箭
欢迎关注更多精彩
关注我,学习常用算法与数据结构,一题多解,降维打击。
往期相关背景半平面求交 点击前往
二分点击前往
题目大意
题目链接
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3222
在坐标系中有很多平行于Y轴的棍子。
现在需要求一条经过0点开口向下的抛物线,与棍子的交点越多越好且棍子的编号要从1开始连续。
问最多可以经过几根棍子。
解析
可以使用二分加判定的形式解决。
二分要求答案有单调性,显然这里的答案是满足要求的。
那问题就转化成判定问题。
即给定固定线段,问是否存在一条抛物线能够都经过线段。
设抛物线为 y=ax^2+bx (+c) , 由于抛物线经过0点,所以c=0。
根据题意初始方向(0到90)度, 可知,b>0, a<0
假设前n根棍子的坐标为
(x1, y1, y1’), (x2, y2, y2’), (x3, y3, y3’), … (xn, yn, yn’),

可以根据条件列出方程
a
x
1
2
+
b
x
1
>
=
y
1
a
x
1
2
+
b
x
1
<
=
y
1
′
a
x
2
2
+
b
x
2
>
=
y
2
a
x
2
2
+
b
x
2
<
=
y
2
′
a
x
3
2
+
b
x
3
>
=
y
3
a
x
3
2
+
b
x
3
<
=
y
3
′
.
.
.
.
.
.
a
x
n
2
+
b
x
n
>
=
y
n
a
x
n
2
+
b
x
n
<
=
y
n
′
\begin{array}{c}ax_1^2+bx_1>=y_1\\ ax_1^2+bx_1<=y_1'\\ ax_2^2+bx_2>=y_2\\ ax_2^2+bx_2<=y_2'\\ ax_3^2+bx_3>=y_3\\ ax_3^2+bx_3<=y_3'\\ ......\\ ax_n^2+bx_n>=y_n\\ ax_n^2+bx_n<=y_n'\end{array}
ax12?+bx1?>=y1?ax12?+bx1?<=y1′?ax22?+bx2?>=y2?ax22?+bx2?<=y2′?ax32?+bx3?>=y3?ax32?+bx3?<=y3′?......axn2?+bxn?>=yn?axn2?+bxn?<=yn′??
只要找到一组(a<0,b>0) 满足上述不等式,就可以。
上述不等式围成的区域就是a, b为坐标轴的半平面求交。
如果区域出现在第二象限则有可行解。
不等式到直线转化。
a
x
1
2
+
b
x
1
<
=
y
1
′
ax_1^2+bx_1<=y_1'
ax12?+bx1?<=y1′?
可以理解为向量的点乘,即投影。
(
a
,
b
)
?
(
x
1
2
,
x
1
)
<
=
y
1
′
(a, b)\cdot (x_1^2, x_1)<=y_1'
(a,b)?(x12?,x1?)<=y1′?
推导一下与单位向量的关系
( a , b ) ? ( x 1 , 1 ) ∣ ∣ ( x 1 , 1 ) ∣ ∣ < = y 1 ′ x 1 ∣ ∣ ( x 1 , 1 ) ∣ ∣ (a, b)\cdot \frac {(x_1, 1)}{|| (x_1, 1)||}<= \frac {y_1'}{x_1|| (x_1, 1)||} (a,b)?∣∣(x1?,1)∣∣(x1?,1)?<=x1?∣∣(x1?,1)∣∣y1′??
P = y 1 ′ ? ( x 1 , 1 ) x 1 ? ∣ ∣ ( x 1 , 1 ) ∣ ∣ 2 P = \frac {y_1' \cdot (x_1, 1)}{x_1\cdot || (x_1, 1)||^2} P=x1??∣∣(x1?,1)∣∣2y1′??(x1?,1)?
用图像表示如下:
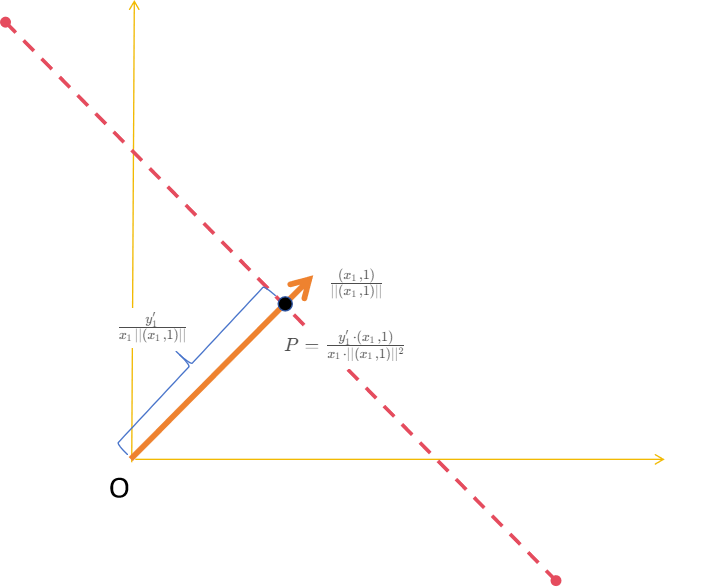
虚线为半平面分割线, 虚线以下为半平面。
特殊情况1 a<0, b>0, 需要判断最后凸包出现在第二象限。
极角排序要用整数。
为了得到一个封闭图形,可以在顶部加入一条直线。
代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <cstring>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
const double EPS = 1e-12;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
namespace FloatSys {
int cmp(double d) {
if (abs(d) < EPS)return 0;
if (d > 0)return 1;
return -1;
}
class Point {
public:
double x, y;
int id;
Point() {}
Point(double a, double b) :x(a), y(b) {}
Point(const Point& p) :x(p.x), y(p.y), id(p.id) {}
void in() {
scanf("%lf %lf", &x, &y);
}
void out() {
printf("%.3f %.3f\n", x, y);
}
double dis() {
return sqrt(x * x + y * y);
}
double dis2() {
return x * x + y * y;
}
Point operator -() const {
return Point(-x, -y);
}
Point operator -(const Point& p) const {
return Point(x - p.x, y - p.y);
}
Point operator +(const Point& p) const {
return Point(x + p.x, y + p.y);
}
Point operator *(double d)const {
return Point(x * d, y * d);
}
Point operator /(double d)const {
return Point(x / d, y / d);
}
void operator -=(Point& p) {
x -= p.x;
y -= p.y;
}
void operator +=(Point& p) {
x += p.x;
y += p.y;
}
void operator *=(double d) {
x *= d;
y *= d;
}
void operator /=(double d) {
this ->operator*= (1 / d);
}
bool operator<(const Point& a) const {
return x < a.x || (abs(x - a.x) < EPS && y < a.y);
}
bool operator==(const Point& a) const {
return abs(x - a.x) < EPS && abs(y - a.y) < EPS;
}
};
// 向量操作
double cross(const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
double cross(const Point& a, const Point& b, const Point& c) {
return cross(b - a, c - a);
}
double dot(const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y;
}
class Line {
public:
Point front, tail;
double ang;
int u, v;
Line() {}
Line(const Point& a, const Point& b) :front(a), tail(b) {
ang = atan2(front.y - tail.y, front.x - tail.x);
}
void initAng() {
ang = atan2(front.y - tail.y, front.x - tail.x);
}
};
int cmp(const Line& a, const Line& b) {
if (a.u == b.u && a.v == b.v)return 0;
//if (a.ang < b.ang)return -1;
if (a.u > b.u)return -1;
if (a.u < b.u)return 1;
if (a.u >= 0) {
if (a.v < b.v)return -1;
return 1;
}
if (a.v < b.v) return 1;
return -1;
}
// 点在直线哪一边>0 左边,<0边
double SideJudge(const Line& a, const Point& b) {
return cmp(cross(a.front - a.tail, b - a.tail));
//return cross(a.front - a.tail, b - a.tail);
}
int LineSort(const Line& a, const Line& b) {
int c = cmp(a, b);
if (c)return c < 0;
return cross(b.front - b.tail, a.front - b.tail) > 0;
}
/*
点p 到 p+r 表示线段1
点q 到 q+s 表示线段2
线段1 上1点用 p' = p+t*r (0<=t<=1)
线段2 上1点用 q' = q+u*s (0<=u<=1)
让两式相等求交点 p+t*r = q+u*s
两边都叉乘s
(p+t*r)Xs = (q+u*s)Xs
pXs + t*rXs = qXs
t = (q-p)Xs/(rXs)
同理,
u = (p-q)Xr/(sXr) -> u = (q-p)Xr/(rXs)
以下分4种情况:
1. 共线,sXr==0 && (q-p)Xr==0, 计算 (q-p)在r上的投影在r长度上的占比t0,
计算(q+s-p)在r上的投影在r长度上的占比t1,查看[t0, t1]是否与范围[0,1]有交集。
如果t0>t1, 则比较[t1, t0]是否与范围[0,1]有交集。
t0 = (q-p)*r/(r*r)
t1 = (q+s-p)*r/(r*r) = t0 + s · r / (r · r)
2. 平行sXr==0 && (q-p)Xr!=0
3. 0<=u<=1 && 0<=t<=1 有交点
4. 其他u, t不在0到范围内,没有交点。
*/
pair<double, double> intersection(const Point& q, const Point& s, const Point& p, const Point& r, bool& oneline) {
// 计算 (q-p)Xr
auto qpr = cross(q - p, r);
auto qps = cross(q - p, s);
auto rXs = cross(r, s);
if (cmp(rXs) == 0) {
oneline = true;
return { -1, -1 }; // 平行或共线
}
// 求解t, u
// t = (q-p)Xs/(rXs)
auto t = qps / rXs;
// u = (q-p)Xr/(rXs)
auto u = qpr / rXs;
return { u, t };
}
Point LineCross(const Line& a, const Line& b, bool& f) {
Point dira = a.front - a.tail;
Point dirb = b.front - b.tail;
bool oneline = false;
auto p = intersection(a.tail, dira, b.tail, dirb, oneline);
if (oneline)f = false;
return a.tail + dira * p.first;
}
class HalfPlane {
public:
vector<Line> lines;
vector<int> q;
vector<Point> t;
int siz;
void init(int n) {
siz = 0;
lines.resize(n);
q.resize(n + 10);
t.resize(n + 10);
}
void addLine(const Line& a) {
lines[siz++] = a;
}
vector<Point> run() {
sort(lines.begin(), lines.begin()+siz, LineSort);
int l = -1, r = 0;
q[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < siz; ++i) {
if (cmp(lines[i], lines[i - 1]) == 0)continue;
while (r - l > 1 && SideJudge(lines[i], t[r]) < 0)r--;
while (r - l > 1 && SideJudge(lines[i], t[l + 2]) < 0)l++;
q[++r] = i;
bool f = true;
t[r] = LineCross(lines[q[r]], lines[q[r - 1]], f);
}
while (r - l > 1 && SideJudge(lines[q[l + 1]], t[r]) < 0)r--;
//return r - l > 2;
if (r - l > 2) {
bool f = true;
t[r + 1] = LineCross(lines[q[l + 1]], lines[q[r]], f);
r++;
//if (!f)puts("xxx");
}
// 统计交点
l++;
vector<Point> ans(r - l);
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); ++i) {
ans[i] = t[i + l + 1];
}
return ans;
}
};
}
FloatSys::Line lines[N];
FloatSys::Line getLine(int x, int y, int dir) {
FloatSys::Line l;
FloatSys::Point d(x, 1);
l.tail = d * y/x/d.dis2();
d = FloatSys::Point(-1, x);
l.front = l.tail+ d * dir;
l.u = -dir;
l.v = dir * x;
l.initAng();
return l;
}
FloatSys::HalfPlane hp;
bool judge(int n) {
hp.siz = 0;
hp.addLine({ FloatSys::Point (1,0), FloatSys::Point (0,0)});
hp.lines[0].u = 1;
hp.lines[0].v = 0;
hp.addLine({ FloatSys::Point (0,1), FloatSys::Point (0,0)});
hp.lines[1].u = 0;
hp.lines[1].v = 1;
double maxd = 1e19;
hp.addLine({ FloatSys::Point(-1,maxd), FloatSys::Point(0,maxd) });
hp.lines[2].u = -1;
hp.lines[2].v = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
hp.addLine(lines[i*2]);
hp.addLine(lines[i*2+1]);
}
auto points = hp.run();
if (points.size() < 3)return false;
bool pp = false;
for (auto& p : points) {
if (FloatSys::cmp(p.x) < 0 && FloatSys::cmp(p.y) > 0) pp = true;
}
return pp;
}
void solve() {
using namespace FloatSys;
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
int a, b, c;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
lines[i*2] = getLine(a, c, 1);
lines[i*2+1] = getLine(a, b, -1);
}
if (n < 1) {
printf("%d\n", n);
return;
}
hp.init(N);
int best = 0;
int l = 1, r = n;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (judge(mid)) {
best = mid;
l = mid+1;
}
else r = mid-1;
}
printf("%d\n", best);
}
int main() {
solve();
return 0;
}
/*
5
2 8 12
5 4 5
3 8 10
6 2 3
1 3 7
1
2 8 12
2
10000 1 2
20000 10 11
2
1 1 2
2 10 11
2
10000 1 2
10010 1 2
2
1 1 2
2 1 2
1
1000000000 1 2
5
10000 1 2
10010 1 2
10010 1 2
10010 1 2
10010 1 2
5
10000 1 2
10010 1 2
10010 3 4
10010 1 2
10010 1 2
5
100000000 2 3
100000200 2 3
100010200 2 3
100110200 2 3
110010200 2 3
5
10 2 3
100000200 2 3
100010200 2 3
100110200 2 3
110010200 2 3
5
1 2 3
100000200 2 3
100010200 1 2
100110200 1 2
110010200 1 2
2
1 1 2
2 3 4
2
1 2 3
2 5 6
2
1 2 3
2 1 2
1
1 2 3
3
1 1 2
3 0 1
2 1 2
3
1 1 2
3 0 1
2 2 3
*/
本人码农,希望通过自己的分享,让大家更容易学懂计算机知识。创作不易,帮忙点击公众号的链接。

本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!