将yolo格式转化为voc格式:txt转xml(亲测有效)
发布时间:2023年12月18日
1.文件目录如下所示:

对以上目录的解释:
1.dataset下面的image文件夹:里面装的是数据集的原图片
2.dataset下面的label文件夹:里面装的是图片对应得yolo格式标签

3.dataset下面的Annotations文件夹:这是一个空文件夹,里面要装得是即将要生成得voc格式标签
2.转换代码如下所示
新建一个convert.py文件,然后将下面代码复制进去
注意:文件夹的格式要与我的一样才行
from xml.dom.minidom import Document
import os
import cv2
# def makexml(txtPath, xmlPath, picPath): # txt所在文件夹路径,xml文件保存路径,图片所在文件夹路径
def makexml(picPath, txtPath, xmlPath): # txt所在文件夹路径,xml文件保存路径,图片所在文件夹路径
"""此函数用于将yolo格式txt标注文件转换为voc格式xml标注文件
"""
dic = {'0': "pedestrian", # 创建字典用来对类型进行转换
'1': "people", # 此处的字典要与自己的classes.txt文件中的类对应,且顺序要一致
'2': "bicycle",
'3': "car",
'4': "van",
'5': "truck",
'6': "tricycle",
'7': "awning-tricycle",
'8': "bus",
'9': "motor",
}
files = os.listdir(txtPath)
for i, name in enumerate(files):
xmlBuilder = Document()
annotation = xmlBuilder.createElement("annotation") # 创建annotation标签
xmlBuilder.appendChild(annotation)
txtFile = open(txtPath + name)
txtList = txtFile.readlines()
img = cv2.imread(picPath + name[0:-4] + ".jpg")
Pheight, Pwidth, Pdepth = img.shape
folder = xmlBuilder.createElement("folder") # folder标签
foldercontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("driving_annotation_dataset")
folder.appendChild(foldercontent)
annotation.appendChild(folder) # folder标签结束
filename = xmlBuilder.createElement("filename") # filename标签
filenamecontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(name[0:-4] + ".jpg")
filename.appendChild(filenamecontent)
annotation.appendChild(filename) # filename标签结束
size = xmlBuilder.createElement("size") # size标签
width = xmlBuilder.createElement("width") # size子标签width
widthcontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(Pwidth))
width.appendChild(widthcontent)
size.appendChild(width) # size子标签width结束
height = xmlBuilder.createElement("height") # size子标签height
heightcontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(Pheight))
height.appendChild(heightcontent)
size.appendChild(height) # size子标签height结束
depth = xmlBuilder.createElement("depth") # size子标签depth
depthcontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(Pdepth))
depth.appendChild(depthcontent)
size.appendChild(depth) # size子标签depth结束
annotation.appendChild(size) # size标签结束
for j in txtList:
oneline = j.strip().split(" ")
object = xmlBuilder.createElement("object") # object 标签
picname = xmlBuilder.createElement("name") # name标签
namecontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(dic[oneline[0]])
picname.appendChild(namecontent)
object.appendChild(picname) # name标签结束
pose = xmlBuilder.createElement("pose") # pose标签
posecontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("Unspecified")
pose.appendChild(posecontent)
object.appendChild(pose) # pose标签结束
truncated = xmlBuilder.createElement("truncated") # truncated标签
truncatedContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("0")
truncated.appendChild(truncatedContent)
object.appendChild(truncated) # truncated标签结束
difficult = xmlBuilder.createElement("difficult") # difficult标签
difficultcontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("0")
difficult.appendChild(difficultcontent)
object.appendChild(difficult) # difficult标签结束
bndbox = xmlBuilder.createElement("bndbox") # bndbox标签
xmin = xmlBuilder.createElement("xmin") # xmin标签
mathData = int(((float(oneline[1])) * Pwidth + 1) - (float(oneline[3])) * 0.5 * Pwidth)
xminContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(mathData))
xmin.appendChild(xminContent)
bndbox.appendChild(xmin) # xmin标签结束
ymin = xmlBuilder.createElement("ymin") # ymin标签
mathData = int(((float(oneline[2])) * Pheight + 1) - (float(oneline[4])) * 0.5 * Pheight)
yminContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(mathData))
ymin.appendChild(yminContent)
bndbox.appendChild(ymin) # ymin标签结束
xmax = xmlBuilder.createElement("xmax") # xmax标签
mathData = int(((float(oneline[1])) * Pwidth + 1) + (float(oneline[3])) * 0.5 * Pwidth)
xmaxContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(mathData))
xmax.appendChild(xmaxContent)
bndbox.appendChild(xmax) # xmax标签结束
ymax = xmlBuilder.createElement("ymax") # ymax标签
mathData = int(((float(oneline[2])) * Pheight + 1) + (float(oneline[4])) * 0.5 * Pheight)
ymaxContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(mathData))
ymax.appendChild(ymaxContent)
bndbox.appendChild(ymax) # ymax标签结束
object.appendChild(bndbox) # bndbox标签结束
annotation.appendChild(object) # object标签结束
f = open(xmlPath + name[0:-4] + ".xml", 'w')
xmlBuilder.writexml(f, indent='\t', newl='\n', addindent='\t', encoding='utf-8')
f.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
picPath = "dataset/image/" # 图片所在文件夹路径,后面的/一定要带上
txtPath = "dataset/label/" # txt所在文件夹路径,后面的/一定要带上
xmlPath = "dataset/Annotations/" # xml文件保存路径,后面的/一定要带上
makexml(picPath, txtPath, xmlPath)
3.需要修改的地方-标签字典
如果你要转换得标签内容与上面标签字典得内容不同得话,请按需求修改成你自己的标签

4.需要修改的地方-文件夹路径
如果你的文件夹路径跟我上面的不一样的话,那么在这里修改成你对应的文件夹路径

5.运行你刚刚创建的convert.py文件,就生成xml格式的标签了

6.使用labelimg验证一下转换之后的格式
先打开图片和标签所在的文件夹

在这里输入cmd

打开命令行窗口

先激活虚拟环境,输入命令:
activate yolo
然后使用labelimg验证
labelimg image在选择标签文件夹的时候选择刚才生成的voc格式标签的文件夹
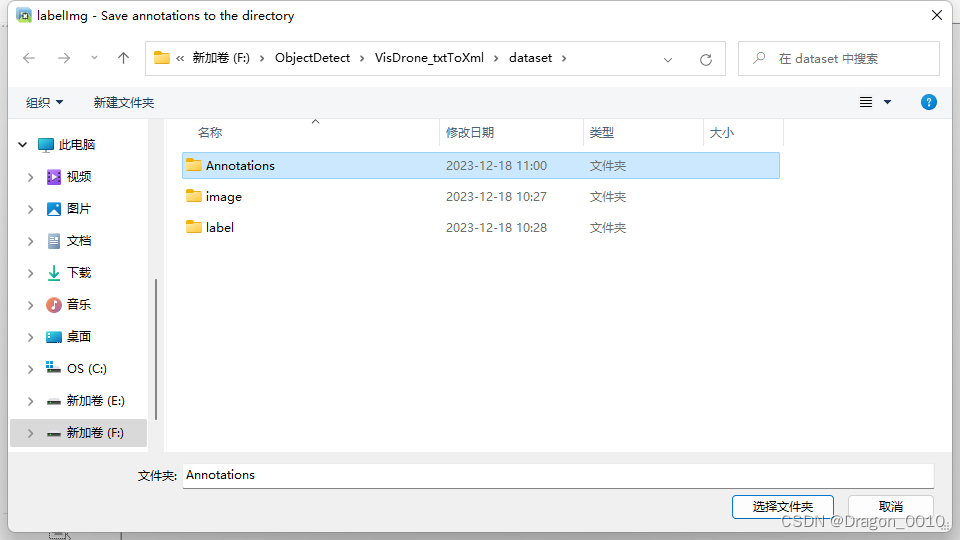
然后进入页面就是这个样子
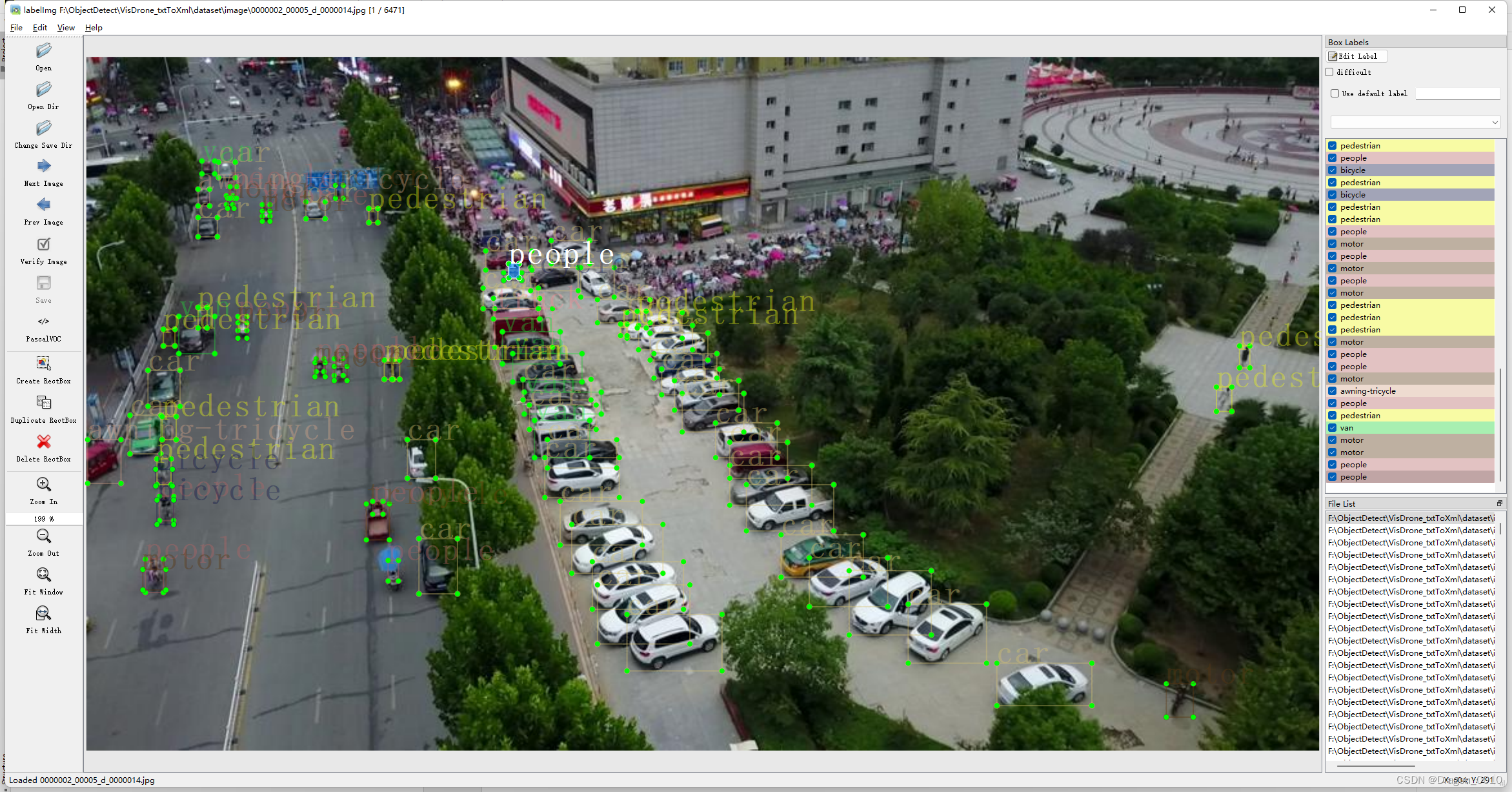

说明转换格式成功啦!!!
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/pyscl01/article/details/135061512
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 代理(Proxy)模式
- 【二】为Python Tk GUI窗口添加一些组件和绑定一些组件事件
- 【C++】POCO学习总结(十四):引用计数、共享指针、缓冲区管理
- 【面试题】使任何数组都可以调用 array.last() 方法,这个方法将返回数组最后一个元素
- PLC-IoT 网关开发札记(2):Xamarin Forms 工程获取App当前的版本号
- 25. string和const char哪个更合理?
- Spark SQL简介与基本用法
- R503S指纹识别模块的指令系统(二)
- Java版直播商城:电商源码、小程序、三级分销及 免 费 搭 建 方案
- 最近使用浏览器的人数上升了30%