【Vue3】计算属性computed和监听属性watch
目录
👉 computed 👈
计算属性computed作用是根据已有数据计算出新数据。它需要返回一个值,返回的值就是该计算属性的值。
🐌只读取不修改
<template>
<div class="app">
姓:<input type="text" v-model="firstName"> <hr>
名:<input type="text" v-model="lastName"> <hr>
全名:{{ fullName }}
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, computed } from "vue"
const firstName = ref('zhang')
const lastName = ref('san')
const fullName = computed(() => {
return `${firstName.value} - ${lastName.value}`
})
</script>??既读取又修改
<template>
<div class="app">
姓:<input type="text" v-model="firstName"> <hr>
名:<input type="text" v-model="lastName"> <hr>
全名:{{ fullName }}
<div>
<button @click="changeFullName">修改全名</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, computed } from "vue"
const firstName = ref('zhang')
const lastName = ref('san')
const fullName = computed({
get(){
return `${firstName.value} - ${lastName.value}`
},
set(val){
console.log('有人修改了fullName',val)
firstName.value = val.split('-')[0]
lastName.value = val.split('-')[1]
}
})
const changeFullName = () => {
fullName.value = 'li-si'
}
</script>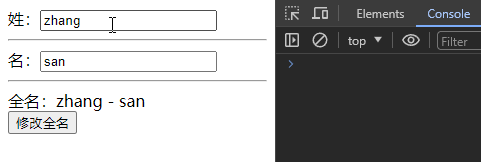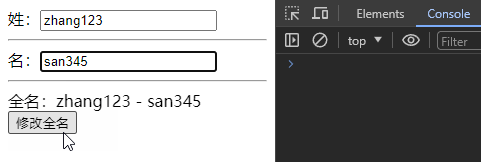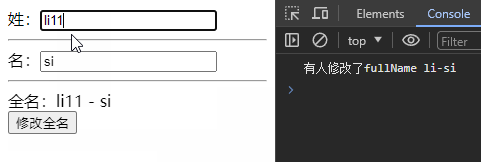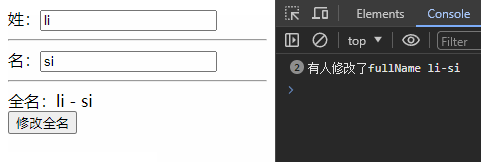
?👉 watch 👈
?监听属性watch作用是监听数据变化。
??vue3中的watch可以监听以下四种数据:
① ref定义的数据(包括计算属性);
② reactive定义的数据;
③ 一个函数,返回一个值(getter函数);
④ 由以上类型的值组成的数组。
??watch有三个参数:
① 被监视的数据
② 监视的回调
③ 配置对象(deep:深度监听、immediate:立即执行.....)???watch会返回一个用于清除监听的函数,可以通过它停止监听。
1、监听?ref 基本类型?数据
监听ref基本类型数据直接写变量名,监视其value值的变化。
<template>
<div class="app">
sum: {{ sum }}
<div>
<button @click="sum++">点击sum加一</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, watch } from "vue"
const sum = ref(0)
const stopWatch = watch(sum, (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log('sum值发生了变化', newValue, oldValue);
// 停止监听
if(newValue >= 5){
stopWatch()
}
})
</script>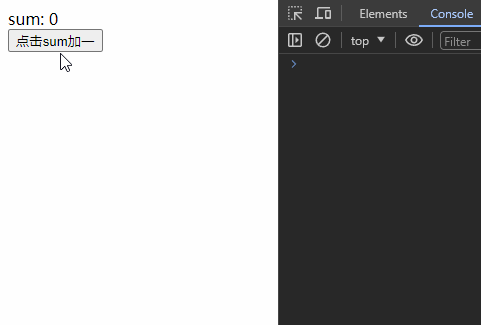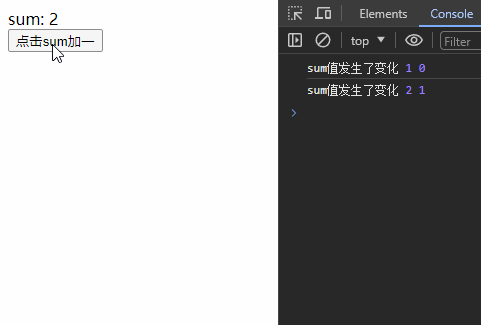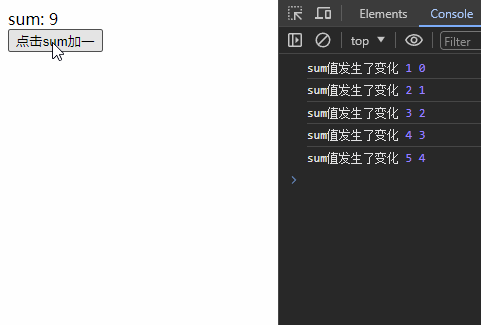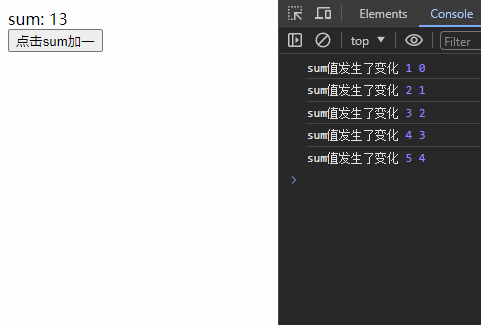
2、监听 ref 对象类型 数据?
?监视ref定义的对象类型数据,监视的是对象的地址值,若想监视对象内部属性的变化,需要手动开启深度监视。({deep:true})
<template>
<div class="app">
姓名:{{ personInfo.name }}
年龄:{{ personInfo.age }}
<div>
<button @click="changeName">修改名字</button>
<button @click="changeAge">修改年龄</button>
<button @click="changePerson">修改姓名和年龄</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, watch } from "vue"
const personInfo = ref({
name: 'zhangsan',
age: 18
})
watch(personInfo, (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log('personInfo发生了变化', newValue, oldValue);
}, {deep:true})
const changeName = () => {
personInfo.value.name += '~'
}
const changeAge = () => {
personInfo.value.age += 1
}
const changePerson = () => {
personInfo.value = {
name: 'yezi',
age: 22
}
}
</script>?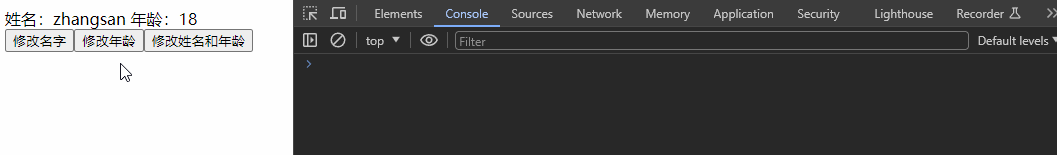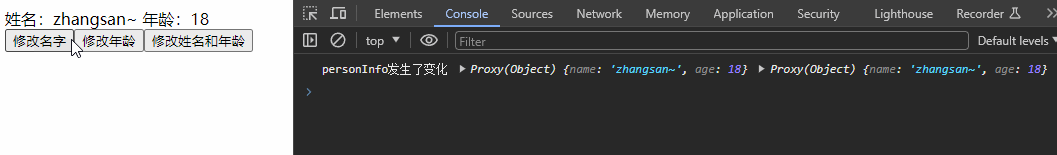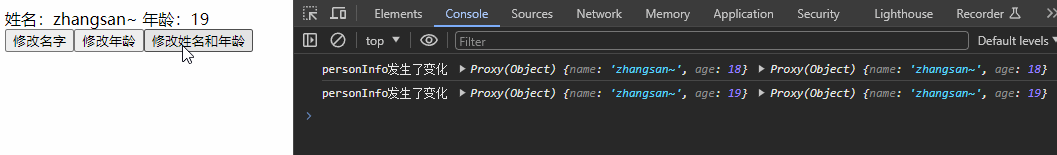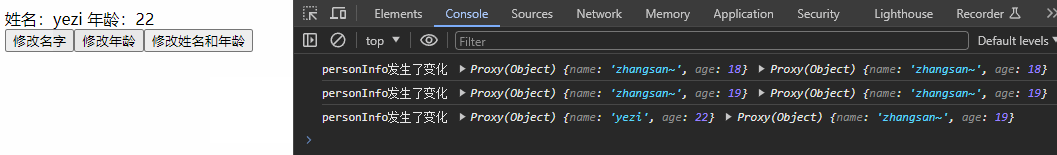
??👉ps:若修改的是ref定义的对象中的属性,newValue 和 oldValue 都是新值,因为它们是同一个对象;若修改整个ref定义的对象,newValue 是新值, oldValue 是旧值,因为不是同一个对象了。
3、监听 reactive 对象类型 数据
默认开启深度监听。
<template>
<div class="app">
姓名:{{ personInfo.name }}
年龄:{{ personInfo.age }}
朋友姓名:{{ personInfo.friend.name }}
朋友年龄:{{ personInfo.friend.age }}
<div>
<button @click="changeName">修改名字</button>
<button @click="changeAge">修改年龄</button>
<button @click="changePerson">修改姓名和年龄</button>
<button @click="changeFriendAge">修改朋友年龄</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { reactive, watch } from "vue"
const personInfo = reactive({
name: 'zhangsan',
age: 18,
friend: {
name: 'wangwu',
age: 20
}
})
watch(personInfo, (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log('personInfo发生了变化', newValue, oldValue);
})
const changeName = () => {
personInfo.name += '~'
}
const changeAge = () => {
personInfo.age += 1
}
const changePerson = () => {
Object.assign(personInfo, {name: 'yezi', age: 22})
}
const changeFriendAge = () => {
personInfo.friend.age += 1
}
</script>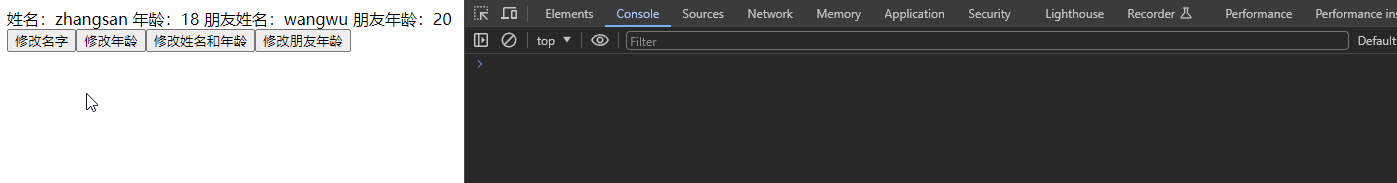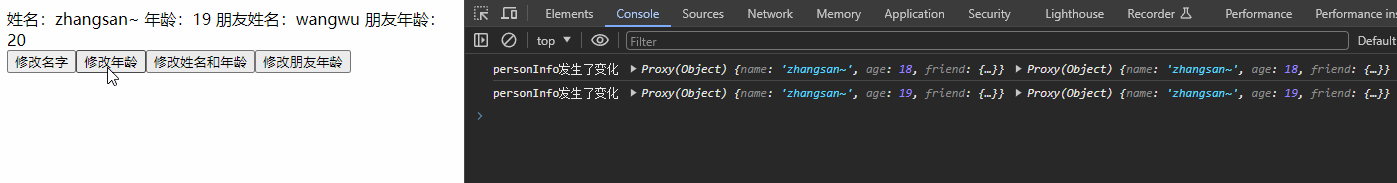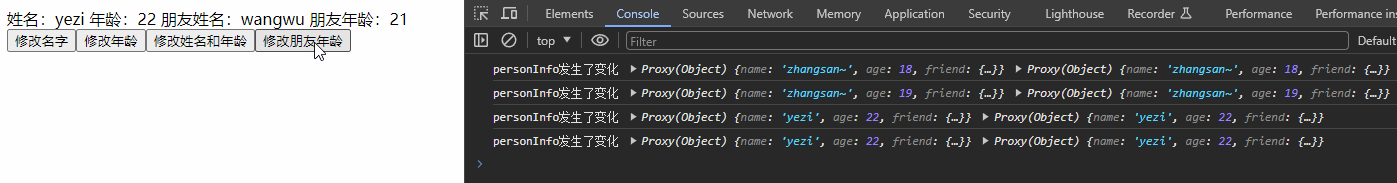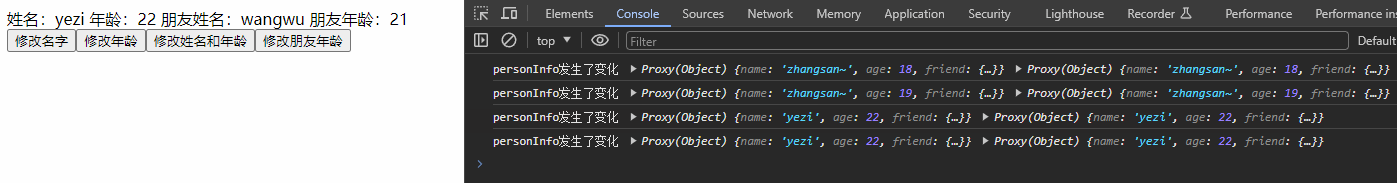
?
4、监听对象类型的某个属性?
监听ref或者reactive定义的对象类型数据中的某个属性时,如果该属性值不是对象类型,需要写成函数的形式,如果是对象类型,可以直接写,也可以写成函数的形式。
<template>
<div class="app">
姓名:{{ personInfo.name }}
年龄:{{ personInfo.age }}
朋友姓名:{{ personInfo.friend.name }}
朋友年龄:{{ personInfo.friend.age }}
<div>
<button @click="changeName">修改名字</button>
<button @click="changeAge">修改年龄</button>
<button @click="changePerson">修改姓名和年龄</button>
<button @click="changeFriendAge">修改朋友年龄</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { reactive, watch } from "vue"
const personInfo = reactive({
name: 'zhangsan',
age: 18,
friend: {
name: 'wangwu',
age: 20
}
})
watch(() => personInfo.name, (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log('personInfo.name发生了变化', newValue, oldValue);
})
watch(() => personInfo.age, (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log('personInfo.age发生了变化', newValue, oldValue);
})
watch(() => personInfo.friend, (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log('personInfo.friend发生了变化', newValue, oldValue);
}, {deep:true}) //需要手动开启深度监视
const changeName = () => {
personInfo.name += '~'
}
const changeAge = () => {
personInfo.age += 1
}
const changePerson = () => {
Object.assign(personInfo, {name: 'yezi', age: 22})
}
const changeFriendAge = () => {
personInfo.friend.age += 1
}
</script>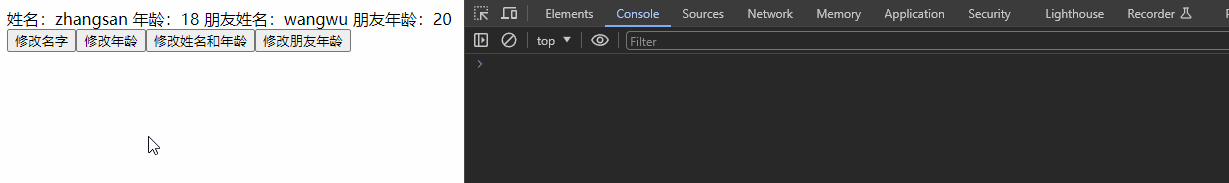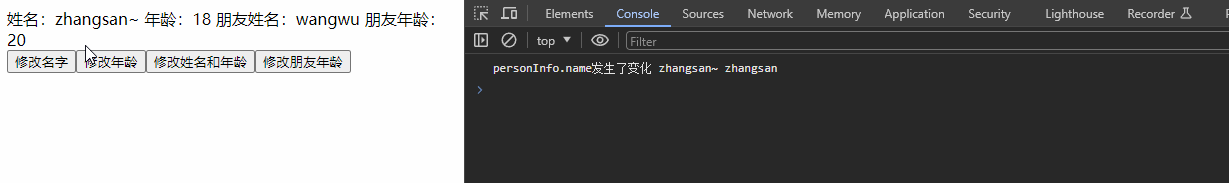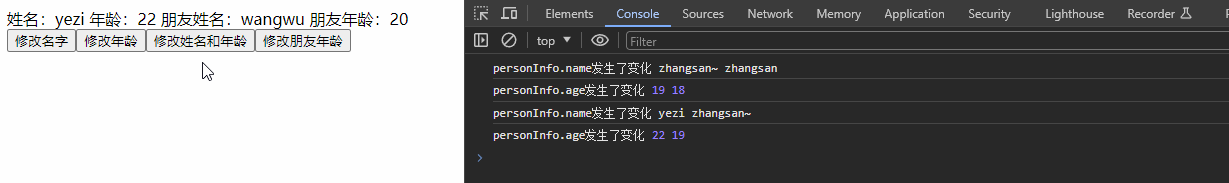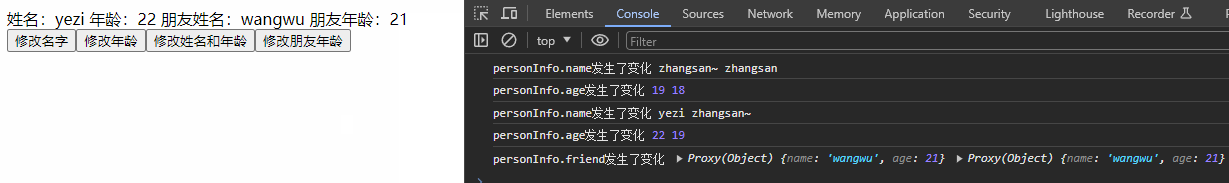 ?
?
5、监视以上多个数据
?监视多个数据,直接把所有数据放到数组中。
<template>
<div class="app">
姓名:{{ personInfo.name }}
年龄:{{ personInfo.age }}
朋友姓名:{{ personInfo.friend.name }}
朋友年龄:{{ personInfo.friend.age }}
<div>
<button @click="changeName">修改名字</button>
<button @click="changeAge">修改年龄</button>
<button @click="changePerson">修改姓名和年龄</button>
<button @click="changeFriendAge">修改朋友年龄</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { reactive, watch } from "vue"
const personInfo = reactive({
name: 'zhangsan',
age: 18,
friend: {
name: 'wangwu',
age: 20
}
})
watch([() => personInfo.name, () => personInfo.age, () => personInfo.friend], (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log(newValue, oldValue);
})
const changeName = () => {
personInfo.name += '~'
}
const changeAge = () => {
personInfo.age += 1
}
const changePerson = () => {
Object.assign(personInfo, {name: 'yezi', age: 22})
}
const changeFriendAge = () => {
personInfo.friend.age += 1
}
</script>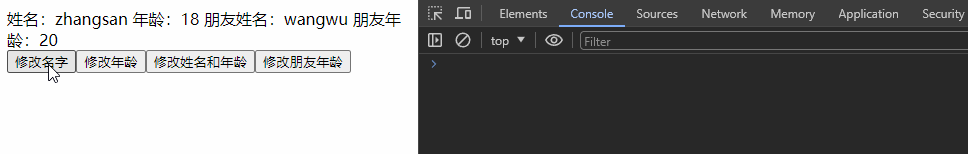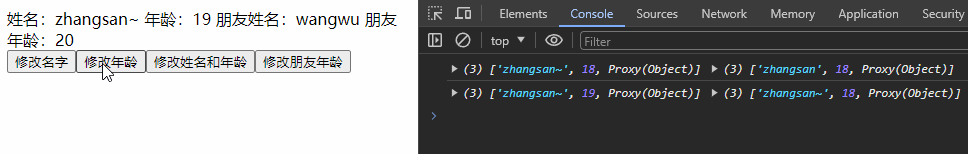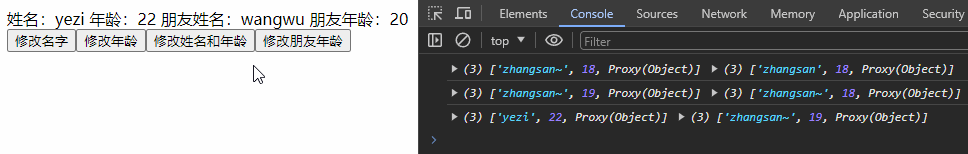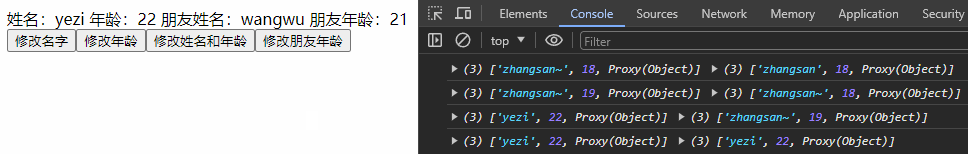
👉 watchEffect 👈
?watchEffect也是用来监听数据的,刚进页面就会立即执行一次,同时响应式地追踪其依赖,并在依赖更改时重新执行该函数。
watchEffect和watch区别:
①?都能监听响应式数据的变化,不同的是监听数据变化的方式不同
② watch要明确指出监视的数据,watchEffect不用明确指定监视的数据,用到哪些属性,就监视哪些属性。
<template>
<div class="app">
姓名:{{ personInfo.name }}
年龄:{{ personInfo.age }}
存款:{{ personInfo.money }}
<div>
<button @click="changeMoney">花钱</button>
<button @click="changeAge">修改年龄</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { reactive, watchEffect } from "vue"
const personInfo = reactive({
name: 'zhangsan',
age: 18,
money: 10000
})
const stopWtach = watchEffect(() => {
console.log('数据发生修改');
if(personInfo.money <= 9500 || personInfo.age >= 20){
console.log('停止监听');
stopWtach()
}
})
const changeMoney = () => {
personInfo.money -= 100
}
const changeAge = () => {
personInfo.age += 1
}
</script>
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 【刷题】前缀树
- Ubuntu 查看某一端口中正在运行的程序
- 调度工具之dolphinscheduler篇
- MATLAB中var函数用法
- 硬件iic和软件iic的区别
- Gitee:远程仓库步骤
- Transformer引领AI领域:从模型到平台,全方位探索与实践
- [python]gym安装报错ERROR: Failed building wheel for box2d-py
- 密码输入时的隐藏显示和显示
- android 常规log的查看与抓取