SQL Server 数据表约束及数据查询
一、常见的约束类型
SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) 提供了一个可视化界面来管理 SQL Server 数据库。在数据库表中,约束是用来指定表中数据的规则,保证数据的准确性和可靠性。以下是几种常用的数据表约束方式:
-
primary key 约束:用于唯一标识表中的每一行,并确保该列(或列组合)不包含 NULL 值。
create table Employees ( StudentID int not null, StudentName varchar(255) not null, StudentName varchar(255), primary key(EmployeeID) );我们看到有一个这样的标记就成功了
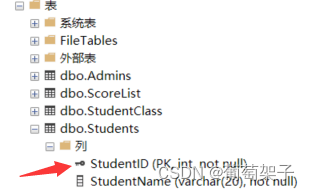
-
forein key 约束:用于在两个表之间创建关系。它指向另一个表的 primary key。
create table table Orders ( OrderID int not null, OrderNumber int not null, EmployeeID int, primary key (OrderID), foreign key (EmployeeID) references Employees(EmployeeID) ); -
unique 约束:保证一列或列组合中的所有值都是唯一的。
create table Users ( UserID int not null, UserName varchar(255) not null, Eunique (UserName) ); -
check约束:用于限制列中值的范围。如果指定了 check约束,那么列中的所有值都必须满足约束条件。
create table Products ( ProductID int NOT NULL, ProductName varchar(255) NOT NULL, Price money NOT NULL, check (Price > 0) ); -
default 约束:用于在未指定值的情况下为列提供默认值。
create table Orders ( OrderID int NOT NULL, OrderDate datetime not null default getdate() ); -
not null 约束:用于确保列不能存储 NULL 值。
create table Customers ( CustomerID int NOT NULL, LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL, FirstName varchar(255) NOT NULL );
在 SQL Server 中,这些约束可以在创建表时(如上所示)或之后使用 alter table 语句添加。约束确保了数据完整性,并且在进行数据修改或更新时帮助避免错误的数据输入。使用 SSMS 可以通过图形界面进行约束的创建和管理,也可以通过编写和执行 SQL 语句来完成这些操作。
二、数据查询
2.1 查询的基本方法
比如我们要查询一个表名为“StudentsDB”的数据表,列名为 Gender,Birthday,Age,按照Age的数据降序排列
查询一般分四个部分:

2.2 具体查询方法
-
选择数据(select):
使用select语句来选择表中的数据。可以选择全部列或特定列。-- 选择所有列 select * from TableName; -- 选择特定列 select Column1, Column2 from TableName; -
筛选数据(WHERE):
使用where子句来筛选查询结果。select * from TableName where Condition; -
连接表(join):
使用join语句来结合两个或多个表中有关联的行。select Column1, Column2 from FirstTable join SecondTable on FirstTable.CommonColumn = SecondTable.CommonColumn; -
排序数据(order by):
使用order by来对结果进行排序。select * from TableName order by ColumnName ASC; -- 升序 -
限制结果(top):
使用top子句来限制查询结果的数量。select top 10 * from TableName; -
聚合数据(group by):
使用group by来将结果集合为基于指定列的小组,并可能配合聚合函数使用,例如count(),max(),min(),sum(),avg()等。select ColumnName, count(*) from TableName group by ColumnName; -
插入数据(insert):
使用insert into语句来插入新的数据行到表中。insert intoTableName (Column1, Column2) values (Value1, Value2); -
更新数据(update):
使用update语句来修改表中的数据。update TableName set Column1 = Value1 where Condition; -
删除数据(delete):
使用delete语句来删除表中的数据。delete from TableName where Condition; -
计算行数(count):
使用count()函数来计算行数。select count(*) from TableName; -
重命名(as 或者 =):
使用count()函数来计算行数。
```sql
use StudentManageDB
go
select StudentName as 姓名, Gender as 性别, 出生日期=birthday from Students where Gender='男'
这个语句块首先选择 StudentManageDB 数据库作为当前操作的数据库。go 是一个批处理命令,它告诉 SSMS 执行前面的语句并开始新的一批命令。接下来的 select 语句选择 Students 表中性别为男的学生的姓名、性别和出生日期。字段名使用了 as 关键字来创建别名,使得结果集的列标头显示为中文。
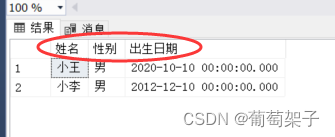
- 选择数据并合并列作为新的列:
比如:
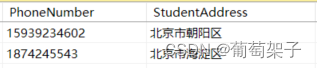
经过代码:
select 姓名=StudentName, 地址和电话=StudentAddress+'【'+PhoneNumber+'】' from Students where Gender='男'
这个 select 语句再次选择性别为男的学生,但这次合并了 StudentAddress 和 PhoneNumber 两列,并在它们之间添加了一些文本。结果会生成一个新的列 地址和电话。
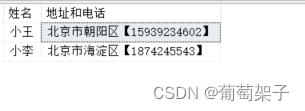
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!