Netty(NIO基础)
@[TOC](一.NIO基础)
##1、三大组件


###1.1多线程版设计
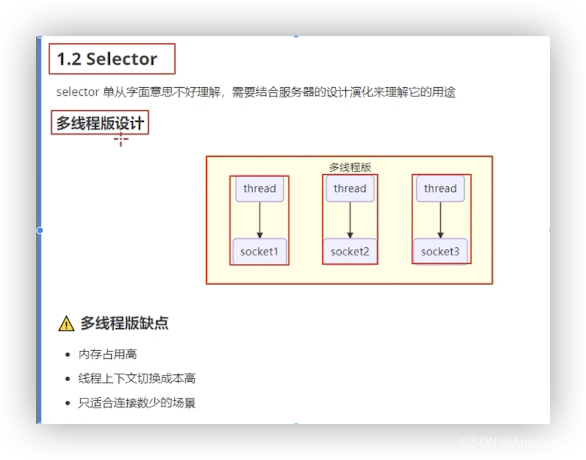
###1.2线程池版设计
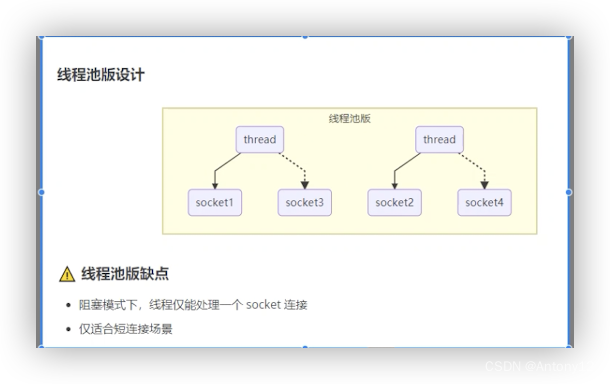
###1.3selector版设计
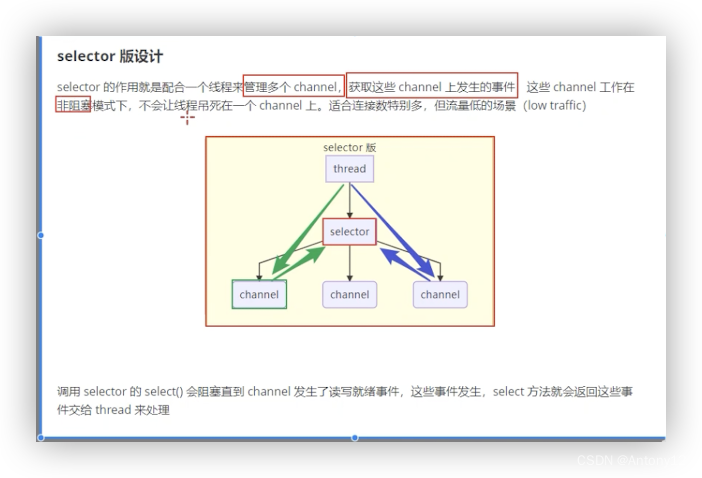
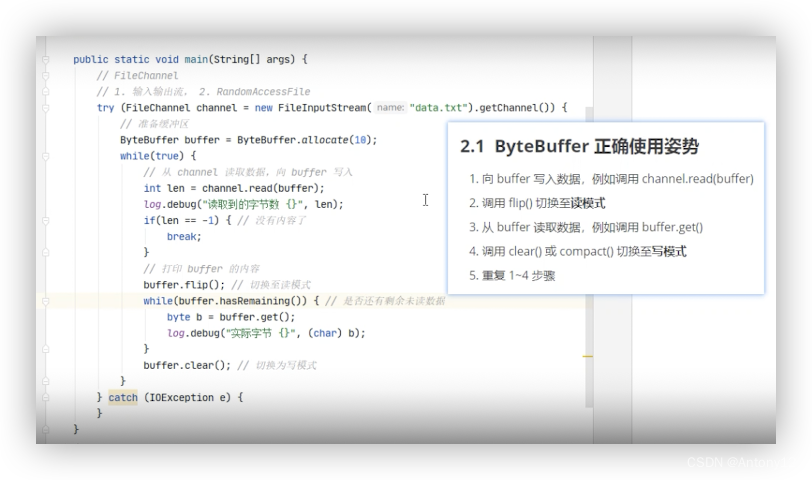
##2、ByteBuffer
###2.1使用
###2.2结构

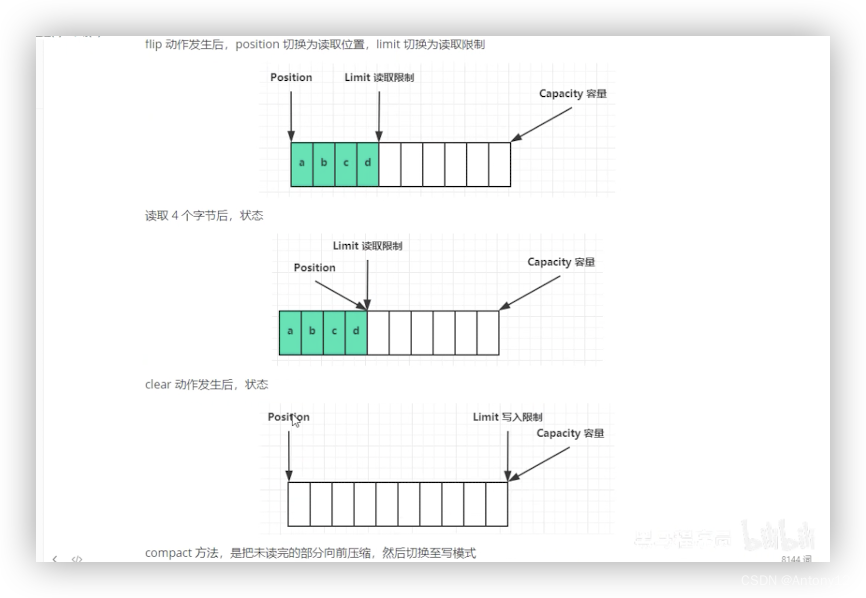
###2.3、ByteBuffer常见方法
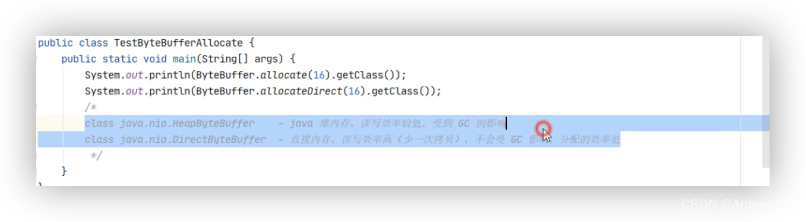
####2.3.1、分配空间
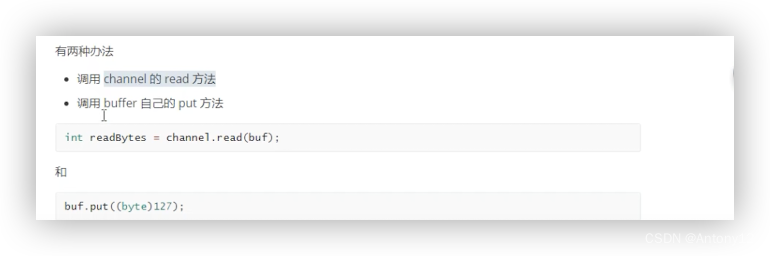
####2.3.2、向buffer写入数据
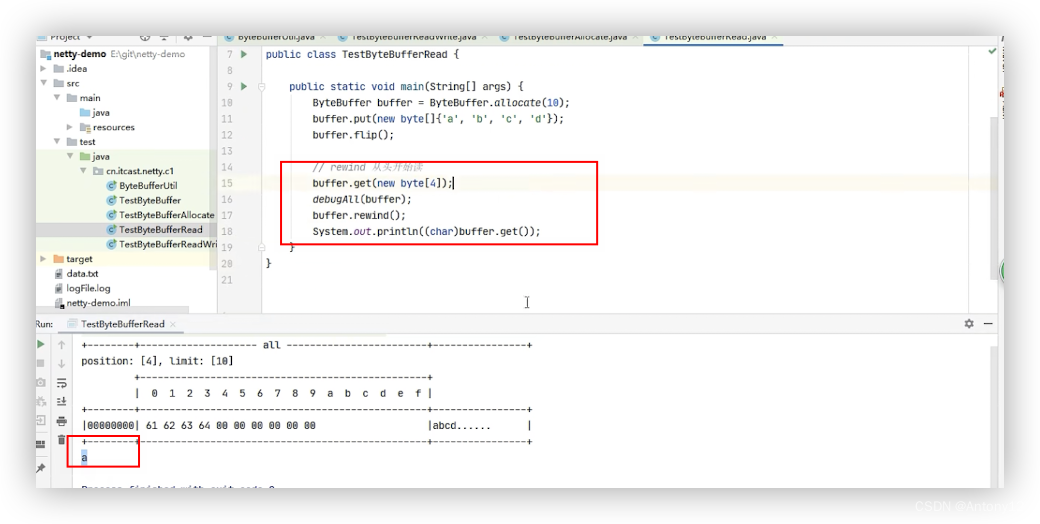
####2.3.3、从buffer读取数据

####2.3.4、rewind 从头开始读
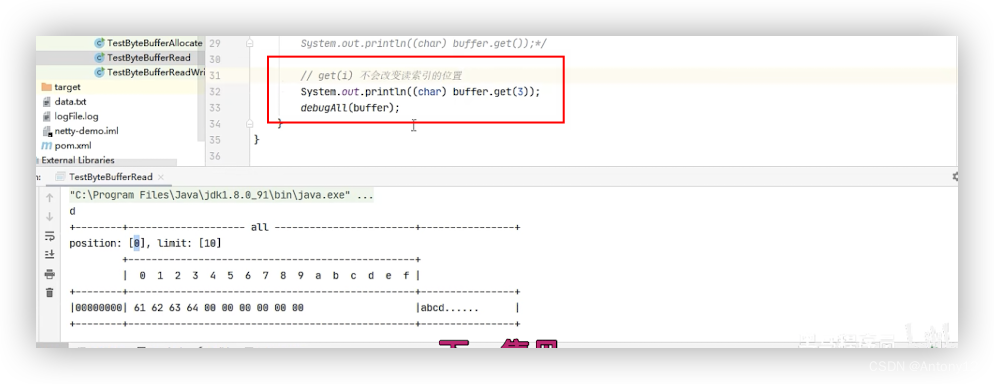
####2.3.5、mark、reset、get(i)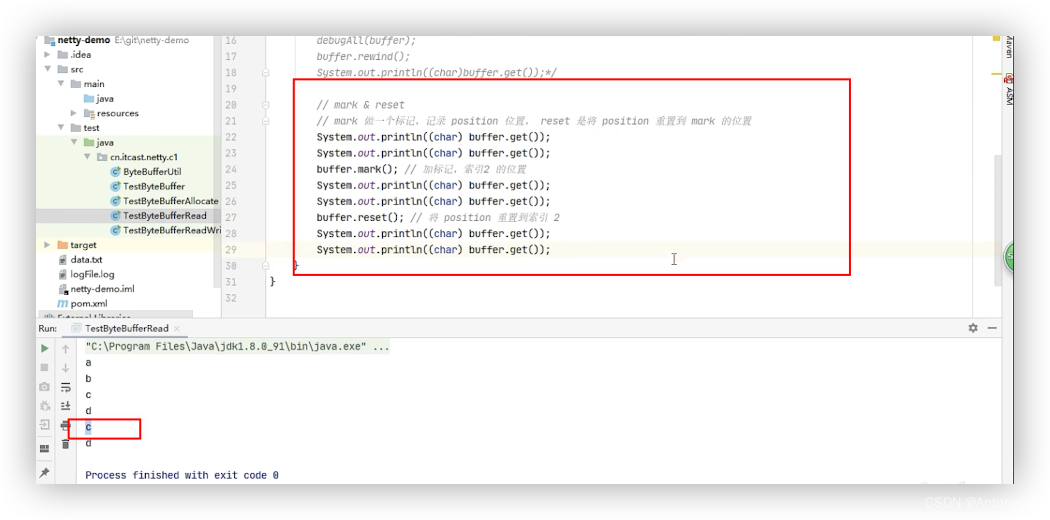
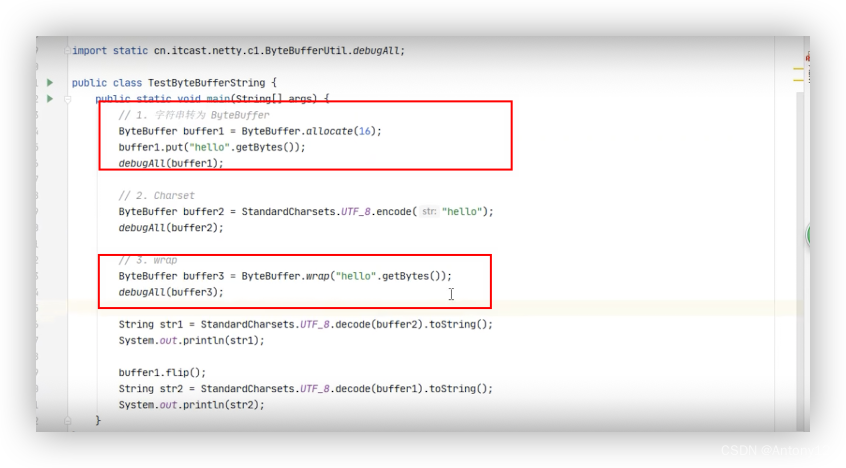
###2.4、字符串与ByteBuffer互转
读模式下才能读取到数据,如果是写模式得先切换到读模式,比如调用*.flip()方法
代码:
package cn.com.agree.netty.demo;
import cn.com.agree.netty.demo.util.ByteBufferUtil;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
/**
* @version 1.0
* @ClassName TestTranslate
* @Description TODO 类描述
* @date 2024/1/18 10:56 上午
**/
public class TestTranslate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义两个字符串
String str1 = "hello";
String str2 = "";
/**
* 第一种方式
* 通过getBytes()方式put
*/
System.out.println("=======================第一种方式 通过getBytes()方式put=================================");
//通过字符串的getBytes方法获得字节数组,放入缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
byteBuffer.put(str1.getBytes());
// byteBuffer.put(str2.getBytes());
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(byteBuffer);
//将缓冲区中的数据转换为字符串
//切换模式
byteBuffer.flip();
// 通过StandardCharsets解码,获得CharBuffer,再通过toString获得字符串
str2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(byteBuffer).toString();
System.out.println(str2);
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(byteBuffer);
/**
* 第二种方式
* 通过StandardCharsets编码、解码
*/
System.out.println("======================第二种方式 通过StandardCharsets编码、解码==========================");
//通过StandardCharsets编码的方式会自动切换到读模式,无需手动切换
ByteBuffer buffer1 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode(str1);
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer1);
str2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buffer1).toString();
System.out.println(str2);
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer1);
/**
* 第三种方式
* wrap()方法
*/
System.out.println("======================第三种方式 wrap()方法=================================");
ByteBuffer buffer2 = ByteBuffer.wrap(str1.getBytes());
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer2);
str2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buffer2).toString();
System.out.println(str2);
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer2);
}
}
###2.5、Scanning Readers

###2.6、黏包半包问题
1)出现的问题(前面消息合在一起叫黏包,后面消息断开叫半包)
2)为什么会出现这种现象?
-
粘包
发送方在发送数据时,并不是一条一条地发送数据,而是将数据整合在一起,当数据达到一定的数量后再一起发送。这就会导致多条信息被放在一个缓冲区中被一起发送出去
-
半包
接收方的缓冲区的大小是有限的,当接收方的缓冲区满了以后,就需要将信息截断,等缓冲区空了以后再继续放入数据。这就会发生一段完整的数据最后被截断的现象 -
解决办法
通过get(index)方法遍历ByteBuffer,遇到分隔符时进行处理。注意:get(index)不会改变position的值
记录该段数据长度,以便于申请对应大小的缓冲区 将缓冲区的数据通过get()方法写入到target中调用compact方法切换模式,因为缓冲区中可能还有未读的数据代码实现
package cn.com.agree.netty.demo;
import cn.com.agree.netty.demo.util.ByteBufferUtil;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
/**
* @version 1.0
* @ClassName TestByteBufferExample
* @Description TODO 类描述
* @date 2024/1/18 3:46 下午
**/
public class TestByteBufferExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer source = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);
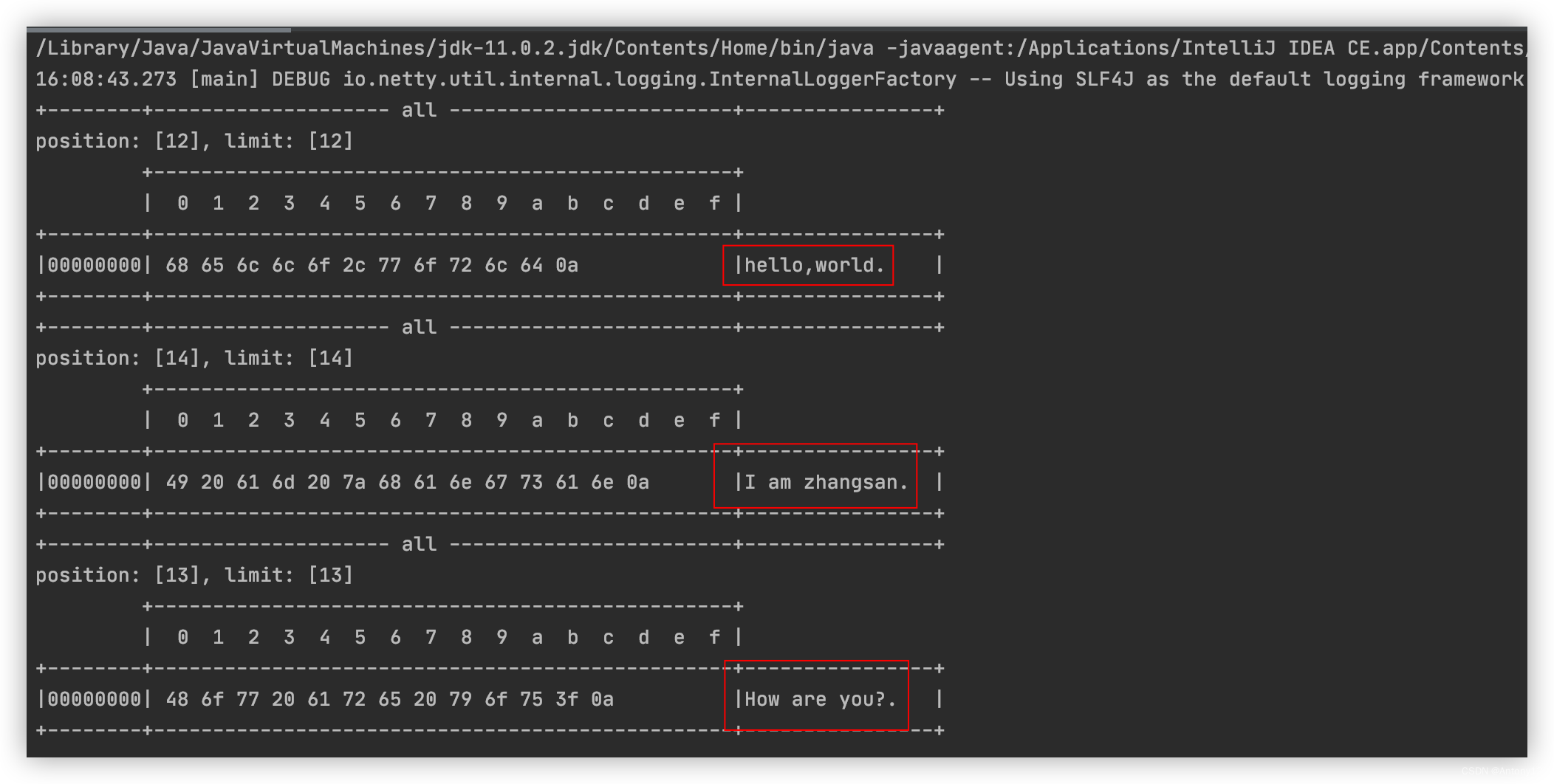
source.put("hello,world\nI am zhangsan\nHo".getBytes());
split(source);
source.put("w are you?\n".getBytes());
split(source);
}
private static void split(ByteBuffer source) {
//先切换到读模式
source.flip();
for (int i = 0; i < source.limit(); i++) {
//找到一条完整信息
if (source.get(i) == '\n') {
int length = i + 1 - source.position();
//把这条完整信息存入到ByteBuffer当中
ByteBuffer target = ByteBuffer.allocate(length);
for (int j = 0; j < length; j++) {
//从source读,从target写
target.put(source.get());
}
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(target);
}
}
//切换为写模式,但是缓冲区可能w未读完,这里需要使用compact()
source.compact();
}
}
运行结果
3、FileChannel
3.1相关方法介绍
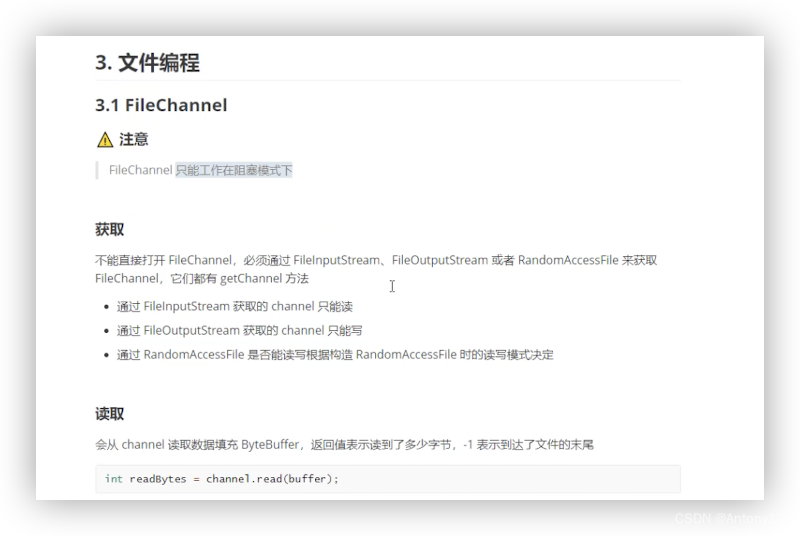
1) 读取
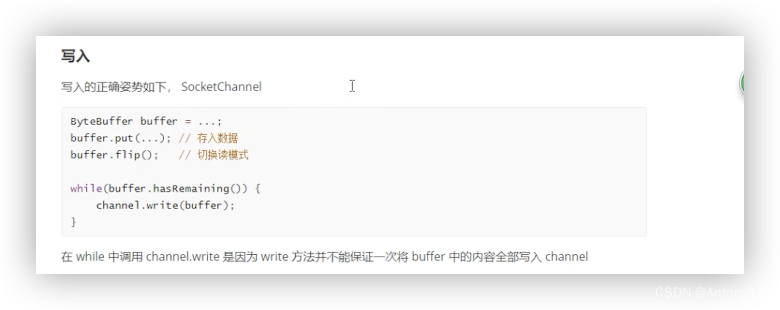
2)写入
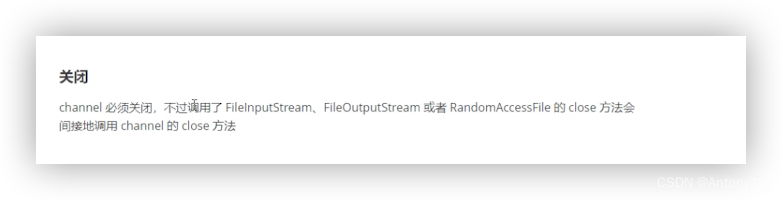
3)关闭
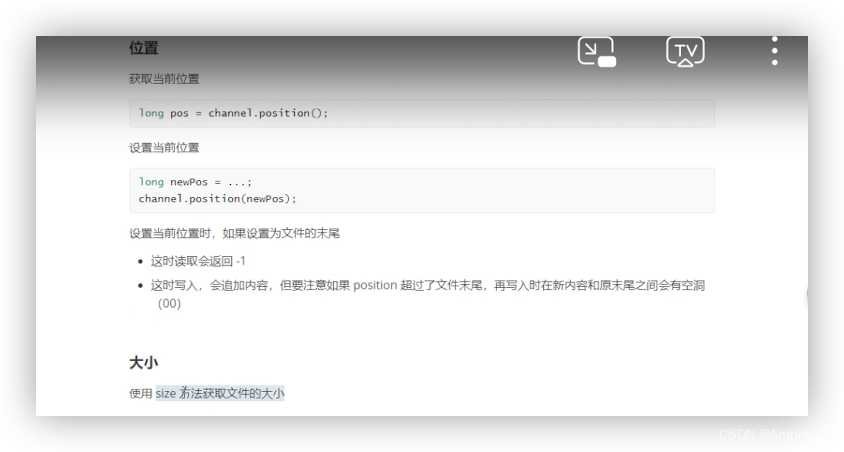
4)位置、大小
5)强制写入
3.2、两个Channel传输数据
1)代码(最多传输2G数据的文件)
package cn.com.agree.netty.demo;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
/**
* @version 1.0
* @ClassName TestFileChannelTransferTo
* @Description TODO 类描述
* @date 2024/1/18 5:15 下午
**/
public class TestFileChannelTransferTo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
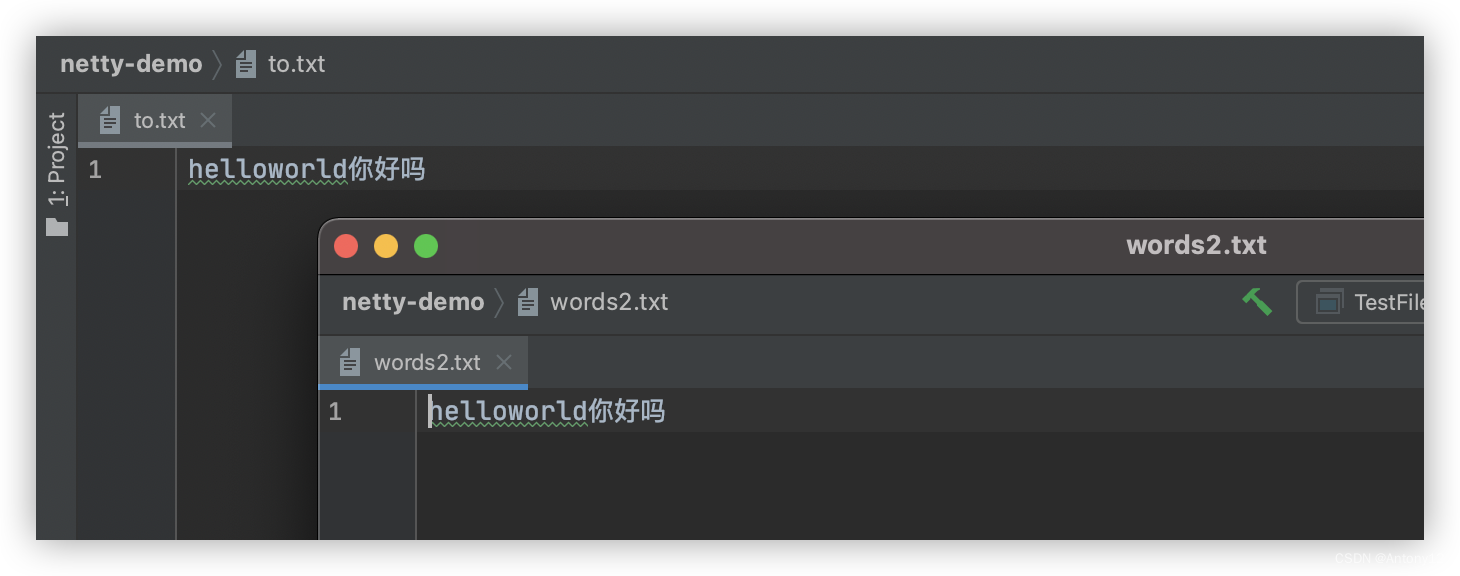
FileChannel from = new FileInputStream("words2.txt").getChannel();
FileChannel to = new FileOutputStream("to.txt").getChannel();
//效率高,底层会利用操作系统的零拷贝进行优化(最多2G数据)
to.transferFrom(from,0,from.size());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
效果
2)代码(优化(传输超过2G数据的文件))
代码
package cn.com.agree.netty.demo;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
/**
* @version 1.0
* @ClassName TestFileChannelTransferTo
* @Description TODO 类描述
* @date 2024/1/18 5:15 下午
**/
public class TestFileChannelTransferTo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileChannel from = new FileInputStream("words2.txt").getChannel();
FileChannel to = new FileOutputStream("to.txt").getChannel();
//效率高,底层会利用操作系统的零拷贝进行优化
long size = from.size();
long left = size;
while (left > 0) {
//返回值为已经传输了的字节数
left -= to.transferFrom(from, size - left, left);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
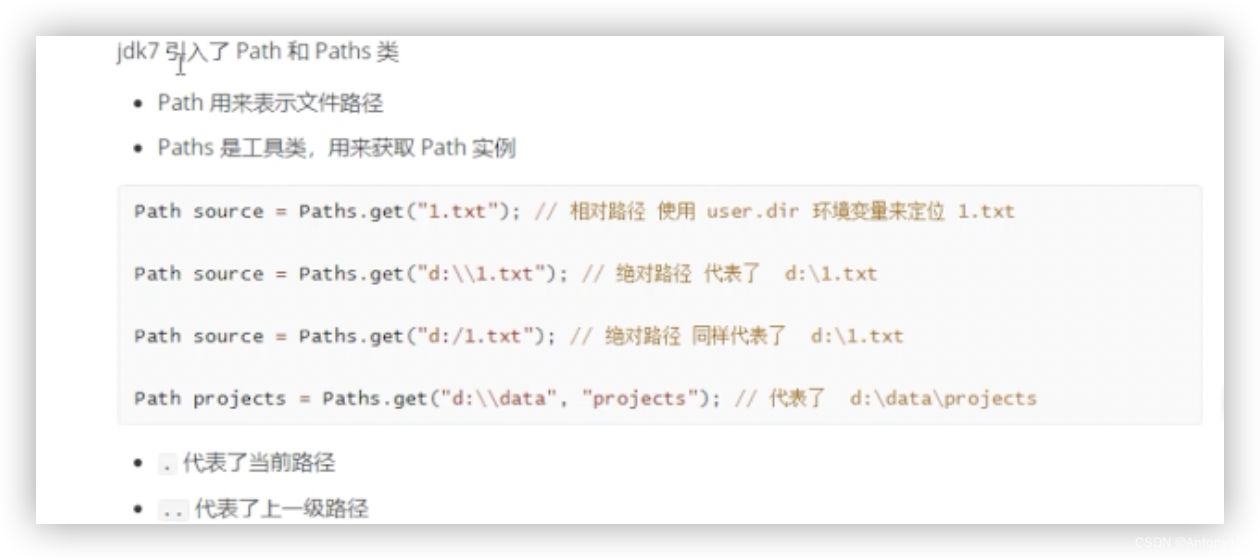
3.3、Path

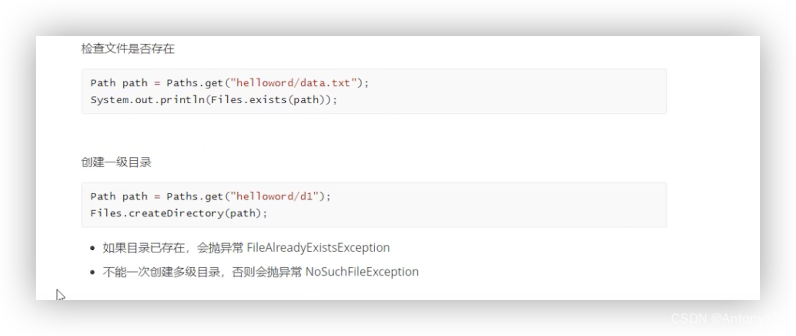
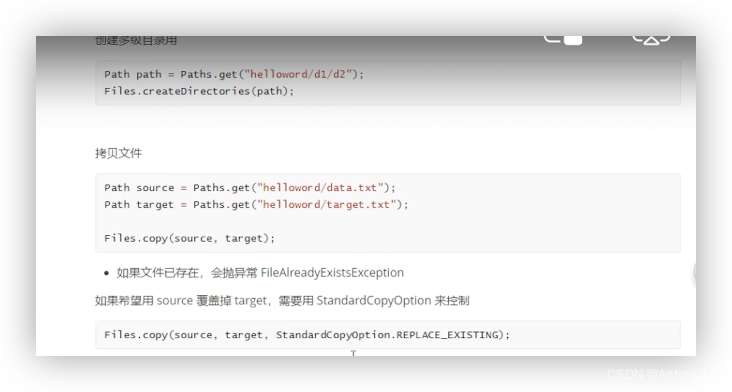
3.4、Files
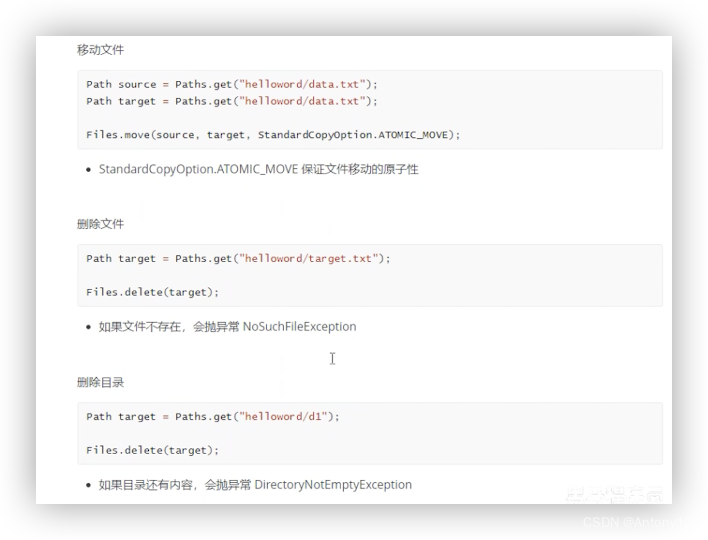
遍历目录
可以使用Files工具类中的walkFileTree(Path, FileVisitor)方法,其中需要传入两个参数
- Path:文件起始路径
- FileVisitor:文件访问器,使用访问者模式
接口的实现类SimpleFileVisitor有四个方法
- preVisitDirectory:访问目录前的操作
- visitFile:访问文件的操作
- visitFileFailed:访问文件失败时的操作
- postVisitDirectory:访问目录后的操作
代码
package cn.com.agree.netty.demo;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.*;
import java.nio.file.attribute.BasicFileAttributes;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* @version 1.0
* @ClassName TestWalkFileTree
* @Description TODO 类描述
* @date 2024/1/19 9:38 上午
**/
@Slf4j
public class TestWalkFileTree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
final Path path = Paths.get("/Users/andong/agree");
final AtomicInteger dirCount = new AtomicInteger();
final AtomicInteger fileCount = new AtomicInteger();
Files.walkFileTree(path, new SimpleFileVisitor<Path>() {
@Override
public FileVisitResult preVisitDirectory(Path dir, BasicFileAttributes attrs) throws IOException {
log.debug("dir:{}",dir);
dirCount.incrementAndGet();
return super.preVisitDirectory(dir, attrs);
}
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs) throws IOException {
log.debug("file:{}",file);
fileCount.incrementAndGet();
return super.visitFile(file, attrs);
}
});
log.debug("dirCount:{}",dirCount);
log.debug("fileCount:{}",fileCount);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果

删除目录:先删除文件在删除目录,此处不做演示有风险
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs) throws IOException {
Files.delete(file);
return super.visitFile(file, attrs);
}
@Override
public FileVisitResult postVisitDirectory(Path dir, IOException exc) throws IOException {
Files.delete(dir);
return super.postVisitDirectory(dir, exc);
}
拷贝目录
package cn.com.agree.netty.demo;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
/**
* @version 1.0
* @ClassName TestFileCopy
* @Description 拷贝目录
* @date 2024/1/19 10:53 上午
**/
public class TestFileCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String source = "/Users/andong/agree/share/platform/target";
String target = "/Users/andong/targe";
try {
Files.walk(Paths.get(source)).forEach(e->{
String targetName = e.toString().replace(source, target);
try {
if (Files.isDirectory(e)) {
//如果是文件夹就创建
Files.createDirectory(Paths.get(targetName));
}
if (Files.isRegularFile(e)) {
//如果是文件就复制
Files.copy(e,Paths.get(targetName));
}
} catch (Exception e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Java中语音url转换成InputStream
- Apache Spark 的基本概念和在大数据分析中的应用。
- 智能机器人与旋量代数(12)
- redis分布式锁
- 探访纳尔逊美术馆里的绝世中华艺术品收藏
- 深度学习中的大模型「幻觉」问题:解析、原因及未来展望
- 文章解读与仿真程序复现思路——电力自动化设备EI\CSCD\北大核心《基于低碳需求响应的含煤制氢与碳捕集电厂的综合能源系统优化调度》
- 循环购的潜力!
- ubuntu 18.04安装ceres-solver
- vcruntime140.dll文件修复的几种常见解决办法,vcruntime140.dll丢失的原因