Java 反射(一)
发布时间:2024年01月09日
反射
1.反射的介绍
-
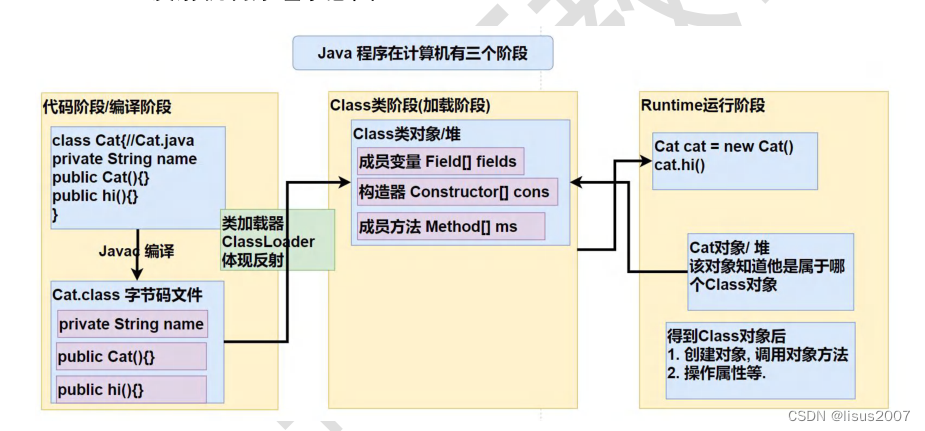
1.反射机制允话程序在执行期间借助于Refelction API取得任何类的信息(比如成员变量,构造器,成员方法等)并能操作对象的属性及方法,反射在设计模式和框架底层都会用到
-
2.加载完类之后,在堆中就产生了一个Class类型的对象(一个类只有一个Class对象),这个对象包含了类的完整信息。通过这个对象得到了类的结构,这个Class对象就像一面镜子,透过这个镜子看到类的结构,所以称之为反射
1.2反射的原理图
1.3反射可以完成的工作
- 1.在运行时判断任意一个对象所属的类
- 2.在运行期间构造一个类的对象
- 3.在运行期间得到任意一个类所具有的成员变量和方法
- 4.在运行时调用任意一个对象的成员变量和方法
- 5.生成动态代理
反射相关的主要类
- 1.java.lang.Class:代表一个类,Class对象表示某个类加载后在堆中的对象
- 2.java.lang.reflect.Method:代表类的方法,Method对象表示某个类的方法
- 3.java.lang.reflect.Field:代表类的成员变量,Field对象表示某个类的成员变量
- 4.java.lang.reflect.Constructor:代表类的构造方法,Constructor表示类构造器
package javareflect.demo;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Reflection01Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchFieldException {
//1.使用Properties类,可以读写配置文件
Properties properties=new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\re.properties"));
String classfullpath = properties.get("classfullpath").toString();
String methodName=properties.get("method").toString();
System.out.println("classfullpath"+classfullpath);
System.out.println("method="+methodName);
//2. 使用反射机制解决
//(1) 加载类, 返回 Class 类型的对象 cls
Class cls = Class.forName(classfullpath);
//(2) 通过 cls 得到你加载的类 javareflec.Cat 的对象实例
Object o =cls.newInstance();
//(3) 通过 cls 得到你加载的类 javareflect.Cat 的 methodName"hi" 的方法对象
Method method1=cls.getMethod(methodName);
//(4) 通过 method1 调用方法: 即通过方法对象来实现调用方法
System.out.println("==============");
method1.invoke(o);
//java.lang.reflect.Field: 代表类的成员变量, Field 对象表示某个类的成员变量
//得到 name 字段
//getField 不能得到私有的属性
Field nameField=cls.getField("age");
System.out.println(nameField.get(o));
//java.lang.reflect.Constructor: 代表类的构造方法, Constructor 对象表示构造器
Constructor constructor=cls.getConstructor();
System.out.println(constructor);
Constructor constructor1=cls.getConstructor(String.class);
System.out.println(constructor1);
}
}
运行结果
D:\jdk17\bin\java.exe "-javaagent:D:\IntelliJ IDEA 2021.3.3\lib\idea_rt.jar=59189:D:\IntelliJ IDEA 2021.3.3\bin" -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -classpath E:\Linuxshare\StartJava\out\production\StartJava;E:\Linuxshare\StartJava\lib\jl-1.0.1.jar;E:\Linuxshare\StartJava\lib\logback-classic-1.2.3.jar;E:\Linuxshare\StartJava\lib\logback-core-1.2.3.jar;E:\Linuxshare\StartJava\lib\slf4j-api-1.7.26.jar;E:\Linuxshare\StartJava\lib\commons-io-2.6.jar;E:\Linuxshare\StartJava\lib\junit-4.9.jar;E:\Linuxshare\StartJava\lib\mysql-connector-java-5.1.49.jar;E:\Linuxshare\StartJava\lib\c3p0-0.9.5.5.jar;E:\Linuxshare\StartJava\lib\druid-1.2.11.jar;E:\Linuxshare\StartJava\lib\commons-dbutils-1.6.jar javareflect.demo.Reflection01Demo
classfullpathjavareflect.Cat
method=hi
==============
hi招财猫
10
public javareflect.Cat()
public javareflect.Cat(java.lang.String)
1.4反射的优缺点
- 优点:可以动态的创建和使用对象(也是框架底层的核心),使用灵活,没有反射机制,框架技术就失去底层支撑
- 缺点:使用反射基本是解释执行,对执行速度有影响
1.5反射调用优化-关闭访问检查

package javareflect.demo;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class ReflectDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException {
Class cls=Class.forName("javareflect.Cat");
Object o = cls.newInstance();
Method hi=cls.getMethod("hi");
hi.setAccessible(true);//在反射调用方法时,取消访问检查
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i=0;i<90000;i++){
hi.invoke(o);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时=" + (end - start));
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/lisus2007/article/details/135485261
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 如何叠加多条宽带,使局域网速度更快?一看就会了!非常简单
- VMware workstation安装FreeBSD14.0虚拟机并配置网络
- 【Spring连载】使用Spring访问 Apache Kafka(十五)----消息头
- 现代科技企业互动体验展厅如何设计
- C# key=value的格式,并按照参数名ASCII字典排序
- 苹果系统盘制作
- SpringBoot核心原理之事件和监听器(生命周期监听、事件触发、监听器、自定义事件发布和订阅)和配置类和Bean加载的时机
- C++语法中宏的用法汇总和代码实战
- 【优先级队列 之 堆的实现】
- 【漏洞复现】ActiveMQ反序列化漏洞(CVE-2015-5254)