《算法通关村——回溯模板如何解决热门问题》
发布时间:2023年12月18日
《算法通关村——回溯模板如何解决热门问题》
39. 组合总和
给你一个 无重复元素 的整数数组 candidates 和一个目标整数 target ,找出 candidates 中可以使数字和为目标数 target 的 所有 不同组合 ,并以列表形式返回。你可以按 任意顺序 返回这些组合。
candidates 中的 同一个 数字可以 无限制重复被选取 。如果至少一个数字的被选数量不同,则两种组合是不同的。
对于给定的输入,保证和为 target 的不同组合数少于 150 个。
示例 1:
输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7
输出:[[2,2,3],[7]]
解释:
2 和 3 可以形成一组候选,2 + 2 + 3 = 7 。注意 2 可以使用多次。
7 也是一个候选, 7 = 7 。
仅有这两种组合。
示例 2:
输入: candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8
输出: [[2,2,2,2],[2,3,3],[3,5]]
示例 3:
输入: candidates = [2], target = 1
输出: []
提示:
1 <= candidates.length <= 302 <= candidates[i] <= 40candidates的所有元素 互不相同1 <= target <= 40
题解
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
dfs(candidates,0,target);
return res;
}
public void dfs(int[] c, int u , int target) {
if(target < 0){
return ;
}
if(target == 0){
res.add(new ArrayList(path));
return;
}
for(int i = u ; i < c.length ; i++){
if(c[i] <= target){
path.add(c[i]);
dfs(c,i,target-c[i]);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
}
78. 子集
给你一个整数数组 nums ,数组中的元素 互不相同 。返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
解集 不能 包含重复的子集。你可以按 任意顺序 返回解集。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3]
输出:[[],[1],[2],[1,2],[3],[1,3],[2,3],[1,2,3]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0]
输出:[[],[0]]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 10-10 <= nums[i] <= 10nums中的所有元素 互不相同
题解
class Solution {
// 存放符合条件结果的集合
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
// 空集合也是一个子集
if(nums.length == 0){
result.add(new ArrayList<>());
return result;
}
subsetsHelper(nums,0);
return result;
}
private void subsetsHelper(int[] nums,int startIndex){
// 遍历这个树的时候,把所有节点都记录下来,就是要求的子集集合
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
if(startIndex >= nums.length){
return;
}
for(int i = startIndex ; i < nums.length ; i++){
path.add(nums[i]);
subsetsHelper(nums,i+1);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
46. 全排列
给定一个不含重复数字的数组 nums ,返回其 所有可能的全排列 。你可以 按任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3]
输出:[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,1]
输出:[[0,1],[1,0]]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [1]
输出:[[1]]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 6-10 <= nums[i] <= 10nums中的所有整数 互不相同
题解
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] used;
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length == 0 ){
return result;
}
used = new boolean[nums.length];
permuteHelper(nums);
return result;
}
private void permuteHelper(int[] nums){
if(path.size() == nums.length){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return ;
}
for(int i = 0 ; i< nums.length ;i++){
if(used[i]){
continue;
}
used[i] = true;
path.add(nums[i]);
permuteHelper(nums);
path.removeLast();
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
784. 字母大小写全排列
给定一个字符串 s ,通过将字符串 s 中的每个字母转变大小写,我们可以获得一个新的字符串。
返回 所有可能得到的字符串集合 。以 任意顺序 返回输出。
示例 1:
输入:s = "a1b2"
输出:["a1b2", "a1B2", "A1b2", "A1B2"]
示例 2:
输入: s = "3z4"
输出: ["3z4","3Z4"]
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 12s由小写英文字母、大写英文字母和数字组成
题解
class Solution {
public List<String> letterCasePermutation(String s) {
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<String>();
dfs(s.toCharArray(),0,ans);
return ans;
}
public void dfs(char[] arr,int pos ,List<String> res){
while(pos < arr.length&&Character.isDigit(arr[pos])){
pos++;
}
if(pos == arr.length) {
res.add(new String(arr));
return;
}
arr[pos] ^= 32;
dfs(arr,pos+1,res);
arr[pos] ^= 32;
dfs(arr,pos+1,res);
}
}
79. 单词搜索
给定一个 m x n 二维字符网格 board 和一个字符串单词 word 。如果 word 存在于网格中,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过相邻的单元格内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母不允许被重复使用。
示例 1:

输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCCED"
输出:true
示例 2:
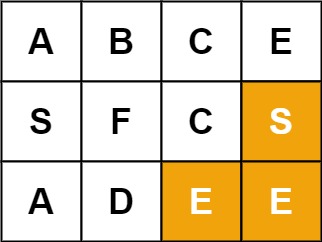
输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "SEE"
输出:true
示例 3:
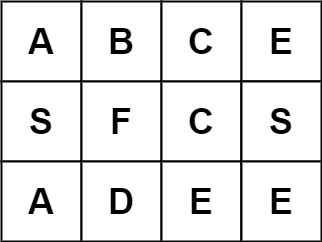
输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCB"
输出:false
提示:
m == board.lengthn = board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 61 <= word.length <= 15board和word仅由大小写英文字母组成
题解
class Solution {
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {
char[] words = word.toCharArray();
for(int i = 0;i<board.length;i++){
for(int j = 0; j<board[0].length;j++){
if(dfs(board,words,i,j,0)) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
boolean dfs(char[][] board ,char[] word,int i ,int j, int k){
if(i >= board.length || i<0|| j>=board[0].length || j<0|| board[i][j] != word[k]) return false;
if( k == word.length -1) return true;
board[i][j] = '\0';
boolean res = dfs(board,word,i+1,j,k+1) || dfs(board,word,i-1,j,k+1)|| dfs(board,word,i,j+1,k+1)||dfs(board,word,i,j-1,k+1);
board[i][j] = word[k];
return res;
}
}
131. 分割回文串
给你一个字符串 s,请你将 s 分割成一些子串,使每个子串都是 回文串 。返回 s 所有可能的分割方案。
回文串 是正着读和反着读都一样的字符串。
示例 1:
输入:s = "aab"
输出:[["a","a","b"],["aa","b"]]
示例 2:
输入:s = "a"
输出:[["a"]]
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 16s仅由小写英文字母组成
题解
class Solution {
List<List<String>> lists = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<String> deque = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
backTracking(s,0);
return lists;
}
private void backTracking(String s, int startIndex) {
if(startIndex >= s.length()){
lists.add(new ArrayList(deque));
return ;
}
for (int i = startIndex ; i< s.length(); i++){
// 如果起始位置大于s的大小,说明找到了一组分割方案
if(isPalindrome(s,startIndex,i)){
// 如果是回文子串,则记录
String str = s.substring(startIndex,i + 1);
deque.addLast(str);
} else {
continue;
}
// 起始位置后移,保证不重复
backTracking(s,i + 1);
deque.removeLast();
}
}
private boolean isPalindrome(String s , int startIndex, int end){
for(int i = startIndex, j = end;i<j;i++,j--){
if(s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/Go_ahead_forever/article/details/134928830
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 书生·浦语大模型全链路开源体系【大模型第3课-笔记】
- 算法训练营Day40
- Spring MVC 之 Restful 风格请求?持
- 2024PMP考试新考纲-【过程领域】近期典型真题和很详细解析(9)
- 计算机组成原理04:一位乘法
- 陪诊小程序|陪诊小程序搭建|陪诊小程序成品开发流程
- python脚本 ssh工具 ssh上传文档 选择文档并上传到ssh服务器
- 如何在Vim/Vi中使用“搜索”功能
- 集群部署篇--Redis 哨兵模式
- 怎样做好医学SCI论文翻译呢?