Zuul1.x 高并发下阻塞分析以及解决方案
背景
由于最近博主在压测接口的时候发现我接口出现卡死状态,最开始以为是我自己接口出现问题,单独压测我自己的服务(不经过网关)200/qps/10 次循环 是没问题,但是加上网关(zuul 1.x) 去发现 经过两次循环基本就不能访问,同时其他接口也不能访问,由此问题出现在zuul ,接着开始排查之路。
确认问题
在刚才背景当时只是怀疑zuul 有问题,因为zuul 没有加降级熔断。是否是它需要排查去确认,我当时(测试环境)通过arthas 查看了内存、线程,发现大量waiting 线程,查询具体waiting 线程详细信息后发现有大量http 请求连接没有唤醒,处于watting 根本原因是连接没有关闭。后来又在本地压测通过jconsole 定位如图
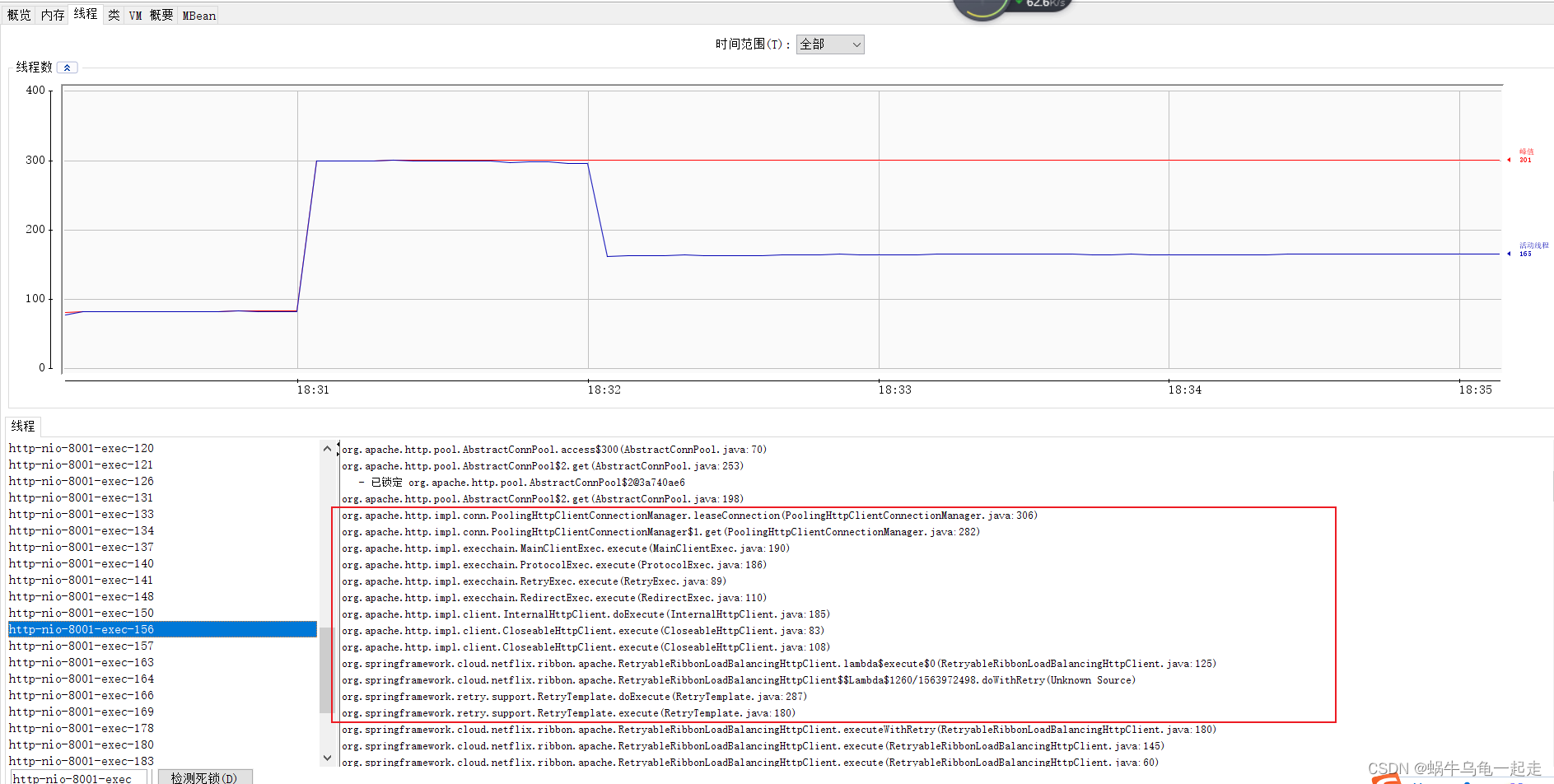
发现和测试环境一样的大量阻塞线程,为啥阻塞就需要看看Zuul 和Ribbon 他们交互逻辑。下面是分析过程。
代码分析
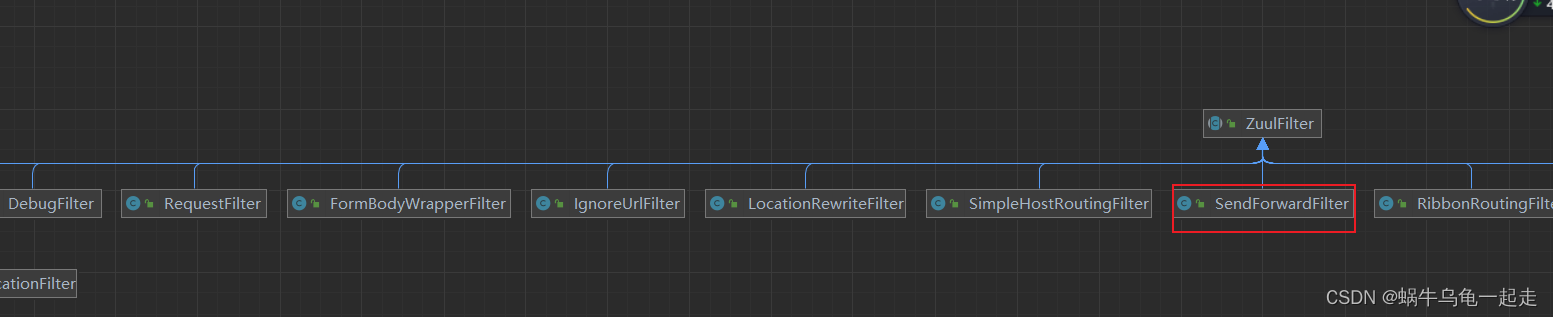
基于之前对zuul 1.x了解执行流程图
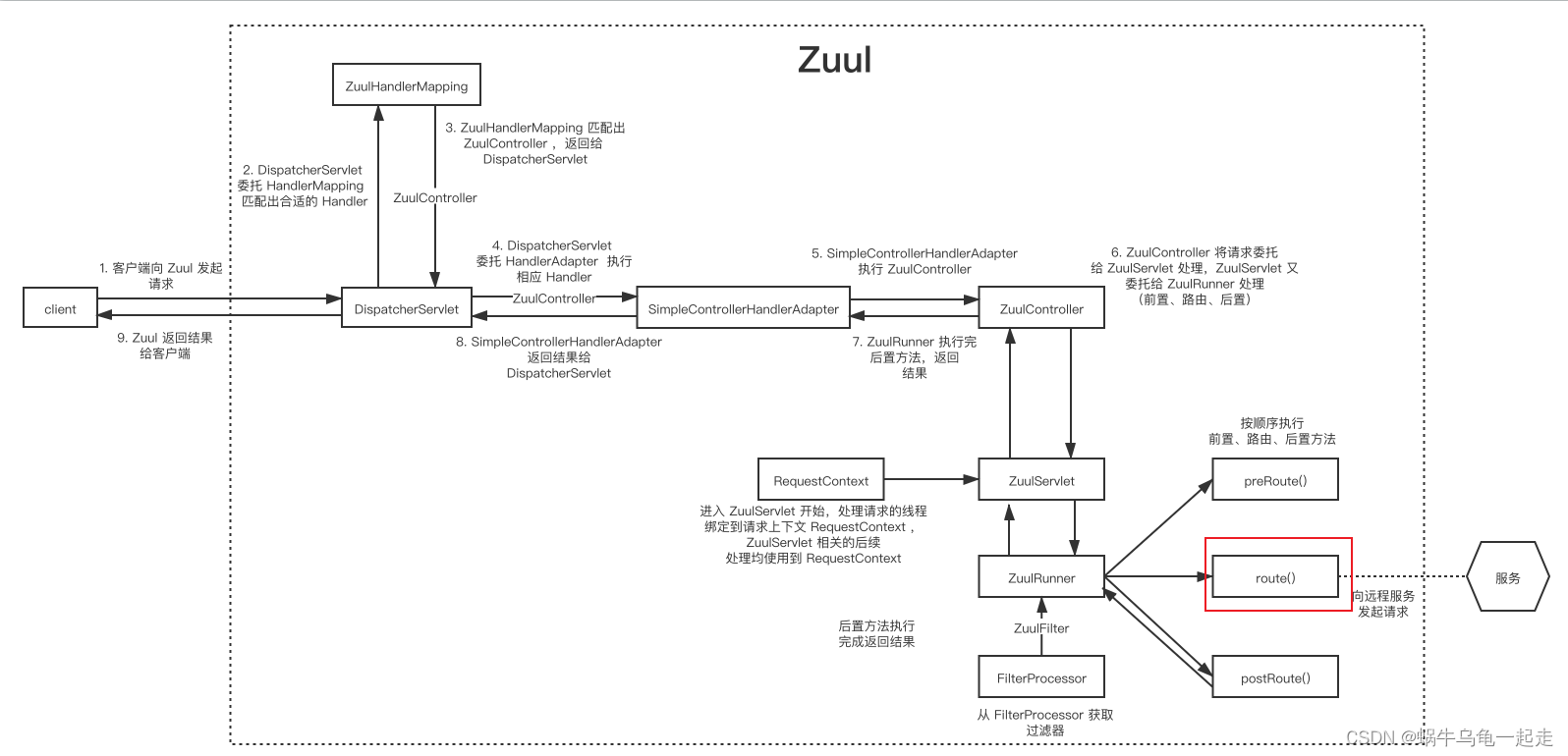
可以看到整个流程也就是route 会建立http连接请求。根据源码之后流程只有两种情况一种是成功执行post 另一种是出现异常执行error。
请求进来代码逻辑
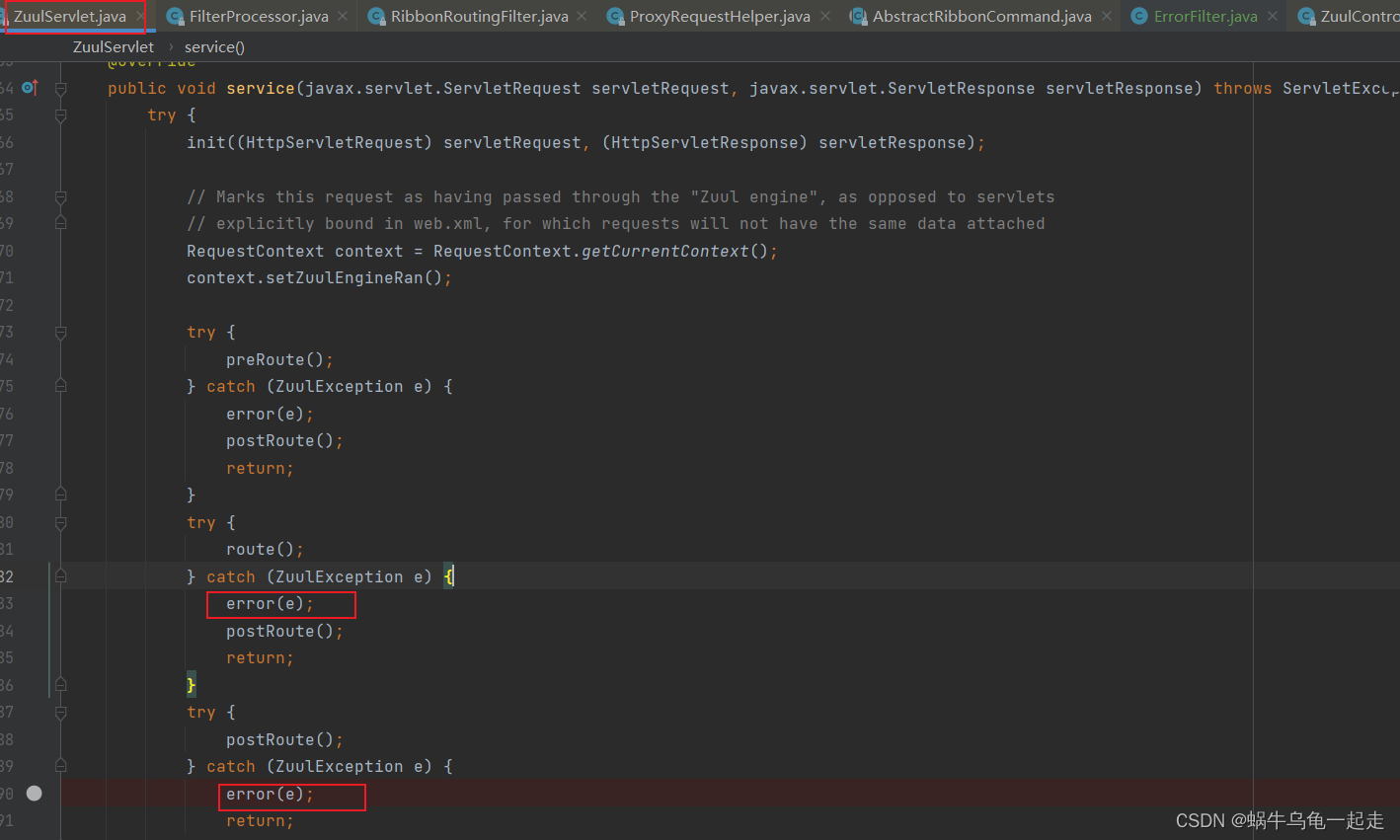
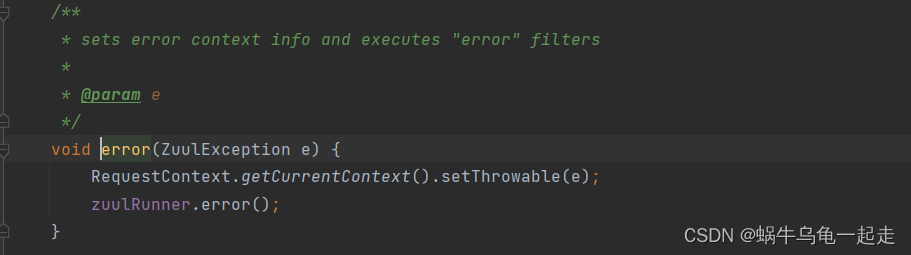
异常后执行代码
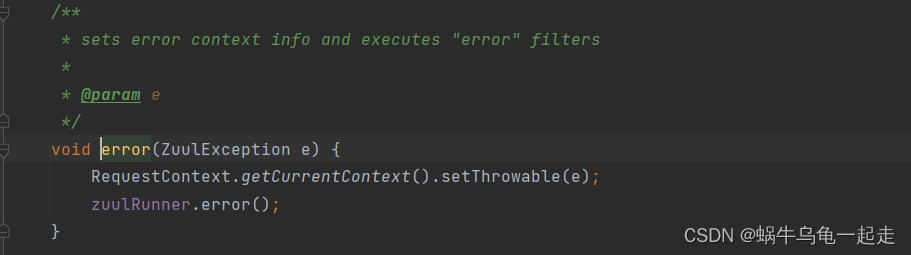
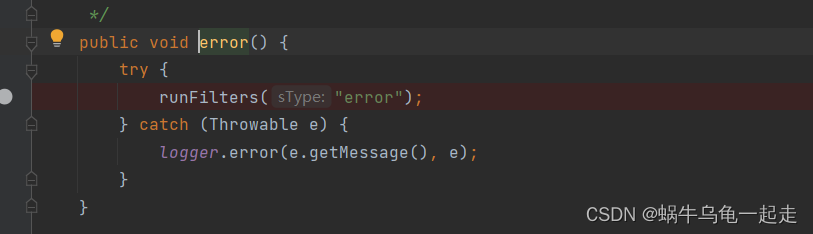
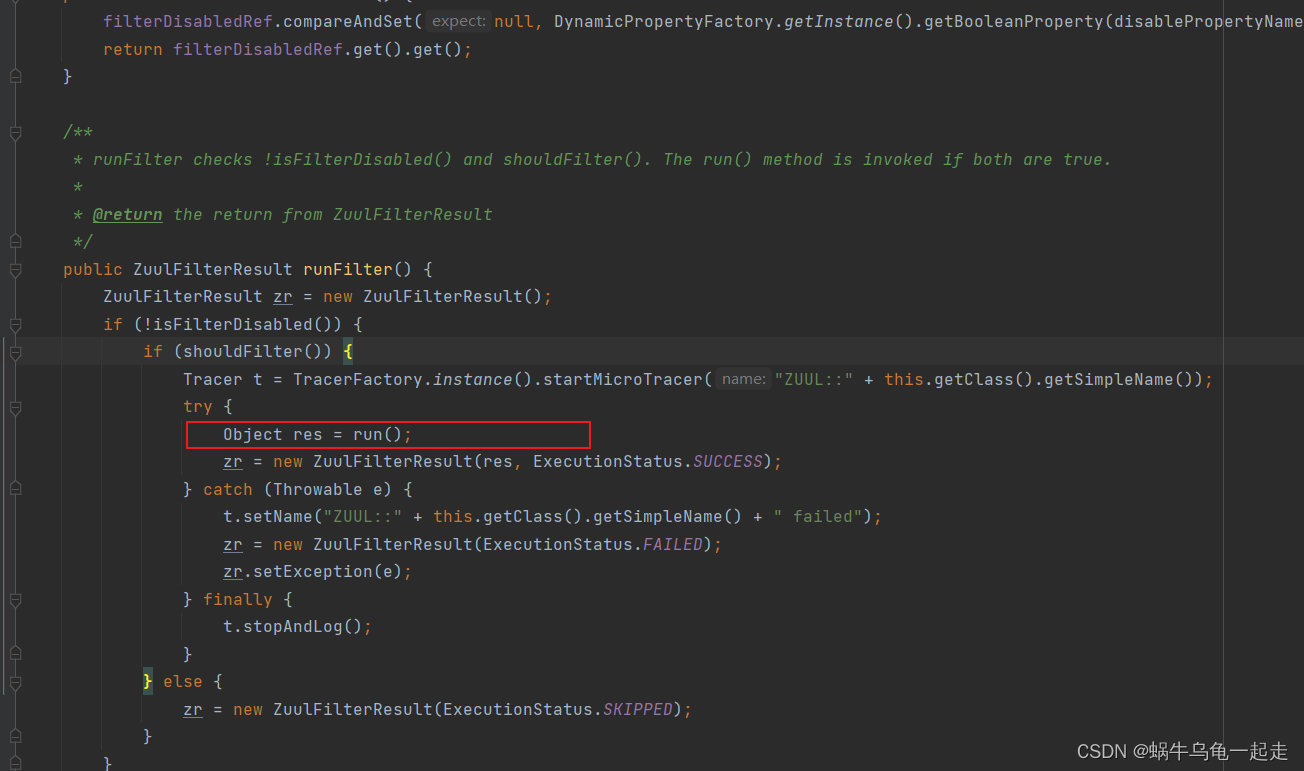
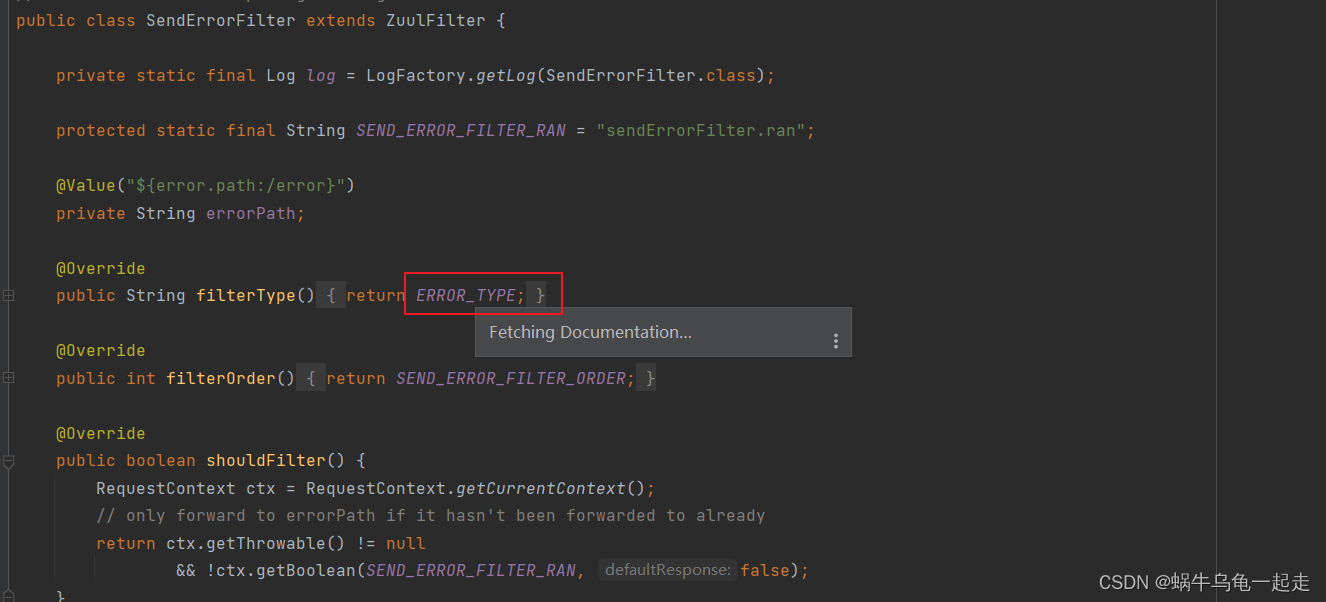
核心出现也就是SendErrorFilter-run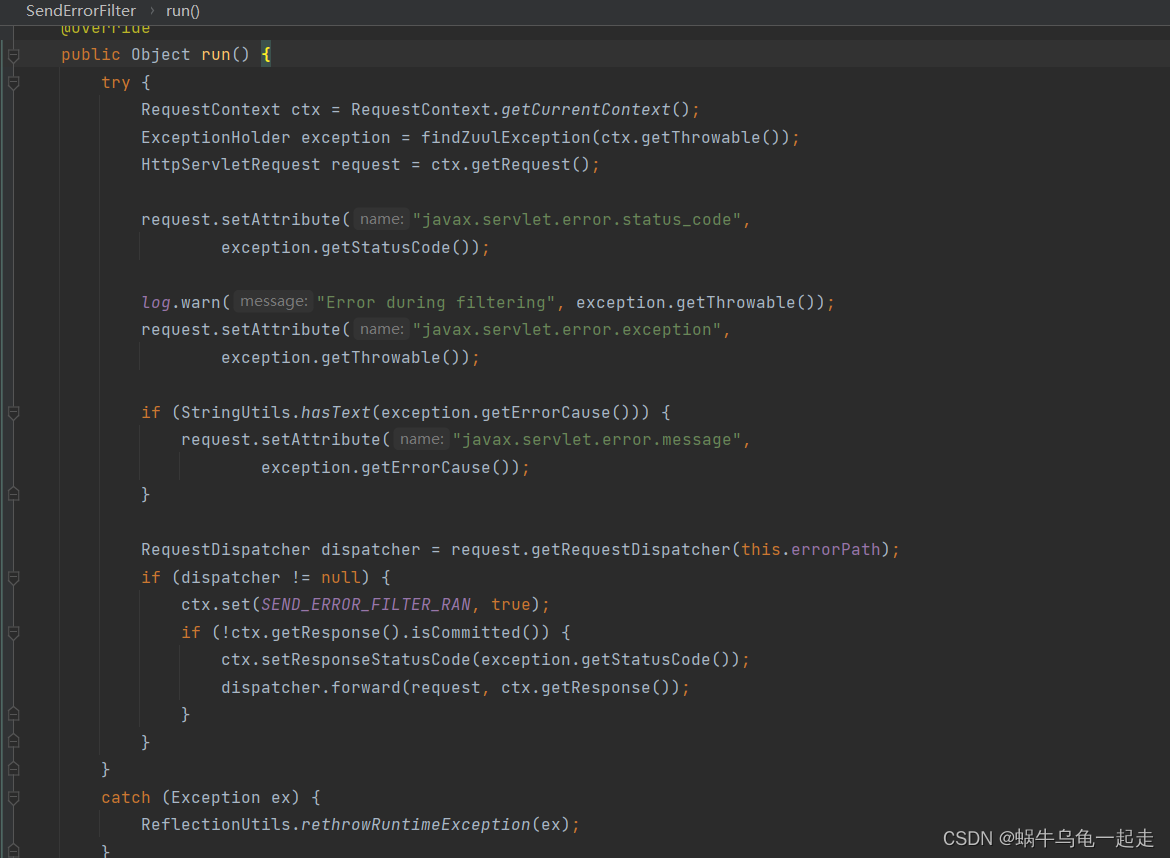
正常不抛异常的话SendResponseFilter 理论是最后一个filter 他会执行关闭操作
private void writeResponse() throws Exception {
RequestContext context = RequestContext.getCurrentContext();
// there is no body to send
if (context.getResponseBody() == null
&& context.getResponseDataStream() == null) {
return;
}
HttpServletResponse servletResponse = context.getResponse();
if (servletResponse.getCharacterEncoding() == null) { // only set if not set
servletResponse.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
}
String servletResponseContentEncoding = getResponseContentEncoding(context);
OutputStream outStream = servletResponse.getOutputStream();
InputStream is = null;
try {
if (context.getResponseBody() != null) {
String body = context.getResponseBody();
is = new ByteArrayInputStream(
body.getBytes(servletResponse.getCharacterEncoding()));
}
else {
is = context.getResponseDataStream();
if (is != null && context.getResponseGZipped()) {
// if origin response is gzipped, and client has not requested gzip,
// decompress stream before sending to client
// else, stream gzip directly to client
if (isGzipRequested(context)) {
servletResponseContentEncoding = "gzip";
}
else {
servletResponseContentEncoding = null;
is = handleGzipStream(is);
}
}
}
if (servletResponseContentEncoding != null) {
servletResponse.setHeader(ZuulHeaders.CONTENT_ENCODING,
servletResponseContentEncoding);
}
if (is != null) {
writeResponse(is, outStream);
}
}
finally {
/**
* We must ensure that the InputStream provided by our upstream pooling
* mechanism is ALWAYS closed even in the case of wrapped streams, which are
* supplied by pooled sources such as Apache's
* PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager. In that particular case, the underlying
* HTTP connection will be returned back to the connection pool iif either
* close() is explicitly called, a read error occurs, or the end of the
* underlying stream is reached. If, however a write error occurs, we will end
* up leaking a connection from the pool without an explicit close()
*
* @author Johannes Edmeier
*/
if (is != null) {
try {
//关闭流 同时org.apache.http.conn.EofSensorInputStream 也会清除http 连接
is.close();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
log.warn("Error while closing upstream input stream", ex);
}
}
// cleanup ThreadLocal when we are all done
if (buffers != null) {
buffers.remove();
}
try {
Object zuulResponse = context.get("zuulResponse");
if (zuulResponse instanceof Closeable) {
((Closeable) zuulResponse).close();
}
outStream.flush();
// The container will close the stream for us
}
catch (IOException ex) {
log.warn("Error while sending response to client: " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
EofSensorInputStream 关闭同时也会归还http连接。
通过上面代码分析,压测的时候发生异常,所以代码执行都会去SendErrorFilter run 方法 他会转发
dispatcher.forward(request, ctx.getResponse());
这个又会重新执行到ZuulServlet 中service 再次请求到之前的微服务接口。因此我们压测那个场景出现阻塞的原因就是:当并发线程高于配置资源后 rabbion http 连接池么有可用连接了,拿不到连接也没有熔断降级配置,抛异常最后执行到SendErrorFilter 这里没有对
public InputStream getResponseDataStream() {
return (InputStream) get("responseDataStream");
}
执行关闭。导致了连接泄露线程阻塞了,从而页面卡死。
不同情况具体分析
- 异常发生在route 阶段
像我们那个场景就是这个阶段,由于线程不够,在获取连接抛出异常,第一次执行到SendErrorFilter 由于没有请求成功 所以getResponseDataStream 是null ,但是由于上面说了会转发会继续走一次ZuulServlet service 这个时候假如有连接释放请求成功后 会对responseDataStream 进行设置赋值 代码如下
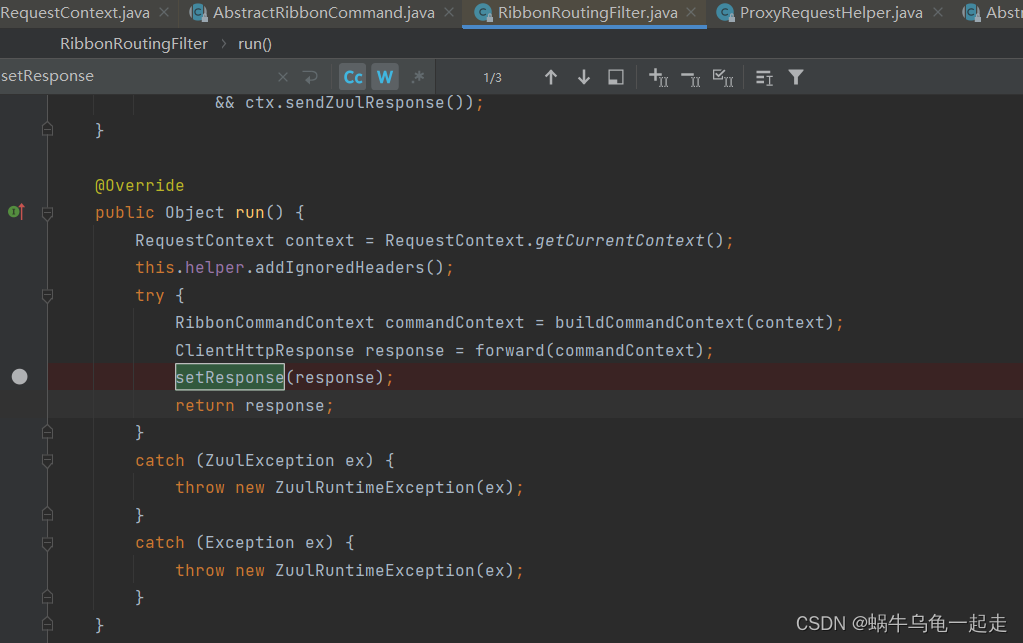
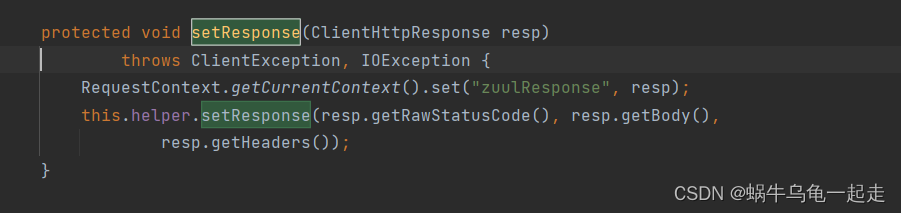
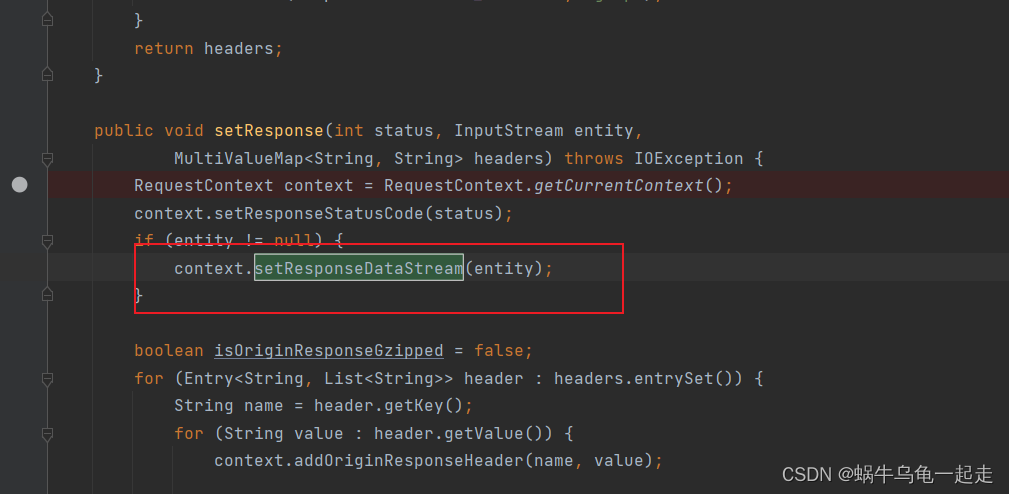
再次回到SendErrorFilter 的时候 getResponseDataStream 就会有值 这个时候没有对他进行关闭,造成连接泄露。 - 异常发生在post 阶段
这个阶段发生异常基本getResponseDataStream 已经有值了,所以说只要你自己定义的post 类型的filter 有异常抛出来没有处理必然发生连接泄露,因为他最后还是执行到SendErrorFilter 。
解决方案
第一步增加熔断降级
@Slf4j
public class CustomFallbackProvider implements FallbackProvider {
@Override
public String getRoute() {
return "*";
}
@Override
public ClientHttpResponse fallbackResponse(String route, Throwable cause) {
return new ClientHttpResponse() {
/**
*ClientHttpResponse的fallback的状态码,返回的是HttpStatus
* @return
*/
@Override
public HttpStatus getStatusCode() throws IOException {
return HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
}
/**
*ClientHttpResponse的fallback的状态码,返回的是int
* @return
*/
@Override
public int getRawStatusCode() throws IOException {
return this.getStatusCode().value();
}
/**
*ClientHttpResponse的fallback的状态码,返回的是String
* @return
*/
@Override
public String getStatusText() throws IOException {
return this.getStatusCode().getReasonPhrase();
}
@Override
public void close() {
}
/**
*设置响应体信息
* @return
*/
@Override
public InputStream getBody() {
String content = "网络异常,请稍后重试!";
return new ByteArrayInputStream(content.getBytes());
}
/**
*设置响应的头信息
* @return
*/
@Override
public HttpHeaders getHeaders() {
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
MediaType mediaType = new MediaType("application", "json", Charset.forName("utf-8"));
headers.setContentType(mediaType);
return headers;
}
};
}
}
为啥增加降级会减少(是大大降低但是不是完全解决)线程阻塞问题?通过代码分析
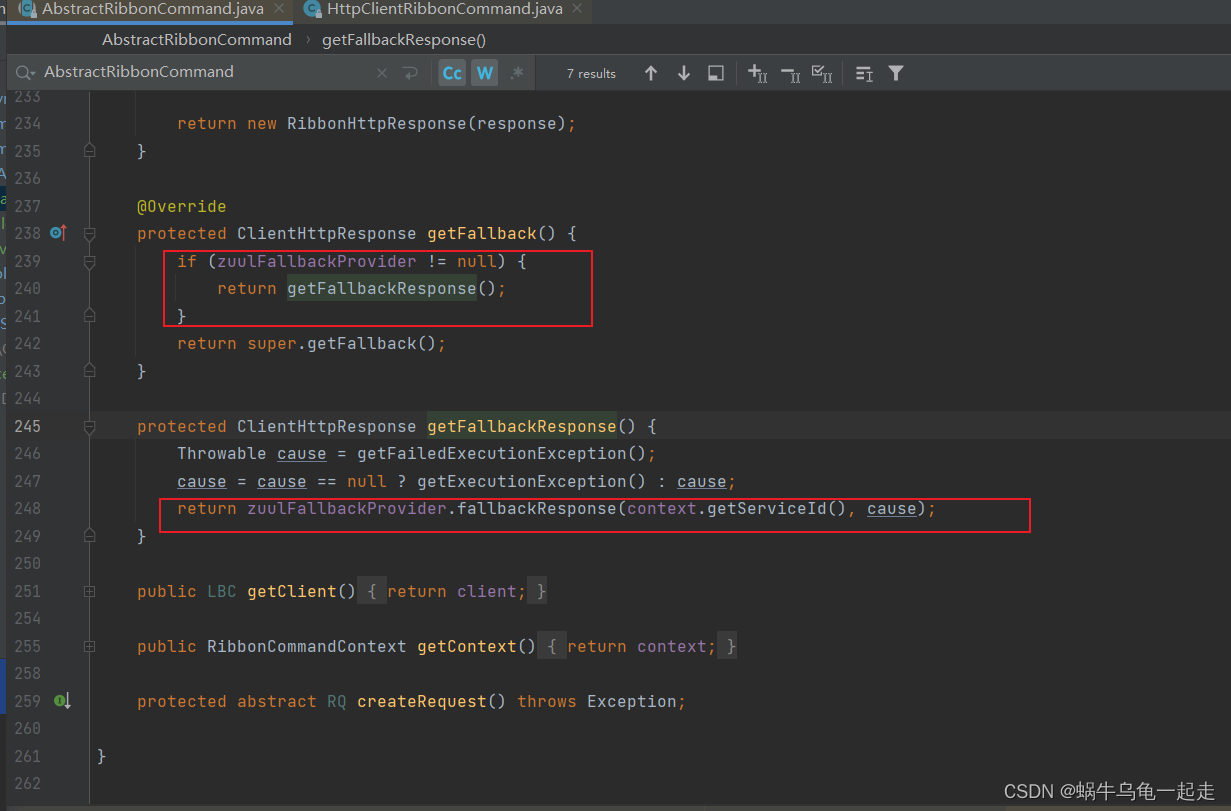
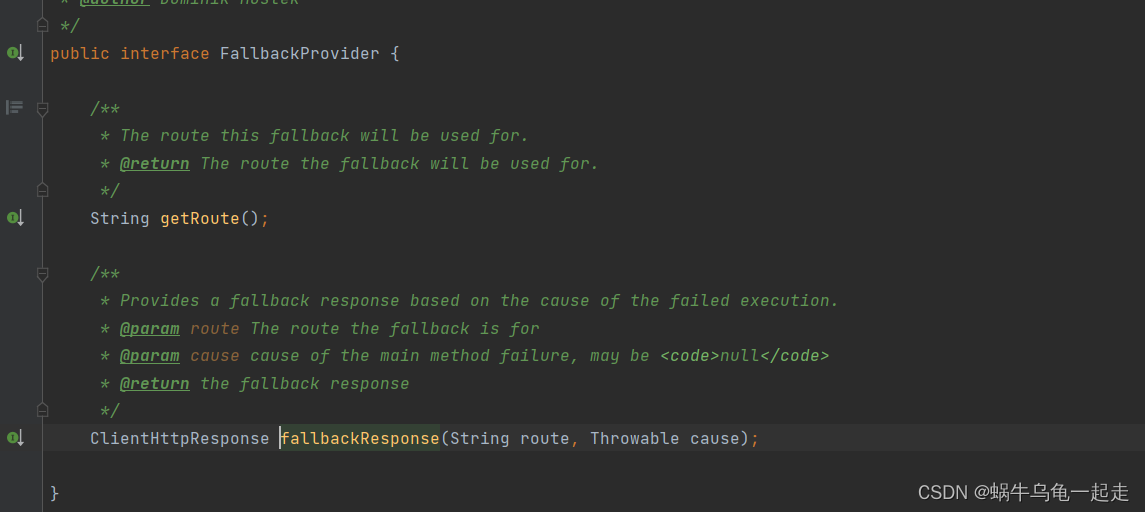
我们有自定义的FallbackProvider 返回ClientHttpResponse 这样不会执行到SendErrorFilter 最后走的还是SendResponseFilter run 方法中关闭流归还连接。
重新写SendErrorFilter
继承ZuulFilter 设置Error 类型 Order 设置-1 保证有异常不去执行SendErrorFilter (context.remove(“throwable”); 之后shouldFilter 返回false 也就不会执行了) 核心代码如下:
@Slf4j
@Component
public class ErrorFilter extends ZuulFilter {
@Override
public String filterType() {
return ERROR_TYPE;
}
@Override
public int filterOrder() {
return -1;
}
protected static final String SEND_ERROR_FILTER_RAN = "sendErrorFilter.ran";
@Override
public boolean shouldFilter() {
RequestContext ctx = RequestContext.getCurrentContext();
return ctx.getThrowable() != null && !ctx.getBoolean(SEND_ERROR_FILTER_RAN, false);
}
@Override
public Object run() {
RequestContext context = RequestContext.getCurrentContext();
PrintWriter writer = null;
InputStream is = null;
try {
context.remove("throwable");
context.set(SEND_ERROR_FILTER_RAN, true);
ZuulException exception = findZuulException(context.getThrowable());
HttpServletResponse response = context.getResponse();
response.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf8");
response.setStatus(exception.nStatusCode);
is = context.getResponseDataStream();
writer = response.getWriter();
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("code", exception.nStatusCode);
map.put("msg", exception.errorCause);
map.put("detail", exception.getMessage());
String retStr = JSON.toJSONString(map);
writer.print(retStr);
writer.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(e.getMessage());
} finally {
if (is != null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (writer != null) {
writer.close();
}
}
return null;
}
protected ZuulException findZuulException(Throwable throwable) {
if (Objects.isNull(throwable)) {
return null;
}
if (throwable.getCause() instanceof ZuulRuntimeException) {
Throwable cause = null;
if (throwable.getCause().getCause() != null) {
cause = throwable.getCause().getCause().getCause();
}
if (cause instanceof ClientException && cause.getCause() != null
&& cause.getCause().getCause() instanceof SocketTimeoutException) {
ZuulException zuulException = new ZuulException("", 504,
ZuulException.class.getName() + ": Hystrix Readed time out");
return zuulException;
}
if (throwable.getCause().getCause() instanceof ZuulException) {
return (ZuulException) throwable.getCause().getCause();
}
}
if (throwable.getCause() instanceof ZuulException) {
return (ZuulException) throwable.getCause();
}
if (throwable instanceof ZuulException) {
return (ZuulException) throwable;
}
return new ZuulException(throwable, HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(), null);
}
}
总结
目前熔断和重新写Error filter 基本可以保证高并发下不发生连接泄露,但是要是性能追求更高 可以使用Nocos、Zuul2.x 等基于Netty 的网关框架。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!