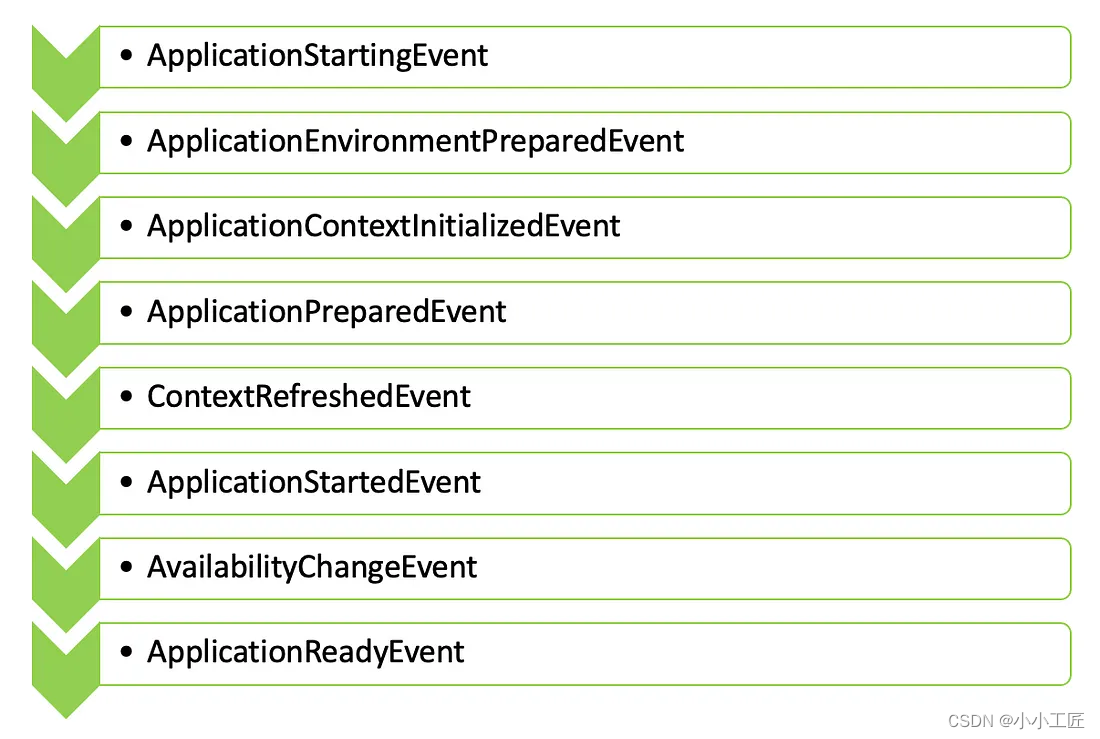
Spring Boot - Application Events 的发布顺序_ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent
Pre
Spring Boot - Application Events 的发布顺序_ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent
概述
Spring Boot 的广播机制是基于观察者模式实现的,它允许在 Spring 应用程序中发布和监听事件。这种机制的主要目的是为了实现解耦,使得应用程序中的不同组件可以独立地改变和复用逻辑,而无需直接进行通信。
在 Spring Boot 中,事件发布和监听的机制是通过 ApplicationEvent、ApplicationListener 以及事件发布者(ApplicationEventPublisher)来实现的。其中,ApplicationEvent 是所有自定义事件的基础,自定义事件需要继承自它。
ApplicationListener 是监听特定事件并做出响应的接口,开发者可以通过实现该接口来定义自己的监听器。事件发布者(通常由 Spring 的 ApplicationContext 担任)负责发布事件。
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件在Spring Boot应用程序中非常有用。当应用程序环境准备就绪时,可以使用此事件来执行一些初始化操作,例如设置系统属性、加载配置文件、动态修改环境等。
通过监听ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件,我们可以在Spring Boot应用程序启动之前对环境进行一些自定义的配置和修改,以满足特定的需求。例如,可以在此事件中动态加载不同的配置文件,根据环境变量设置不同的系统属性,或者执行其他与环境相关的初始化操作
Code
package com.artisan.event;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment;
import org.springframework.core.env.MapPropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.PropertiesPropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* @author 小工匠
* @version 1.0
* @mark: show me the code , change the world
*/
public class ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent> {
/**
* ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent 在应用程序环境准备时触发,此时应用程序上下文尚未初始化。
* <p>
* 通过侦听此事件,我们可以访问环境的属性、配置文件和配置源。
* 然后,我们可以执行一些任务,例如修改属性值、添加或删除配置源、激活特定配置文件或根据环境状态应用自定义逻辑。
* <p>
* <p>
* 为了处理事件 ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent ,我们可以通过实现 ApplicationListener ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent 作为泛型类型的接口来创建自定义事件侦听器。
* 此侦听器可以在主应用程序类中手动注册
*
* @param event the event to respond to
*/
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
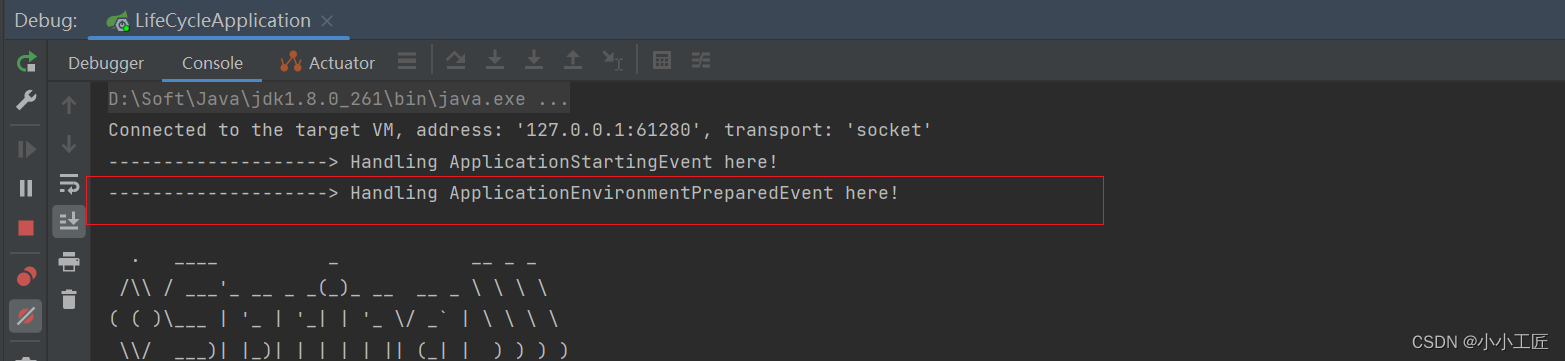
System.out.println("--------------------> Handling ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent here!");
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = event.getEnvironment();
// 添加自定义属性创建一个Map对象
Map<String, Object> propertiesMap = new HashMap<>();
propertiesMap.put("myDynamicProperty", "myValue");
// 将Map转换为Properties
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.putAll(propertiesMap);
// 创建一个PropertiesPropertySource
PropertySource<?> propertySource = new PropertiesPropertySource("dynamicProperties", properties);
// 将PropertiesPropertySource添加到环境属性源中
environment.getPropertySources().addFirst(propertySource);
SpringApplication springApplication = event.getSpringApplication();
springApplication.setDefaultProperties(properties);
}
}
如何使用呢?
方式一:
@SpringBootApplication
public class LifeCycleApplication {
/**
* 除了手工add , 在 META-INF下面 的 spring.factories 里增加
* org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=自定义的listener 也可以
*
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication springApplication = new SpringApplication(LifeCycleApplication.class);
// 当我们运行 Spring Boot 应用程序时,将调用 的方法 ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedListener#onApplicationEvent() 允许我们根据需要访问和修改应用程序的环境
springApplication.addListeners(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedListener());
springApplication.run(args);
}
}
方式二: 通过spring.factories 配置
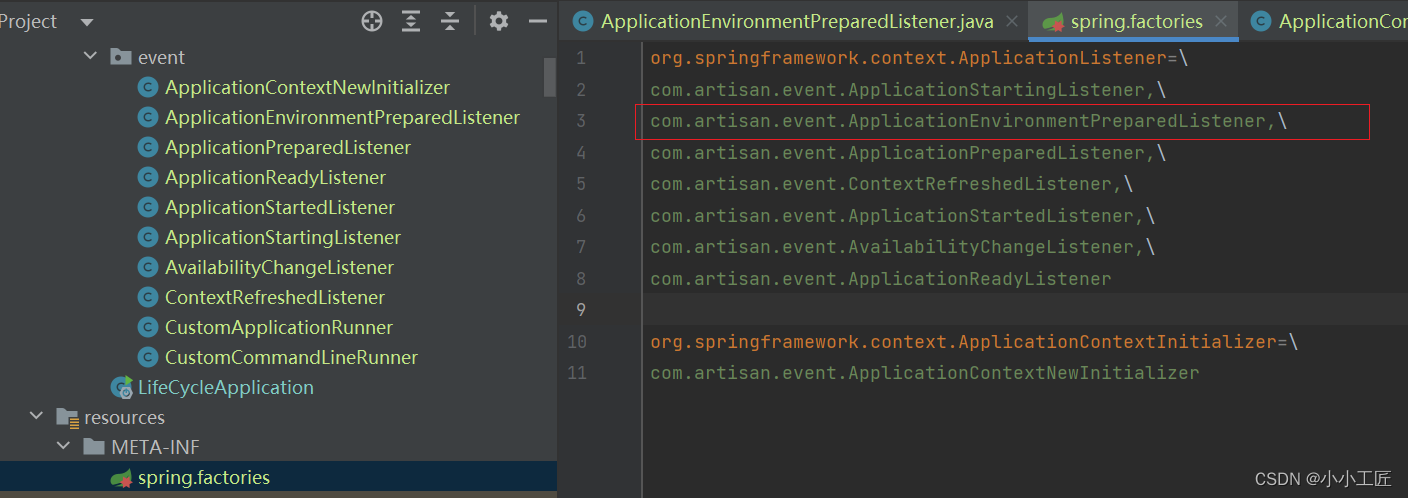
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
com.artisan.event.ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedListener
运行日志
源码分析
首先main方法启动入口
SpringApplication.run(LifeCycleApplication.class, args);
跟进去
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
继续
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
这里首先关注 new SpringApplication(primarySources)
new SpringApplication(primarySources)
/**
* Create a new {@link SpringApplication} instance. The application context will load
* beans from the specified primary sources (see {@link SpringApplication class-level}
* documentation for details. The instance can be customized before calling
* {@link #run(String...)}.
* @param resourceLoader the resource loader to use
* @param primarySources the primary bean sources
* @see #run(Class, String[])
* @see #setSources(Set)
*/
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
this.bootstrappers = new ArrayList<>(getSpringFactoriesInstances(Bootstrapper.class));
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
聚焦 setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
run
继续run
// 开始启动Spring应用程序
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); // 创建一个计时器
stopWatch.start(); // 开始计时
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext(); // 创建引导上下文
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; // Spring应用上下文,初始化为null
configureHeadlessProperty(); // 配置无头属性(如:是否在浏览器中运行)
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); // 获取运行监听器
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass); // 通知监听器启动过程开始
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args); // 创建应用参数
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments); // 预备环境
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment); // 配置忽略BeanInfo
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment); // 打印Banner
context = createApplicationContext(); // 创建应用上下文
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup); // 设置应用启动状态
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); // 准备上下文
refreshContext(context); // 刷新上下文,执行Bean的生命周期
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); // 刷新后的操作
stopWatch.stop(); // 停止计时
if (this.logStartupInfo) { // 如果需要记录启动信息
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); // 记录启动信息
}
listeners.started(context); // 通知监听器启动完成
callRunners(context, applicationArguments); // 调用Runner
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners); // 处理运行失败
throw new IllegalStateException(ex); // 抛出异常
}
try {
listeners.running(context); // 通知监听器运行中
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null); // 处理运行失败
throw new IllegalStateException(ex); // 抛出异常
}
return context; // 返回应用上下文
}
我们重点看
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
继续
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// 获取或创建环境对象
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 使用应用程序参数配置环境
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
// 将配置属性源附加到环境中
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 通知监听器环境已经准备好
listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
// 将默认属性属性源移动到环境的末尾
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment);
// 配置额外的配置文件
configureAdditionalProfiles(environment);
// 将环境绑定到Spring应用程序
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
// 如果不是自定义环境,则转换环境
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
// 再次将配置属性源附加到环境,确保所有属性源都被正确加载
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 返回配置好的环境对象
return environment;
}
重点关注: listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
doWithListeners("spring.boot.application.environment-prepared",
(listener) -> listener.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment));
}
继续 listener.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment)
发布事件
@Override
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(
new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(bootstrapContext, this.application, this.args, environment));
}
继续
@Override
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
multicastEvent(event, resolveDefaultEventType(event));
}
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
// 如果eventType不为null,则直接使用它;否则,使用resolveDefaultEventType方法来解析事件的默认类型。
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
// 获取一个线程池执行器,它用于异步执行监听器调用。
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
// 获取所有对应该事件类型的监听器。
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
// 如果执行器不为null,则使用它来异步执行监听器调用;
// 否则,直接同步调用监听器。
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
继续
private void doInvokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
try {
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
catch (ClassCastException ex) {
......
}
}
就到了我们自定义实现的代码逻辑中了。
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
System.out.println("--------------------> Handling ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent here!");
.....
.....
}

本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- NOIP2009提高组T4:靶形数独
- 输电线路定位:精确导航,确保电力传输安全
- Parasoft C++Test安装指南_含独立版和插件版
- Mysql事务的处理
- 【数据分享】2019-2023年我国区县逐年二手房房价数据(Excel/Shp格式)
- 【华为OD】统一考试C卷真题 100%通过: 传递悄悄话 二叉树遍历 C语言源码实现【思路+源码】
- BLHeli_S 代码分析—BLHeli.asm函数lock_byte_ok分析
- 3、非数值型的分类变量
- springboot代码混淆及反混淆代码工具
- 【COMP9319】Web Data Compresssion and Search