python超详细基础文件操作【建议收藏】
文章目录
- 前言
- 发现宝藏
- 1 文件操作
-
- 1.1 文件打开与关闭
-
- 1.1.1 打开文件
- 1.1.2 关闭文件
- 1.2 访问模式及说明
- 2 文件读写
-
- 2.1 写数据(write)
- 2.2 读数据(read)
- 2.3 读数据(readlines)
- 2.3 读数据(readline)
- 2.4 readlines 和 readline的区别
- 3 文件的相关操作
-
- 3.1 文件重命名
- 3.2 删除文件
- 3.3 创建文件
- 3.4 获取当前目录
- 4 示例
-
- 4.1 目录.txt自动清洗
- 4.2 批量修改文件夹下的文件命名
- 4.3 检测同级目录下是否存在同名文件夹
- 总结
前言
为了巩固所学的知识,作者尝试着开始发布一些学习笔记类的博客,方便日后回顾。当然,如果能帮到一些萌新进行新技术的学习那也是极好的。作者菜菜一枚,文章中如果有记录错误,欢迎读者朋友们批评指正。
(博客的参考源码可以在我主页的资源里找到,如果在学习的过程中有什么疑问欢迎大家在评论区向我提出)
发现宝藏
前些天发现了一个巨牛的人工智能学习网站,通俗易懂,风趣幽默,忍不住分享一下给大家。【宝藏入口】。
1 文件操作
1.1 文件打开与关闭
1.1.1 打开文件
在Python中,你可以使用 open() 函数来打开文件。以下是一个简单的例子:
# 打开文件(默认为只读模式)
file_path = 'example.txt'
with open(file_path, 'r') as file:
# 执行文件操作,例如读取文件内容
file_content = file.read()
print(file_content)
# 文件在with块结束后会自动关闭,无需显式关闭文件
在上述示例中:
'example.txt'是文件的路径和名称,你可以根据实际情况修改为你想要打开的文件。'r'表示只读模式。如果你想要写入文件,可以使用'w'模式,如果想要追加内容,可以使用'a'模式等。with open(...) as file: 是使用上下文管理器的方式,确保文件在使用后被正确关闭,即使在处理文件时发生异常也能保证关闭。
1.1.2 关闭文件
在 Python 中关闭文件有两种主要的方法:
1. 使用 with 语句:
with 语句是一种上下文管理器,当它的代码块执行完毕时,会自动关闭文件。这是推荐的方式,因为它确保文件在使用完毕后被正确关闭,即使发生异常也能保证关闭。
file_path = 'example.txt'
with open(file_path, 'r') as file:
# 执行文件操作,例如读取文件内容
file_content = file.read()
print(file_content)
# 文件在这里已经被自动关闭
2. 使用 close() 方法:
你可以显式调用文件对象的 close() 方法来关闭文件。这种方法适用于一些特殊情况,但相对来说不如 with 语句简洁和安全。
file_path = 'example.txt'
file = open(file_path, 'r')
try:
# 执行文件操作,例如读取文件内容
file_content = file.read()
print(file_content)
finally:
file.close()
在使用 with 语句时,不需要显式调用 close() 方法。如果你在代码中打开了文件而没有使用 with,请确保在适当的地方调用 close() 以关闭文件,以避免资源泄漏。
1.2 访问模式及说明
| 访问模式 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| r | 以只读方式打开文件。文件的指针将会放在文件的开头。这是默认模式。 |
| w | 打开一个文件只用于写入。如果该文件已存在则将其覆盖。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件。 |
| a | 打开一个文件用于追加。如果该文件已存在,文件指针将会放在文件的结尾。也就是说,新的内容将会被写入到已有内容之后。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件进行写入。 |
| rb | 以二进制格式打开一个文件用于只读。文件指针将会放在文件的开头。这是默认模式。 |
| wb | 以二进制格式打开一个文件只用于写入。如果该文件已存在则将其覆盖。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件。 |
| ab | 以二进制格式打开一个文件用于追加。如果该文件已存在,文件指针将会放在文件的结尾。也就是说,新的内容将会被写入到已有内容之后。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件进行写入。 |
| r+ | 打开一个文件用于读写。文件指针将会放在文件的开头。 |
| w+ | 打开一个文件用于读写。如果该文件已存在则将其覆盖。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件。 |
| a+ | 打开一个文件用于读写,如果该文件已存在,文件指针将会放在文件的结尾。文件打开时会是追加模式。如果改文件不存在,创建新文件用于读写。 |
| rb+ | 以二进制格式打开一个文件用于读写。文件指针将会放在文件的开头 |
| wb+ | 以二进制格式打开一个文件用于读写。如果改文件已存在则会覆盖。如果改文件不存在,创建新文件。 |
| ab+ | 以二进制格式打开一个文件用于追加。如果该文件已存在,文件指针将会放在文件的结尾。如果改文件不存在,创建新文件用于读写。 |
2 文件读写
2.1 写数据(write)
写入数据通常涉及将信息保存到文件、数据库或其他持久性存储介质中。以下是一些常见的数据写入场景的示例:
1. 写入文本文件
使用内置的 open 函数来打开文件并写入内容。确保使用适当的模式(例如,'w' 表示写入)。
file_path = 'example.txt'
# 写入文件
with open(file_path, 'w') as file:
file.write("Hello, this is some data.")
2. 写入CSV文件
使用 csv 模块来写入CSV格式的文件。
import csv
csv_file_path = 'example.csv'
data = [['Name', 'Age', 'Occupation'],
['John Doe', 30, 'Engineer'],
['Jane Smith', 25, 'Designer']]
with open(csv_file_path, 'w', newline='') as csvfile:
csv_writer = csv.writer(csvfile)
csv_writer.writerows(data)
3. 写入JSON文件
使用内置的 json 模块来写入JSON格式的文件。
import json
json_file_path = 'example.json'
data = {"name": "John Doe", "age": 30, "occupation": "Engineer"}
with open(json_file_path, 'w') as jsonfile:
json.dump(data, jsonfile)
4. 写入数据库
使用数据库连接库(如 sqlite3、mysql-connector-python 等)与相应的数据库进行交互。
import sqlite3
# 连接到SQLite数据库(假设有一个名为 example.db 的数据库)
conn = sqlite3.connect('example.db')
# 创建一个游标对象
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 执行SQL插入语句
cursor.execute("INSERT INTO users (name, age, occupation) VALUES (?, ?, ?)", ('John Doe', 30, 'Engineer'))
# 提交更改
conn.commit()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
2.2 读数据(read)
读取数据通常涉及从文件、数据库或其他存储介质中检索信息。以下是一些读取数据的常见示例:
1. 读取文本文件
使用内置的 open 函数来打开文件并读取内容。
file_path = 'example.txt'
# 读取文件
with open(file_path, 'r') as file:
data = file.read()
print(data)
2. 读取CSV文件
使用 csv 模块来读取CSV格式的文件。
import csv
csv_file_path = 'example.csv'
# 读取CSV文件
with open(csv_file_path, 'r') as csvfile:
csv_reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
for row in csv_reader:
print(row)
3. 读取JSON文件
使用内置的 json 模块来读取JSON格式的文件。
import json
json_file_path = 'example.json'
# 读取JSON文件
with open(json_file_path, 'r') as jsonfile:
data = json.load(jsonfile)
print(data)
4. 从数据库中读取数据
使用数据库连接库(如 sqlite3、mysql-connector-python 等)与相应的数据库进行交互。
import sqlite3
# 连接到SQLite数据库(假设有一个名为 example.db 的数据库)
conn = sqlite3.connect('example.db')
# 创建一个游标对象
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 执行SQL查询语句
cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM users")
# 检索所有行
rows = cursor.fetchall()
# 打印每一行
for row in rows:
print(row)
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
2.3 读数据(readlines)
readlines 是 Python 中用于读取文件的方法之一,它用于逐行读取文件内容,并将每一行作为字符串存储在一个列表中。下面是对 readlines 方法的详细解释:
使用 readlines 方法的基本语法
with open('file.txt', 'r') as file:
lines = file.readlines()
解释:
open('file.txt', 'r'): 打开文件'file.txt'以供读取。第一个参数是文件名,第二个参数是打开文件的模式。'r'表示只读模式。with ... as ...: 使用with语句可以确保在读取完成后自动关闭文件,不需要显式调用file.close()。lines = file.readlines():readlines方法用于读取文件的所有行,并将每一行作为一个字符串存储在列表lines中。- 每个列表元素对应文件中的一行文本。你可以使用列表索引来访问特定行,例如
lines[0]表示文件的第一行。
例子:假设 ‘file.txt’ 包含以下内容:
Hello, this is line 1.
This is line 2.
And this is line 3.
使用 readlines 后:
with open('file.txt', 'r') as file:
lines = file.readlines()
# lines 现在是一个包含每一行文本的列表
print(lines)
# 输出:
# ['Hello, this is line 1.\n', 'This is line 2.\n', 'And this is line 3.\n']
# 访问特定行
print(lines[0].strip()) # 输出:Hello, this is line 1.
注意事项:
- 每一行的末尾都包含换行符
\n,你可以使用strip()方法去除这些额外的空白字符。 readlines方法适用于处理包含多行文本的文件,但对于大型文件,可能需要考虑逐行读取而不是将整个文件加载到内存中。这可以通过循环遍历文件对象来实现,而不是使用readlines。
2.3 读数据(readline)
readline 是 Python 中用于读取文件的方法之一,它用于逐行读取文件内容,并返回文件中的一行作为字符串。以下是对 readline 方法的详细解释:
使用 readline 方法的基本语法
with open('file.txt', 'r') as file:
line = file.readline()
解释:
open('file.txt', 'r'): 打开文件'file.txt'以供读取。第一个参数是文件名,第二个参数是打开文件的模式。'r'表示只读模式。with ... as ...: 使用with语句可以确保在读取完成后自动关闭文件,不需要显式调用file.close()。line = file.readline():readline方法用于读取文件的一行,并将该行作为一个字符串存储在变量line中。
例子:假设 ‘file.txt’ 包含以下内容:
Hello, this is line 1.
This is line 2.
And this is line 3.
使用 readline 后:
with open('file.txt', 'r') as file:
line1 = file.readline()
line2 = file.readline()
line3 = file.readline()
print(line1) # 输出:Hello, this is line 1.
print(line2) # 输出:This is line 2.
print(line3) # 输出:And this is line 3.
注意事项:
- 每个
readline调用都会读取文件的下一行。 - 返回的字符串包含行末尾的换行符
\n。如果不需要换行符,可以使用strip()方法去除它。 - 当文件读取完毕后,
readline将返回空字符串 ‘’,因此可以在循环中使用while line != ''来逐行读取整个文件。
循环读取整个文件:
with open('file.txt', 'r') as file:
line = file.readline()
while line != '':
print(line.strip()) # 去除换行符
line = file.readline()
这个循环将逐行读取整个文件,直到文件末尾。
2.4 readlines 和 readline的区别
readlines 和 readline 是 Python 中用于读取文件的两种不同方法,它们之间有一些重要的区别:
1. readlines 方法:
- 返回类型:
readlines方法返回一个包含文件所有行的列表,其中每个元素都是文件中的一行文本字符串。 - 使用情况: 适用于处理包含多行文本的文件,可以一次性将整个文件加载到内存中。这种方法适用于文件较小,可以完全装入内存的情况。
- 例子:
with open('file.txt', 'r') as file:
lines = file.readlines()
2. readline 方法:
- 返回类型:
readline方法每次调用只返回文件中的一行作为字符串。如果再次调用,将返回下一行。当文件读取完毕后,返回空字符串 ‘’。 - 使用情况: 适用于逐行处理大型文件,可以有效地降低内存使用。因为它一次只读取一行,可以在循环中逐行处理文件,而不必将整个文件加载到内存中。
- 例子:
with open('file.txt', 'r') as file:
line = file.readline()
while line != '':
print(line.strip()) # 去除换行符
line = file.readline()
3. 区别总结:
readlines一次性读取整个文件的所有行,并返回一个包含所有行的列表。readline逐行读取文件,每次调用返回文件中的一行,适用于处理大型文件,减少内存占用。readlines返回包含换行符的每一行,而readline返回单独的行,需要手动去除换行符。
选择使用哪个方法取决于文件的大小和处理需求。如果文件较小,可以完全装入内存,使用 readlines;如果文件较大,可以逐行处理,使用 readline。
3 文件的相关操作
3.1 文件重命名
Python 文件重命名是文件管理中的一个基本操作,可以通过 Python 的内置库来实现。以下是一个超详细的入门指南,介绍如何使用 Python 重命名文件:
1. 导入必要的库
首先,您需要导入 Python 的 os 库,它提供了许多与操作系统交互的函数。
import os
2. 准备文件列表
要重命名文件,您需要先列出指定目录中的所有文件。可以使用 os.listdir() 函数来获取目录中的文件列表。
# 列出指定目录中的所有文件和文件夹
files = os.listdir('path_to_directory')
3. 遍历文件列表
接着,您需要遍历文件列表,对每一个文件进行重命名。
for file in files:
# 获取文件的完整路径
full_path = os.path.join('path_to_directory', file)
# 检查是否是文件
if os.path.isfile(full_path):
# 新的文件名
new_filename = 'new_name'
# 重命名操作
os.rename(full_path, os.path.join('path_to_directory', new_filename))
print(f'Renamed {file} to {new_filename}')
4. 异常处理
在重命名文件时,可能会出现各种异常,例如目标文件已存在、没有足够权限等。为了确保程序的健壮性,应该添加异常处理。
try:
for file in files:
# ...(上面的代码)
except OSError as e:
print(f'Error occurred: {e}')
5. 完整的脚本示例
import os
# 指定要重命名文件的目录
directory = 'path_to_directory'
# 列出目录中的所有文件
files = os.listdir(directory)
# 遍历文件列表并进行重命名
for file in files:
if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(directory, file)):
# 设定新的文件名
new_filename = 'new_name'
# 重命名文件
try:
os.rename(
os.path.join(directory, file),
os.path.join(directory, new_filename)
)
print(f'Renamed {file} to {new_filename}')
except OSError as e:
print(f'Error renaming {file}: {e}')
6. 注意安全性和效率
在批量重命名文件时,应确保:
- 不要同时进行多个重命名操作,以避免潜在的竞争条件。
- 确保目标目录存在,避免在重命名时创建不存在的目录。
- 考虑到操作系统对文件重命名的限制,例如在 Windows 中,文件名不能超过 255 个字符,而在 Unix/Linux 中则没有这个限制。
7. 高级用法
对于更复杂的重命名任务,您可以使用正则表达式或者其他文本处理方法来生成新的文件名。
import os
import re
# 指定目录
directory = 'path_to_directory'
# 列出目录中的所有文件
files = os.listdir(directory)
# 遍历文件列表并进行重命名
for file in files:
if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(directory, file)):
# 使用正则表达式匹配文件名模式,并替换为新的模式
new_filename = re.sub(r'\d+', 'new_prefix', file)
# 重命名文件
try:
os.rename(
os.path.join(directory, file),
os.path.join(directory, new_filename)
)
print(f'Renamed {file} to {new_filename}')
except OSError as e:
print(f'Error renaming {file}: {e}')
这个脚本会将指定目录中所有以数字开头的文件重命名为新的前缀。
3.2 删除文件
在Python中,删除文件是一个相对简单的操作。我们可以使用os库中的os.remove()函数来实现。以下是一个超详细的入门指南,介绍如何使用Python删除文件:
1. 导入必要的库
首先,您需要导入Python的 os 库,它提供了许多与操作系统交互的函数。
import os
2. 准备文件路径
要删除文件,您需要知道要删除的文件的路径。
file_path = 'path_to_file'
3. 检查文件是否存在
在删除文件之前,最好检查该文件是否存在,以避免错误。
if os.path.isfile(file_path):
print(f'File {file_path} exists, proceed to delete.')
else:
print(f'File {file_path} does not exist, skip deletion.')
- 执行删除操作
如果文件存在,您可以使用 os.remove() 函数来删除它。
try:
os.remove(file_path)
print(f'File {file_path} deleted successfully.')
except OSError as e:
print(f'Error occurred: {e}')
5. 完整的脚本示例
import os
# 指定要删除的文件的目录
file_path = 'path_to_file'
# 检查文件是否存在
if os.path.isfile(file_path):
print(f'File {file_path} exists, proceed to delete.')
else:
print(f'File {file_path} does not exist, skip deletion.')
# 执行删除操作
try:
os.remove(file_path)
print(f'File {file_path} deleted successfully.')
except OSError as e:
print(f'Error occurred: {e}')
6. 注意安全性和效率
在批量删除文件时,应确保:
- 不要同时进行多个删除操作,以避免潜在的竞争条件。
- 确保目标目录存在,避免在删除时创建不存在的目录。
- 考虑到操作系统对文件删除的操作限制,例如在 Windows 中,文件名不能超过 255 个字符,而在 Unix/Linux 中则没有这个限制。
通过以上步骤,您应该能够掌握如何使用Python删除文件。
3.3 创建文件
在Python中,创建文件是一个相对简单的操作。我们可以使用 os 库中的 os.open() 函数或者 with 语句来创建文件。以下是一个超详细的入门指南,介绍如何使用Python创建文件:
1. 导入必要的库
首先,您需要导入Python的 os 库,它提供了许多与操作系统交互的函数。
import os
2. 准备文件路径
要创建文件,您需要知道要创建的文件的路径。
file_path = 'path_to_file'
3. 检查文件路径是否存在
在创建文件之前,最好检查该文件路径是否存在,以避免覆盖其他文件。
if not os.path.exists(file_path):
print(f'File path {file_path} does not exist, proceed to create.')
else:
print(f'File path {file_path} already exists, skip creation.')
4. 执行创建操作
如果文件路径不存在,您可以使用 os.open() 函数来创建文件。
try:
with open(file_path, 'w') as f:
print(f'File {file_path} created successfully.')
except IOError as e:
print(f'Error occurred: {e}')
这里,我们使用 with 语句来确保文件在操作完成后会被正确关闭。'w' 参数表示以写入模式打开文件,如果文件不存在,会创建一个新文件。
5. 完整的脚本示例
import os
# 指定要创建的文件的目录
file_path = 'path_to_file'
# 检查文件路径是否存在
if not os.path.exists(file_path):
print(f'File path {file_path} does not exist, proceed to create.')
else:
print(f'File path {file_path} already exists, skip creation.')
# 执行创建操作
try:
with open(file_path, 'w') as f:
print(f'File {file_path} created successfully.')
except IOError as e:
print(f'Error occurred: {e}')
6. 注意安全性和效率
在创建文件时,应确保:
- 拥有创建文件的足够权限。
- 避免在内存不足的情况下创建大型文件。
通过以上步骤,您应该能够掌握如何使用Python创建文件。
3.4 获取当前目录
在Python中,我们可以使用 os 库中的 os.getcwd() 函数来获取当前目录的路径。以下是一个示例:
import os
current_directory = os.getcwd()
print(f'Current directory is: {current_directory}')
这将会打印出当前Python脚本所在目录的路径。
4 示例
4.1 目录.txt自动清洗
- 需要在二级标题所在行最前面空4个格子,一级标题不用
- 需要在章和节字的后面加上一个空格
- 需要在页码前面加上=>符号
# 获取桌面路径
import os
import re
desktop_path = os.path.join(os.path.expanduser("~"), "Desktop")
# 目标文件路径
file_path = os.path.join(desktop_path, "目录.txt")
# 打开文件并读取内容
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
lines = file.readlines()
modified_lines = []
for line in lines:
# 去除空格
line = line.replace(" ", "")
if len(line) == 1:
continue
# 使用正则表达式在'章'或'节'后面添加一个空格,仅在后面没有空格的情况下
line = re.sub(r'(章|节)(?![ ])', r'\1 ', line)
# 在小数点后添加空格
line = re.sub(r'(\.\d)', r'\1 ', line)
if '章' not in line:
# 二级标题添加4个空格
line = ' ' * 4 + line
# 匹配并去除最外层的英文括号
pattern_en = r'\(([\d\s]+)\)'
line = re.sub(pattern_en, r'\1', line)
# 匹配并去除最外层的中文括号及其内部内容(包括除数字和空格以外的字符)
pattern = r'(([^)]+))'
line = re.sub(pattern, r'\1', line)
# 确保每行只有一个 =>
if '=>' not in line:
# 在页码数字前添加 =>(只在行尾)
line = re.sub(r'(\d+)$', r'=>\1', line)
# 去除中文汉字和'=>整体符号左边的冗余符号
pattern = r'([\u4e00-\u9fff]+)[^\w\s]+=>'
line = re.sub(pattern, r'\1=>', line)
modified_lines.append(line)
# 将修改后的内容写回文件
with open(file_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.writelines(modified_lines)
# 读取文件内容
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
content = file.read()
print(content)
4.2 批量修改文件夹下的文件命名
D:\231127\试卷\00159高级财务会计 目录下的所有图片命名中有_,确保_前面的字符串为00159231127
你可以使用 Python 的 os 模块来实现对文件名的批量修改,结合字符串操作来确保文件名中的规定格式。以下是一个示例代码:
import os
# 指定目录路径
directory_path = r'D:\231127\试卷\00159高级财务会计'
# 获取目录下所有文件名
files = os.listdir(directory_path)
# 遍历文件
for file_name in files:
# 构建完整的文件路径
file_path = os.path.join(directory_path, file_name)
# 检查文件是否是图片文件,并且文件名中包含下划线
if file_name.lower().endswith(('.png', '.jpg', '.jpeg', '.gif')) and '_' in file_name:
# 分割文件名,以下划线为界
parts = file_name.split('_')
# 确保分割后的第一部分为'00159231127'
if parts[0] != '00159231127':
# 构建新文件名
new_file_name = '00159231127' + '_' + '_'.join(parts[1:])
# 构建新文件路径
new_file_path = os.path.join(directory_path, new_file_name)
# 重命名文件
os.rename(file_path, new_file_path)
print(f'Renamed: {file_name} -> {new_file_name}')
在上述代码中:
1.使用 os.listdir 获取目录下的所有文件名,然后遍历这些文件名。
2.通过 os.path.join 构建完整的文件路径,确保路径的正确性。
3.检查文件是否是图片文件(以 .png, .jpg, .jpeg, .gif 结尾的文件),并且文件名中包含下划线。
4.使用 split('_') 分割文件名,确保分割后的第一部分为'00159231127'。
5.构建新文件名,并使用 os.rename 来重命名文件。
在运行前,请确保备份文件或者在测试环境中运行,以免意外损坏文件。
4.3 检测同级目录下是否存在同名文件夹
检测 D:\231127\试卷 下的文件夹命名前5位是否存在一样的,如果一样打印出来
你可以使用 Python 来检查指定目录下的文件夹,查找前5位命名相同的文件夹。以下是一个示例代码:
import os
# 指定目录路径
directory_path = r'D:\231127\试卷'
# 获取目录下所有文件夹名
folders = [folder for folder in os.listdir(directory_path) if os.path.isdir(os.path.join(directory_path, folder))]
# 创建一个空字典,用于存储前5位相同的文件夹名
same_prefix_folders = {}
# 遍历文件夹
for folder in folders:
# 获取前5位文件夹名
prefix = folder[:5]
# 检查前5位文件夹名是否已经在字典中
if prefix in same_prefix_folders:
# 将文件夹名添加到对应的键值中
same_prefix_folders[prefix].append(folder)
else:
# 若字典中没有该前5位文件夹名,则创建键值对
same_prefix_folders[prefix] = [folder]
# 输出前5位相同的文件夹名
for prefix, folders in same_prefix_folders.items():
if len(folders) > 1:
print(f"前5位为 '{prefix}' 的文件夹有以下重复命名:")
print(', '.join(folders))
这段代码执行以下操作:
1.使用 os.listdir 获取指定目录下的所有文件夹名。
2.然后遍历这些文件夹名,提取前 5 位名称,并将具有相同前缀的文件夹放入一个字典中。
3.最后打印出前 5 位相同的文件夹名。
CSDN大礼包:全网最全《全套Python学习资料》免费分享🎁
学习资源推荐
除了上述分享,如果你也喜欢编程,想通过学习Python获取更高薪资,这里给大家分享一份Python学习资料。
这里给大家展示一下我进的兼职群和最近接单的截图

😝朋友们如果有需要的话,可以V扫描下方二维码联系领取,也可以内推兼职群哦~
学好 Python 不论是就业还是做副业赚钱都不错,但要学会 Python 还是要有一个学习规划。最后大家分享一份全套的 Python 学习资料,给那些想学习 Python 的小伙伴们一点帮助!
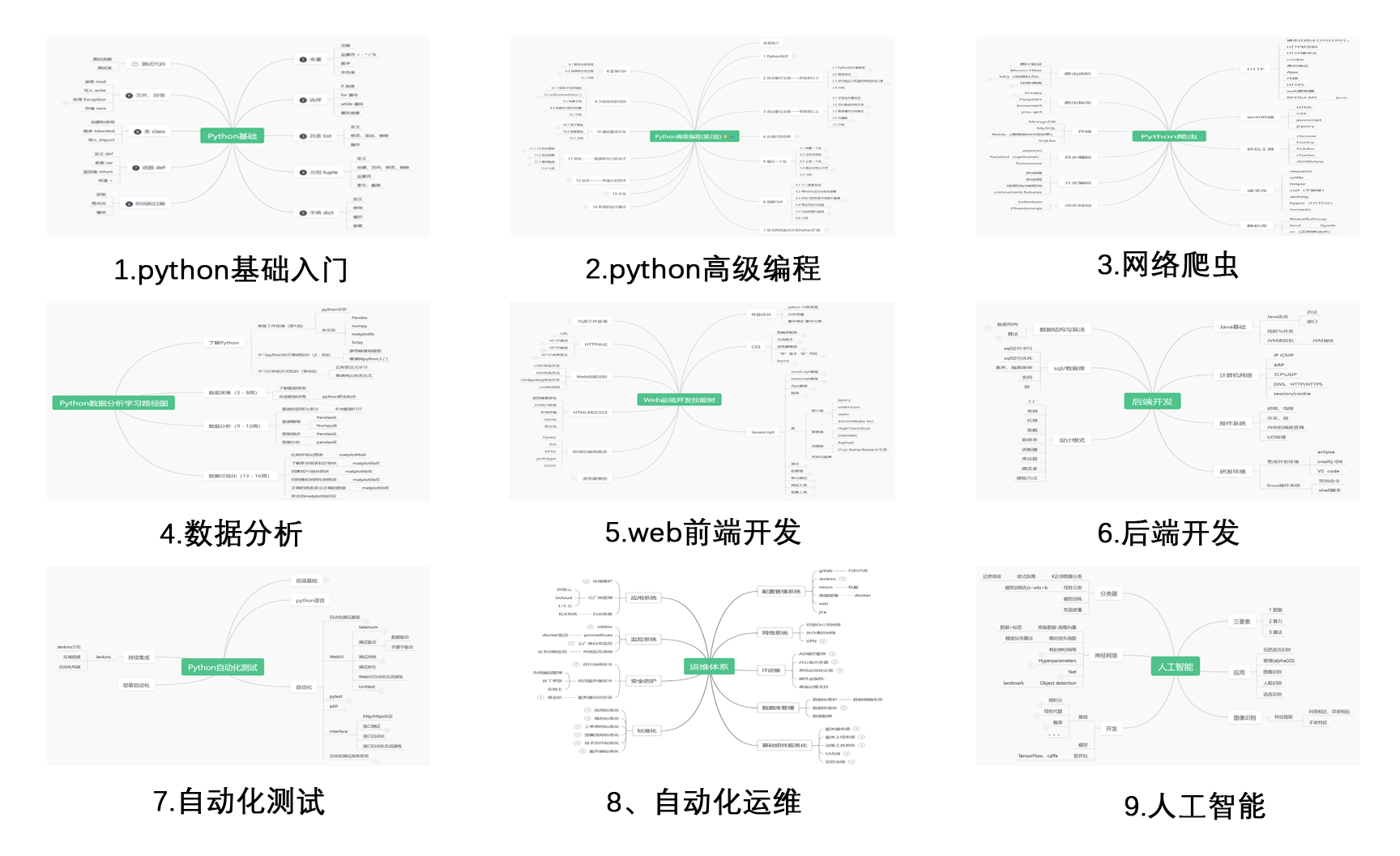
 ### 1.Python学习路线
### 1.Python学习路线

2.Python基础学习
01.开发工具

02.学习笔记
03.学习视频
3.Python小白必备手册

4.数据分析全套资源

5.Python面试集锦
01.面试资料
02.简历模板

因篇幅有限,仅展示部分资料,添加上方即可获取👆
------ 🙇?♂? 本文转自网络,如有侵权,请联系删除 🙇?♂? ------
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 代码随想录算法训练营第二十五天 | 216.组合总和III、 17.电话号码的字母组合
- ubuntu20部署Bringing-Old-Photos-Back-to-Life
- 汇编指令学习
- Ubuntu开机自启动文件
- SpringBoot 3.2.0 程序部署(Linux)
- 啊哈c语言——4.5逻辑挑战4(60秒倒计时)
- 计算机服务器中了_locked勒索病毒怎么办,_locked勒索病毒解密数据恢复
- 解决nginx 代理后报 Mixed Content: The page at ‘https://www.xxx.com‘
- java-使用quartz报错‘?‘ can only be specified for Day-of-Month -OR- Day-of-Week
- MySql数据库基础