SpringBoot + Mybatis 实现多数据源原来如此简单
1、为什么需要整合多数据源
在开发的过程中,我们可能会遇到一个工程使用多个数据源的情况,总体而言分为以下几个原因
a、数据隔离:将不同的数据存储在不同的数据库中,如多租户场景
b、性能优化:将数据分散到多个数据库中,提高系统的性能。常见的如读写分离,将读操作分散到读库中,减轻主数据库的负载,提高读取操作的性能
c、业务场景:某些业务场景可能需要使用其他数据库中的数据,这种场景也可以通过调用第三方 rpc 接口获取数据
2、实现多数据源过程
a、maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.7.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.1.7.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
b、创建动态数据源对象
// 多数据源持有对象
public class DBContextHolder {
public static final String DB_PRIMARY = "primaryDataSource";
public static final String DB_SECOND = "secondDataSource";
private static ThreadLocal<String> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal();
public static String getDB() {
return contextHolder.get();
}
public static void setDB(String dbName) {
DBContextHolder.contextHolder.set(dbName);
}
public static void cleanDB() {
contextHolder.remove();
}
}
// 决定使用那个数据源
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Nullable
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return DBContextHolder.getDB();
}
}c、在mybatis配置 sqlSessionFactory 中指定动态数据源
@Bean("sqlSessionFactory")
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DynamicDataSource dynamicDataSource) throws Exception {
MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactory = new MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean();
//设置数据源
sqlSessionFactory.setDataSource(dynamicDataSource);
sqlSessionFactory.setTypeAliasesPackage("com.jyt.service.testdb.entity");
sqlSessionFactory.setGlobalConfig(globalConfiguration());
sqlSessionFactory.setPlugins(new Interceptor[]{ //OptimisticLockerInterceptor(),performanceInterceptor()
paginationInterceptor()});
sqlSessionFactory.setConfiguration(mybatisConfiguration());
return sqlSessionFactory.getObject();
}d、通过 aop 动态指定 DBContextHolder 中的 dbName
// 设置默认数据源,不指定时使用
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
public @interface DB {
String name() default DBContextHolder.DB_PRIMARY;
}
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class DynamicAop implements Ordered {
// 此处也可以按自己的想法实现按目录区分
@Around("@annotation(db)")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, DB db) throws Throwable {
try {
DBContextHolder.setDB(db.name());
log.info("setDB {}", DBContextHolder.getDB());
joinPoint.proceed();
} finally {
log.info("threadLocal cleanDB {}", DBContextHolder.getDB());
DBContextHolder.cleanDB();
}
}
/**aop要在spring事务开启之前设置*/
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 1;
}
}e、准备数据源配置信息
spring:
datasource:
druid:
primary:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/basefun?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&allowMultiQueries=true&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
username: root
password: root
second:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/basefun2?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&allowMultiQueries=true&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
username: root
password: root
@Configuration
public class DatabaseConfig {
@Bean(DBContextHolder.DB_PRIMARY)
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.druid.primary")
public DruidDataSource primaryDataSource() {
return new DruidDataSource();
}
@Bean(DBContextHolder.DB_SECOND)
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.druid.second")
public DataSource secondDataSource() {
return new DruidDataSource();
}
@Bean
public DynamicDataSource dynamicDataSource() {
DynamicDataSource dynamicDataSource = new DynamicDataSource();
// 维护了所有的数据源列表
dynamicDataSource.setTargetDataSources(ImmutableMap.of(DBContextHolder.DB_PRIMARY, primaryDataSource(), DBContextHolder.DB_SECOND, secondDataSource()));
// 设置默认使用的数据源
dynamicDataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(primaryDataSource());
return dynamicDataSource;
}
}至此配置工作已经完成,启动既可以验证多数据源了
@Service
public class TestDBService {
@Resource
private StudentDao studentDao;
@DB
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED, rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void testDB() {
studentDao.insert(new Student().setAge(10).setName("张三"));
}
@DB(name = DBContextHolder.DB_SECOND)
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED, rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void testDB1() throws Exception {
studentDao.insert(new Student().setAge(11).setName("里斯"));
//int i = 1 / 0; 回滚 保存失败,上面执行成功
}
}3、分析下 spring 是如何帮我们实现多数据源的 ?
? ? ?首先我们看下? DynamicDataSource#determineCurrentLookupKey 何时会被调用?
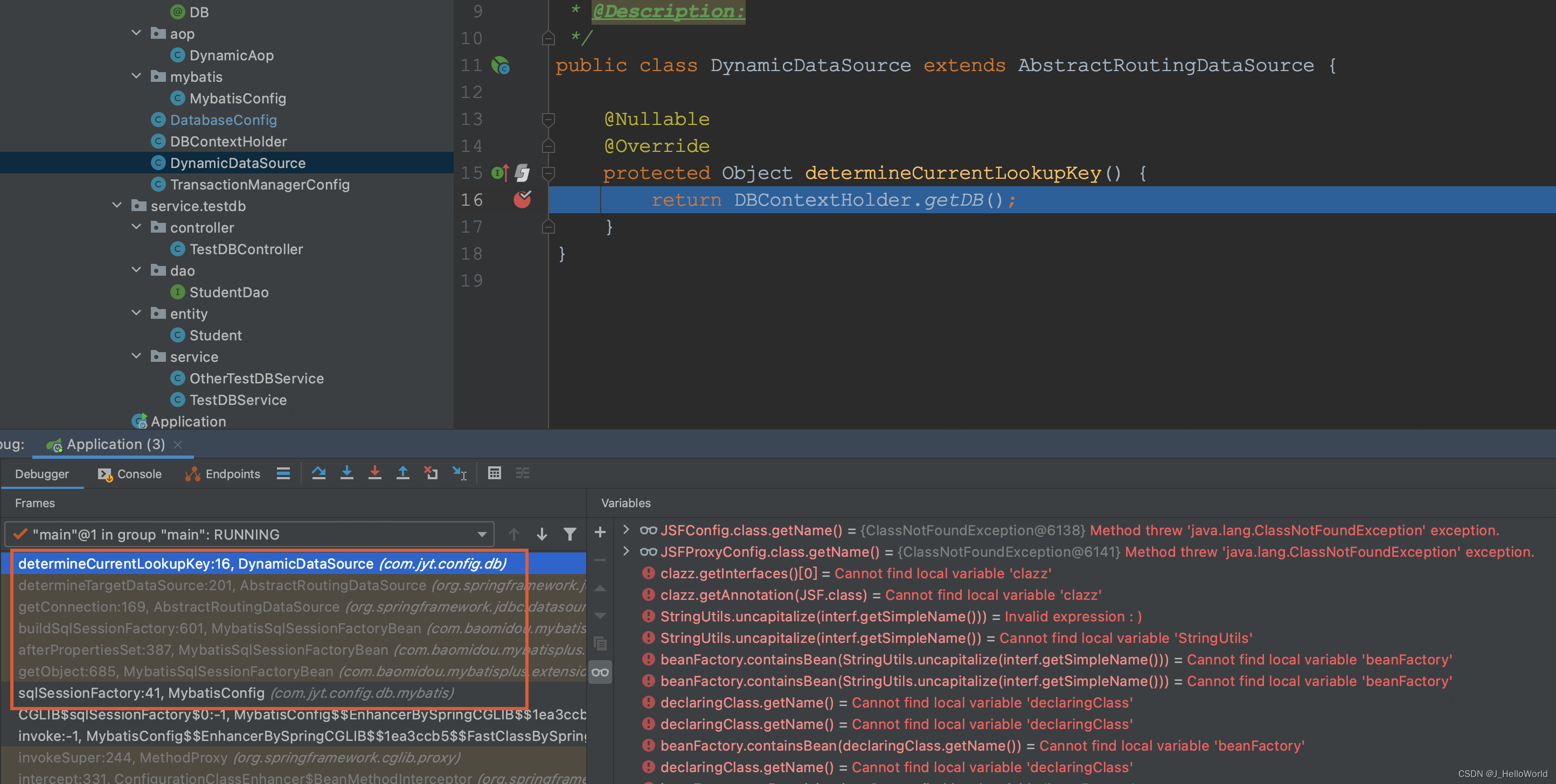
? ? ? ?如图所示,sqlSessionFactory.getObject() 初始化时会调用?afterPropertiesSet() 方法,在这个方法中集中初始化,点进去查看源码,我们发现在MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean#buildSqlSessionFactory 中会我们调用我们指定数据源的?getConnection 方法

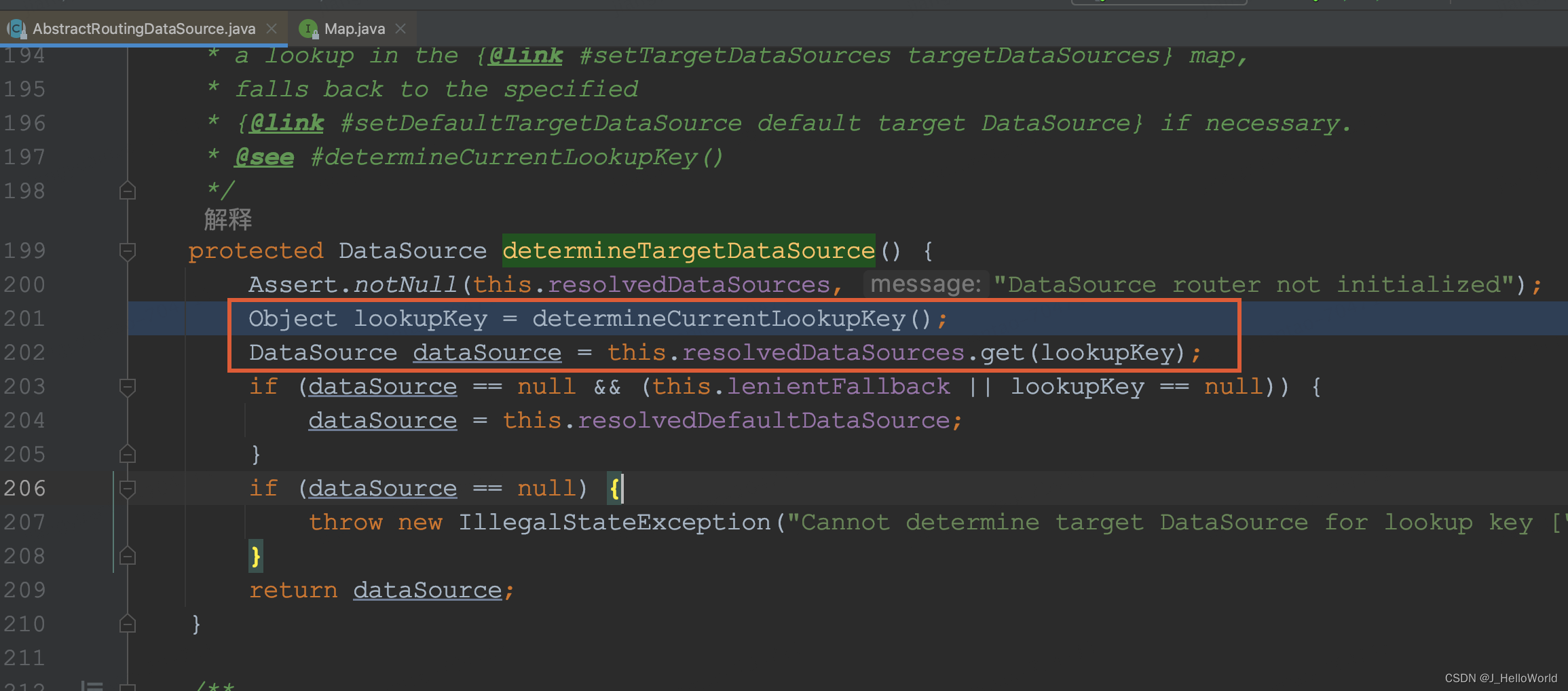
? ? ? ?而 spring 提供的 AbstractRoutingDataSource#determineTargetDataSource 会回调我们接口,获取数据源对应的 key,从?resolvedDataSources(map)中获取数据源返回
? ? ? ?在看下 resolvedDataSources 的初始化,会使用我们在 DatabaseConfig#dynamicDataSource 中指定的?setTargetDataSources 全部的数据源列表
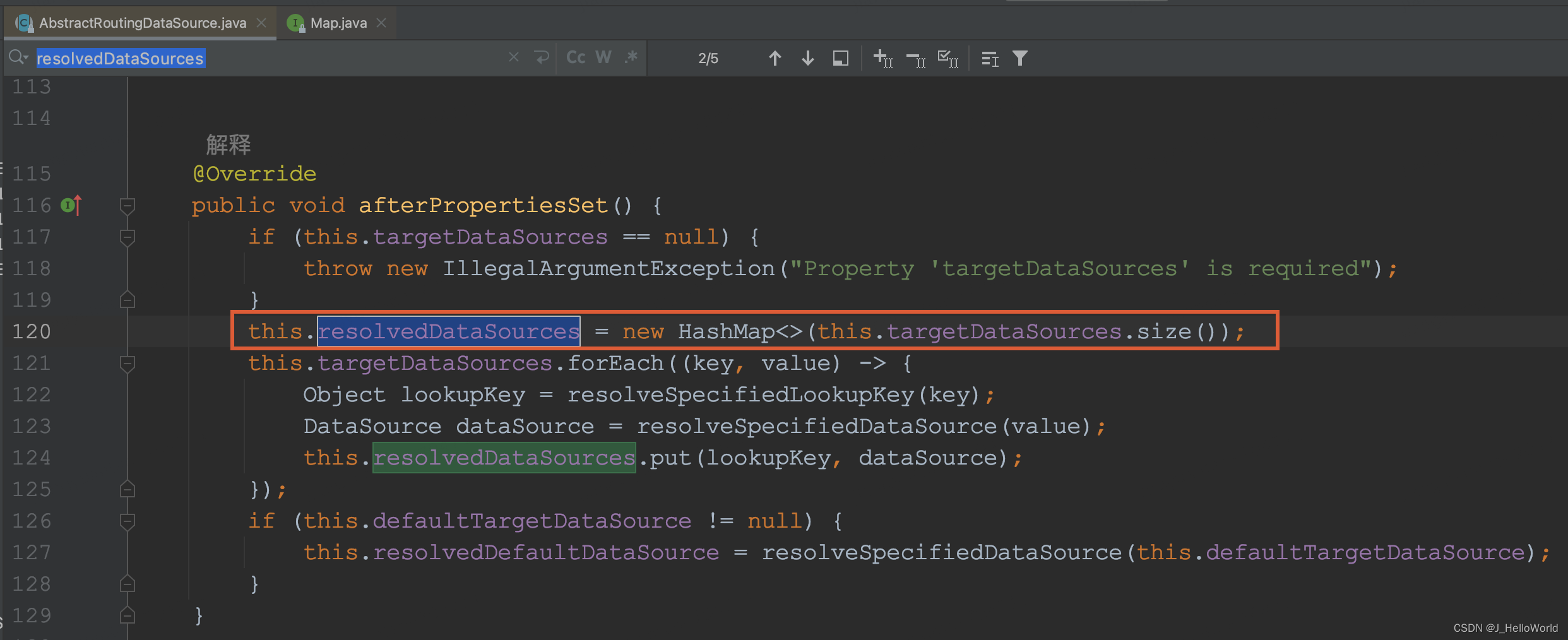
? ? ? ?这也是为什么我们需要通过 aop 动态修改?DBContextHolder 中的 key( dbName)?的原因,同理程序在运行时获取数据源时也是通过 DynamicDataSource#determineCurrentLookupKey 返回的 key 来决策使用那个数据源
以上如有不清楚或不描述不恰当之处,还请批评指正,感谢?
具体源码:DBProject: DB 多数据源集成技术选型:springboot + druid + mybatisplus + mysql - Gitee.com
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!