MyBatis入门基础篇
MyBatis基础篇
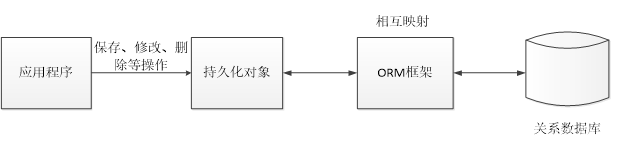
MyBatis是一款优秀的特久层框架,用于简化JDBC开发。其是Apache的一个开源项目iBatis,2010年这个项目由apache software foundation迁移到了google code,并且改名为MyBatis。2013年11月迁移到Github。由于MyBatis中的大部分API参数与数据库事务息息相关,因此事先了解下事务的知识,我个人觉得是很有必要的,我个人推荐zhihu的一篇文章《一文搞懂什么是事务》
官网:MyBatis中文网
- 持久层
- 负责将数据到保存到数据库的那一层代码
- JavaEE三层架构:表现层、业务层、持久层
- 持久层框架:Spring Data JPA、MyBatis、MyBatis-Plus、Hibernate等
- 框架
- 框架就是一个半成品软件,是一套可重用的、通用的、软件基础代码模型。半成品相当于一个蛋糕胚子,你可以在上面画奶油,做成自己想要的蛋糕。
- 在框架的基础之上构建软件编写更加高效、规范、通用、可扩展。
为了应对JDBC内容中的硬编码和操作繁琐(见之前的文章),例如注册驱动、获取Connection连接以及SQL语句中的过程需要输入数据库驱动、数据库的账号密码,这需要重新编译和打包,然后后面获取petmt对象以及后续过程中,我们需要去手动设置参数或手动封装结果集,这都是繁琐的操作。因此MyBaits应运而生。MyBatis免除了几乎所有的JDBC代码以及设置参数和获取结果集的工作。
MyBatis快速入门(基本方式开发)
这里是自定义的名字,只是为了更好地引入Mapper映射地概念,所引入地一小节,其实也用到了Mapper映射。
-
首先再数据库里面创建一张user表,并添加数据
create database mybatis; use mybatis; drop table if exists tb_user; create table tb_user( id int primary key auto_increment, username varchar (20), password varchar(20), gender char(1), addr varchar(30) ); INSERT INTO tb_user VALUES(1,'zhangsan','123','男','北京'); INSERT INTO tb_user VALUES(2,'李四','234','女','天津'); INSERT INTO tb_user VALUES(3,'王五','11','男','西安'); -
创建模块,导入坐标
-
创建新的模块,创建一个Maven的项目,然后再pom文件中添加mybatis的依赖(记得自行添加数据库等其他依赖)
<!--pom.xml--> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <!-- 记得更改版本--> <version>x.x.x</version> </dependency>
-
-
编写MyBatis核心配置文件->替换连接信息解决硬编码问题,创建资源文件mybatis-config.xml
<!-- 这里仅提供一个实例--> <!-- mybatis-config.xml--> <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <!-- 环境配置,用于配置数据库连接环境信息。这里配置的是开发时期所使用的数据库, 其可以配置多个environment,通过default属性来切换不同的其可以配置多个environment --> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <!-- 事务的管理方式 --> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <!-- 数据库连接池 --> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <!-- 这里类似于${driver}的信息需要修改为自己原本的数据库信息 以本地MySQL数据库为例,我们进行修改演示 <property name="driver" value="${driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${url}"/> <property name="username" value="${username}"/> <property name="password" value="${password}"/> --> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///mybatis?useSSL=false"/> <property name="username" value="$root"/> <property name="password" value="1234"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <!--用来加载sql映射文件--> <mappers> <mapper resource="UserMapper.xml"/> </mappers> </configuration> <!-- 类型别名(typeAliases) <typeAliases <package name="com.test.entity"/> </typeAliases> 当我们配置好别名以后,如上,则可以将对应的SQL映射配置文件中的 <select id="selectAll" resultType="com.test.entity.user"> 修改为 <select id="selectAll" resultType="user"> --> -
编写SQL映射文件->统一管理sq语句,解决硬编码问题,取名规则:取名规则一般按照需要操作的实体进行命名,例如我们这里举例为user为实体,则可以创建为UserMapper.xml
<!--pom.xml--> <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!-- UserMapper.xml namespace:命名空间 这里取名为test id 取名为selectAll 查询所有信息 resultType返回类型,输入具体的实体类 --> <mapper namespace="test"> <select id="selectAll" resultType="com.test.entity.User"> select * from tb_user </select> </mapper> -
编码
// 定义P0J0类 package com.test.entity; //αLt+鼠标左键整列编辑 public class User{ private Integer id; private String username; private String password; private String gender; private String addr; public Integer getId(){ return id; } public void setId(Integer id){ this.id = id; } public String getUsername(){ return username; } public void setUsername(String username){ this.username = username; } public String getPassword(){ return password; } public void setPassword(String password){ this.password = password; } public String getGender(){ return gender; } public void setGender(String gender){ this.gender = gender; } public String getAddr(){ return addr; } public void setAddr(String addr){ this.gender = addr; } public String tostring(){ return "User{" + "id=" + id + ", username='" + username + '\'' + ", password='" + password + '\'' + ", gender='" + gender + '\'' + ", addr='" + addr + '\'' + '}'; } } // 加载核心配置文件,获取SqlSessionFactory对象 // 定义MyBaitsDemo类 package com.test; /* *Mybatis快速入门代码 */ package com.test; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.List; public class MyBatisDemo{ public static void main(String[]args) throws IOException{ //1.加截ybatis的核心置文件,获取SqlSessionFactory,同事这里包含了加载数据库驱动等一系列操作 String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); //2.SqlSession对象,用它来执行Sql SqlSession sqlSession sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); //3.获取SqlSession对象,执行SQL语句 这里传入的字符串等于当时配置文件中写的标签 List<User> users = sqlSession.selectList("test.selectAll"); System.out.printIn(users); // 释放资源 sqlSession.close(); } } -
解决Sql语句警告提示
如果在编译器中,Sql语句会标红,这是因为编译器(IDEA)与数据库没有没有建立连接,不识别表信息
**解决方案:**在Idea中配置MySQL数据库连接

输入账号密码和数据库名称,点击测试,没有报错,则连接成功。

Mapper代理开发
在上面我们使用了“test.selectAll”的方式来执行sql语句,但是这样也不是很方便,因为我们需要写很多select id,而且不利于后期维护,并没有很好地改变硬编码的方式。于是我们引入了Mapper代理开发
-
目的
- 解决原生方式中的硬编码
- 简化后期执行SQL
//原来的方式: List<User>users = sqlSession.selectList(statemert:"test.selectAll"); System.out.println(users); //现在的方式: //3. 获取接口代理对象 UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); //4: 执行方法,其实就是执行sq1语句 List<User> users = userMapper.selectAll();这样的方法有很多优势,首先它不依赖于字符串字面值,会更安全一点;其次,如果你的 IDE 有代码补全功能,那么代码补全可以帮你快速选择到映射好的 SQL 语句。
-
步骤
-
定义与SQL映射文件同名的Mapper接口,并且将Mapper接口和SQL映射文件放置在同一目录下,使用方式,在资源文件夹resources文件中创建对应路径的文件夹,例如com/test/mapper,注意这里一定是斜杠,不是点,并将对应的XML文件放入到该文件夹中。
-
设置SQL映射文件的namespace属性为Mapper接口全限定名
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!-- 将上面的UserMapper.xml文件中的 <mapper namespace="test"> 修改为 <mapper namespace="com.test.mapper.UserMapper"> namespace:命名空间 这里取名为test id 取名为selectAll 查询所有信息 resultType返回类型,输入具体的实体类 --> <mapper namespace="com.test.mapper.UserMapper"> <select id="selectAll" resultType="com.test.entity.User"> select * from tb_user </select> </mapper> -
在Mapper接口中定义方法,方法名就是SQL映射文件中sql语句的id,并保持参数类型和返回值类型一致
// UserMapper.java package com.test.mapper; import com.test.entity.User; import java.util.List; public interface UserMapper{ List<User> selectAll(); }-
编码
<!-- 在编码之前,需要先将对应的mapper文件地址进行修改,因为我们之前移动了位置 用来加载sql映射文件 --> <mappers> <mapper resource="com/test/mapper/UserMapper.xml"/> </mappers>-
通过SqlSession的getMapper方法获取Mapper接口的代理对象
//3. 获取接口代理对象
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
* 调用对应方法完成sq的执行 ```java //4: 执行方法,其实就是执行sq1语句 List<User> users = userMapper.selectAll(); -
-
-
细节:如果Mapper接口名称和SQL映射文件名称相同,并在同一目录下,则可以使用包扫描的方式简化SQL映射文件的加载
<!-- 如果Mapper接口名称和SQL映射文件名称相同,并在同一目录下 则可以将下面的mapper中的resource修改为package 用来加载sql映射文件 --> <mappers> <!-- <mapper resource="com/test/mapper/UserMapper.xml"/> --> <package name="com.test.mapper"/> </mappers>
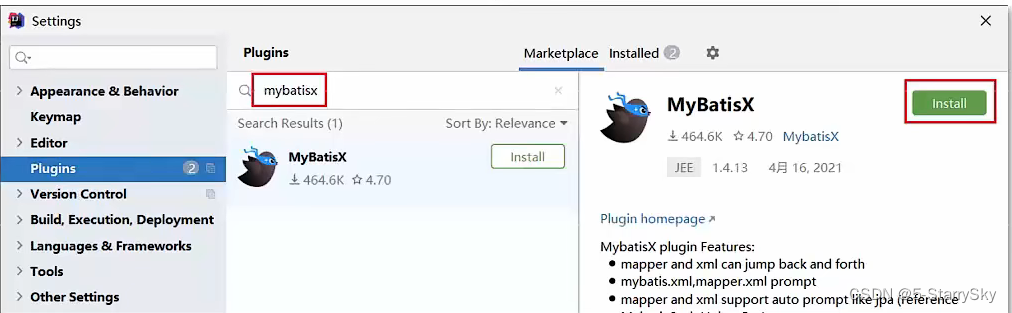
安装MyBatisX 插件
MybatisX是一款基于IDEA的快速开发插件,为效率而生。
-
主要功能:
- XML和接口方法相互跳转
- 根据接口方法生成statement,即对应的ID和地址
-
安装:
注解完成增删改查
使用注解来映射简单语句会使代码显得更加简洁,但对于稍微复杂一点的语句,Java 注解不仅力不从心,还会让你本就复杂的 SQL 语句更加混乱不堪。 因此,如果你需要做一些很复杂的操作,最好用 XML 来映射语句。
-
查询:在对应接口方法上写如下注解
@Select("select * from tb_user where id = #{id}") -
添加
@Insert() -
修改
@Update() -
删除
@Delete()
动态SQL
SQL语句会随着用户的输入或外部条件的变化而变化,这就是动态SQL。
-
动态多条件查询
<!-- 假设现在存在一个商品的多选项,例如有公司名称,品牌名称以及产品状态,但是我不希望全部输入所有的参数,我希望我只填一或两个参数,就能查出我需要的值,这个时候我们就需要引入动态SQL\ * if:条件判断 * test:逻辑表达式 * 问题:如果不添加恒等式,则在查询时如果不添加恒等式,则会报错,解决办法除了恒等式外,可以使用<where>标签 修改为: <where> <if test="status != null"> and status = #{status} </if> <if test="companyName != null and companyName != '' "> and company_name like #{companyName} </if> <if test="brandName != null and brandName != '' "> and brand_name like #{brandName} </if> </where> --> <select id="selectByCondition"resultMap="brandResultMap"> select * from tb_brand where 1 = 1 <if test="status != null"> and status = #{status} </if> <if test="companyName != null and companyName != '' "> and company_name like #{companyName} </if> <if test="brandName != null and brandName != '' "> and brand_name like #{brandName} </if> </select> -
动态单条件查询
<!-- 从多个条件中选择一个 choose(when,otherwise):选择,类似于Java中的switch语句 同理这里也可以通过<where>标签来取代掉恒等式 --> <select id="selectByConditionSingle" resultMap="brandResultMap"> select * from tb_brand where <choose><!--类似于switch--> <when test="status != null"><!--类似于case--> status = #{status} </when> <when test="companyName != null and companyName != ''"> company_name like #{companyName} </when> <when test="brandName != null and brandName != ''"> brand_name like #{brandName} </when> <otherwise><!--类似于default--> 1 = 1 </otherwise> </choose> </select> -
MyBatis事务
openSession():默认开启事务,进行增删改操作后需要使用sqlSession.commit(); //手动提交事务 openSession(true):可以设置为自动提交事务(关闭事务) -
添加-主键返回
<!-- 在数据添加成功后,需要获取插入数据库数据的主键的值 >比如:添加订单和订单项 1.添加订单 2.添加订单项,订单项中需要设置所属订单的id --> <insert id="addOrder" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"> insert into tb_order(payment,payment_type,status) values (#{payment},#{paymentType},#{status}); </insert> <insert id="addOrderltem"> insert into tb_order_item(goods_name, goods_price, count, order_id) values (#{goodsName},#{goodsPrice},#{count},#{orderId}); </insert> -
修改-修改动态字段
<!-- * 编写接口方法:Mapper接口 * 参数:部分数据,封装到对象中 * 结果:void * 编写SQL语句:SQL映射文件 * 执行方法,测试 set标签可以解决逗号和全部都不修改的问题 --> <update id="update"> update tb_brand <set> <if test="brandName != null and brandName !=''"> brand_name = #{brandName}, </if> <if test="companyName !=null and companyName !=''"> company_name = #{companyName}, </if> <if test="ordered != null"> ordered = #{ordered}, </if> <if test="description != null and description !=''"> description = #{description}, </if> <if test="status != null"> status = #{status} </if> </set> where id =#{id}; </update> -
批量删除
<!-- mybatis会将数组参数,封装为一个Map集合。 * 默认:array = 数组,因此将collection赋值为array * 或使用@Param注解改变map集合的默认key的名称 在接口方法中加上注解的解释,例如 @Param(ids) --> <delete id="deleteByIds"> delete from tb_brand where id in ( <foreach collection="ids" item="id" separator=","> #{id} </foreach> ); </delete> <!--为了书写的美观,上述代码也可修改为如下代码--> <delete id="deleteByIds"> delete from tb_brand where id in <foreach collection="ids" item="id" separator="," open="(" close=")"> #{id} </foreach> ; </delete>
细节处理
-
映射中数据库标的字段名称 和 实体类的属性名称 不一样
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!-- namespace:命名空间 这里取名为test id 取名为selectAll 查询所有信息 resultType返回类型,输入具体的实体类 !!! 注意如果数据库标的字段名称 和 实体类的属性名称 不一样,则不能自动封装数据!!! 因此可以采取三种方案 * 起别名 clientName 实体类的属性名称 client_name 数据库标的字段名称 缺点是每次查询都要定义一次别名 select client_name as clientName from User * 加入sql片段 别名均放到sql中间 缺点不灵活 <sql id="user_column"> id,client_name as clientName </sql> * resultMap id:唯一标识 type: 映射的类型,支持别名 <resultMap id="userResultMap"type="User"> <result column="client_name"property="clientName"/> </resultMap> result:完成一般字段的映射 column:表的列名 property:实体类的属性名 这里如果id需要取别名则不选用result 而是选择使用id. 按照以上要求修改以后,需要修改下面的句段 将 <select id="selectAll" resultType="com.test.entity.user"> 修改为 <select id="selectAll" resultMap="userResultMap"> --> <mapper namespace="test"> <!-- <select id="selectAll" resultType="com.test.entity.User"> --> <select id="selectAll" resultMap="userResultMap"> select * from tb_user </select> </mapper> -
参数占位符、参数类型以及特殊字符处理
<!-- * 参数占位符: 1. #{} :会将其替换为? 2. ${} :拼接sql,会存在SQL注入的问题 使用实际: * 参数传递的时候:#{} 8 表名或者列名不固定的情况下:${} * 参数类型:parameterType: 可以省略 * 特殊字符处理:例如小于符号 1.转义字符 <:< 2.CDATA区 <![CDATA[ < ]]> --> <select id="selectById"resultMap="userResultMap"> select from tb_user where id = ${id}; </select> -
多条件查询下的多参数接收
-
散装参数:如果方法中有多个参数,需要使用@Param
selectByC(@Param(id)int id, @Param(client_name) String client_name));//在Mapper接口中通过注解告知所对应的参数 -
对象参数:对象的属性名称要与参数占位符的名称一致
selectByC(User user); //在Mapper接口中传递对象,在调用接口方法之前,必须先封装对象,并提供对应的属性值 -
map集合参数:键值的名称必须与参数占位符的名称一致
selectByC(Map map) //在Mapper接口中传递对象,在调用接口方法之前,必须先封装map集合对象,并提供键值对
-
-
MyBatis参数传递
-
单个参数
-
POJO类型:直接使用, 属性名 与 参数占位符名称 一致
-
Map集合:直接使用, 键名 与 参数占位符名称 一致
-
Collection:封装为Map集合
map.put("arg0",collection集合); map.put("collection",collection集合); -
List:封装为Map集合
map.put("arg0",List集合); map.put("collection",List集合); map.put("List",List集合); -
Array
map.put("arg0",数组); map.put("array",数组); -
其他类型:直接使用
-
-
多个参数
- 需要使用@Param注解来保持参数名称与占位符名称一致
-
ParamNameResolver类进行参数封装
-
默认将多个参数封装为集Map集合
// 在类ParamNameResolver类中使用getNameParams方法对参数进行封装,可以使用@Param注解,天幻Map集合中默认的arg键名 map.put("arg0",参数值1) map.put("param1",参数值1) map.pUt("param2",参数值2) map.pUt("arg1",参数值2)
-
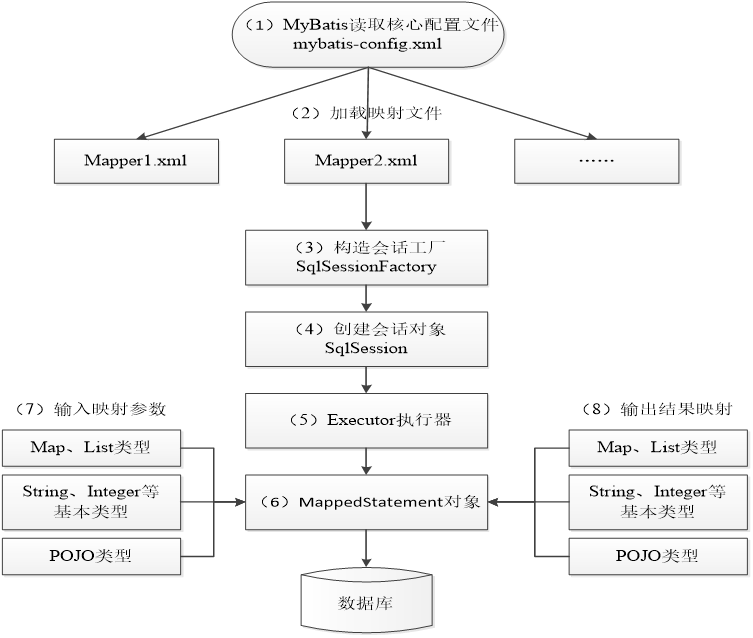
-
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Java异常处理--throw手动抛出异常对象
- laravel 中间件记录日志
- UWB校准(矫正天线延时)
- QT基础篇(13)QT5数据库
- 智慧博物馆信息化系统建设(1)
- 带备忘录的斐波那契递归(c++)
- ZooKeeper 应用场景深度解析
- 拼题A 跨年挑战赛 2024 赛后提交入口 + 题目 + 题解
- 解读 $mash 通证 “Fair Launch” 规则,将公平发挥极致
- 从无到有制作docker镜像、容器详细步骤