Mini Mybatis-Plus(中)
发布时间:2023年12月26日
作者简介:大家好,我是smart哥,前中兴通讯、美团架构师,现某互联网公司CTO
联系qq:184480602,加我进群,大家一起学习,一起进步,一起对抗互联网寒冬
这一篇是用来过渡的,目的只有一个:模拟MyBatis-Plus的LambdaQueryWrapper。我相信,每一位用过MyBatis-Plus的同学都会惊叹于它对查询条件的精准控制,通过QueryWrapper几乎拼接出任何你想要的查询SQL。

原本我只打算模拟普通的QueryWrapper:
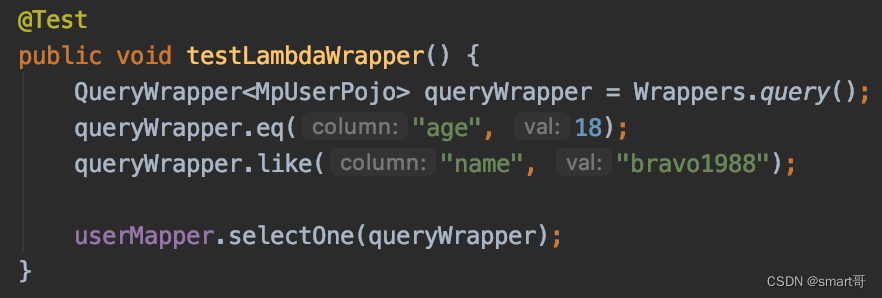
但后来想想,虽然是玩具,但做得逼真一点总是赏心悦目些。
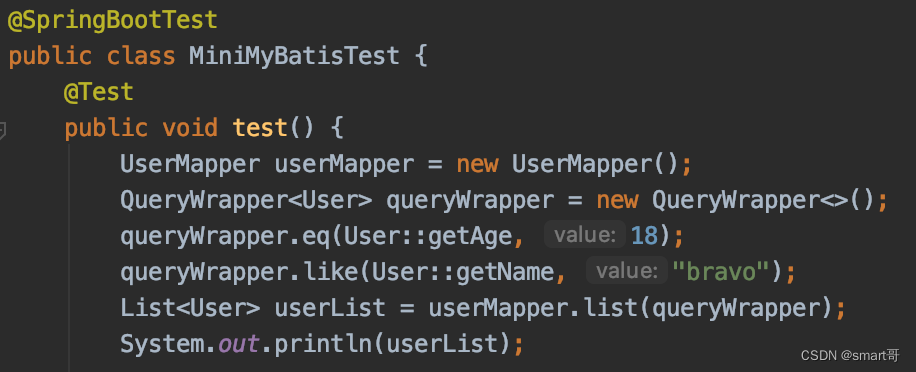
其实LambdaQueryWrapper底层就是为我们自动拼装查询条件,所以实现的难点有两个:
- 怎么通过Lambda表达式得到当前条件对应的columnName?
- 怎么收集条件?
第一点是最难的,我原本打算从思路上模拟一下MyBatis-Plus的做法,结果发现实在太复杂了,直接放弃了。
最终我封装的QueryWrapper是这样的:
/**
* 模拟MyBatis-Plus的LambdaQueryWrapper(思路完全不同,仅仅是形似)
*
* @author mx
*/
public class QueryWrapper<T> {
// conditionMap,收集查询条件
// {
// " LIKE ": {
// "name": "mx123"
// },
// " = ": {
// "age": 18
// }
// }
private final Map<String, SqlParam> conditionMap = new HashMap<>();
// 操作符类型,比如 name like 'bravo' 中的 LIKE
private static final String OPERATOR_EQ = " = ";
private static final String OPERATOR_GT = " > ";
private static final String OPERATOR_LT = " < ";
private static final String OPERATOR_LIKE = " LIKE ";
public QueryWrapper<T> eq(ConditionFunction<T, ?> fn, Object value) {
String columnName = Reflections.fnToColumnName(fn);
conditionMap.put(OPERATOR_EQ, new SqlParam(columnName, value));
return this;
}
public QueryWrapper<T> gt(ConditionFunction<T, ?> fn, Object value) {
String columnName = Reflections.fnToColumnName(fn);
conditionMap.put(OPERATOR_GT, new SqlParam(columnName, value));
return this;
}
public QueryWrapper<T> lt(ConditionFunction<T, ?> fn, Object value) {
String columnName = Reflections.fnToColumnName(fn);
conditionMap.put(OPERATOR_LT, new SqlParam(columnName, value));
return this;
}
public QueryWrapper<T> like(ConditionFunction<T, ?> fn, Object value) {
String columnName = Reflections.fnToColumnName(fn);
conditionMap.put(OPERATOR_LIKE, new SqlParam(columnName, "%" + value + "%"));
return this;
}
public Map<String, SqlParam> build() {
return conditionMap;
}
}
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class SqlParam {
private String columnName;
private Object value;
}
// ************* 辅助工具类 ***********
/**
* 扩展java.util.function包下的Function接口:支持Serializable
* 搭配Reflections工具类一起使用,用于获取Lambda表达式的方法名
*
* @author mx
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ConditionFunction<T, R> extends Function<T, R>, Serializable {
}
/**
* 获取Lambda入参的方法名
*
* @author mx
*/
public class Reflections {
private static final Pattern GET_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("^get[A-Z].*");
private static final Pattern IS_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("^is[A-Z].*");
/**
* 注意: 非标准变量(非小驼峰)调用这个方法可能会有问题
*
* @param fn
* @param <T>
* @return
*/
public static <T> String fnToColumnName(ConditionFunction<T, ?> fn) {
try {
Method method = fn.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("writeReplace");
method.setAccessible(Boolean.TRUE);
SerializedLambda serializedLambda = (SerializedLambda) method.invoke(fn);
String getter = serializedLambda.getImplMethodName();
// 对于非标准变量生成的Get方法这里可以直接抛出异常,或者打印异常日志
if (GET_PATTERN.matcher(getter).matches()) {
getter = getter.substring(3);
} else if (IS_PATTERN.matcher(getter).matches()) {
getter = getter.substring(2);
}
return Introspector.decapitalize(getter);
} catch (ReflectiveOperationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}主要思路是:把所有查询条件封装到Map中,key是操作符,比如=、like、>或<,value是SqlParam对象,包括columName和columnValue。
{
" LIKE ": {
"name": "mx123"
},
" = ": {
"age": 18
}
}key的空格是为了拼接SQL时方便,比如 name LIKE '%mx%',如果不加空格会变成 nameLIKE'%mx%'。
学习必须往深处挖,挖的越深,基础越扎实!
阶段1、深入多线程
阶段2、深入多线程设计模式
阶段3、深入juc源码解析
阶段4、深入jdk其余源码解析
阶段5、深入jvm源码解析
?
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/smart_an/article/details/135213934
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 艾思控AQMD6008BLS-TE无刷电机驱动使用笔记(配合STM32)
- 【Proteus仿真】【STM32单片机】红外无线遥控器系统
- 图解设计模式-中介者模式(Mediator)
- C++线性表
- [SpringBoot2.6.13]FastJsonHttpMessageConverter不生效
- 代码随想录训练营第五十七天| ● 647. 回文子串 ● 516.最长回文子序列● 动态规划总结篇
- 设计PCB阻抗
- 如何判断光模块失效以及光模块应用注意点
- 配方(c++题解)
- ffmpeg windows开发之一(编译安装及入门指南)