【HTML5、CSS3】新增特性总结!
文章目录
23 HTML5 新增特性
23.1 语义化标签

以前我们布局基本上都是使用div盒子,但是div盒子对于搜索引擎而言没有任何语义。我们可以将div再细分一下,生成一些语义化的布局标签。于是,HTML5新增加了一些新的标签、新的表单和新的表单属性等。
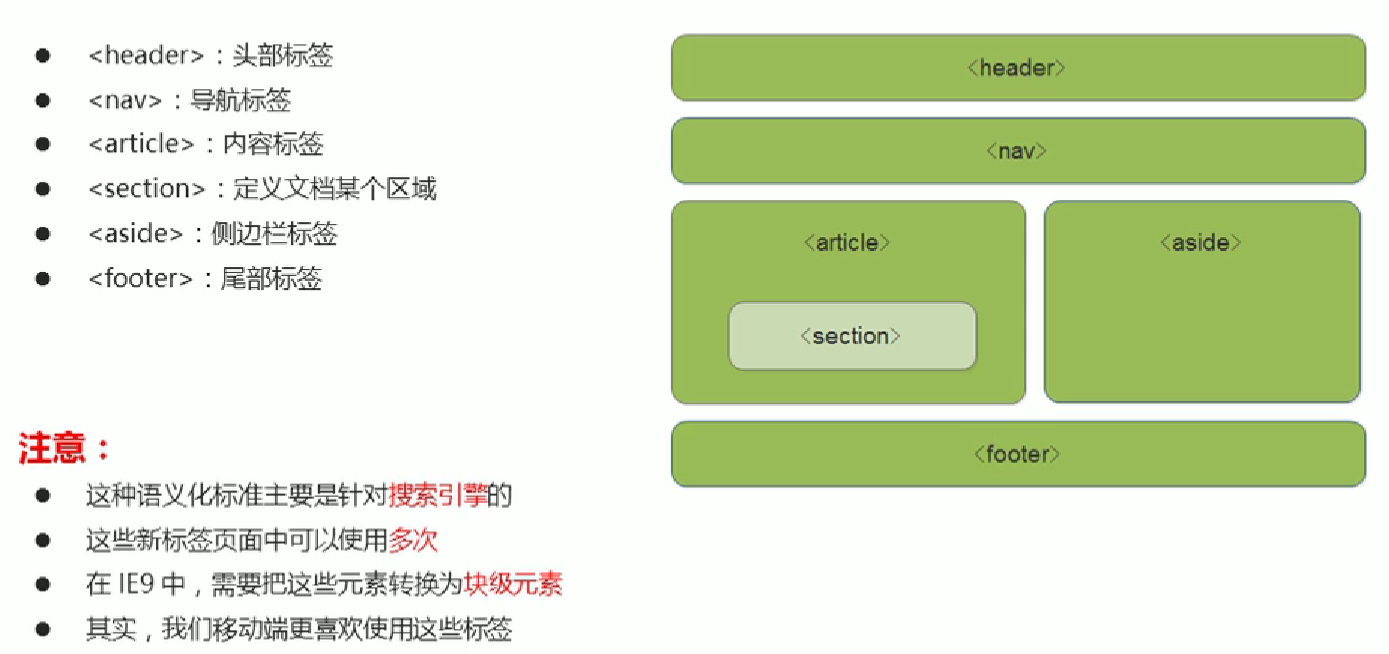
注意,这些新特性都有兼容性问题,基本是IE9+以上版本的浏览器才支持。
23.2 多媒体标签
使用多媒体标签可以很方便地在页面中嵌入音频和视频,不再使用flash和其他浏览器插件。
23.2.1 视频<video>标签
<video src="文件路径" controls="controls"></video>
里面可以添加的属性(部分):
- autoplay: autoplay 视频自动播放(谷歌浏览器还需要添加“静音播放”)
- controls: controls 显示播放控件
- width: 100% 设置播放器的宽度
- height: 400 设置播放器的高度
- loop: loop 设置循环播放
- src: “xxx” 视频的url地址
- poster: imgurl 加载等待的画面图片
- muted: muted 静音播放
<video src="move.mp4" autoplay="autoplay" muted="muted" controls="controls" loop="loop" width="500px">
</video>
尽量使用mp4格式,对各个浏览器兼容性更好,不行再执行ogg格式的视频,还是不行就显示文字,写法如下:

23.2.2 音频<audio>标签
<audio src="文件路径" controls="controls"></audio>
里面可以添加的属性(部分):
- autoplay: autoplay 自动播放(谷歌禁用了,JS可以解决)
- controls: controls 显示控件
- loop: loop 循环播放

23.3 input属性值
之前的input无论是啥都为text,满足不了所有的需求。于是HTML5新增了以下input属性值:
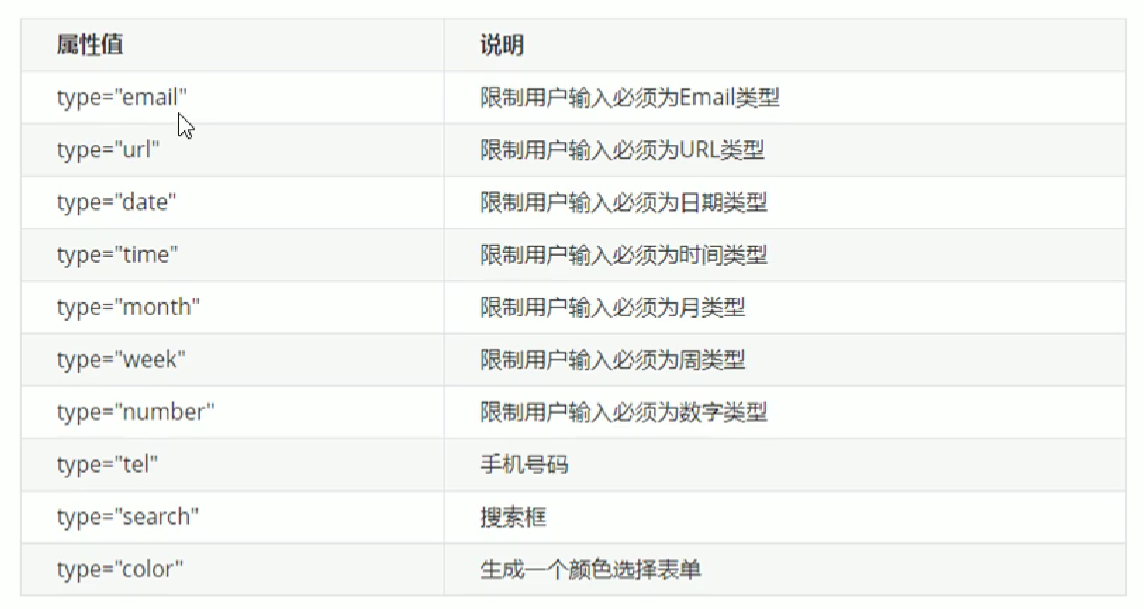
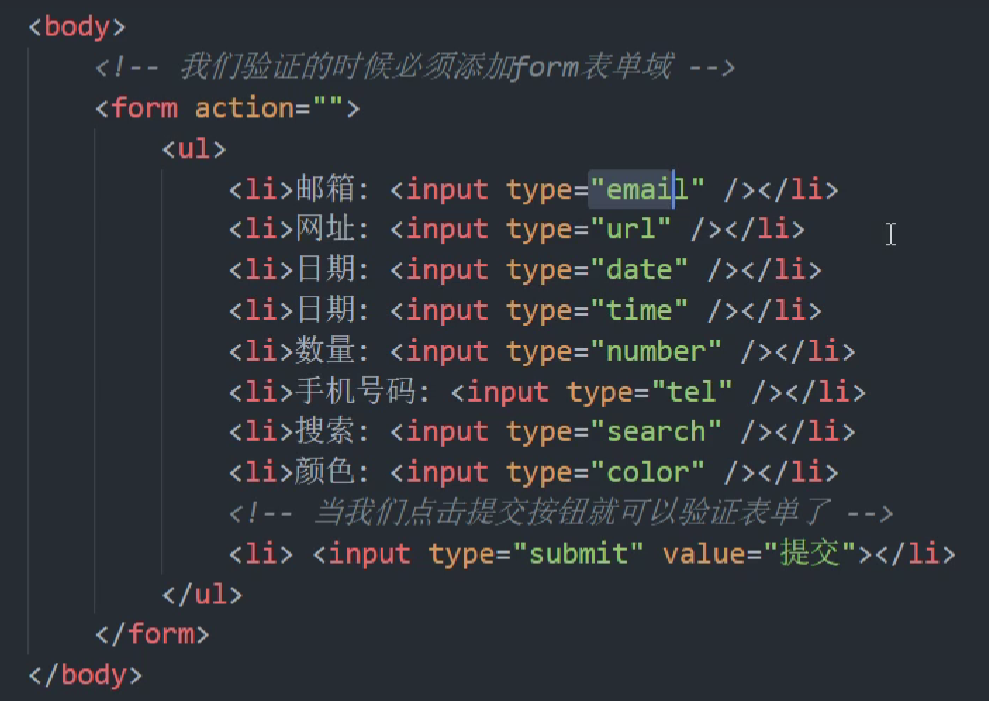
将这些放到input里面,就会有新的效果。
23.4 表单属性

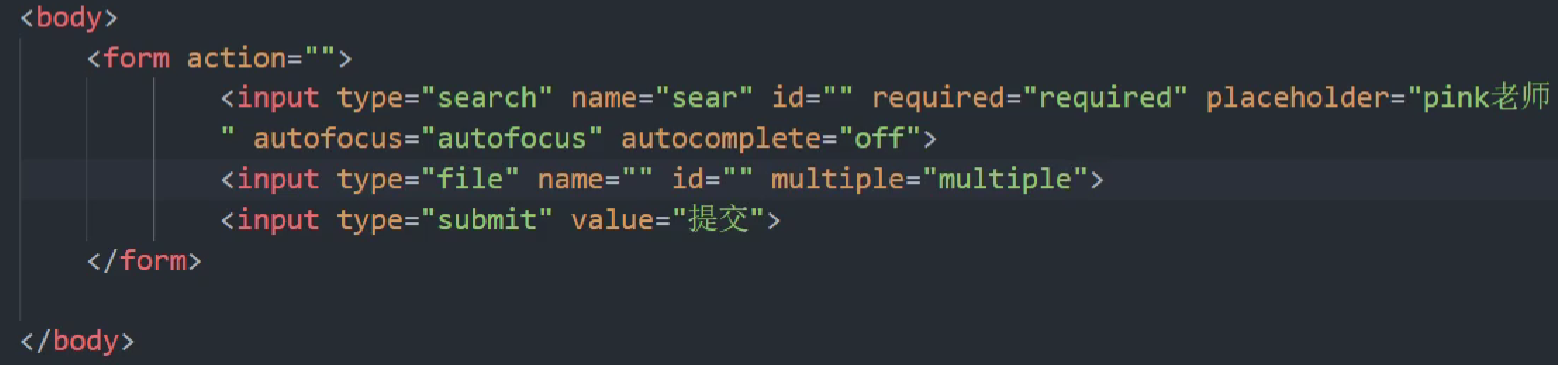

可以通过以下设置方式修改placeholder里面的字体颜色:
input::placeholder {
color: pink;
}
同时注意:search和submit是一对的,这两个都需要在form盒子里面,才能够成为一对。
<form action="">
<input type="search" name="搜索" id="搜索" required="required">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
24 CSS3 新增特性
- 新增的CSS3特性有兼容性问题,ie9+才支持
- 移动端支持优于PC端
24.1 属性选择器

- 通过
属性选择input[id]
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
input[id] { /* 有id属性的input才会被选中 */
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form action="">
<input type="search" name="搜索" id="搜索">
<input type="text" name="搜索" >
</form>
</body>
</html>
- 通过
属性值选择input[type="text"]
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
input[type="text"] { /* type="text"的input才会被选中 */
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form action="">
<input type="search" name="搜索" id="搜索">
<input type="text" name="搜索" >
</form>
</body>
</html>
- 选择属性值
开头/结尾名称相同的标签input[class^=icon]/input[class$=icon]
- 如果想要选取下面前3个text表单,可以使用
^,选择属性值为icon开头的所有元素:
<form action="">
<input type="text" class="icon1">
<input type="text" class="icon2">
<input type="text" class="icon3">
<input type="text" class="lihaile">
</form>
input[class^=icon]
{
background-color: pink;
}
- 使用
$,选择属性值为icon**结尾**的所有元素:
<form action="">
<input type="text" class="1icon">
<input type="text" class="2icon">
<input type="text" class="3icon">
<input type="text" class="lihaile">
</form>
input[class$=icon]
{
background-color: pink;
}
- 选择包含某些元素的属性值
input[class*=icon]
<form action="">
<input type="text" class="1icon1">
<input type="text" class="2icon2">
<input type="text" class="3icon3">
<input type="text" class="lihaile">
</form>
选取前三个元素,使用 input[class*=icon],选择属性值中包含icon的元素:
input[class*=icon] /*此处权重为 标签选择器1+属性选择器10=11*/
{
background-color: pink;
}
注意:类选择器、属性选择器、伪类选择器,权重都是10
24.2 结构伪类选择器
主要根据文档结构来选择某个元素,常用于选择父级选择器里面的某个子元素
24.2.1 选择第n个元素
当遇到这种情况,我们选择里面的某个元素时,使用class会非常麻烦。
<ul>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
</ul>
- 选择里面的第一个元素
li:first-child
ul li:first-child {
background-color: pink;
}
- 选择里面的最后一个元素
li:last-child
ul li:last-child {
background-color: pink;
}
- 选择中间的第几个元素
li:nth-child(3)
ul li:nth-child(3){
background-color: aqua;
}
- 选择里面的所有偶数元素
li:nth-child(even)
ul li:nth-child(even){
background-color: aqua;
}
- 选择里面的所有奇数元素
li:nth-child(odd)
ul li:nth-child(odd){
background-color: aqua;
}
- 依据公式进行选择
li:nth-child(n)
ul li:nth-child(n){
background-color: aqua;
}
这里的变量必须用n来表示,用n来表示公式,如:2n,(2n)^2等,其中,n从0开始增加,每次增加1。

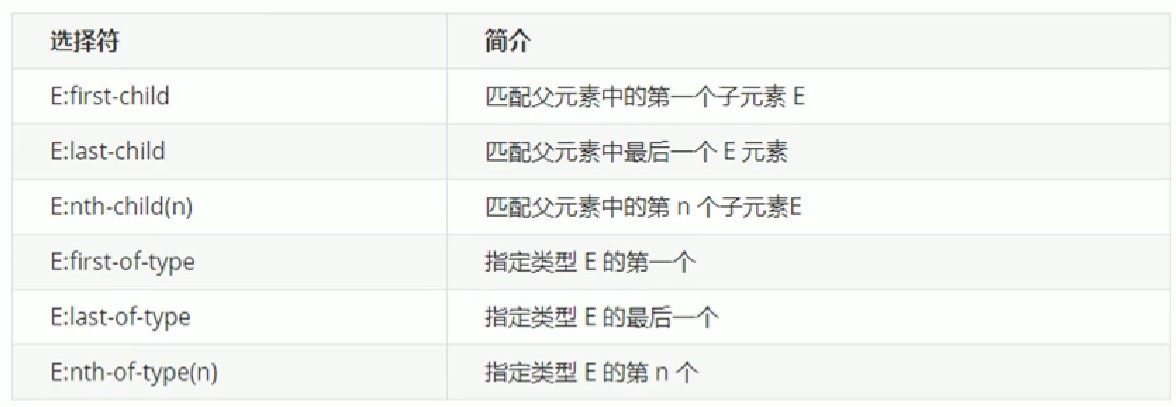
24.2.2 常用的6个结构伪类选择器
- :first-child 得到父元素中的第一个子元素
- :last-child 得到父元素中最后一个子元素
- :nth-child(n) 得到父元素中第n个子元素
- :first-of-type 得到指定类型的第一个子元素
- :last-of-type 得到指定类型的最后一个子元素
- :nth-of-type(n) 得到指定类型的第n个子元素
注意::nth-child(n)和:nth-of-type (n) 的区别:
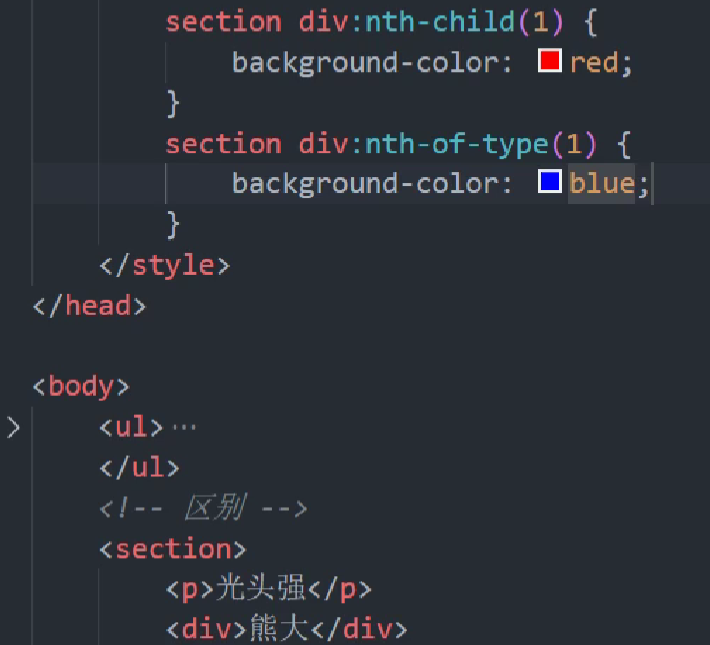
div: nth-child(1)是先从所有子元素中拿到第一个子元素,然后判断是不是div,是则选中,不是则不选。
div: nth-of-type(1)是先拿出父元素中所有的div盒子,然后再选择第一个子div。
24.3 伪元素选择器
当我们想要实现这个小三角
或者实现鼠标放在图片上,图片就会有一个小的遮罩的效果
往常我们是需要给小三角和遮罩一个div,放到html结构中,很麻烦。
现在,可以利用CSS创建新标签元素,而不需要HTML标签,从而简化HTML结构,语法: element::before {}

before和after会创建一个行内元素- 新创建的这个元素在文档树中是找不到的,所以我们称为
伪元素 - before和after必须有
content属性 - before在父元素内容的前面创建元素,after在父元素内容的后面插入元素
伪元素选择器和标签选择器一样,权重为1
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div::before{ /* 权重为1+1=2 */
content: "你";
}
div::after{
content: "猪";
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>是</div>
</body>
</html>
伪元素就是在父级元素里面的前面/后面插入一个行内元素,如上,我们在父级元素的前面插入一个你,在父级元素的后面插入一个猪。
其中伪元素里面必须包含content属性。
24.5 盒子模型
原来的盒子模型:边框和padding都会撑大盒子。
现在:
-
box-sizing: content-box; (默认)
盒子大小为width+padding+border,padding和border会撑开盒子
-
box-sizing: border-box;
盒子大小为width和height,padding和border不会撑开盒子
如下div,最终大小为300*300:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div{
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: aqua;
border: 20px solid black;
padding: 5px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
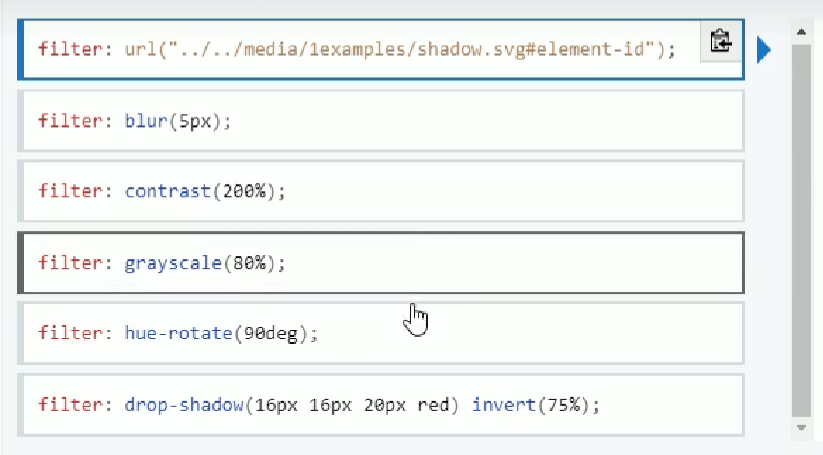
24.6 模糊滤镜 filter:blur(5px);
filter属性:将元素加上模糊/颜色偏移等效果
filter:函数();
filter:blur(5px); blur模糊处理,数值越大越模糊
24.7 calc 函数 calc()
calc() 可以在声明CSS属性值时执行一些计算:
width: calc(100% - 80px);
效果:子盒子永远比父盒子小80像素
注意:括号里面可以使用+- */来计算
24.8 过渡效果 transition: width 1s;
不使用Flash动画和JavaScript就可以实现动画效果(一个样式变化为另一个样式)
transition:变化的属性 花费时间 运动曲线 何时开始
- 变化的属性:如果宽度变化,那么这里就为
width - 花费时间:完成变化所需要的时间
0.5s - 运动曲线:默认为
ease - 何时开始:默认为
0s
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div{
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
transition: width 1s ease 0s;
background-color: blueviolet
}
div:hover{
width: 600px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
我们定义了一个300X300px的紫色盒子,这个盒子加了一个过渡动画:当鼠标放到盒子上时,就将宽度变为600px,执行时间为1s。
注意:过渡一般搭配hover进行使用
如果想要多个属性同时过渡变化,有两种方式:
- ①加逗号
transition: width 1s, height 1s;
- ②直接all
transition: all 1s ease 0s;
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!