LeetCode(94)二叉树的中序遍历?
发布时间:2024年01月11日

给定一个二叉树的根节点?root?,返回?它的?中序?遍历?。
示例 1:
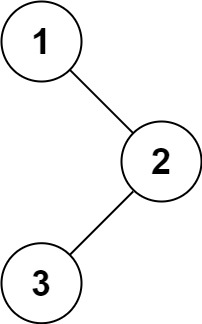
输入:root = [1,null,2,3] 输出:[1,3,2]
示例 2:
输入:root = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1] 输出:[1]
思路1:
递归??
递归的实现就是:每一次递归调用都会把函数的局部变量、参数值和返回地址等压入调用栈中
三要素:递归函数的参数定义和返回值,递归终止条件,单层递归逻辑
在Java中,树的定义
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}中序递归写法:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
inorder(root, ans);
return ans;
}
public void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> ans) {
if (root == null)
return;
inorder(root.left, ans);
ans.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right, ans);
}
}思路2:
迭代
前序遍历顺序:中-左-右,入栈顺序:中-右-左
中序遍历顺序:左-中-右,入栈顺序:左-右
?后序遍历顺序 左-右-中 入栈顺序:中-左-右 出栈顺序:中-右-左, 最后翻转结果
前序迭代
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)
return ans;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
ans.add(node.val);
if (node.right != null)
stack.push(node.right);
if (node.left != null)
stack.push(node.left);
}
return ans;
}
}中序迭代
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)
return ans;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
} else {
cur = stack.pop();
ans.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return ans;
}
}后序迭代方法1最后翻转
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)
return ans;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
ans.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null)
stack.push(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
stack.push(node.right);
}
Collections.reverse(ans);
return ans;
}
}方法2:使用头插法
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
LinkedList<Integer> result = new LinkedList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack();
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
result.addFirst(root.val);
root = root.right;
} else {
root = stack.pop();
root = root.left;
}
}
return result;
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_48590589/article/details/135508640
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 海外 proxy代理Croxyproxy使用教程
- 自学黑客(网络安全),一般人我劝你还是算了吧
- Python集合模块:高效处理数据集合的利器
- darts,一个超强的 Python 库!
- MES系统中的电子看板:真正实现数字化车间可视化
- Redis 缓存与数据库双写不一致如何解决
- 安卓开发--proj4j坐标转换快速上手
- macbook怎么卸载软件,有哪些常用方法
- 卫星接收LNBs的专用电路
- 计算机毕业设计 | SpringBoot+vue的教务管理系统