编译原理 SLR(1)分析技术识别字符串
发布时间:2024年01月05日
- 实验名称
SLR(1)分析技术识别字符串
- 实验目的
- 掌握自底向上语法分析方法的原理
- 编程完成LR分析法
- 实验内容和要求
本实验要求通过已给的SLR(1)分析表,利用LR分析技术实现对输入串的句型分析,具体包括六个部分:
- 设计思路;
- 主函数main;
- SLR(1)分析表的录入;
- 分析栈的设计与实现;
- 用LR分析技术对输入串进行句型分析;
- 输出LR分析过程。
- 实验环境
VS 2022
- 算法设计思想
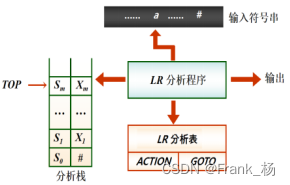
- 分析栈设计:建立两个栈,一个状态栈,一个符号栈。
- LR分析表设计:分为ACTION表和GOTO表处理。ACTION表由于表内存放的为多个不同类型字符,用结构体实现二维数组,结构体内存放两个成员,即两个int型变量,第一个变量option表示移进操作还是归约操作(值为1为s操作,2为r为归约操作,默认为0)。第二个变量state,若为移进则表下一个要到达的状态,若为归约,则表要用到的第几条文法,若为0且option为1,则表accept。GOTO表由于表内只存数值,因此用一个int类型二维数组表示即可。
- 主函数由两个函数和一个用户交互构成,slr_creat函数负责读取终结符集和非终结符集以及SLR表,并将其输出;Analysis函数负责主要分析。主分析过程为使用两个分析栈,在while循环里通过两个分析栈对待分析字符串的交叉同时分析,输出分析过程。
- 详解均在代码里,请自看注释。
- 主要问题与解决方法
问题:分析过程需要输出相关信息,当涉及输出两个分析栈里的信息时,由于无可用函数可以直接从栈底到栈顶将栈元素依次输出,因此需要自行构造一子函数,得以将栈元素按需输出。
解决:构建了两个函数,一个是输出int类栈的state_Printf函数,另一个是输出char类栈的alphebet_Printf函数。 ????????????????????????????????????????????
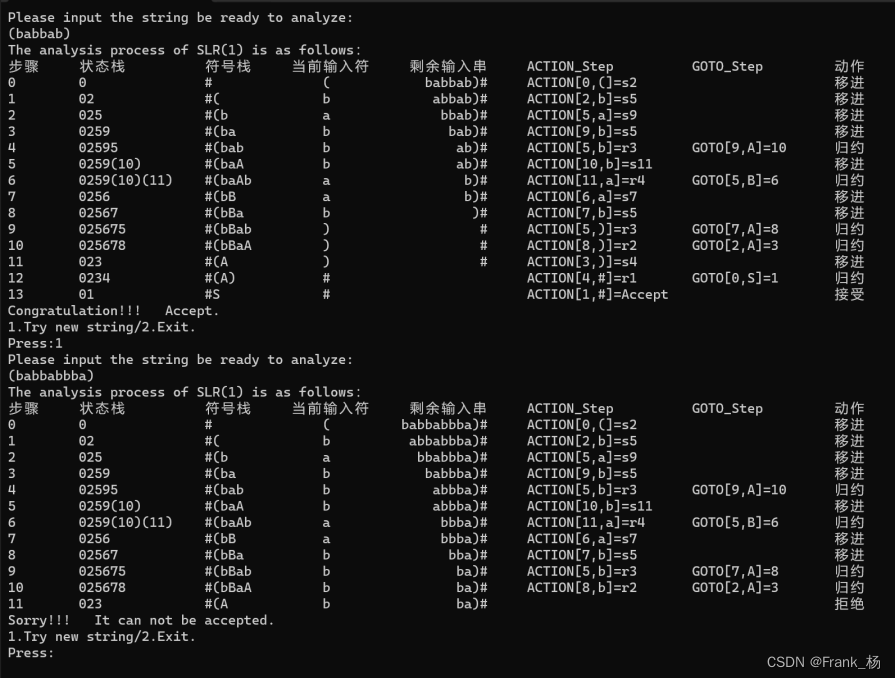
- 实验结果
匹配成功与失败:
- 体会、质疑、建议
代码中的奥妙,其乐无穷!!!
- 源代码
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<iomanip>
#define N 100
using namespace std;
/**************************************全局变量定义**********************************************/
struct
{
int option; //1为s操作,2为r为归约操作,默认为0
int state = -1; //若为移进则表下一个要到达的状态,若为归约,则表要用到的第几条文法,若为0且option为1,则表accept。
}ACTION[N][N],action;
int GOTO[N][N];
string str, VT, VN, Rule[N];
/**************************************函数声明**************************************************/
void slr_creat();
void state_Printf(stack<int>state);
void alphebet_Printf(stack<char>alphebet);
void Analysis();
/**************************************函数区****************************************************/
int main()
{
/********************************主函数实现部分************************************************/
int choice = 0;
slr_creat();
Analysis();
/********************************简单的用户交互设计********************************************/
while (1) {
cout << "1.Try new string/2.Exit." << endl << "Press:";
cin >> choice;
if (choice == 1)Analysis();
else exit(0); //如果选择不是1,则退出系统
}
return 0;
}
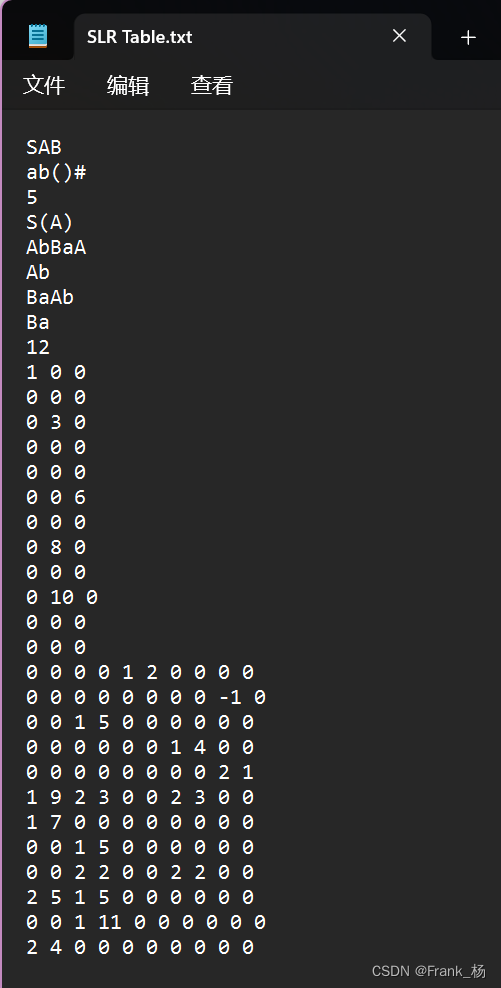
void slr_creat()
{
/********************************SLR表文件读入************************************************/
int sum; //读取个数需求
ifstream f("SLR Table.txt"); //C++读取文件方式:ifstream
getline(f, VN); //整行读入非终结符字符到VN的string类字符串中
getline(f, VT); //整行读入终结符字符到VT的string类字符串中
/********************************SLR表总共分三部分********************************************/
/********************************Rule表:文法表输入,string类一维数组**************************/
f >> sum; //读入文法个数
for (int i = 0;i <= sum;i++)
getline(f, Rule[i]);
/********************************GOTO表读入***************************************************/
f >> sum; //读入状态行数
for (int i = 0;i < sum;i++)
for (int j = 0;j < VN.size();j++)
f >> GOTO[i][j];
/********************************ACTION表读入************************************************/
for(int i=0;i<sum;i++)
for (int j = 0;j < VT.size();j++) {
f >> ACTION[i][j].option; //读入操作
f >> ACTION[i][j].state; //读入转入状态
}
f.close();
}
void Analysis()
{
/********************************主分析过程**************************************************/
int step=0; //步骤
char now_char; //此即为当前输入符
stack<int>state; //定义一个int型状态栈
stack<char>alphebet; //定义一个char型符号栈
/********************************初始化******************************************************/
state.push(0); //初始先对状态栈入0
alphebet.push('#'); //初始先对符号栈入#号
/********************************读取用户待分析字符串****************************************/
cout << "Please input the string be ready to analyze:" << endl;
cin >> str;
str.push_back('#'); //对待分析字符串尾部入个#号,为后期分析做准备
/********************************输出分析过程************************************************/
cout << "The analysis process of SLR(1) is as follows:" << endl;
cout << left << setw(9) << "步骤" << setw(16) << "状态栈" << setw(11) << "符号栈"; //分析表标题部分
cout<< setw(15) << "当前输入符" << setw(15) << "剩余输入串" << setw(21) << "ACTION_Step" << setw(18) << "GOTO_Step" << "动作" << endl;//分析表标题部分
now_char = str.front(); //首先取待分析字符串首字符
str.erase(0, 1); //删去首字符,str.erase(0,1)表示在“0”位置删除“1”个字符
while (1) {
cout << left << setw(9) << step++; //输出步骤
state_Printf(state); //利用state_Printf函数将state栈输出
alphebet_Printf(alphebet); //利用alphebet_Printf函数将alphebet栈输出
cout << setw(4) << "" << left << setw(6) << now_char; //输出当前输入符
cout << right << setw(15) << str<<setw(5)<<""; //输出当前剩余待分析字符串
if (VT.find(now_char) > VT.size()) { //如果如果当前输入字符找不到,则报错,输出该字符无法识别,
cout << now_char << "无法识别" << endl; //VT.find()如果找不到当前字符,则会返回一个很大的数,这里便用大于size()来判断该字符是否存在
break; //break退出Analysis函数
}
action = ACTION[state.top()][VT.find(now_char)]; //为避免分析复杂,用单变量action取值得ACTION[state.top()][VT.find(now_char)],然后方便做分析
/********************************做移进操作********************************************************************************************************/
if (action.option==1) { //option表操作,1表示s操作,即移进操作
if (!action.state) { //这里我将Accept的option也置为1,且state置为0,因此这里做判断,看是否到达结束分析
cout << "ACTION[" << state.top() << "," << now_char << "]=Accept" << setw(21) << ""<<"接受"<<endl;//如果是0,接受
cout << "Congratulation!!! Accept." << endl;
break;
}
cout << "ACTION[" << state.top() << "," << now_char << "]=s" << action.state; //输出ACTION步骤,ACTION占用6+10+5=21位(格式)
if (state.top() > 9 && action.state > 9)cout << setw(5) << ""; //这几个判断是为了格式对齐
else if (state.top() > 9 || action.state > 9)cout << setw(6) << ""; //
else cout << setw(7) << ""; //
state.push(action.state); //移进操作,因此状态栈入新状态,即当前action.state
alphebet.push(now_char); //同样符号栈也入掉当前字符,然后取新字符
now_char = str.front(); //从待分析字符串首位取新的当前字符
str.erase(str.begin()); //取完之后,将首位字符删除
cout << setw(18) << ""; //移进操作中,无GOTO步骤输出
cout << "移进" << endl; //输出“移进”,进入下一行分析
}
/********************************做归约操作********************************************************************************************************/
else if(action.option==2){ //option表操作,2表示r操作,即归约操作
int k = 7; //对齐格式需要,引进一个k值,并无其他用处
cout << "ACTION[" << state.top() << "," << now_char << "]=r" << action.state; //正常输出ACTION步骤,ACTION占用6+10+5=21位(格式)
if (state.top() > 9 && action.state > 9)cout << setw(5) << ""; //同样,这几个判断是为了格式对齐
else if (state.top() > 9 || action.state > 9)cout << setw(6) << ""; //
else cout << setw(7) << ""; //
for (int i = 1;i < Rule[action.state].size();i++) { //归约,利用单条文法大小个数对状态栈,符号栈进行精确出栈
alphebet.pop(); //符号栈出栈操作
state.pop(); //状态栈出栈操作
} //上下无关文法,文法左部必定是一个非终结符
alphebet.push(Rule[action.state].front()); //将文法首字符,即归约的最终非终结符
cout << "GOTO[" << state.top() << "," << alphebet.top() << "]="; //state入新状态之前,输出GOTO表等号前半部分
if (state.top() > 9)k--; //对齐格式需求,因为大于10,输出就会多占一位,因此k--
state.push(GOTO[state.top()][VN.find(alphebet.top())]); //此时输出GOTO表前半部分之后,对state栈入新状态
if (state.top() > 9)k--; //同样对齐格式需求,因为大于10,输出就会多占一位,因此k--
cout << state.top(); //输出GOTO表等号后半部分,等号前后state.top()不一样,得前后分开输出
cout << setw(k) << ""; //格式对齐输出
cout << "归约" << endl; //输出“归约”,进入下一行分析
}
/********************************做报错操作********************************************************************************************************/
else {
cout << right<<setw(43)<<"拒绝" << endl;
cout << "Sorry!!! It can not be accepted." << endl;
break;
}
}
}
void state_Printf(stack<int>state) //由于栈无法直接输出,因此构造此函数
{
/********************************状态栈输出函数************************************************/
vector<int>state_lite; //利用一个vector动态数组
while (!state.empty()) { //采用表头插入,在形参栈state空之前,依次插入数组state_lite
state_lite.insert(state_lite.begin(), state.top()); //.insert(state_lite.begin(), state.top())表示在“state_lite.begin()”位置插入“state.top()”,state_lite.begin()是一个迭代器
state.pop(); //插入一个,state出栈一个
}
int sum = (int )state_lite.size(); //为了格式对齐需求,引进sum
for (vector<int>::iterator i = state_lite.begin();i != state_lite.end();i++)//利用vector迭代器i,依次将state_lite数组遍历输出
if (*i < 10)cout << *i; //如果小于10,则正常输出
else { //如果大于10,则需要括号,因此这里做特别处理
cout << "(" << *i << ")"; //加括号输出
sum += 3; //格式需求,两个括号加2位,两位数比一位数多一位,因此加3位
} //
cout << setw(16 - sum) << ""; //做格式对齐输出
}
void alphebet_Printf(stack<char>alphebet) //由于栈无法直接输出,因此构造此函数
{
/********************************字符栈输出函数************************************************/
string alphebet_lite; //利用一个string类字符串alphebet_lite
while (!alphebet.empty()) { //利用表头插入法,将形参alphebet的栈顶元素依次入alphebet_lite字符串
alphebet_lite.insert(alphebet_lite.begin(), alphebet.top()); //解释同上state_lite.insert
alphebet.pop(); //插入一个,出栈一个
} //
cout << left << setw(11) << alphebet_lite; //格式对齐直接输出string字符串alphebet_lite
}样例识别字符串:(babbab)
样例SLR表:
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/Frank_Yy03Aug/article/details/135387199
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- thinkadmin表单上传单图,多图,单文件,多文件
- android悬浮窗气泡点击穿透事件
- flink operator 拉取阿里云私有镜像(其他私有类似)
- springboot/java/php/node/python高校重点学科建设管理系统【计算机毕设】
- java数据结构与算法刷题-----LeetCode378. 有序矩阵中第 K 小的元素
- Y9000P + ubuntu22.04 配置Anaconda+pycharm +pytorch
- 24、文件上传漏洞——Apache文件解析漏洞
- IPFoxy运营干货|谷歌广告Google Ads建立广告需要注意什么?
- Oracle中的dblink简介
- Android获取电池充电状态是否为快充