树定义及遍历
发布时间:2024年01月09日
1、定义树
可以参考链表,链表遍历不方便,如果单链表有多个next指针,则就形成了树。
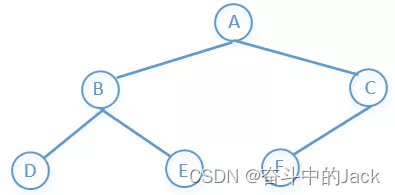
Java:
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left, right;
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}Python:
class TreeNode(object):
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left, self.right = None, NoneC++:
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(null), right(null) {}
};C:
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
};?2、树的遍历
-
前序遍历:根节点→左子树→右子树

-
中序遍历:左子树→根节点→右子树

-
后序遍历:左子树→右子树→根节点

-
BFS(广度优先搜索):先访问上一层,在访问下一层,一层一层的往下访问

-
DFS(深度优先搜索):先访根节点,然后左结点,一直往下,直到最左结点没有子节点的时候然后往上退一步到父节点,然后父节点的右子节点在重复上面步骤……

代码:
1)Python前序、中序、后序遍历:
def preorder(self, root):
if root:
self.traverse_path.append(root.val);
self.preorder(root.left);
self.preorder(root.right);
def inorder(self, root):
if root:
self.preorder(root.left);
self.traverse_path.append(root.val);
self.preorder(root.right);
def postorder(self, root):
if root:
self.preorder(root.left);
self.preorder(root.right);
self.traverse_path.append(root.val);2)Java遍历:
前序遍历:
// 递归
public static void preOrder(TreeNode tree) {
if (tree == null)
return;
System.out.printf(tree.val + "");
preOrder(tree.left);
preOrder(tree.right);
}
// 非递归
public static void preOrder(TreeNode tree) {
if (tree == null) return;
Stack<TreeNode> q1 = new Stack<>();
q1.push(tree);//压栈
while (!q1.empty()) {
TreeNode t1 = q1.pop();//出栈
System.out.println(t1.val);
if (t1.right != null) {
q1.push(t1.right);
}
if (t1.left != null) {
q1.push(t1.left);
}
}
}中序遍历:
// 递归
public static void inOrder(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return;
inOrder(node.left);
System.out.println(node.val);
inOrder(node.right);
}
// 非递归
public static void inOrder(TreeNode tree) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while (tree != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (tree != null) {
stack.push(tree);
tree = tree.left;
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
tree = stack.pop();
System.out.println(tree.val);
tree = tree.right;
}
}
}后序遍历:
// 递归
public static void postOrder(TreeNode tree) {
if (tree == null) return;
postOrder(tree.left);
postOrder(tree.right);
System.out.println(tree.val);
}
// 非递归
public static void postOrder(TreeNode tree) {
if (tree == null)
return;
Stack<TreeNode> s1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<TreeNode> s2 = new Stack<>();
s1.push(tree);
while (!s1.isEmpty()) {
tree = s1.pop();
s2.push(tree);
if (tree.left != null) {
s1.push(tree.left);
}
if (tree.right != null) {
s1.push(tree.right);
}
}
while (!s2.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(s2.pop().val + " ");
}
}
public static void postOrder(TreeNode tree) {
if (tree == null)
return;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(tree);
TreeNode c;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
c = stack.peek();
if (c.left != null && tree != c.left && tree != c.right) {
stack.push(c.left);
} else if (c.right != null && tree != c.right) {
stack.push(c.right);
} else {
System.out.print(stack.pop().val + " ");
tree = c;
}
}
}BFS(广度优先搜索):
// 递归
public static void levelOrder(TreeNode tree) {
int depth = depth(tree);
for (int level = 0; level < depth; level++) {
printLevel(tree, level);
}
}
private static int depth(TreeNode tree) {
if (tree == null) return 0;
int leftDepth = depth(tree.left);
int rightDepth = depth(tree.right);
return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
private static void printLevel(TreeNode tree, int level) {
if (tree == null) return;
if (level == 0) {
System.out.print(" " + tree.val);
} else {
printLevel(tree.left, level - 1);
printLevel(tree.right, level - 1);
}
}
// 非递归
public static void levelOrder1(TreeNode tree) {
if (tree == null) return;
LinkedList<TreeNode> list = new LinkedList<>(); // 链表,可以把它看做队列
list.add(tree); // 相当于把数据加入到队列尾部
while (!list.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = list.poll(); // poll方法相当于移除队列头部的元素
System.out.println(node.val);
if (node.left != null) list.add(node.left);
if (node.right != null) list.add(node.right);
}
}
// 结果存放到list中
public static List<List<Integer>> levelOrder2(TreeNode tree) {
if (tree == null)
return null;
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
bfs(tree, 0, list);
return list;
}
private static void bfs(TreeNode tree, int level, List<List<Integer>> list) {
if (tree == null)
return;
if (level >= list.size()) {
List<Integer> subList = new ArrayList<>();
subList.add(tree.val);
list.add(subList);
} else {
list.get(level).add(tree.val);
}
bfs(tree.left, level + 1, list);
bfs(tree.right, level + 1, list);
}DFS(深度优先搜索):
// 递归
public static void treeDFS(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
System.out.println(root.val);
treeDFS(root.left);
treeDFS(root.right);
}
// 非递归
public static void treeDFS1(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.add(root);
while (!stack.empty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
System.out.println(node.val);
if (node.right != null) {
stack.push(node.right);
}
if (node.left != null) {
stack.push(node.left);
}
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38304915/article/details/135491167
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- vue-cli-service requires Node ^12.0.0 || >= 14.0.0
- 《Kotlin核心编程》笔记:反射、注解和加锁
- 【docker】安装 CentOS
- ATA-2081高压放大器在超声切割磨削中的具体应用
- 【Kubernetes】kubectl 常用命令
- 【ModelScope】部署一个属于自己的AI服务
- el-dialog嵌套使用,只显示遮罩层的问题
- 苍穹外卖Day01——解决总结1中存在的问题
- 【基础篇】二、字节码文件的组成 && Arthas + jclasslib +javap
- 【揭秘APT攻击】——内网渗透实战攻略,带你领略网络安全的绝密世界!