【Python学习】Python学习20- 面向对象(2)
发布时间:2024年01月17日

目录
文章所属专区 Python学习
前言
本章节主要说明Python的面向对象的处理。
类的继承
通过继承创建的新类称为子类或派生类,被继承的类称为基类、父类或超类
语法:
class 派生类名(基类名)
...
特点
1、如果在子类中需要父类的构造方法就需要显式的调用父类的构造方法,或者不重写父类的构造方法。详细说明可查看:
python 子类继承父类构造函数说明 。
2、在调用基类的方法时,需要加上基类的类名前缀,且需要带上 self 参数变量。区别在于类中调用普通函数时并不需要带上 self 参数
3、Python 总是首先查找对应类型的方法,如果它不能在派生类中找到对应的方法,它才开始到基类中逐个查找。(先在本类中查找调用的方法,找不到才去基类中找)。
实例
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
class Parent:
parentParam = 0
def __init__(self):
#父类构造函数
self.name = "parent"
self.age = 18
def parentMethod(self):
print "parent method"
def setParam(self,param):
Parent.parentParam = param
def getParam(self):
print "父类属性:",Parent.parentParam
class Child(Parent):
def __init__(self):
print "child __init__"
def childMethod(self):
print "child method"
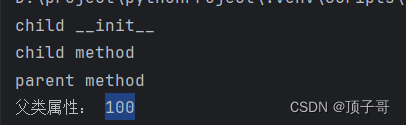
c = Child() #实例化子类Child
c.childMethod() #调用子类方法
c.parentMethod() #调用父类方法
c.setParam(100) #调用父类方法设置参数
c.getParam() #用父类方法获取参数
方法重写
如果你的父类方法的功能不能满足你的需求,你可以在子类重写你父类的方法:
def parentMethod(self, param):
print "子类重写父类方法 获取子类参数:",param
c.parentMethod(1) #调用重写后的父类方法
基础重载方法
#!/usr/bin/python
class Vector:
def __init__(self, a, b):
self.a = a
self.b = b
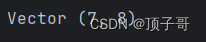
def __str__(self):
return 'Vector (%d, %d)' % (self.a, self.b)
def __add__(self,other):
return Vector(self.a + other.a, self.b + other.b)
v1 = Vector(2,10)
v2 = Vector(5,-2)
print v1 + v2
参考
给个三连吧 谢谢谢谢谢谢了

文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43238568/article/details/135660382
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 【三维分割】SAGA:Segment Any 3D Gaussians
- GitEE-GitHub实现加速访问与下载项目
- C++day6作业
- 惰性加载函数(js的问题)
- mybatis的生命周期
- 【Python 千题 —— 基础篇】元组的不可修改性
- CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES:控制在固定的某些设备上运行Python程序
- R语言下载安装及VScode配置
- springBoot如何动态切换数据源
- 3. SQL - 查询