代码随想录算法训练营第27天 | 39. 组合总和 40.组合总和II 131.分割回文串
目录
39. 组合总和
给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
说明:
- 所有数字(包括 target)都是正整数。
- 解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
- 输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7,
- 所求解集为: [ [7], [2,2,3] ]
示例 2:
- 输入:candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8,
- 所求解集为: [ [2,2,2,2], [2,3,3], [3,5] ]
💡解题思路
本题搜索的过程抽象成树形结构如下:
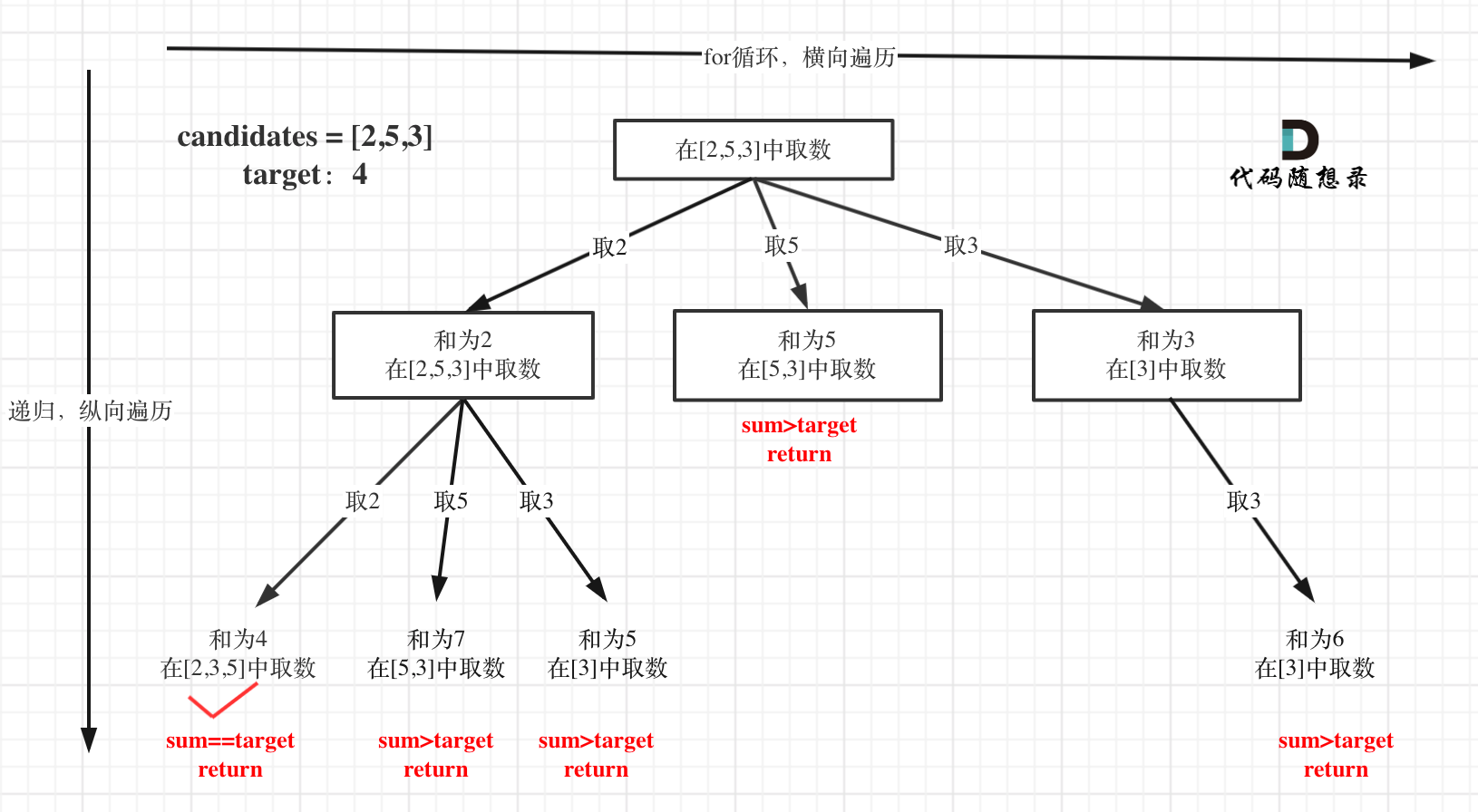
注意图中叶子节点的返回条件,因为本题没有组合数量要求,仅仅是总和的限制,所以递归没有层数的限制,只要选取的元素总和超过target,就返回!
💻实现代码
// 剪枝优化
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(candidates); // 先进行排序
backtracking(res, new ArrayList<>(), candidates, target, 0, 0);
return res;
}
public void backtracking(List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> path, int[] candidates, int target, int sum, int idx) {
// 找到了数字和为 target 的组合
if (sum == target) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = idx; i < candidates.length; i++) {
// 如果 sum + candidates[i] > target 就终止遍历
if (sum + candidates[i] > target) break;
path.add(candidates[i]);
backtracking(res, path, candidates, target, sum + candidates[i], i);
path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯,移除路径 path 最后一个元素
}
}
}
40.组合总和II
给定一个数组?candidates?和一个目标数?target?,找出?candidates?中所有可以使数字和为?target?的组合。
candidates?中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
说明: 所有数字(包括目标数)都是正整数。解集不能包含重复的组合。
- 示例?1:
- 输入: candidates =?[10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target =?8,
- 所求解集为:
[
[1, 7],
[1, 2, 5],
[2, 6],
[1, 1, 6]
]
- 示例?2:
- 输入: candidates =?[2,5,2,1,2], target =?5,
- 所求解集为:
[
? [1,2,2],
? [5]
]
💡解题思路
这道题目和39.组合总和如下区别:
- 本题candidates?中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
- 本题数组candidates的元素是有重复的,而39.组合总和是无重复元素的数组candidates
本题的难点在于区别2中:集合(数组candidates)有重复元素,但还不能有重复的组合。
- 递归函数参数
(opens new window)套路相同,此题还需要加一个bool型数组used,用来记录同一树枝上的元素是否使用过。
这个集合去重的重任就是used来完成的。
代码如下:
vector<vector<int>> result; // 存放组合集合
vector<int> path; // 符合条件的组合
void backtracking(vector<int>& candidates, int target, int sum, int startIndex, vector<bool>& used) {
- 递归终止条件
(opens new window)相同,终止条件为 sum > target 和 sum == target。
代码如下:
if (sum > target) { // 这个条件其实可以省略
return;
}
if (sum == target) {
result.push_back(path);
return;
}
sum > target 这个条件其实可以省略,因为在递归单层遍历的时候,会有剪枝的操作,下面会介绍到。
- 单层搜索的逻辑
这里与39.组合总和
(opens new window)最大的不同就是要去重了。
前面我们提到:要去重的是“同一树层上的使用过”,如何判断同一树层上元素(相同的元素)是否使用过了呢。
如果candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] 并且 used[i - 1] == false,就说明:前一个树枝,使用了candidates[i - 1],也就是说同一树层使用过candidates[i - 1]。
此时for循环里就应该做continue的操作。
这块比较抽象,如图:

我在图中将used的变化用橘黄色标注上,可以看出在candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]相同的情况下:
- used[i - 1] == true,说明同一树枝candidates[i - 1]使用过
- used[i - 1] == false,说明同一树层candidates[i - 1]使用过
可能有的录友想,为什么 used[i - 1] == false 就是同一树层呢,因为同一树层,used[i - 1] == false 才能表示,当前取的 candidates[i] 是从 candidates[i - 1] 回溯而来的。
而 used[i - 1] == true,说明是进入下一层递归,去下一个数,所以是树枝上,如图所示:
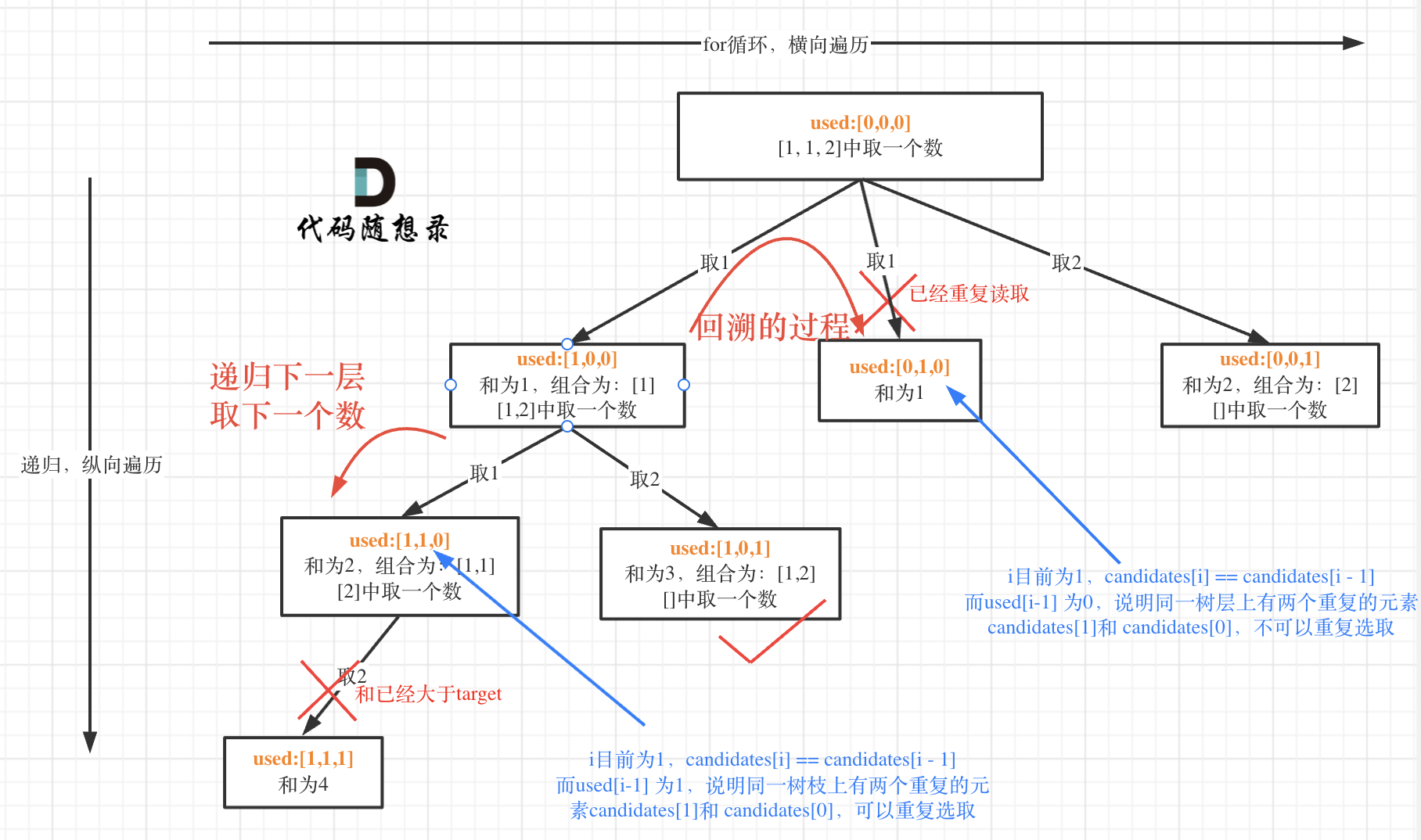
这块去重的逻辑很抽象,网上搜的题解基本没有能讲清楚的,如果大家之前思考过这个问题或者刷过这道题目,看到这里一定会感觉通透了很多!
那么单层搜索的逻辑代码如下:
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.size() && sum + candidates[i] <= target; i++) {
// used[i - 1] == true,说明同一树枝candidates[i - 1]使用过
// used[i - 1] == false,说明同一树层candidates[i - 1]使用过
// 要对同一树层使用过的元素进行跳过
if (i > 0 && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false) {
continue;
}
sum += candidates[i];
path.push_back(candidates[i]);
used[i] = true;
backtracking(candidates, target, sum, i + 1, used); // 和39.组合总和的区别1:这里是i+1,每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次
used[i] = false;
sum -= candidates[i];
path.pop_back();
}
💻实现代码
使用标记数组
class Solution {
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] used;
int sum = 0;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
used = new boolean[candidates.length];
// 加标志数组,用来辅助判断同层节点是否已经遍历
Arrays.fill(used, false);
// 为了将重复的数字都放到一起,所以先进行排序
Arrays.sort(candidates);
backTracking(candidates, target, 0);
return ans;
}
private void backTracking(int[] candidates, int target, int startIndex) {
if (sum == target) {
ans.add(new ArrayList(path));
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (sum + candidates[i] > target) {
break;
}
// 出现重复节点,同层的第一个节点已经被访问过,所以直接跳过
if (i > 0 && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] && !used[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
used[i] = true;
sum += candidates[i];
path.add(candidates[i]);
// 每个节点仅能选择一次,所以从下一位开始
backTracking(candidates, target, i + 1);
used[i] = false;
sum -= candidates[i];
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
不使用标记数组
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
int sum = 0;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2( int[] candidates, int target ) {
//为了将重复的数字都放到一起,所以先进行排序
Arrays.sort( candidates );
backTracking( candidates, target, 0 );
return res;
}
private void backTracking( int[] candidates, int target, int start ) {
if ( sum == target ) {
res.add( new ArrayList<>( path ) );
return;
}
for ( int i = start; i < candidates.length && sum + candidates[i] <= target; i++ ) {
//正确剔除重复解的办法
//跳过同一树层使用过的元素
if ( i > start && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] ) {
continue;
}
sum += candidates[i];
path.add( candidates[i] );
// i+1 代表当前组内元素只选取一次
backTracking( candidates, target, i + 1 );
int temp = path.getLast();
sum -= temp;
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
131.分割回文串
给定一个字符串 s,将 s 分割成一些子串,使每个子串都是回文串。
返回 s 所有可能的分割方案。
示例: 输入:?"aab" 输出: [ ["aa","b"], ["a","a","b"] ]
💡解题思路
本题这涉及到两个关键问题:
- 切割问题,有不同的切割方式
- 判断回文
切割问题,也可以抽象为一棵树形结构,如图:

递归用来纵向遍历,for循环用来横向遍历,切割线(就是图中的红线)切割到字符串的结尾位置,说明找到了一个切割方法。
- 递归函数参数
全局变量数组path存放切割后回文的子串,二维数组result存放结果集。 (这两个参数可以放到函数参数里)
本题递归函数参数还需要startIndex,因为切割过的地方,不能重复切割,和组合问题也是保持一致的。
代码如下:
vector<vector<string>> result;
vector<string> path; // 放已经回文的子串
void backtracking (const string& s, int startIndex) {
- 递归函数终止条件

从树形结构的图中可以看出:切割线切到了字符串最后面,说明找到了一种切割方法,此时就是本层递归的终止条件。
那么在代码里什么是切割线呢?
在处理组合问题的时候,递归参数需要传入startIndex,表示下一轮递归遍历的起始位置,这个startIndex就是切割线。
所以终止条件代码如下:
void backtracking (const string& s, int startIndex) {
// 如果起始位置已经大于s的大小,说明已经找到了一组分割方案了
if (startIndex >= s.size()) {
result.push_back(path);
return;
}
}
- 单层搜索的逻辑
来看看在递归循环中如何截取子串呢?
在for (int i = startIndex; i < s.size(); i++)循环中,我们 定义了起始位置startIndex,那么 [startIndex, i] 就是要截取的子串。
首先判断这个子串是不是回文,如果是回文,就加入在vector<string> path中,path用来记录切割过的回文子串。
代码如下:
for (int i = startIndex; i < s.size(); i++) {
if (isPalindrome(s, startIndex, i)) { // 是回文子串
// 获取[startIndex,i]在s中的子串
string str = s.substr(startIndex, i - startIndex + 1);
path.push_back(str);
} else { // 如果不是则直接跳过
continue;
}
backtracking(s, i + 1); // 寻找i+1为起始位置的子串
path.pop_back(); // 回溯过程,弹出本次已经添加的子串
}
注意切割过的位置,不能重复切割,所以,backtracking(s, i + 1); 传入下一层的起始位置为i + 1。
# 判断回文子串
最后我们看一下回文子串要如何判断了,判断一个字符串是否是回文。
可以使用双指针法,一个指针从前向后,一个指针从后向前,如果前后指针所指向的元素是相等的,就是回文字符串了。
那么判断回文的C++代码如下:
bool isPalindrome(const string& s, int start, int end) {
for (int i = start, j = end; i < j; i++, j--) {
if (s[i] != s[j]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
💻实现代码
class Solution {
List<List<String>> res =new ArrayList<>();
Deque<String> deque=new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
backtracking(s,0);
return res;
}
private void backtracking(String s,int index){
if(index>=s.length()){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(deque));
return;
}
for(int i=index;i<s.length();i++){
if(isHuiwen(s,index,i)){
String str=s.substring(index,i+1);
deque.addLast(str);
}else{
continue;
}
backtracking(s,i+1);
deque.removeLast();
}
}
private boolean isHuiwen(String s,int index,int end){
for(int i=index, j=end;i<j;i++,j--){
if(s.charAt(i)!=s.charAt(j)){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 太原理工大学javaee程序修改题
- 适用于电脑的 10 款最佳文件恢复软件
- 介绍 Apache Spark 的基本概念和在大数据分析中的应用。
- 网络安全事件分级指南
- Java的继承和实现、接口和抽象类,它们的区别?
- 深入理解JVM虚拟机第三十八篇:JVM中OOM的说明和举例
- SDRAM小项目(1)
- 如何用表情捕捉技术,赋予虚拟角色真实面部细节?
- Java中List转Map的几种方式
- 山区老人爱的礼物丨走进武隆区土地乡为山区老人送温暖