Yjs学习
Yjs学习
YJS介绍
Yjs 是一个用于实现实时协同编辑的开源框架,它基于 CRDT(Conflict-free Replicated Data Type)算法,可以让多个用户在同时编辑一个文档或数据结构时进行协同操作,而不会出现冲突或数据丢失。
Yjs 实现协同编辑的关键在于以下几个方面:
- 数据结构:Yjs 提供了一系列的 CRDT 数据类型,如 YArray、YMap、YText 等,这些数据类型能够在不同用户之间实现协同编辑,保证最终收敛到一致的状态。
- 更新传播:当一个用户对文档进行编辑时,Yjs 会将编辑操作转换成一系列的数据更新,并使用网络传输协议(如 WebSockets 或 WebRTC)将这些更新传播给其他参与协同编辑的用户。
- 同步策略:Yjs 提供了多种同步策略,包括基于共享状态、基于事件等,可以根据应用场景和网络环境选择合适的同步策略,以保证数据同步的效率和稳定性。
包括yjs核心库、yjs-protocols,yjs-websocket三个主要的库
-
yjs核心库:实现了CRDT协同算法,提供了一系列的 CRDT 数据类型,如 YArray、YMap、YText 等,这些数据类型能够在不同用户之间实现协同编辑,保证最终收敛到一致的状态
-
yjs-protocols:主要负责定义协同编辑消息的格式、数据序列化和反序列化,确保消息的正确传输和解释;以及用户状态。包含下面三个类文件
- sync:Sync 类文件定义了 Yjs 协同编辑过程中的数据同步协议。它负责定义了消息格式、数据的序列化和反序列化,以及在客户端之间同步数据的过程。
消息格式定义:定义了协同编辑过程中客户端之间交换的消息的格式,包括不同类型的操作(如插入、删除、格式变更等)的表示方法,以及消息头部的标识和元数据信息的定义。 序列化与反序列化:实现了将 Yjs 的数据类型(如 YArray、YMap、YText 等)序列化为消息,以及将从消息中解析出的操作反序列化为对应的数据类型操作。 数据同步:定义了客户端之间如何交换消息,以进行数据同步。这包括了在客户端 A 对文档进行操作后如何将操作封装成消息,并发送给其他客户端,以及其他客户端如何解析消息并根据消息更新自己的数据。 - Awareness:Awareness 类文件定义了用于跟踪用户状态和用户操作的协议。它负责维护一个用户状态的列表,用于展示所有参与协同编辑的用户,在编辑过程中可以展示其他用户的光标位置、聚焦位置、在线状态等信息。
- Auth:Auth 类文件定义了 Yjs 协同编辑中的用户认证和权限控制的协议。在实际的应用场景中,可能需要对用户进行认证,以及根据用户的身份和权限控制用户对文档的编辑和访问。Auth 模块定义了在协同编辑过程中进行用户认证和权限控制的相关协议和机制。
- sync:Sync 类文件定义了 Yjs 协同编辑过程中的数据同步协议。它负责定义了消息格式、数据的序列化和反序列化,以及在客户端之间同步数据的过程。
-
yjs-websocket 是 Yjs 框架中用于 WebSocket 通信的插件库。它提供了在 WebSocket 连接上发送和接收消息的逻辑,以便在客户端之间进行协同编辑时进行实时通信。yjs-websocket 的作用是在 Yjs 框架中实现了 WebSocket 的传输层,使得多个客户端能够通过 WebSocket 进行实时通信,从而在协同编辑过程中进行数据同步和消息传递。
yjs-websocket会通过this.doc.on('update', this._updateHandler)监听共享数据的变化,并再updateHandler中将变化的事件通过broadcastMessage发送到远程服务器或其他客户端
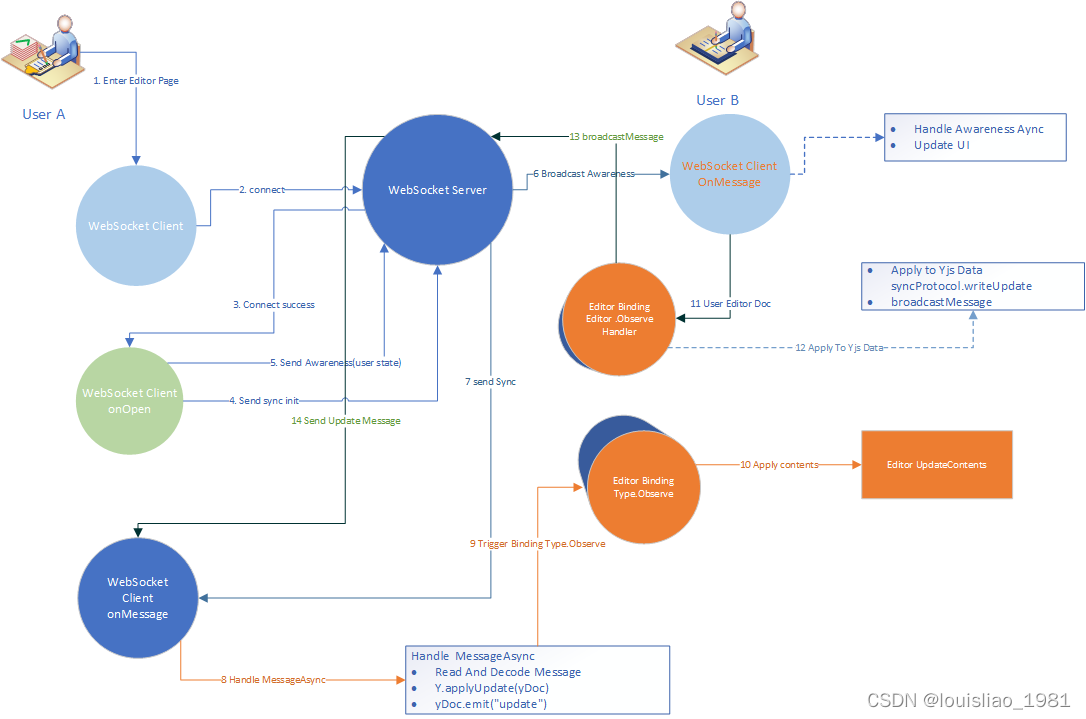
协作流程图
基本用法
import * as Y from 'yjs';
function onSync(doc1: Y.Doc, doc2: Y.Doc) {
console.log('\n同步前的两个文档');
console.log('doc1:', doc1.getArray('shared_array').toArray());
console.log('doc2:', doc2.getArray('shared_array').toArray());
// 将 doc1 的状态转换为更新,并应用于 doc2
console.log("将 doc1 的状态转换为更新")
const update1 = Y.encodeStateAsUpdate(doc1);
console.log("将更新应用到doc2中")
Y.applyUpdate(doc2, update1);
// 将 doc2 的状态转换为更新,并应用于 doc1
console.log("将 doc2 的状态转换为更新")
const update2 = Y.encodeStateAsUpdate(doc2);
console.log("将更新应用到doc1中")
Y.applyUpdate(doc1, update2);
// 检查同步后两个文档的状态
console.log('\n同步后的两个文档');
console.log('doc1:', doc1.getArray('shared_array').toArray());
console.log('doc2:', doc2.getArray('shared_array').toArray());
}
// 创建两个 Yjs 文档 (doc1 和 doc2)
const doc1 = new Y.Doc();
const sharedArray1 = doc1.getArray('shared_array');
sharedArray1.insert(0, ['A']);
const doc2 = new Y.Doc();
const sharedArray2 = doc2.getArray('shared_array');
sharedArray2.insert(0, ['B']);
// 将两个文档同步前的状态打印
onSync(doc1, doc2);
// 添加新元素到 doc1
sharedArray1.insert(1, ['C']);
// 为了模拟并发更新,同时将新元素添加到 doc2
sharedArray2.insert(1, ['D']);
sharedArray1.observe(event => {
// Log a delta every time the type changes
// Learn more about the delta format here: https://quilljs.com/docs/delta/
console.log('sharedArray1变化:', event.changes.delta)
})
sharedArray2.observe(event => {
// Log a delta every time the type changes
// Learn more about the delta format here: https://quilljs.com/docs/delta/
console.log('sharedArray2变化:', event.changes.delta)
})
doc1.on("update", (update: Uint8Array, origin: any, doc: Y.Doc, trans: Y.Transaction) => {
//decodeUpdate会解析更新的数据成一个JSON数据,里面包含structs和ds两个key
//structs
const decodeInfo = Y.decodeUpdate(update);
console.log("doc1变化")
console.log("structs", decodeInfo.structs);
console.log("DeleteSet", decodeInfo.ds);
})
// 将两个文档的并发更改同步并打印状态
onSync(doc1, doc2);
DOC事件和事务
事件API
# The event handler is called right before every transaction.
doc.on('beforeTransaction', function(tr: Transaction, doc: Y.Doc))
# The event handler is called right before observers on shared types are called.
doc.on('beforeObserverCalls', function(tr: Transaction, doc: Y.Doc))
# The event handler is called right after every transaction.
doc.on('afterTransaction', function(tr: Transaction, doc: Y.Doc))
#Listen to update messages on the shared document
doc.on('update', function(update: Uint8Array, origin: any, doc: Y.Doc, tr: Transaction))
# (另一种更新数据格式,效率更高,但还处于初级验证阶段,不能用于生产环境)
doc.on('updateV2', function(update: Uint8Array, origin: any, doc: Y.Doc, tr: Transaction))
# Event is triggered when subdocuments are added/removed or loaded. See Subdocuments on how this event can be used.
doc.on('subdocs', function(changes: { loaded: Set<Y.Doc>, added: Set<Y.Doc>, removed: Set<Y.Doc> }))
# The event handler is called just before the Y.Doc is destroyed. Bindings and providers should listen to this event and destroy themselves when the event is called.
doc.on('destroy', function(doc: Y.Doc))
文档更新事件执行顺序
在 Yjs 中,所有的更改(包括添加、删除和更新)都是在一个事务(y.transact(()=>{..}))中进行(utils/Transaction.js)的。在 Yjs 中,事件被调用的顺序如下:
ydoc.on('beforeTransaction', event => { .. })
The transaction is executed.
ydoc.on('beforeObserverCalls', event => {})
ytype.observe(event => { .. })
ytype.observeDeep(event => { .. })
ydoc.on('afterTransaction', event => {})
ydoc.on('update', update => { .. })
以上的事件都是通过Transaction.js中的transact方法中通过doc.emit(‘xxxxx’)后,就可收到通知;在cleanupTransactions方法中通过doc.emit(“afterTransactionCleanup”)后,会检查是否为doc设置了update的observer;如果设置了则通过doc.emit(“update”)通知有更新
// @todo Merge all the transactions into one and provide send the data as a single update message
doc.emit('""afterTransactionCleanup""', [transaction, doc])
if (doc._observers.has('update')) {
const encoder = new UpdateEncoderV1()
const hasContent = writeUpdateMessageFromTransaction(encoder, transaction)
if (hasContent) {
doc.emit('update', [encoder.toUint8Array(), transaction.origin, doc, transaction])
}
}
if (doc._observers.has('updateV2')) {
const encoder = new UpdateEncoderV2()
const hasContent = writeUpdateMessageFromTransaction(encoder, transaction)
if (hasContent) {
doc.emit('updateV2', [encoder.toUint8Array(), transaction.origin, doc, transaction])
}
Connect Provider
网络通信提供库
y-websocket 解析
Yjs 框架中用于 WebSocket 通信的插件库。它提供了在 WebSocket 连接上发送和接收消息的逻辑,以便在客户端之间进行协同编辑时进行实时通信。yjs-websocket 的作用是在 Yjs 框架中实现了 WebSocket 的传输层,使得多个客户端能够通过 WebSocket 进行实时通信,从而在协同编辑过程中进行数据同步和消息传递。
大概的思路如下
(1). 和WebSocket服务器建立链接
(2). 定义onopen处理函数,处理本端和服务端建立链接成功事件的处理函数;这个函数中基本上会向服务端发送一个sync的消息和发送一个用户状态(用户信息)的信息
(3). 定义doc.on(“update”)的处理函数,用于接收到本端的文档变化,并使用broadcastMessage方法向服务端和其他客户端(同一个浏览器的不同Tab<这个在使用WebRTC的Connection 的Provider时会触发>)发送同步消息
/**
* Listens to Yjs updates and sends them to remote peers (ws and broadcastchannel)
* @param {Uint8Array} update
* @param {any} origin
*/
this._updateHandler = (update, origin) => {
if (origin !== this) {
const encoder = encoding.createEncoder()
encoding.writeVarUint(encoder, messageSync)
syncProtocol.writeUpdate(encoder, update)
broadcastMessage(this, encoding.toUint8Array(encoder))
}
}
this.doc.on('update', this._updateHandler)
(4). 定义websocket的onmessage的处理函数,用于接收其他客户端的同步消息;这个函数的思路大概如下
- decoding.readVarUint(decoder) 用于解码消息类型
- const messageHandler = provider.messageHandlers[messageType] 根据消息类型拿到不同的消息处理函数(一般有messageSync 数据同步,messageQueryAwareness 状态查询,messageAwareness 状态同步,messageAuth 认证),
- 执行处理函数(同步的会执行y-protocols中的sync类,Awareness的会执行y-protocols中的Awareness类,auth的会执行y-protocols中的auth类)
- sync类中的readSyncMessage执行顺序为readSyncStep1->writeSyncStep2->readUpdate->readSyncStep2;
- readSyncStep2总会执行Y.applyUpdate将更新信息应用到本端的doc中,并在YJS的trans的(见上面的事件执行章节)cleanupTransactions方法中通过doc.emit(“update”)发送更新事件
- 最后本端的editor-binding中定义的shareType.observe处理函数就会执行,将更新内容应用到编辑器中
协同编辑器实现大体步骤
- 初始化编辑器
- 初始化YDOC和用于共享的数据ShareType
- 使用Connect Provider将通信和YDOC绑定
- 使用Editor Binding将YJS和编辑绑定
// A Yjs document holds the shared data
const ydoc = new Y.Doc()
// Define a shared text type on the document
const shareType = ydoc.getText('quill')
// or yodc.get('xxxxx',Y.XmlElement) as Y.XmlElement
Quill.register('modules/cursors', QuillCursors)
// Use Connection providers handle syncing with the network
const provider = new WebsocketProvider(
'ws://demos.yjs.dev', 'quill-demo-room', ydoc
)
provider.awareness.setLocalStateField("user", { name, color });
// Create an editor-binding which
// "binds" the xxxx editor to a Y.Text type.
const binding = new EditorBinding(shareType,editor,provider.awareness)
Editor Binding说明
其中editor-binding的主要需要做的事情是将shareType与编辑器同步;思路大概如下
- (1). 监听编辑器内容的变化操作,将操作组装成yjs的Delta;如果shareType是yText,则通过shareType.applyDelta()方法(这个方法会根据情况执行insertText,formatText,deleteText)进行应用;如果是XmlElement,则需要定义自己的transform并执行相应的shareType.insert进行应用;类似于下面这样的代码
this._quillObserver = (eventType, delta, state, origin) => { if (delta && delta.ops) { // update content const ops = delta.ops ops.forEach(op => { if (op.attributes !== undefined) { for (let key in op.attributes) { if (this._negatedUsedFormats[key] === undefined) { this._negatedUsedFormats[key] = false } } } }) if (origin !== this) { doc.transact(() => { type.applyDelta() }, this) } } // always check selection if (awareness && quillCursors) { const sel = quill.getSelection() const aw = /** @type {any} */ (awareness.getLocalState()) if (sel === null) { if (awareness.getLocalState() !== null) { awareness.setLocalStateField('cursor', /** @type {any} */ (null)) } } else { const anchor = Y.createRelativePositionFromTypeIndex(type, sel.index) const head = Y.createRelativePositionFromTypeIndex(type, sel.index + sel.length) if (!aw || !aw.cursor || !Y.compareRelativePositions(anchor, aw.cursor.anchor) || !Y.compareRelativePositions(head, aw.cursor.head)) { awareness.setLocalStateField('cursor', { anchor, head }) } } // update all remote cursor locations awareness.getStates().forEach((aw, clientId) => { updateCursor(quillCursors, aw, clientId, doc, type) }) } } quill.on('editor-change', this._quillObserver) - (2). 定义shareType相应的observe处理函数(在上面的应用成功后或者Connection Provider中的读取到广播的消息并读取后主动使用doc.emit(‘update’) )会调用这个函数;函数中会判断是否是本端,如果不是本端则会将更新应用到编辑器中,类似于下面这样的代码
this._typeObserver = event => { if (event.transaction.origin !== this) { const eventDelta = event.delta // We always explicitly set attributes, otherwise concurrent edits may // result in quill assuming that a text insertion shall inherit existing // attributes. const delta = [] for (let i = 0; i < eventDelta.length; i++) { const d = eventDelta[i] if (d.insert !== undefined) { delta.push(Object.assign({}, d, { attributes: Object.assign({}, this._negatedUsedFormats, d.attributes || {}) })) } else { delta.push(d) } } quill.updateContents(delta, this) } } shareType.observe(this._typeObserver)
编辑器的消息接收处理流程图
readUpdateV2会调用yjs中的utils的readClientsStructRefs函数去解码接收到的更新内容为一个结构体struct
之后当其他用户编辑内容时,都会接收到消息,然后执行y-protocols中的sync的readSyncMessage->readUpdate->readSyncStep2;且每次接收到的信息都是增量的信息
其他知识收集
Yjs中的Observe
Yjs 中的 ShareType 类型都有一个名为 observe 的方法,它用于监听对数据的编辑操作。通过 observe 方法,可以注册一个回调函数,当对数据进行编辑操作时,Yjs 会触发这个回调函数,从而实现对编辑操作的监听和处理。
具体来说,observe 方法的作用包括但不限于以下几个方面:
-
监听数据变更:通过 observe 方法注册的回调函数会在数据类型发生变更时被调用。这包括对数据的插入、删除、格式变更等编辑操作,都会触发 observe 注册的回调函数。
-
实时同步:通过 observe 方法监听编辑操作,可以在编辑操作发生时实时捕获并进行相应的操作,比如将编辑操作同步给其他客户端。
-
数据处理和响应:observe 方法可以用于在数据发生变更时进行相应的处理和响应,比如更新 UI、触发其他业务逻辑等。
在 Yjs 中,通过使用 observe 方法,可以在 ShareType 类型的数据发生编辑操作时实时感知和处理这些编辑操作,从而实现协同编辑和数据同步的功能。
Yjs的同步策略
在 Yjs 中,同步策略有基于共享状态和基于事件两种不同的方式。
-
基于共享状态的同步策略:
基于共享状态的同步策略是指在进行协同编辑时,所有参与协同的客户端共享同一个状态或数据结构。每个客户端都会维护这个共享的状态,当有编辑操作发生时,每个客户端都会对这个共享状态进行更新,并确保所有客户端保持一致的状态。 这种同步策略通常适用于需要每个客户端都维护完整的数据副本以支持离线编辑和缓存的场景,比如在线协同编辑、多端同步等。Yjs 中的数据类型(如 YArray、YMap、YText 等)就是基于这种共享状态的同步策略来实现协同编辑和数据同步的。 -
基于事件的同步策略:
基于事件的同步策略是指在进行协同编辑时,客户端之间通过事件进行通信和同步。当有编辑操作发生时,会触发相应的事件,然后将事件消息通过网络传输给其他客户端进行处理,从而实现协同编辑和数据同步。 这种同步策略通常适用于需要实时通信和消息传递的场景,比如实时聊天、通知推送等。在 Yjs 中,使用 WebSocket 进行数据传输和同步就是基于事件的同步策略的一种实现方式。 总的来说,基于共享状态的同步策略主要用于实现协同编辑和数据同步,活跃的共享状态被发送到其他客户端,而基于事件的同步策略主要用于实现实时通信和消息传递,通过事件触发和消息传递实现客户端之间的实时同步和交互。Yjs 融合了这两种同步策略的特点,并提供了对协同编辑和实时通信的全面支持。
参考文档
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 为什么需要在bean上使用@EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = true)这个注解
- CountDownLatch(倒计时锁)使用场景
- CHS_01.1.1.1+1.1.3+操作系统的概念、功能
- Python 表达式计算详解(eval)
- 如何拥有自己的大模型
- AWS认证SAA-C03每日一题
- 智能商品系统如何协同其他系统共享数据和优化供应链决策?
- 电脑如何pdf转图片?pdf转图片工具介绍
- GEE:面对对象(斑块/超像素)尺度的随机森林回归教程
- SpringBoot+SSM项目实战 苍穹外卖(7)(Spring Cache)