LeetCode 25. K 个一组翻转链表
发布时间:2023年12月20日
Given the?head?of a linked list, reverse the nodes of the list?k?at a time, and return?the modified list.
k?is a positive integer and is less than or equal to the length of the linked list. If the number of nodes is not a multiple of?k?then left-out nodes, in the end, should remain as it is.
You may not alter the values in the list's nodes, only nodes themselves may be changed.
Example 1:
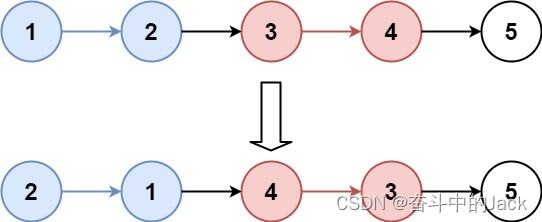
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
Output: [2,1,4,3,5]
Example 2:

Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3
Output: [3,2,1,4,5]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is n.
- 1 <= k <= n <= 5000
- 0 <= Node.val <= 1000
Follow-up:?Can you solve the problem in?O(1)?extra memory space?
解题思路:
- 迭代
- 递归?
法一:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(1)
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode tail = dummy;
while (true) {
int count = 0;
while (tail != null && count != k) {
count++;
tail = tail.next;
}
if (tail == null) break;
ListNode head1 = pre.next;
while (pre.next != tail) {
ListNode cur = pre.next;
pre.next = cur.next;
cur.next = tail.next;
tail.next = cur;
}
pre = head1;
tail = head1;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}法二:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(1)
ListNode cur = head;
int count = 0;
while (cur != null && count != k) {
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
if (count == k) {
cur = reverseKGroup(cur, k);
while (count-- > 0) {
ListNode tmp = head.next;
head.next = cur;
cur = head;
head = tmp;
}
head = cur;
}
return head;
}
}?
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38304915/article/details/135077610
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 如何做好一个信息系统项目经理,一个项目经理的个人体会和经验总结(二)
- 自动驾驶场景库
- MyBatis-Plus之内置接口&Service接口&Mapper接口
- React.Children.map 和 js 的 map 有什么区别?
- 华为常用命令大全
- 架构师的36项修炼-07高可用系统架构设计
- SpringBoot 使用 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 移除 Bean
- docker(Dockerfile、 关键字解释、Dockerfile编写、构建) -day04
- Verilog刷题笔记15
- MyBatis中的XML文件中SQL的<=判断符号处理