07. HTTP接口请求重试怎么处理?
?目录
1、前言
HTTP接口请求重试是指在请求失败时,再次发起请求的机制。在实际应用中,由于网络波动、服务器故障等原因,HTTP接口请求可能会失败。为了保证系统的可用性和稳定性,需要对HTTP接口请求进行重试。
2、实现方式
今天给大家分享一些常见的接口请求重试的方式。本地模拟了一个请求接口,后面的代码示例均模拟请求该接口:
@GetMapping("http_test")
public String getHttpTest(){
return "接口请求成功,返回:OK";
}2.1、循环重试
循环重试是最简单最粗暴的方式,就是在请求接口代码中加入循环机制,如果接口请求失败,则循环继续发起接口请求,直到请求成功或接口重试次数达到上限。如果请求成功,则不进行重试。
简单代码示例如下:
@GetMapping("retry_demo_loop")
public String retry_demo_loop(){
// 重试上限次数为3次
int maxRetryTime = 3;
String result = null;
// 接口循环请求
for (int i = 1; i <= maxRetryTime; i++) {
try {
// 模拟请求接口
result = HttpUtil.get("http://localhost:8080/http_test");
// 模拟一次请求失败
if(i == 1){
int co = i / 0;
}
// 请求成功,跳出循环
break;
} catch (Exception e) {
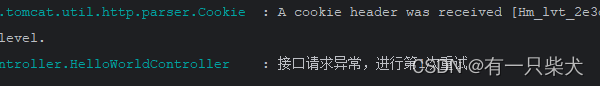
log.error("接口请求异常,进行第{}次重试", i);
result = "接口请求失败,请联系管理员";
}
}
return result;
}请求结果:
重试日志打印:
2.2、递归重试
除了循环,还可以使用递归来实现接口的请求重试。递归是我们都比较熟悉的编程技巧,在请求接口的方法中调用自身,如果请求失败则继续调用,直到请求成功或达到最大重试次数。
@GetMapping("retry_demo_rec")
public String retry_demo_rec(){
// 重试上限次数为3次
int maxRetryTime = 3;
return retryRequest(maxRetryTime);
}
/**
* 递归方法
* @param maxRetryTime
* @return
*/
private String retryRequest(int maxRetryTime){
if (maxRetryTime <= 0) {
return "接口请求失败,请联系管理员";
}
int retryTime = 0;
try {
// 模拟请求接口
String result = HttpUtil.get("http://localhost:8080/http_test");
// 模拟一次请求失败
if(maxRetryTime == 3){
int co = 1 / 0;
}
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
// 处理异常
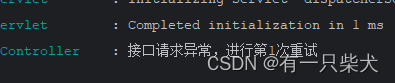
log.error("接口请求异常,进行第{}次重试", ++retryTime);
return retryRequest(maxRetryTime - 1);
}
}请求结果:
重试日志打印:
2.3、Spring Retry
第三种便是使用Spring Retry依赖实现。首先我们需要集成相关依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.retry</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-retry</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 由于retry使用到了aop,所以还需要加入aop依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>加入@EnableRetry启动:
@EnableRetry
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}添加retry方法注解:
public interface MyRetryService {
/**
* retryable注解表示该方法需要重试
* value:出现该指定异常后,进行重试
* maxAttempts:重试次数上限,这里指定为3次
* backoff:重试策略,这里指定200ms间隔一次
* @param code
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Retryable(value = {Exception.class}, maxAttempts = 3, backoff = @Backoff(200))
String retry(int code) throws Exception;
/**
* 当重试达到上限后还是失败,则作为异常回调方法
* @param th
* @param code
* @return
*/
@Recover
String recover(Throwable th, int code);
}MyReretService实现类:
@Slf4j
@Service
public class MyRetryServiceImpl implements MyRetryService {
@Override
public String retry(int code) throws Exception {
log.info("请求retry接口");
String result = HttpUtil.get("http://localhost:8080/http_test");
if(code != 200){
throw new Exception("接口请求异常");
}
return result;
}
@Override
public String recover(Throwable th, int code) {
log.error("回调方法执行!!!!");
return "异常码为:" + code + ",异常信息:" + th.getMessage();
}
}Controller:
@Autowired
private MyRetryService myRetryService;
/**
* 当请求code参数为200时,直接成功
* 当code参数!=200时,会出发重试
* @param code
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@GetMapping("retry_demo_spring_retry")
public String retry_demo_spring_retry(Integer code) throws Exception {
return myRetryService.retry(code);
}访问地址:http://localhost:8080/retry_demo_spring_retry?code=123
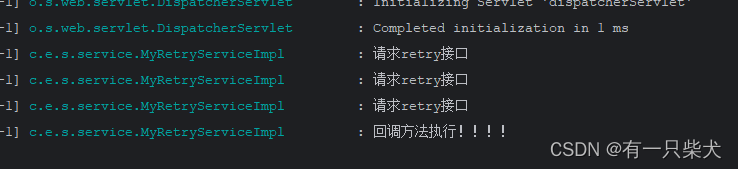
查看结果:可以看到接口重试了3次,最后执行了@Recover方法最后的回调。

2.4、Resilience4j
Resilience4j是一个轻量级、易于使用的轻量级“容错”包。它受Neflix Hystrix启发但只有一个依赖(Vavr),而不像Hystrix很多很多的依赖。同时它是一个 Java 库,可以帮助我们构建弹性和容错的应用程序。Resilience4j在“容错”方面提供了各种模式:断路器(Circuit Breaker)、重试(Retry)、限时器(Time Limiter)、限流器(Rate Limiter)、隔板(BulkHead)。我们今天讨论的话题是重试,那么今天就来演示下Retry。
首先,添加相应依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.resilience4j</groupId>
<artifactId>resilience4j-spring-boot2</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0</version>
</dependency>application.yml配置相关策略,配置官方文档:https://resilience4j.readme.io/docs/retry
resilience4j:
retry:
instances:
retry_demo:
max-attempts: 3 # 重试的上限次数
wait-duration: 1s # 重试的间隔时间,配置为1s我们改造一下上面spring-retry的demo。
controller:
@GetMapping("retry_demo_spring_retry")
@Retry(name = "retry_demo", fallbackMethod = "recover")
public String retry_demo_spring_retry(Integer code) throws Exception {
return myRetryService.retry(code);
}
public String recover(Throwable th) {
log.error("回调方法执行!!!!");
return "异常信息:" + th.getMessage();
}myRetryService:
@Override
public String retry(int code) throws Exception {
log.info("请求retry接口");
String result = HttpUtil.get("http://localhost:8080/http_test");
if(code != 200){
throw new Exception("接口请求异常");
}
return result;
}程序执行,打印结果:
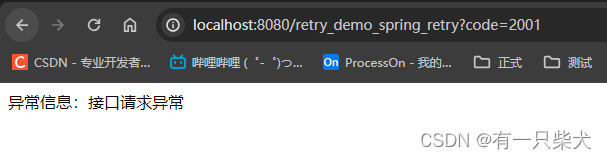
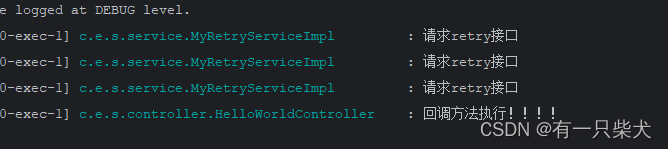
同样接口请求了3次,均失败后执行了fallback回调方法。
2.5、http请求网络工具内置重试方式
通常一些外部的http网络工具,都会内置一些重试的策略。如Apache HttpClient。这里以httpclient5为例。
首先添加依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents.client5</groupId>
<artifactId>httpclient5</artifactId>
<version>5.1.4</version>
</dependency>定义HttpClient相关类,指定重试策略。可以使用默认的DefaultHttpRequestRetryStrategy,也可以自定义重试策略CustomRetryStrategy。
private static volatile CloseableHttpClient HTTP_CLIENT = null;
static {
if(HTTP_CLIENT == null){
synchronized (HelloWorldController.class) {
if(HTTP_CLIENT == null){
HTTP_CLIENT = HttpClients.custom()
// 设置重试策略
// .setRetryStrategy(new DefaultHttpRequestRetryStrategy(3, TimeValue.NEG_ONE_SECOND))
// 自定义重试策略
.setRetryStrategy(new CustomRetryStrategy())
.build();
}
}
}
}CustomRetryStrategy:
public static class CustomRetryStrategy implements HttpRequestRetryStrategy {
@Override
public boolean retryRequest(HttpRequest httpRequest, IOException e, int executeCount, HttpContext httpContext) {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean retryRequest(HttpResponse httpResponse, int executeCount, HttpContext httpContext) {
System.out.println("进入重试策略");
if(executeCount > 3){
System.out.println("重试超过3次,终止重试");
return false;
}
if(httpResponse.getCode() != 200){
System.out.println("http状态码不等于200,进行重试");
return true;
}
// 其他情况,不重试
return false;
}
@Override
public TimeValue getRetryInterval(HttpResponse httpResponse, int executeCount, HttpContext httpContext) {
return null;
}
}Controller代码:
@GetMapping("retry_demo_httpclient")
public String retry_demo_httpclient(Integer code) throws Exception {
return httpclientRetry(code);
}
private String httpclientRetry(int code) throws Exception {
log.info("请求retry接口");
// 这里模拟了一个不存在的地址
HttpGet request = new HttpGet("http://localhost:8080/http_test1");
CloseableHttpResponse httpResponse = HTTP_CLIENT.execute(request);
String result = IoUtil.read(httpResponse.getEntity().getContent()).toString();
if(code != 200){
throw new Exception("接口请求异常");
}
return result;
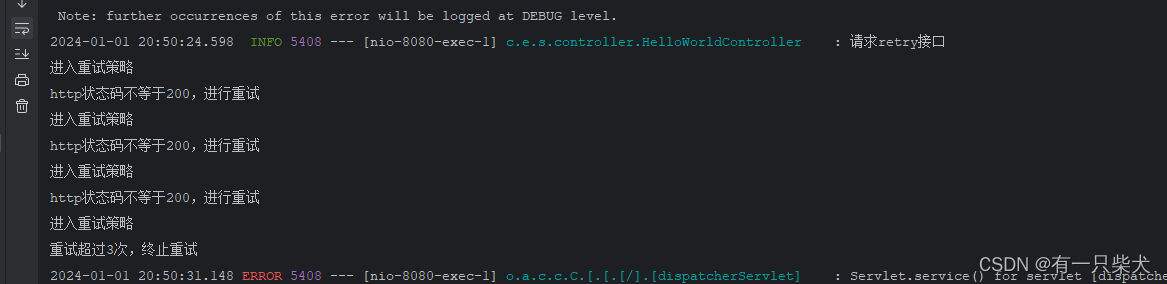
}访问接口地址:http://localhost:8080/retry_demo_httpclient?code=200。查看控制台日志打印:
2.6、自定义重试工具
装X的话,我们还可以自定义我们的重试工具。其实无非以下几个步骤:
- 自定义重试的工具类
- 接收一个方法调用,并对该方法进行异常捕获
- 如果捕获了该异常,则进行一定间隔,然后重新请求
- 记录请求次数,如果超过上限,则提示异常信息
直接定义一个重试的工具类RetryUtil.java:
import cn.hutool.core.thread.ThreadUtil;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
@Slf4j
public class RetryUtil {
/**
* 重试方法
* @param invokeFunc 原方法调用
* @param maxAttempts 重试次数上限
* @param deplay 重试的间隔时间
* @param timeUnit 重试的间隔时间单位
* @param faultFunc 如果超过重试上限次数,那么会执行该错误回调方法
* @return
* @param <T>
*/
public static <T> T retry(Supplier<T> invokeFunc, int maxAttempts, long deplay, TimeUnit timeUnit, Function<Throwable, T> faultFunc) {
AtomicInteger retryTimes = new AtomicInteger(0);
for(;;) {
try{
return invokeFunc.get();
} catch (Throwable th) {
if(retryTimes.get() > maxAttempts){
log.error("重试次数超过{}次,进入失败回调", retryTimes.get());
return faultFunc.apply(th);
}
ThreadUtil.sleep(deplay, timeUnit);
retryTimes.getAndAdd(1);
}
}
}
}工具类使用:
@GetMapping("retry_demo_custom")
public String retry_demo_custom(Integer code) {
return RetryUtil.retry(() -> {
String result = null;
try {
result = customRetry(code);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return result;
}, 3, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, Throwable::getMessage);
}
private String customRetry(int code) throws Exception {
log.info("请求customRetry接口");
String result = HttpUtil.get("http://localhost:8080/http_test");
if(code != 200){
throw new Exception("接口请求异常");
}
return result;
}执行完后,访问地址:http://localhost:8080/retry_demo_custom?code=2001
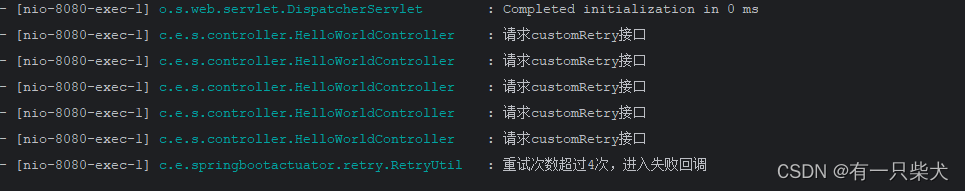
这里只是简单的进行了定义,如果项目中使用肯定需要考虑更复杂的因素。如进入重试时不一定只有异常的时候需要重试,可以指定重试策略,然后制定进入重试策略的规则。
2.7、并发框架异步重试
在 Java 并发框架中,异步重试通常涉及到使用线程池和定时器,以便在异步任务失败后进行重试。以下是一个简单的示例,演示了如何使用 CompletableFuture、ScheduledExecutorService 和 CompletableFuture.supplyAsync 来实现异步任务的重试。
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class AsyncRetryExample {
private static final ScheduledExecutorService scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 示例异步任务,这里使用 supplyAsync,你可以根据实际情况选择其他异步任务
CompletableFuture<String> asyncTask = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> performAsyncTask("Task"));
// 异步任务失败后的重试逻辑
retryAsyncTask(asyncTask, 3, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
private static CompletableFuture<String> performAsyncTask(String taskName) {
// 模拟异步任务,这里可以是任何异步操作
System.out.println("Performing async task: " + taskName);
// 这里模拟任务失败的情况
throw new RuntimeException("Task failed");
}
private static <T> void retryAsyncTask(CompletableFuture<T> asyncTask, int maxRetries, long delay, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
asyncTask.exceptionally(throwable -> {
// 异步任务失败后的处理逻辑
System.out.println("Task failed: " + throwable.getMessage());
// 重试逻辑
if (maxRetries > 0) {
System.out.println("Retrying...");
CompletableFuture<T> retryTask = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> performAsyncTask("Retry Task"));
// 递归调用,进行重试
retryAsyncTask(retryTask, maxRetries - 1, delay, timeUnit);
} else {
System.out.println("Max retries reached. Task failed.");
}
return null; // 必须返回 null,否则会影响链式调用
});
}
}
示例中,performAsyncTask 模拟了一个异步任务,如果任务失败,它会抛出一个运行时异常。retryAsyncTask 方法用于处理异步任务的失败情况,并进行重试。在重试时,它使用 CompletableFuture.supplyAsync 创建一个新的异步任务,模拟了重试的过程。请注意,这只是一个简单的示例,实际应用中可能需要更复杂的重试策略和错误处理逻辑。
2.8、消息队列
网上还有一种消息队列的方式来实现,这里没过多的去研究过,目前以上几种方式应该也是够用的了。这里直接贴出网上的部分代码,使用 RabbitMQ 作为消息队列,演示了请求重试的实现:
首先添加依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.rabbitmq</groupId>
<artifactId>amqp-client</artifactId>
<version>5.13.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
然后,创建一个发送者和接收者类:
消息发送者(Producer)
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
public class MessageProducer {
private static final String QUEUE_NAME = "retry_queue";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
try (Connection connection = factory.newConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel()) {
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 模拟发送请求
String request = "Your request data";
// 将请求发送到队列
channel.basicPublish("", QUEUE_NAME, null, request.getBytes());
System.out.println(" [x] Sent '" + request + "'");
}
}
}
消息接收者(Consumer)
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
public class MessageConsumer {
private static final String QUEUE_NAME = "retry_queue";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
try (Connection connection = factory.newConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel()) {
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 设置消息监听器
DeliverCallback deliverCallback = (consumerTag, delivery) -> {
String request = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8");
// 模拟处理请求,这里可能会出现处理失败的情况
boolean processingSucceeded = processRequest(request);
if (processingSucceeded) {
System.out.println(" [x] Received and processed: '" + request + "'");
} else {
// 处理失败,将请求重新放入队列,进行重试
channel.basicPublish("", QUEUE_NAME, null, delivery.getBody());
System.out.println(" [x] Processing failed. Retrying: '" + request + "'");
}
};
// 消费消息
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, true, deliverCallback, consumerTag -> {
});
}
}
private static boolean processRequest(String request) {
// 模拟处理请求的方法
// 在实际应用中,这里应该是对请求的处理逻辑
// 返回 true 表示处理成功,返回 false 表示处理失败,需要进行重试
// 这里简单地模拟了一个失败的情况
return !request.equals("Your request data");
}
}
示例中,消息发送者(MessageProducer)将请求发送到名为 "retry_queue" 的队列中。消息接收者(MessageConsumer)监听队列,当接收到消息时,模拟处理请求的逻辑。如果处理失败,将请求重新放入队列进行重试。
3、小结
接口请求重试机制对保证系统高可用非常关键,需要根据业务需求选择合适的重试策略。常用的组合策略包括带最大次数的定时/指数退避重试、故障转移重试等。重试机制需要综合设置以达到容错效果 又避免产生过大的系统负载。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 物联网协议Coap中Californium CoapClient解析
- 谷歌社区说|聊聊Compose跨平台与KMM
- 代码随想录刷题题Day22
- TransXNet:使用双动态令牌混合器学习全局和局部动态以实现视觉识别
- 如何从 iPhone 上恢复已删除的照片教程分享
- 破局:国内市场确实存在“消费升级”和“消费降级”,3.0全新新零售商业模式
- GitHub注册新账号的操作流程(详细)
- python:检查是否有重复的库文件
- 进程和计划任务
- 配置策略路由(基于IP地址)示例