linux系统和网络(一):文件IO
? ? ? ? 本文主要探讨linux系统编程的文件IO相关知识。
文件IO
????????文件存在块设备中为静态文件,open打开文件,内核在进程中建立打开文件的数据结构在内存中用于记录文件的文件参数,开辟一段内存用于存放内容,将静态文件转为动态文件
????????打开文件后对文件的读写操作都为对动态文件操作,close关闭文件时内核将内存中的动态文件同步到块设备中的静态文件
文件描述符
????????文件描述符是数字,打开文件时,系统在内存中构建数据结构来表示动态文件并返回数字作为文件描述符,该数字和动态文件数据结构挂钩绑定,API对描述符操作可实现对文件操作
????????文件描述符用于区分程序打开多个文件
open的flag
????????同时使用O_TRUNC和O_APPEND,O_TRUNC的优先级高
????????O_CREAT创建不存在文件,文件存在,创建这个文件,原来内容清除
????????O_EXCL和O_CREAT结合使用,文件不存在创建文件,文件存在报错
????????O_NONBLOCK非阻塞模式,文件打开默认是阻塞
????????O_SYNC:write阻塞等待底层完成写入才返回到应用层,无O_SYNC时write将内容写入底层缓冲区即可返回,底层适时将buf中内容同步硬盘,使用O_SYNC,内容直接写入硬盘
errno和perror
????????linux系统对错误做了编号,函数执行错误时,函数返回errno编号
????????errno是由OS的全局变量,用于给上层调用反馈错误
????????perror函数读取errno并将errno数字转为对应的错误信息打印
标准IO和系统IO
????????API的read和write的count参数表示想要写或读入字节数,返回值表示实际写或读取字节数
????????标准IO函数是由文件IO封装而来,标准IO加了应用层缓冲机制,写入内容不直接写入内核buf,先写入应用层标准IObuf中,标准IO库根据操作系统单次最佳count写入内核buf,内核将内核buf数据写入硬盘
????????ffulsh(int fflush(FILE *stream);)将IO buf中的数据同步到内核buf,无需等待
????????API在不同操作系统间不能通用,C库函数函数可以,可移植性强
????????文件IO不带缓存,标准IO带缓存的,标准IO性能高
linux系统管理文件
????????硬盘分为两区域:内容管理表项(文件名,扇区号,块号...(inode节点,结构体))和内容
????????快速格式化是删除硬盘内容管理表(inode),内容还在
????????vnode:程序运行后是进程,程序中打开的文件就该进程,进都有数据结构记录进程所有信息(进程信息表),进程信息表包含文件管理表(文件管理结构体vnode)包含fd和其他文件相关信息
????????空洞文件:文件有一段是空的,write时lseek跳过一段,再write会构成空洞文件
多线程通过文件指针的不同位置,同时对同一文件写入
文件描述符解析
????????重复打开同一文件,多个fd数值不同且有各自的文件指针,但表示同一文件,用这些fd同时对文件写入,后一个写入会覆盖前一个,加O_APPEND可解决覆盖
????????文件描述符是数字,是进程表中文件描述符表的一个表项,描述符作为index去索引查表得到文件表指针,再间接访问文件对应的文件表
????????文件描述符是open系统调用时由操作系统自动分配,fd从0开始依次增加,分配最小的未被占用的描述符,文件描述符表是数组,fd是index,文件表指针是value
????????linux内核占用0、1、2(stdin、stdout、stderr)描述符
文件描述符复制(dup,dup2,fcntl)
int dup(int oldfd);
int dup2(int oldfd, int newfd);
int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, ... /* arg */ );????????dup复制后得到的fd由操作系统内部分配,dup2可指定描述符
????????close(1)关闭标准输出,该程序不显示输出内容,使用dup重新分配1为fd(open一个文件)就把fd和1绑定,则该程序的输出重定位到该文件
????????dup和dup2通过复制fd同时写入同一文件是接续写入内容,不会覆盖
????????cmd为F_DUPFD作用是复制文件描述符(dup和dup2),从fd列表中找(>=arg的最小数)
文件类型
????????-:普通文件:文件内容本质上是数字(1,0),不同的解析方式将文件解析为文本文件,二进制文件等,使用不对应的解析器解析文件会乱码
????????d:目录文件是特殊文件,内容:文件的路径,文件列表和其他(vim查看)
????????c:字符设备文件,b:块设备文件,设备文件对应硬件设备,存在文于件系统中,不存在于硬盘上(/dev,/sys,/proc等)
????????p:管道文件,s套接字文件,l:符号链接文件
文件属性
int stat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);
int fstat(int fd, struct stat *buf);
int lstat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);
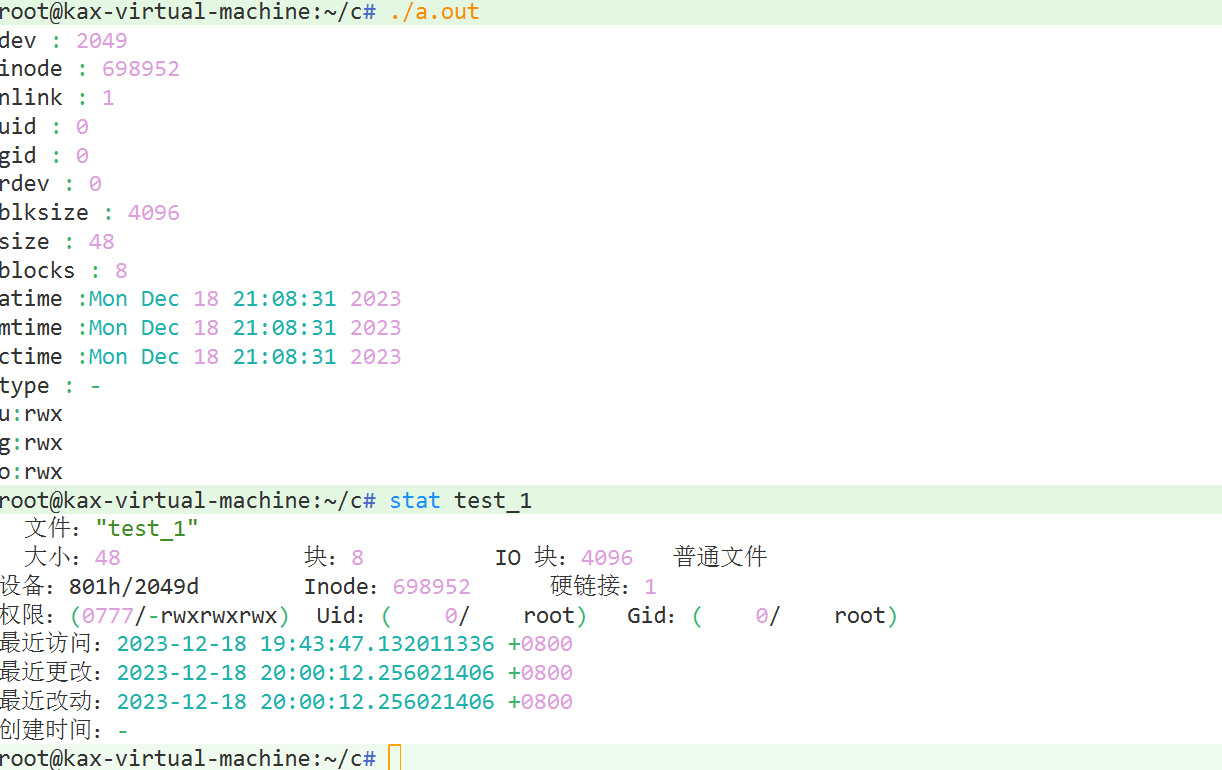
????????stat(linux)命令查看文件属性,调用stat API实现的,内核将文件属性信息结构体值存放在stat函数buf中并打印
????????stat从文件名得到文件属性信息结构体,fstat是文件fd得到文件属性信息,文件已打则fstat效率高,stat从磁盘读取文件,fstat从内存读取动态文件
????????lstat和stat/fstat:stat和fstat获得符号链接文件指向的文件属性,lstat获得符号链接文件本身的属性
????????struct stat是内核定义的结构体,在<sys/stat.h>中声明
struct stat ?
{ ??
? ? dev_t ? ? ? st_dev; ? ? /* ID of device containing file -文件所在设备的ID*/ ?
? ? ino_t ? ? ? st_ino; ? ? /* inode number -inode节点号*/ ? ?
? ? mode_t ? ? ?st_mode; ? ?/* protection -保护模式?*/ ? ?
? ? nlink_t ? ? st_nlink; ? /* number of hard links -链向此文件的连接数(硬连接)*/ ? ?
? ? uid_t ? ? ? st_uid; ? ? /* user ID of owner -user id*/ ? ?
? ? gid_t ? ? ? st_gid; ? ? /* group ID of owner - group id*/ ? ?
? ? dev_t ? ? ? st_rdev; ? ?/* device ID (if special file) -设备号,针对设备文件*/ ? ?
? ? off_t ? ? ? st_size; ? ?/* total size, in bytes -文件大小,字节为单位*/ ? ?
? ? blksize_t ? st_blksize; /* blocksize for filesystem I/O -系统块的大小*/ ? ?
? ? blkcnt_t ? ?st_blocks; ?/* number of blocks allocated -文件所占块数*/ ? ?
? ? time_t ? ? ?st_atime; ? /* time of last access -最近存取时间*/ ? ?
? ? time_t ? ? ?st_mtime; ? /* time of last modification -最近修改时间*/ ? ?
? ? time_t ? ? ?st_ctime; ? /* time of last status change - */ ? ?
}; ?????????st_mode按位标志文件权限,S_ISREG宏返回1表示普通文件,不是普通文件返回是0
S_ISREG(m) ?is it a regular file?
S_ISDIR(m) ?directory?
S_ISCHR(m) ?character device?
S_ISBLK(m) ?block device?
S_ISFIFO(m) FIFO (named pipe)?
S_ISLNK(m) ?symbolic link? ?(Not in POSIX.1-1996.)
S_ISSOCK(m) socket? ?(Not in POSIX.1-1996.)????????位掩码来判断文件类型,st_mode & S_IFMT 等于文件类型的hex,通过文件类型的hex判断文件类型
????????位掩码来判断文件权限,st_mode & name ? 等于文件权限的hex,通过文件类型的hex判断文件权限
????????位掩码来判断文件id,st_mode & S_ISUID(S_ISGID) 获得文件的id
hex ? ?name ? ? ? ls ? octal ? ?description
f000 ? S_IFMT ? ? ? ? ?170000 ? 文件类型掩码
1000 ? S_IFIFO ? ?p ? ?010000 ? 字符设备文件
2000 ? S_IFCHR ? ?c ? ?020000 ? 字符设备文件
4000 ? S_IFDIR ? ?d ? ?040000 ? 文件目录
6000 ? S_IFBLK ? ?b ? ?060000 ? 块设备文件
8000 ? S_IFREG ? ?- ? ?100000 ? 普通文件
a000 ? S_IFLNK ? ?l ? ?120000 ? 链接文件
c000 ? S_IFSOCK ? s ? ?140000 ? 套接字文件
?? ? ? S_ISUID ? ? ? ? 0004000 ? 用户id
? ? ? ?S_ISGID ? ? ? ? 0002000 ? 用户组id
1c0 ? ?S_IRWXU ? ? ? ? 00700 ? ? 用户权限掩码
100 ? ?S_IRUSR ? ? ? ? 00400 ? ? 用户读权限
80 ? ? S_IWUSR ? ? ? ? 00200 ? ? 用户写权限
40 ? ? S_IXUSR ? ? ? ? 00100 ? ? 用户执行权限
38 ? ? S_IRWXG ? ? ? ? 00070 ? ? 用户组权限掩码
20 ? ? S_IRGRP ? ? ? ? 00040 ? ? 用户组读权限
10 ? ? S_IWGRP ? ? ? ? 00020 ? ? 用户组写权限
08 ? ? S_IXGRP ? ? ? ? 00010 ? ? 用户组执行限
07 ? ? S_IRWXO ? ? ? ? 00007 ? ? 其他用户掩码
04 ? ? S_IROTH ? ? ? ? 00004 ? ? 其他用户读权限
02 ? ? S_IWOTH ? ? ? ? 00002 ? ? 其他用户写权限
01 ? ? S_IXOTH ? ? ? ? 00001 ? ? 其他用户执行权限? ? ? ? access判断文件权限,文件主组其他都不存在该权限时,返回-1,有一个存在则返回0
int access(const char *pathname, int mode);
#define R_OK 4 /* 读权限*/
#define W_OK 2 /* 写权限*/
#define X_OK 1 /* 执行权限*/
#define F_OK 0 /* 文件存在*/? ? ? ? 修改文件权限chmod/fchmod
int chmod(const char *path, mode_t mode);
int fchmod(int fd, mode_t mode);同linux(1,2,4.如0777)
S_ISUID ?(04000) ?set-user-ID?
S_ISGID ?(02000) ?set-group-ID?
S_ISVTX ?(01000) ?sticky bit?
S_IRUSR ?(00400) ?read by owner
S_IWUSR ?(00200) ?write by owner
S_IXUSR ?(00100) ?execute/search ?by ?owner ?
S_IRGRP ?(00040) ?read by group
S_IWGRP ?(00020) ?write by group
S_IXGRP ?(00010) ?execute/search by group
S_IROTH ?(00004) ?read by others
S_IWOTH ?(00002) ?write by others
S_IXOTH ?(00001) ?execute/search by others? ? ? ? 修改文件属主chown/fchown/lchown
int chown(const char *path, uid_t owner, gid_t group);
int fchown(int fd, uid_t owner, gid_t group);
int lchown(const char *path, uid_t owner, gid_t group);????????umask
????????设置创建的文件掩码,即设置创建的文件权限的补码,不论权限大小,都无执行权限
mode_t umask(mode_t mask);????????目录文件
????????opendir打开目录得到DIR类型指针,readdir函数调用DIR类型指针返回struct dirent类型指针
DIR *opendir(const char *name);
DIR *fdopendir(int fd);struct dirent * readdir(DIR * dir);struct dirent {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?ino_t ? ? ? ? ?d_ino; ? ? ? /* inode number 文件inode节点号*/
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?off_t ? ? ? ? ?d_off; ? ? ? /* not an offset; 文件相对首文件偏移量*/
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?unsigned short d_reclen; ? ?/* length of this record 文件长度(大小)*/
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?unsigned char ?d_type; ? ? ?/* type of file; 文件类型*/ ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?char ? ? ? ? ? d_name[256]; /* filename 文件名*/
? ? ? ? ? ? ? };demo1:
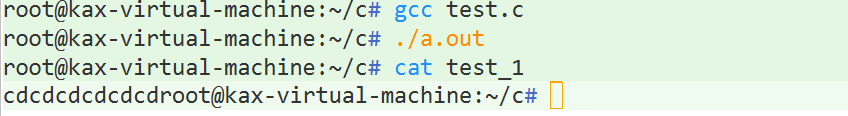
? ? ? ? 文件续写和覆盖(fd,dup,dup2,fcntl)
覆盖:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int num = 0;
int fd_1 = open("test_1",O_RDWR);
if(fd_1 < 0)
{
perror("open");
exit(-1);
}
int fd_2 = open("test_1",O_RDWR);
if(fd_2 < 0)
{
perror("open");
exit(-1);
}
while(1)
{
if(num >=6)
{
break;
}
write(fd_1,"ab",2);
write(fd_2,"cd",2);
num++;
}
close(fd_1);
close(fd_2);
return 0;
}结果显示:
?续写:?
????????fd/dup/dup2/fcntl?
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int num = 0;
int fd_1 = open("test_1",O_RDWR|O_APPEND);
if(fd_1 < 0)
{
perror("open");
exit(-1);
}
int fd_2 = open("test_1",O_RDWR|O_APPEND);
if(fd_2 < 0)
{
perror("open");
exit(-1);
}
//int fd_2 = dup(fd_1);
//int fd_2 = dup2(fd_1,10);
//int fd_2 = fcntl(fd_1,F_DUPFD,10);
while(1)
{
if(num >=6)
{
break;
}
write(fd_1,"ab",2);
write(fd_2,"cd",2);
num++;
}
close(fd_1);
close(fd_2);
return 0;
}结果显示:

?demo2:
? ? ? ? ?stat函数获取stat命令的结果
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <string.h>
char buf[32] = {0};
void get_time(unsigned long file_time)
{
memset(buf,0,32);
time_t time_f = file_time;
time(&time_f);
struct tm* timeinfo = localtime(&time_f);
strcpy(buf,asctime(timeinfo));
}
int main()
{
int ret = -1;
struct stat file;
memset(&file, 0, sizeof(struct stat));
stat("test_1",&file);
printf("dev : %d\n",file.st_dev);
printf("inode : %d\n",file.st_ino);
printf("nlink : %ld\n",file.st_nlink);
printf("uid : %ld\n",file.st_uid);
printf("gid : %ld\n",file.st_gid);
printf("rdev : %ld\n",file.st_rdev);
printf("blksize : %ld\n",file.st_blksize);
printf("size : %ld\n",file.st_size);
printf("blocks : %ld\n",file.st_blocks);
get_time(file.st_atime);
printf("atime :%s",buf);
get_time(file.st_mtime);
printf("mtime :%s",buf);
get_time(file.st_ctime);
printf("ctime :%s",buf);
ret = file.st_mode & S_IFREG;
if (ret == 0x8000)
printf("type : -\n");
ret = file.st_mode & S_IRWXU;
if(ret == 0x1c0)
printf("u:rwx\n");
ret = file.st_mode & S_IRWXG;
if(ret == 0x38)
printf("g:rwx\n");
ret = file.st_mode & S_IRWXO;
if(ret == 0x07)
printf("o:rwx\n");
return 0;
}
demo3:?
? ? ? ? 获取文件权限,修改文件权限,修改文件属主属组,修改文件掩码
? ? ? ? 注意:
????????????????文件的执行权限不能通过文件掩码来设置,需要用chmod,掩码能设置的最大权限为0666
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?umask函数设置的权限,仅仅只在程序运行中成立,程序结束以当前操作系统设置的掩码为准
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
int ret = -1;
if(access("test_1",F_OK) == 0)
printf("test exited\n");
if(access("test_1",R_OK) == 0)
printf("read premisson\n");
if(access("test_1",W_OK) == 0)
printf("write premisson\n");
if(access("test_1",X_OK) == 0)
printf("operaton premisson\n");
chmod("test_1",0777);
chown("test_1",1000,1000);
umask(0222);
system("touch file");
return 0;
}结果示例:

demo4:
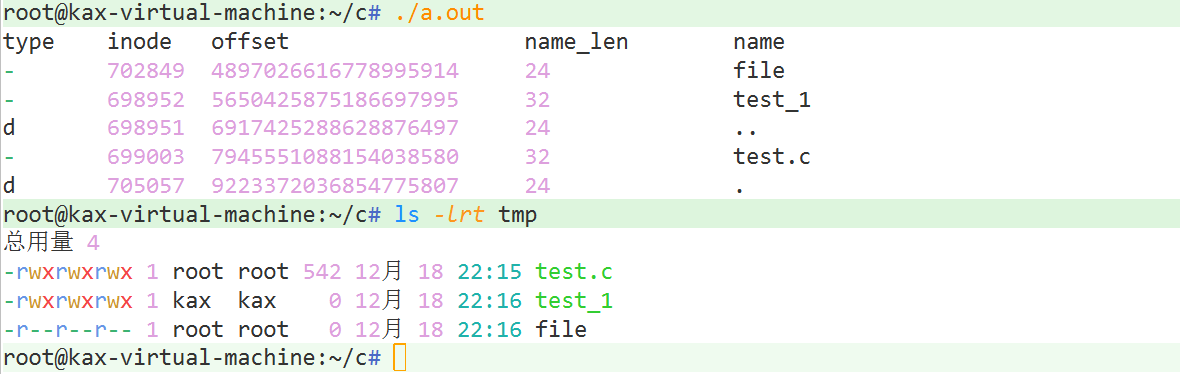
?????????显示文件夹中文件的名称,大小,类型,inode,offsset
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
DIR * dir;
struct dirent * ptr;
char type;
dir = opendir("tmp");
if(dir == NULL)
{
perror("opendir");
exit(-1);
}
printf("type\tinode\toffset\t\t\tname_len\tname\n");
while((ptr = readdir(dir)) != NULL)
{
if(ptr->d_type == 8)
{
type = '-';
}
else if(ptr->d_type == 4)
{
type = 'd';
}
else
{
printf("have no type file\n");
}
printf("%c\t%ld\t%ld\t%d\t\t%s\n",type,ptr->d_ino,ptr->d_off,ptr->d_reclen,ptr->d_name);
}
closedir(dir);
return 0;
}
结果示例:
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 【电商API接口Python实例】100个Python爬虫实例
- Footprint 批量下载方案:为机器学习提供优质区块链数据
- TikTok云手机:突破传统社媒营销方式的黑科技
- 【从零开始学习JVM | 第九篇】了解 常见垃圾回收器
- 记录 - SpringBoot 自动配置的坑 isXXX失效
- 丝印丢失怎么快速找回
- 使用uni-app editor富文本组件设置富文本内容及解决@Ready先于onload执行,无法获取后端接口数据的问题
- 基于Spring Boot、Mybatis、Redis和Layui的企业电子招投标系统源码实现与立项流程
- 【XDOJ】C语言结构体综合题带练(2020期末真题)
- mysql(48) : java生成随机测试数据