LeetCode 141. 环形链表
发布时间:2023年12月18日
给你一个链表的头节点?head?,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪?next?指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数?pos?来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos?不作为参数进行传递?。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环?,则返回?true?。 否则,返回?false?。
示例 1:

示例 2:
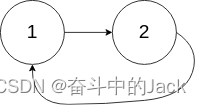
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 3:

输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:false
解释:链表中没有环。
?
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是 [0, 10^4]
- -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
- pos 为 -1 或者链表中的一个 有效索引 。
?
进阶:你能用 O(1)(即,常量)内存解决此问题吗?
解题思路:
1、粗暴法遍历判断 head 是否为空
2、暴力循环遍历,使用 Set 判重(类似dog走路,留点味道)
3、快慢指针(龟兔赛跑),快慢指针再次相遇说明有环
法一:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
// 粗暴循环
int count = 100000;
while (head != null && count > 0) {
head = head.next;
count--;
}
if (head != null) return true;
return false;
}
}?法二:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
// 暴力循环遍历,使用 Set 判断是否包含节点(类似dog走路,留点味道)
// Time: O(n)
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
while (head != null) {
if (set.contains(head)) return true;
set.add(head);
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}
}法三:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
// 快慢指针(龟兔赛跑),快慢指针再次相遇说明有环
// Time: O(n)
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (slow != null && fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38304915/article/details/135071212
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- AlphaGeometry:DeepMind 大算力再造奇迹,但「算力代替智力」或许并非最优解
- 介绍Silabs一款zigbee芯片:MG21
- C++使用OpenCV实现多元线性回归及求回归系数
- 云迈ERP销售管理——提升销售业绩与运营效率的关键!
- CSS 3D旋转正方形
- 为什么杭州的独角兽公司的技术专家都是阿里巴巴出来的?
- 教程:在Django中实现微信授权登录
- 【podman】podman学习
- LLM(七)| Mamba:LLM新架构的浅探
- ChatGPT 和文心一言哪个更好用?