Redis源码精读:字符串
发布时间:2023年12月25日
前言
Redis中实现了sds(simple dynamic string)这种字符串,它比c语言标准库的char*字符串更加实用
代码位置
src/sdc.h
src/sdc.c
核心类型
// 底层字符数组
typedef char *sds;
// 不同大小的sds的元数据和底层字符数组
/* Note: sdshdr5 is never used, we just access the flags byte directly.
* However is here to document the layout of type 5 SDS strings. */
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr5 {
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, and 5 msb of string length */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 {
uint8_t len; /* used */
uint8_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr16 {
uint16_t len; /* used */
uint16_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr32 {
uint32_t len; /* used */
uint32_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr64 {
uint64_t len; /* used */
uint64_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
SDS结构
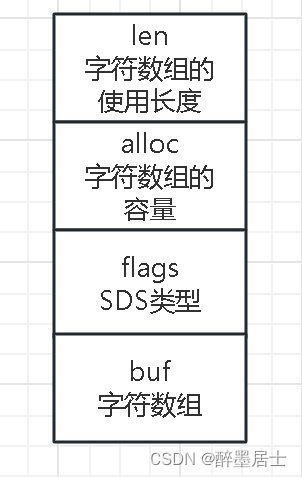
类型别名sds实际就是底层的字符数组
获取sds字符串的元数据的宏
#define SDS_HDR(T,s) ((struct sdshdr##T *)((s)-(sizeof(struct sdshdr##T))))
获取字符串长度
static inline size_t sdslen(const sds s) {
// 根据偏移获取sds类型
unsigned char flags = s[-1];
// 根据相应sds类型获取sds对应的元数据,最后获取长度
switch(flags&SDS_TYPE_MASK) {
case SDS_TYPE_5:
return SDS_TYPE_5_LEN(flags);
case SDS_TYPE_8:
return SDS_HDR(8,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_16:
return SDS_HDR(16,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_32:
return SDS_HDR(32,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_64:
return SDS_HDR(64,s)->len;
}
return 0;
}
重新设置sds长度
// newlen: sds新长度
static inline void sdssetlen(sds s, size_t newlen) {
// 根据偏移获取sds类型
unsigned char flags = s[-1];
// 根据相应sds类型获取sds对应的元数据,然后设置其长度
switch(flags&SDS_TYPE_MASK) {
case SDS_TYPE_5:
{
unsigned char *fp = ((unsigned char*)s)-1;
*fp = SDS_TYPE_5 | (newlen << SDS_TYPE_BITS);
}
break;
case SDS_TYPE_8:
SDS_HDR(8,s)->len = newlen;
break;
case SDS_TYPE_16:
SDS_HDR(16,s)->len = newlen;
break;
case SDS_TYPE_32:
SDS_HDR(32,s)->len = newlen;
break;
case SDS_TYPE_64:
SDS_HDR(64,s)->len = newlen;
break;
}
}
创建字符串
// initlen: 初始化的长度
sds _sdsnewlen(const void *init, size_t initlen, int trymalloc) {
//sds指针
void *sh;
// sds变量
sds s;
// 判定sds的类型
char type = sdsReqType(initlen);
/* Empty strings are usually created in order to append. Use type 8
* since type 5 is not good at this. */
if (type == SDS_TYPE_5 && initlen == 0) type = SDS_TYPE_8;
int hdrlen = sdsHdrSize(type);
unsigned char *fp; /* flags pointer. */
size_t usable;
assert(initlen + hdrlen + 1 > initlen); /* Catch size_t overflow */
// 分配内存
sh = trymalloc?
s_trymalloc_usable(hdrlen+initlen+1, &usable) :
s_malloc_usable(hdrlen+initlen+1, &usable);
if (sh == NULL) return NULL;
if (init==SDS_NOINIT)
init = NULL;
else if (!init)
memset(sh, 0, hdrlen+initlen+1);
// 指向sh底层的字符数组
s = (char*)sh+hdrlen;
fp = ((unsigned char*)s)-1;
usable = usable-hdrlen-1;
if (usable > sdsTypeMaxSize(type))
usable = sdsTypeMaxSize(type);
// 根据类型进行相应元数据的设置
switch(type) {
case SDS_TYPE_5: {
*fp = type | (initlen << SDS_TYPE_BITS);
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_8: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(8,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = usable;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_16: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(16,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = usable;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_32: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(32,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = usable;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_64: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(64,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = usable;
*fp = type;
break;
}
}
if (initlen && init)
// 拷贝指定长度的字符串给s
memcpy(s, init, initlen);
// 设置结束符
s[initlen] = '\0';
// 返回底层字符数组
return s;
}
// 创建指定长度的字符串
sds sdsnewlen(const void *init, size_t initlen) {
return _sdsnewlen(init, initlen, 0);
}
感悟
- 相比于c语言char*,sds更加易用,可以通过元数据获取信息,无需像char*每次获取长度时进行遍历
- sds可以表示含有“\0”的数据,因为sds是通过长度来界定字符串的,而不是像char*通过"\0"来确定字符串
- sds使用不同类型来表示不同大小的字符串,不同类型的sds使用attribute ((packed))的紧凑型内存布局来节省内存
最后
我是醉墨居士,我会继续分享Redis源码相关内容😊
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_67733273/article/details/135188116
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- ARM的一些基础知识
- 设计模式之-享元模式,快速掌握享元模式,通俗易懂的讲解享元模式以及它的使用场景
- C语言编译器(C语言编程软件)完全攻略(第十四部分:CLion下载、安装和汉化教程)
- Java8 lambda如何对Map的集合进行分组并求和
- K8s 重设解决 “The connection to the server xxx:6443 was refused” 问题
- 关键字:public关键字
- Pattern Recognition投稿经验+latex模板
- 开发可复用的WebService接口并将其封装成Java库(jar包),如何做技术选型?
- file.seek规定从txt文档的某个区间开始读取文件内容
- RabbitMQ基础知识