PRU pruss, rproc_pru和prueth uboot源码分析
概述
首先看一下PRU_ICSSG的功能框图,对于AM64来说,包含两个PRU_ICSSG模块。每个PRU_ICSSG共包含两个slice。
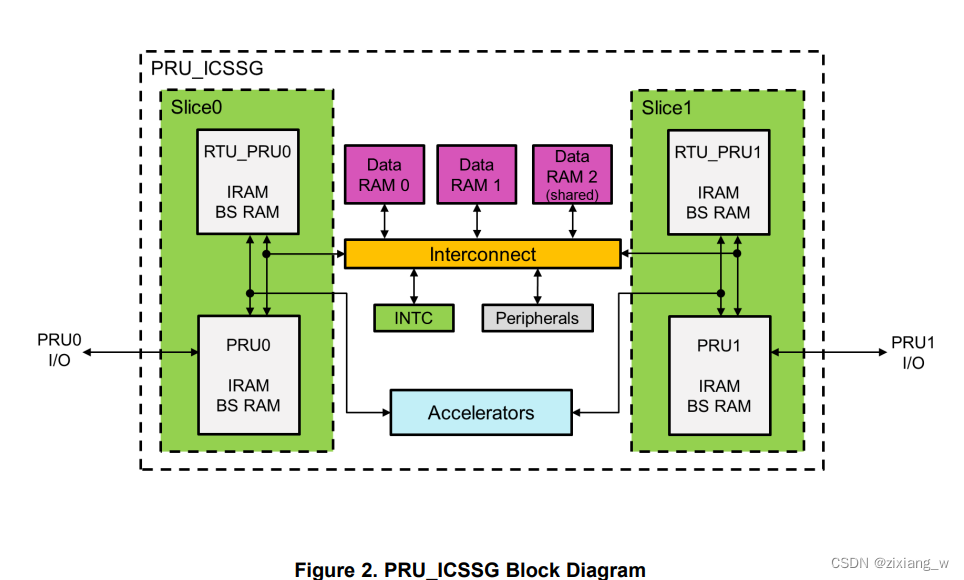
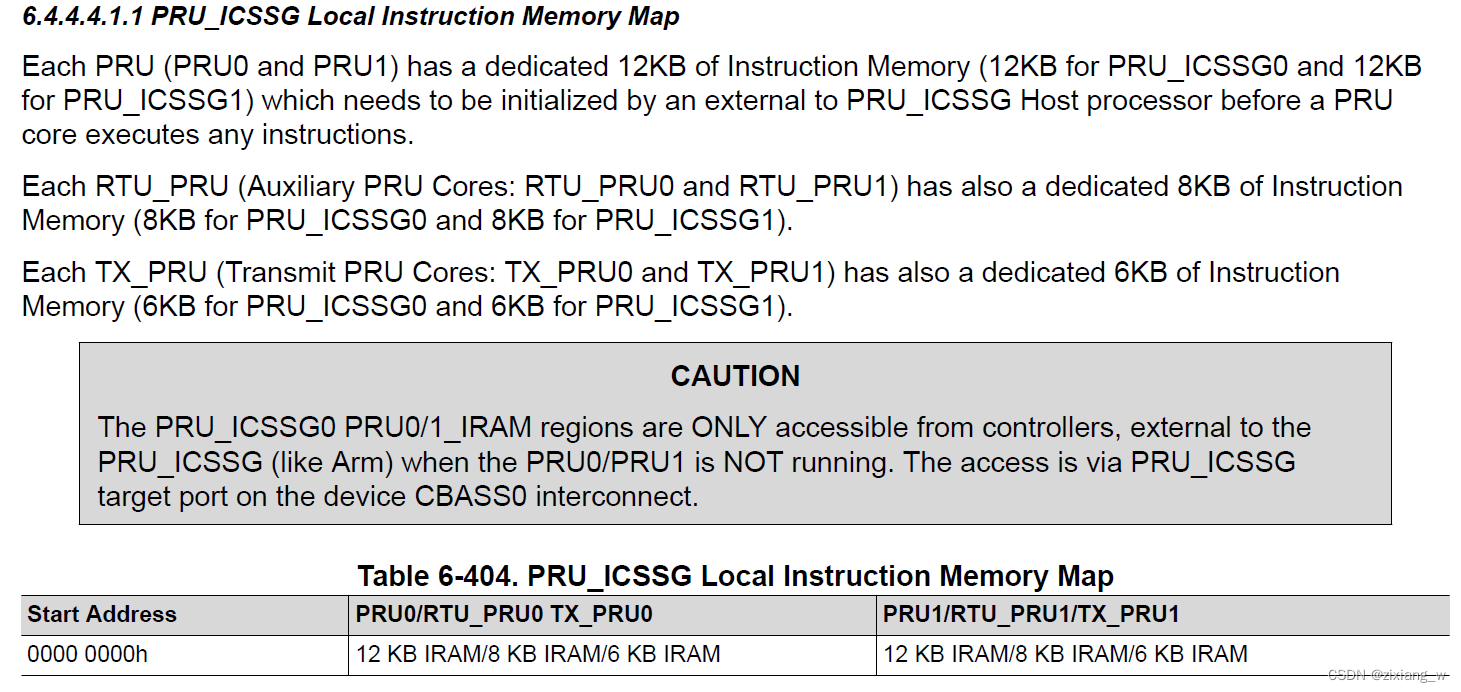
每个PRU core自己Local Instruction RAM, 容量不同。 PRU 内核执行任何指令之前,需要由外部 PRU_ICSSG 主机处理器对其进行初始化。关于IRAM跟详细的信息,可以参考TRM
除了IRAM外,还有DRAM, 需要注意的是,从 PRU0 能直接访问数据 DRAM 1 以及 PRU1 能直接访问数据 DRAM 0, Shared RAM
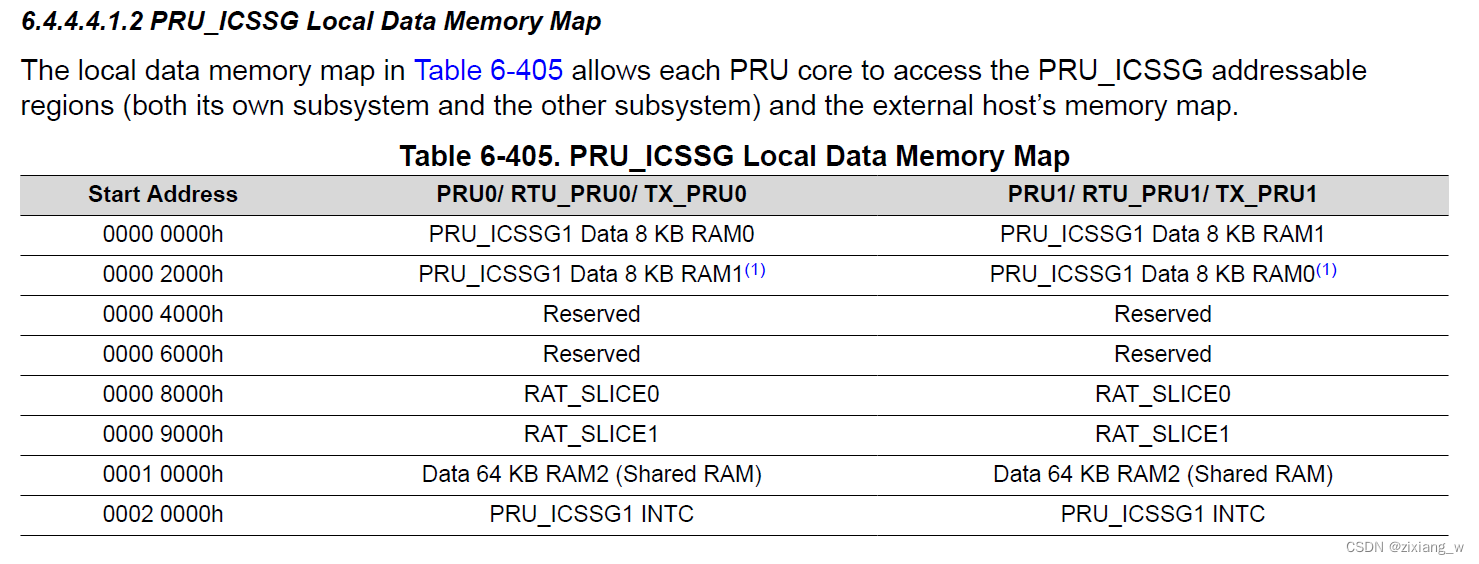
Shared RAM有以下三个作用:
- PRU Constant Table for c28_pointer
- Used to store the Rn register value.
- Used to store preconfigured list and send list.



pruss驱动
include/linux/pruss_driver.h: 主要定义了PRU_ICSSG_CFG寄存器的offset地址及寄存器位,还包括一些枚举变量的定义
GPI/O Mux modes:类似ARM引脚复用,包括GP,ENDAT,RESERVED,SD,MII2几种复用模式
GPI configuretion modes:包括DIRECT,PARALLEL,28BIT_SHIFT和MII
PRU core ID: PRU0_id=0, PRU1_id=1
Configurable Constant table index: C24-C31,值为0-7
PRUSS memory range:DRAM0,DRAM1和SHRD_RAM2
结构体:
pruss_mem_region
pruss
pruss主要完成memory的配置,cfg配置(时钟等)。
PRUSS相关结构体:
/**
* enum pruss_pru_id - PRU core identifiers
*/
enum pruss_pru_id {
PRUSS_PRU0 = 0,
PRUSS_PRU1,
PRUSS_NUM_PRUS,
};
/**
* enum pru_ctable_idx - Configurable Constant table index identifiers
*/
enum pru_ctable_idx {
PRU_C24 = 0,
PRU_C25,
PRU_C26,
PRU_C27,
PRU_C28,
PRU_C29,
PRU_C30,
PRU_C31,
};
/**
* enum pruss_mem - PRUSS memory range identifiers
*/
enum pruss_mem {
PRUSS_MEM_DRAM0 = 0,
PRUSS_MEM_DRAM1,
PRUSS_MEM_SHRD_RAM2,
PRUSS_MEM_MAX,
};
/**
* struct pruss_mem_region - PRUSS memory region structure
* @va: kernel virtual address of the PRUSS memory region
* @pa: physical (bus) address of the PRUSS memory region
* @size: size of the PRUSS memory region
*/
struct pruss_mem_region {
void __iomem *va;
phys_addr_t pa;
size_t size;
};
/**
* struct pruss - PRUSS parent structure
* @dev: pruss device pointer
* @cfg: regmap for config region
* @mem_regions: data for each of the PRUSS memory regions
* @mem_in_use: to indicate if memory resource is in use
*/
struct pruss {
struct udevice *dev;
struct regmap *cfg;
struct pruss_mem_region mem_regions[PRUSS_MEM_MAX];
struct pruss_mem_region *mem_in_use[PRUSS_MEM_MAX];
};
设备树相关节点:
icssg0_mem: memories@0 {
reg = <0x0 0x2000>,
<0x2000 0x2000>,
<0x10000 0x10000>;
reg-names = "dram0", "dram1", "shrdram2";
};
icssg0_cfg: cfg@26000 {
compatible = "ti,pruss-cfg", "syscon";
reg = <0x26000 0x200>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <1>;
ranges = <0x0 0x26000 0x2000>;
clocks {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
icssg0_coreclk_mux: coreclk-mux@3c {
reg = <0x3c>;
#clock-cells = <0>;
clocks = <&k3_clks 81 0>, /* icssg0_core_clk */
<&k3_clks 81 20>; /* icssg0_iclk */
assigned-clocks = <&icssg0_coreclk_mux>;
assigned-clock-parents = <&k3_clks 81 20>;
};
icssg0_iepclk_mux: iepclk-mux@30 {
reg = <0x30>;
#clock-cells = <0>;
clocks = <&k3_clks 81 3>, /* icssg0_iep_clk */
<&icssg0_coreclk_mux>; /* icssg0_coreclk_mux */
assigned-clocks = <&icssg0_iepclk_mux>;
assigned-clock-parents = <&icssg0_coreclk_mux>;
};
};
};
drivers/soc/ti/pruss.c是驱动的源文件
在pruss_probe()首先解析了设备树中memoery节点,得到dram0,dram1和shdram2的物理地址和大小。然后解析cfg节点,并设置时钟源。
static int pruss_probe(struct udevice *dev)
{
const char *mem_names[PRUSS_MEM_MAX] = { "dram0", "dram1", "shrdram2" };
ofnode sub_node, node, memories;
struct udevice *syscon;
struct pruss *priv;
int ret, idx, i;
priv = dev_get_priv(dev);
node = dev_ofnode(dev);
priv->dev = dev;
memories = ofnode_find_subnode(node, "memories");
for (i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE(mem_names); i++) {
idx = ofnode_stringlist_search(memories, "reg-names", mem_names[i]);
priv->mem_regions[i].pa = ofnode_get_addr_size_index(memories, idx,
(u64 *)&priv->mem_regions[i].size);
}
sub_node = ofnode_find_subnode(node, "cfg");
ret = uclass_get_device_by_ofnode(UCLASS_SYSCON, sub_node,
&syscon);
priv->cfg = syscon_get_regmap(syscon);
if (IS_ERR(priv->cfg)) {
dev_err(dev, "unable to get cfg regmap (%ld)\n",
PTR_ERR(priv->cfg));
return -ENODEV;
}
/*
* ToDo: To be modelled as clocks.
* The CORE block uses two multiplexers to allow software to
* select one of three source clocks (ICSSGn_CORE_CLK, ICSSGn_ICLK or
* ICSSGn_IEP_CLK) for the final clock source of the CORE block.
* The user needs to configure ICSSG_CORE_SYNC_REG[0] CORE_VBUSP_SYNC_EN
* bit & ICSSG_IEPCLK_REG[0] IEP_OCP_CLK_EN bit in order to select the
* clock source to the CORE block.
*/
ret = regmap_update_bits(priv->cfg, ICSSG_CFG_CORE_SYNC,
ICSSG_CORE_VBUSP_SYNC_EN,
ICSSG_CORE_VBUSP_SYNC_EN);
if (ret)
return ret;
ret = regmap_update_bits(priv->cfg, PRUSS_CFG_IEPCLK,
PRUSS_IEPCLK_IEP_OCP_CLK_EN,
PRUSS_IEPCLK_IEP_OCP_CLK_EN);
if (ret)
return ret;
dev_dbg(dev, "pruss successfully probed %s\n", dev->name);
return 0;
}
pru_rproc驱动
pru_probe()会解析设备树节点,读取pru_iram, pru_ctrl 和pru_debug的起始地址及大小。
pru_load()会加载固件中具体的内容拷贝到每个PRU的IRAM和DRAM.
/**
* enum pru_mem - PRU core memory range identifiers
*/
enum pru_mem {
PRU_MEM_IRAM = 0,
PRU_MEM_CTRL,
PRU_MEM_DEBUG,
PRU_MEM_MAX,
};
struct pru_privdata {
phys_addr_t pru_iram;
phys_addr_t pru_ctrl;
phys_addr_t pru_debug;
fdt_size_t pru_iramsz;
fdt_size_t pru_ctrlsz;
fdt_size_t pru_debugsz;
const char *fw_name;
u32 iram_da;
u32 pdram_da;
u32 sdram_da;
u32 shrdram_da;
u32 bootaddr;
int id;
struct pruss *prusspriv;
};
在pru_start()函数里会为每个PRU设置constant table index
static int pru_start(struct udevice *dev)
{
struct pru_privdata *priv;
int val = 0;
priv = dev_get_priv(dev);
pru_rproc_set_ctable(priv, PRU_C28, 0x100 << 8);
val = CTRL_CTRL_EN | ((priv->bootaddr >> 2) << 16);
writel(val, priv->pru_ctrl + PRU_CTRL_CTRL);
return 0;
}
PRU设备空间地址如何转换成pa
/*
* Convert PRU device address (data spaces only) to kernel virtual address
*
* Each PRU has access to all data memories within the PRUSS, accessible at
* different ranges. So, look through both its primary and secondary Data
* RAMs as well as any shared Data RAM to convert a PRU device address to
* kernel virtual address. Data RAM0 is primary Data RAM for PRU0 and Data
* RAM1 is primary Data RAM for PRU1.
*/
static void *pru_d_da_to_pa(struct pru_privdata *priv, u32 da, int len)
{
u32 offset;
void *pa = NULL;
phys_addr_t dram0, dram1, shrdram2;
u32 dram0sz, dram1sz, shrdram2sz;
if (len <= 0)
return NULL;
dram0 = priv->prusspriv->mem_regions[PRUSS_MEM_DRAM0].pa;//0x0000
dram1 = priv->prusspriv->mem_regions[PRUSS_MEM_DRAM1].pa;//0x2000
shrdram2 = priv->prusspriv->mem_regions[PRUSS_MEM_SHRD_RAM2].pa;//0x10000
dram0sz = priv->prusspriv->mem_regions[PRUSS_MEM_DRAM0].size;//8KB
dram1sz = priv->prusspriv->mem_regions[PRUSS_MEM_DRAM1].size;//8KB
shrdram2sz = priv->prusspriv->mem_regions[PRUSS_MEM_SHRD_RAM2].size;//64KB
/* PRU1 has its local RAM addresses reversed */
//对于slice1来说,所对应的dram0和dram1所对应的物理地址是相反的
//参考TRM Local Data momery map
if (priv->id == 1) {
dram1 = dram0;
dram1sz = dram0sz;
dram0 = priv->prusspriv->mem_regions[PRUSS_MEM_DRAM1].pa;
dram0sz = priv->prusspriv->mem_regions[PRUSS_MEM_DRAM1].size;
}
//下边是将连续的da对应到并不连续的dram0,dram1和shrdram2上
//判断da合法性,da>0 && da+len <= 8KB
if (da >= priv->pdram_da && da + len <= priv->pdram_da + dram0sz) {
offset = da - priv->pdram_da;//实际上offset=pa
pa = (__force void *)(dram0 + offset);
//da > 0x2000(8KB) && da+len <=8KB+8KB
} else if (da >= priv->sdram_da &&
da + len <= priv->sdram_da + dram1sz) {
offset = da - priv->sdram_da;//offset=
pa = (__force void *)(dram1 + offset);
//da > 0x10000(64KB) && da+len <=64KB+64KB
} else if (da >= priv->shrdram_da &&
da + len <= priv->shrdram_da + shrdram2sz) {
offset = da - priv->shrdram_da;
pa = (__force void *)(shrdram2 + offset);
}
return pa;
}
如何加载固件?固件是elf32格式
zane@ti:~/AM64$ readelf am65x-pru0-prueth-fw.elf -h
ELF Header:
Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 01 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Class: ELF32
Data: 2's complement, little endian
Version: 1 (current)
OS/ABI: UNIX - System V
ABI Version: 0
Type: EXEC (Executable file)
Machine: TI PRU I/O processor
Version: 0x1
Entry point address: 0x0
Start of program headers: 15736 (bytes into file)
Start of section headers: 15832 (bytes into file)
Flags: 0x0
Size of this header: 52 (bytes)
Size of program headers: 32 (bytes)
Number of program headers: 3
Size of section headers: 40 (bytes)
Number of section headers: 29
Section header string table index: 28
/**
* pru_load() - Load pru firmware
* @dev: corresponding k3 remote processor device
* @addr: Address on the RAM from which firmware is to be loaded
* @size: Size of the pru firmware in bytes
*
* Return: 0 if all goes good, else appropriate error message.
*/
static int pru_load(struct udevice *dev, ulong addr, ulong size)
{
struct pru_privdata *priv;
Elf32_Ehdr *ehdr;//Elf header structure pointer
Elf32_Phdr *phdr;//Elf program header structure poniter
int i, ret = 0;
priv = dev_get_priv(dev);
ehdr = (Elf32_Ehdr *)addr;//elf 入口地址
phdr = (Elf32_Phdr *)(addr + ehdr->e_phoff);//程序头部表格(Program Header Table)的偏移量
/* go through the available ELF segments */
//e_phnum表示程序头部表格的表项数目,下边的for循环是将位于DDR上的elf拷贝到PRU
for (i = 0; i < ehdr->e_phnum; i++, phdr++) {
u32 da = phdr->p_paddr;//物理地址
u32 memsz = phdr->p_memsz;//段在地址空间中的长度
u32 filesz = phdr->p_filesz;//该段在二进制文件中的长度,单位为字节。
u32 offset = phdr->p_offset;//该段在二进制文件中的偏移量,单位为字节
void *ptr;
//如果p_type(段的类型,有NULL,LOAD,DYNAMIC,INTERP,NOTE,SHLIB)不是PT_LOAD, 则不需要进行LOAD
if (phdr->p_type != PT_LOAD)
continue;
//
dev_dbg(dev, "phdr: type %d da 0x%x memsz 0x%x filesz 0x%x\n",
phdr->p_type, da, memsz, filesz);
if (filesz > memsz) {
dev_dbg(dev, "bad phdr filesz 0x%x memsz 0x%x\n",
filesz, memsz);
ret = -EINVAL;
break;
}
if (offset + filesz > size) {
dev_dbg(dev, "truncated fw: need 0x%x avail 0x%zx\n",
offset + filesz, size);
ret = -EINVAL;
break;
}
/* grab the kernel address for this device address */
//p_flags保存了标志信息,定义了该段的访问权限
//#define PF_R 0x4 //该段可读
//#define PF_W 0x2 //该段可写
//#define PF_X 0x1 //该段可执行
//pru_da_to_pa()将根据p_flags,将决定是放入IRAM(可执行)还是DRAM
ptr = pru_da_to_pa(priv, da, memsz,
RPROC_FLAGS_ELF_PHDR | phdr->p_flags);
if (!ptr) {
dev_dbg(dev, "bad phdr da 0x%x mem 0x%x\n", da, memsz);
ret = -EINVAL;
break;
}
/* skip the memzero logic performed by remoteproc ELF loader */
if (!phdr->p_filesz)
continue;
//逐字节的拷贝到PRU的IRAM和DRAM
ret = pru_rproc_memcpy(ptr,
(void *)addr + phdr->p_offset, filesz);
if (ret) {
dev_dbg(dev, "PRU custom memory copy failed for da 0x%x memsz 0x%x\n",
da, memsz);
break;
}
}
priv->bootaddr = ehdr->e_entry;//程序入口地址,0x00
return ret;
}
pru_start()主要是操作PRU_CONTROL寄存器
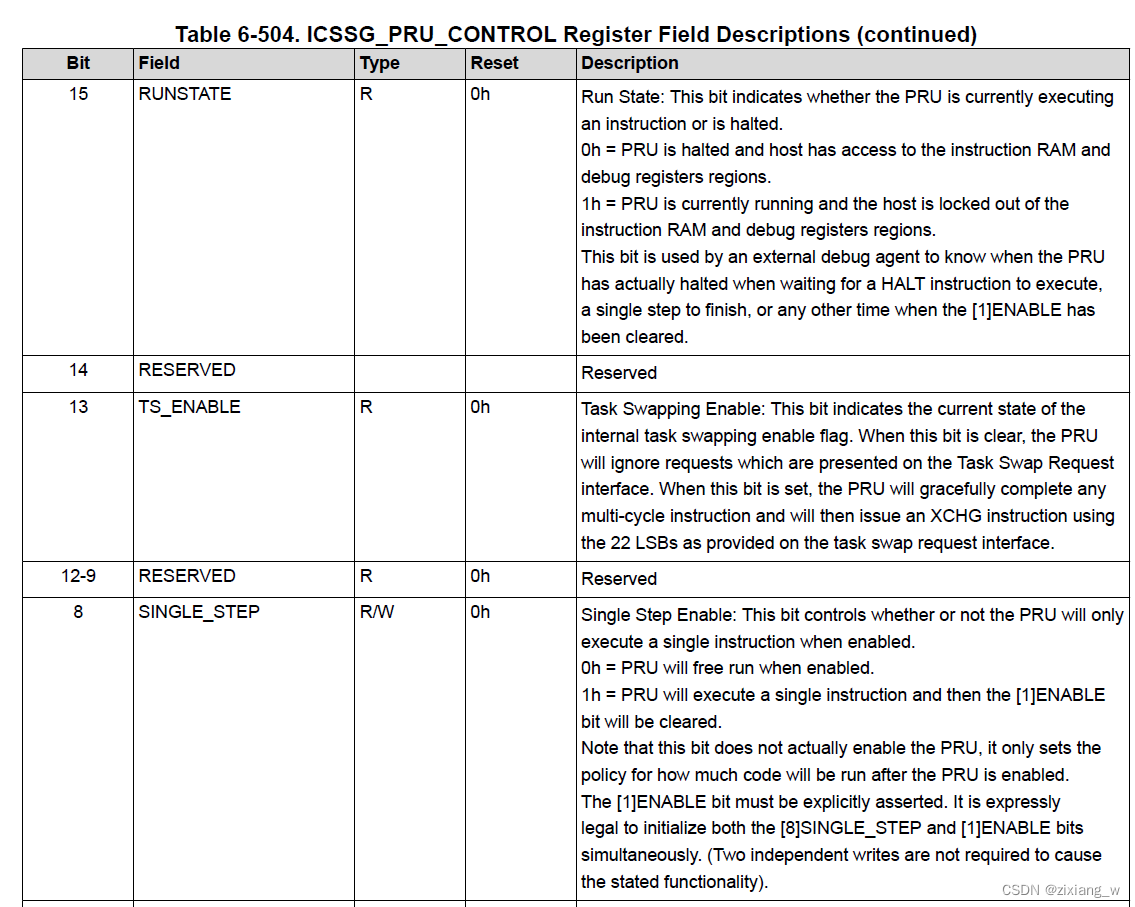
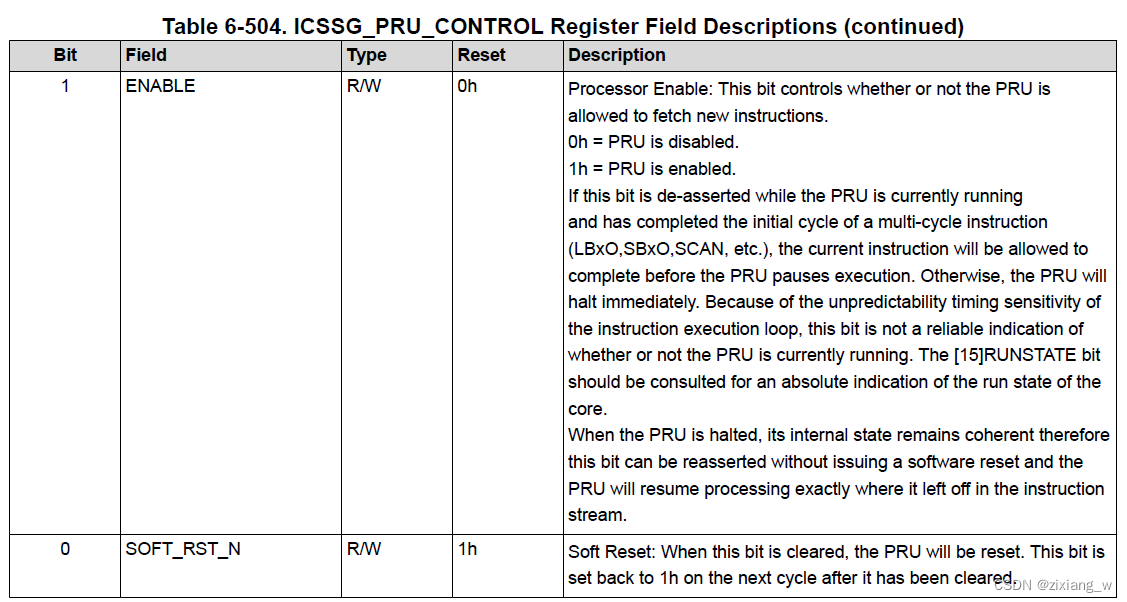
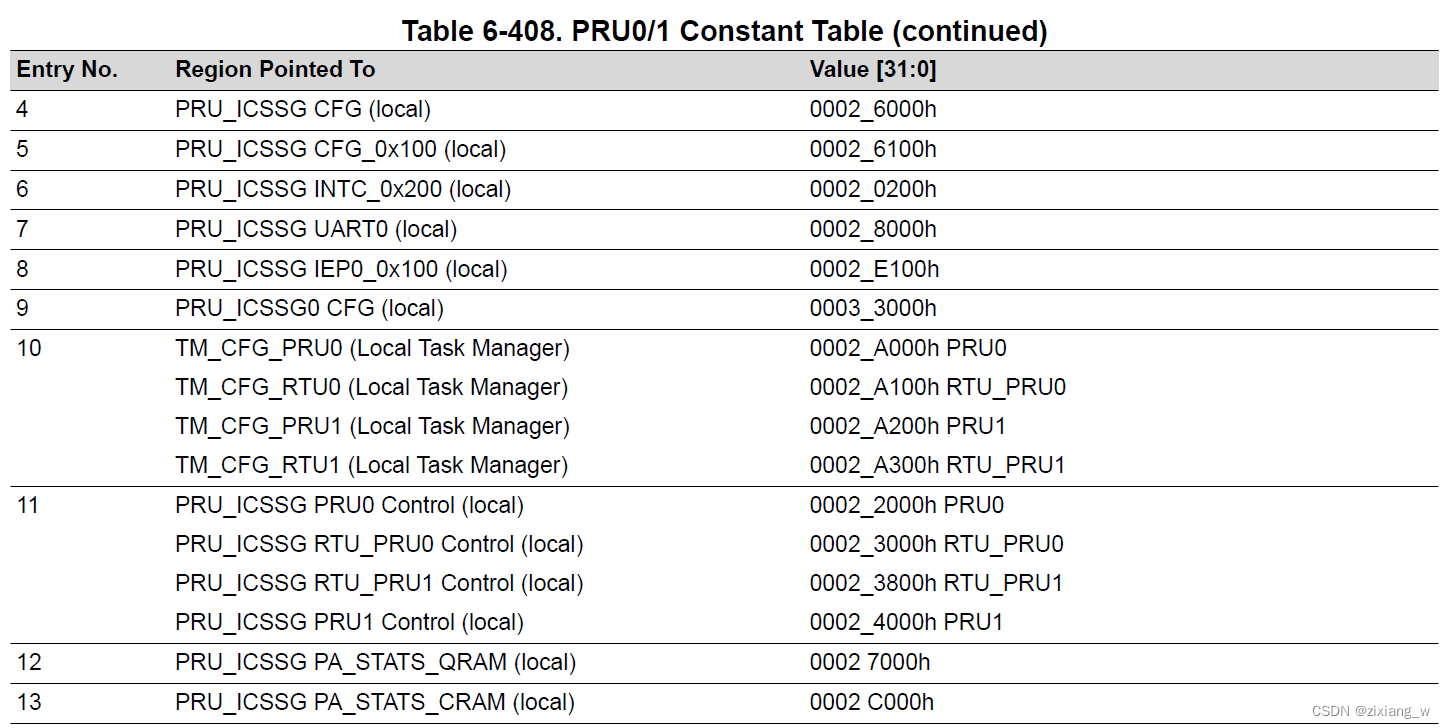
pru_start()函数设置了PRU Constants Table(更有效地将数据加载/存储到这些常用访问的地址)
static int pru_start(struct udevice *dev)
{
struct pru_privdata *priv;
int val = 0;
priv = dev_get_priv(dev);
//PRU_C28 Region Pointed To PRU_ICSSG Shared RAM (local)
pru_rproc_set_ctable(priv, PRU_C28, 0x100 << 8);//0x100<<8=0x10000
// CTRL_CTRL_EN 表示pru is allowed to fetch new instructions
// ((priv->bootaddr >> 2) << 16) 表示 Program Counter Reset Value: This field controls the address where the PRU will start executing code from after it is taken out of reset.
val = CTRL_CTRL_EN | ((priv->bootaddr >> 2) << 16);
writel(val, priv->pru_ctrl + PRU_CTRL_CTRL);
return 0;
}
可以看到在pru_start()中调用了pru_rproc_set_ctable(),
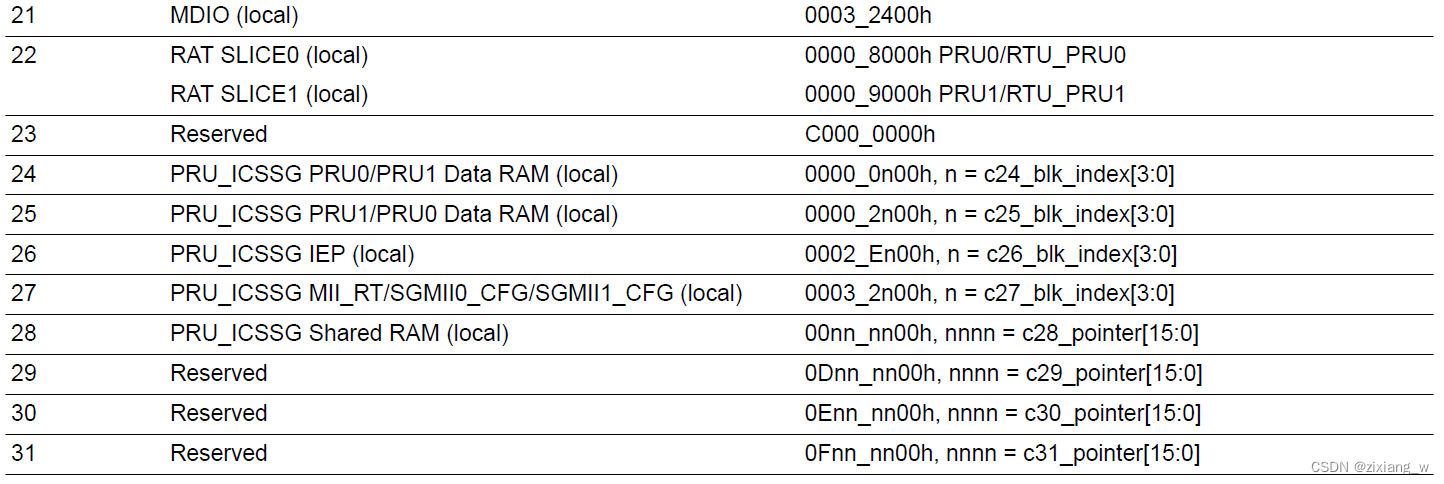
Constant Table Block Index Register 0 —>24,25
Constant Table Block Index Register 1 —>26,27
此功能非常有用,因为 PRU 经常处理多个处理线程,这需要它更改上下文。 PRU 可以使用该寄存器来避免需要过多的代码来进行重复的上下文切换。
Constant Table Programmable Pointer Register 0 —>28,29
Constant Table Programmable Pointer Register 1 —>30,31
该寄存器允许 PRU 为 PRU 常量表中的条目 28-31 设置 256 字节页面索引,这些索引用作通用指针,可配置为指向会话路由器地址映射内的任何位置。当 PRU 需要频繁访问会话路由器地址空间内的某些结构(其位置未硬编码,例如暂存存储器中的表)时,此寄存器非常有用。
上述几个寄存器所配置的值将会出现在PRU Constant Table中。
对于24-27是有8bit的对应改变
对于28-32是有16bit的对应改变
/**
* pru_rproc_set_ctable() - set the constant table index for the PRU
* @rproc: the rproc instance of the PRU
* @c: constant table index to set
* @addr: physical address to set it to
*/
static int pru_rproc_set_ctable(struct pru_privdata *pru, enum pru_ctable_idx c, u32 addr)
{
unsigned int reg;
u32 mask, set;
u16 idx;
u16 idx_mask;
/* pointer is 16 bit and index is 8-bit so mask out the rest */
idx_mask = (c >= PRU_C28) ? 0xFFFF : 0xFF;
/* ctable uses bit 8 and upwards only */
idx = (addr >> 8) & idx_mask;
/* configurable ctable (i.e. C24) starts at PRU_CTRL_CTBIR0 */
reg = PRU_CTRL_CTBIR0 + 4 * (c >> 1);//例如c=4 reg=PRU_CTRL_CTBIR0+8,对应ICSSG_PRU_CTPPR0
mask = idx_mask << (16 * (c & 1));
set = idx << (16 * (c & 1));
pru_control_set_reg(pru, reg, mask, set);
return 0;
}

本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!