js的防抖与节流
认识防抖与节流
在JavaScript中,大量操作都会触发事件,这些事件又会被添加到事件队列中进行排队处理
某些事件如果频繁触发的话会对浏览器的性能造成损耗,我们就可以使用防抖或者节流操作来限制事件的执行频率
防抖
防抖即当一个事件被触发时不会立即执行,而是会等待一段时间后执行,在等待期间如果此事件被重复触发,则等待时间也会重新计算,只有在等待期间内没有事件触发,等待时间结束后才会触发事件的回调函数
简单地说,王者里的回城就是一种防抖
节流
节流即当事件触发时会执行事件的回调函数,之后这个事件将会等待一段时间,在这段时间内触发的事件都将不会执行,直到等待时间结束后如果依旧此事件触发才会执行此事件的回调函数,之后继续等待
简单地说,王者里的技能就是一种节流
如下图所示
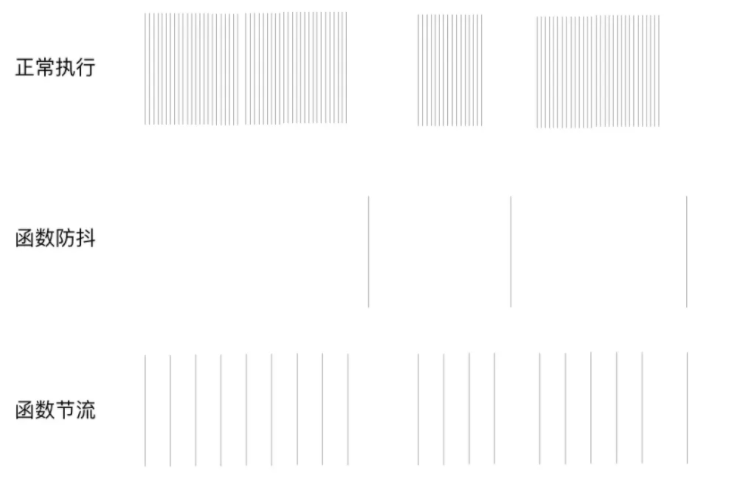
手写防抖函数
const debounce = (fn, delay) => {
let timer = null
return () => {
timer && clearTimeout(timer)
timer = setTimeout(fn, delay)
}
}
const resize = debounce(() => {
console.log('resize')
}, 1000)
window.addEventListener('resize', resize)
结果如下
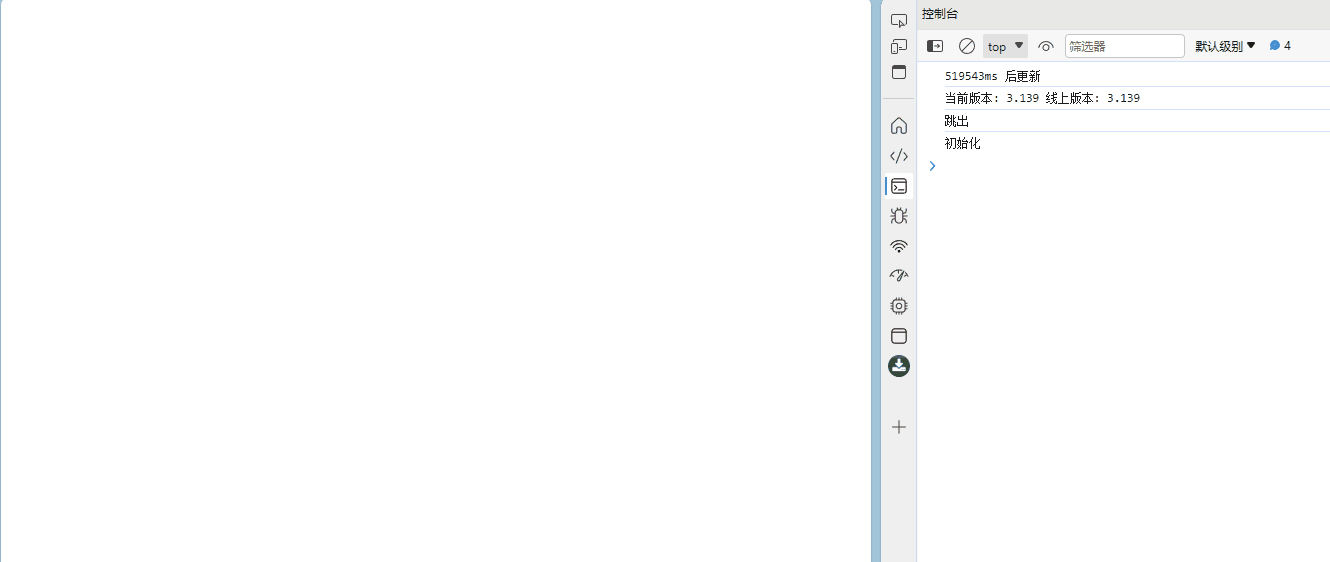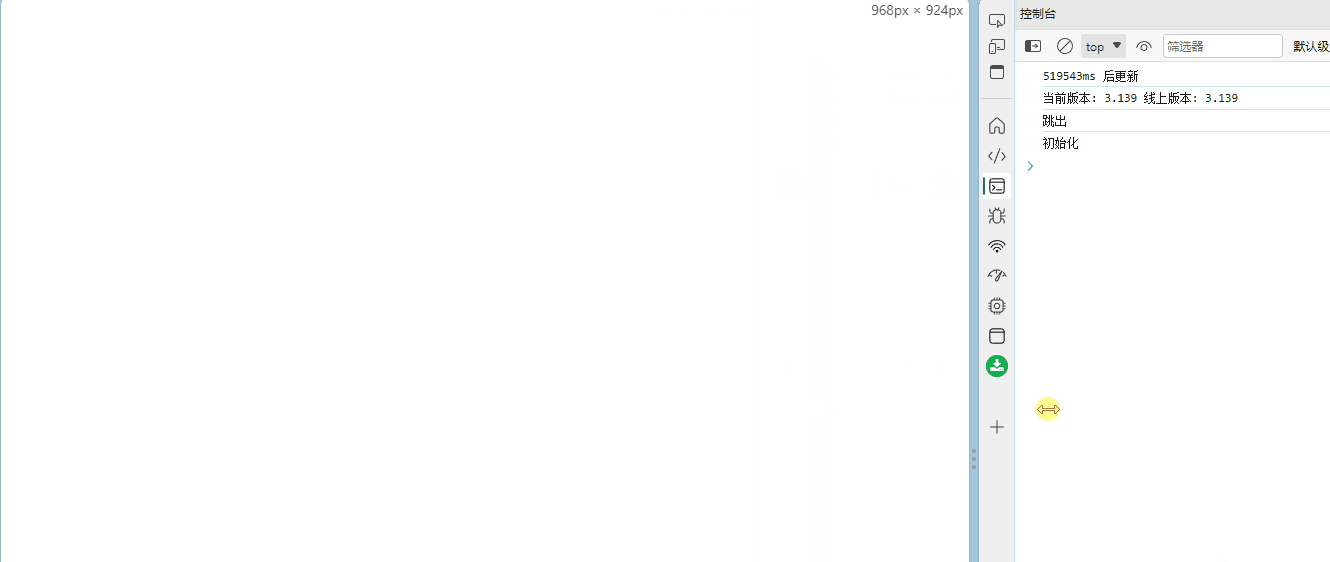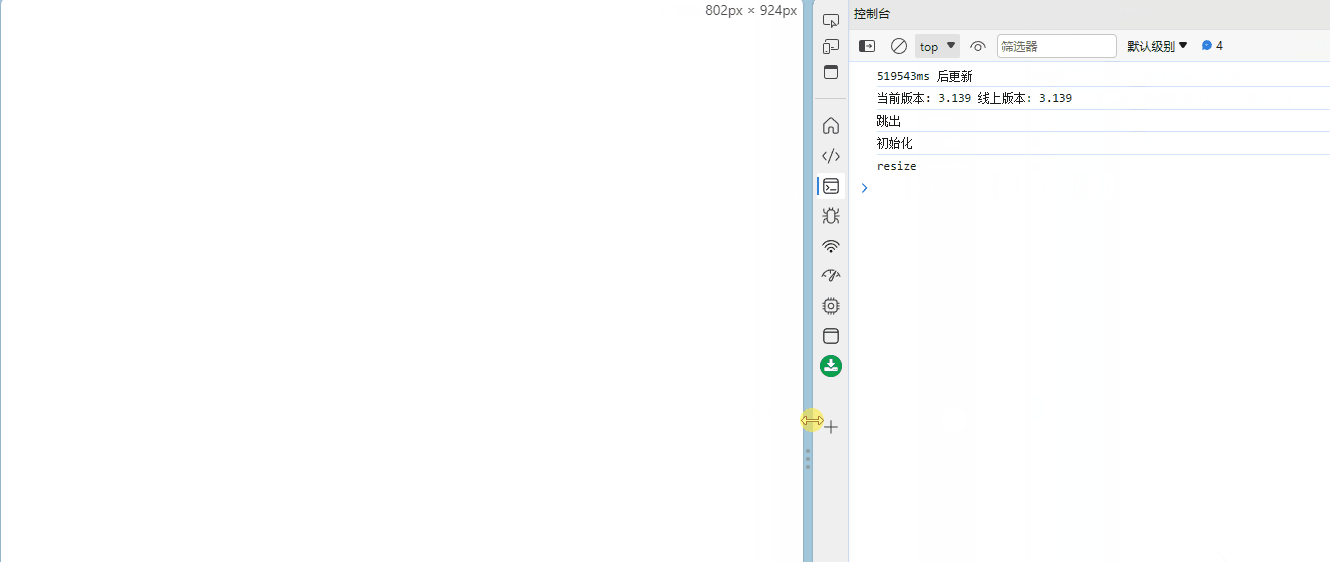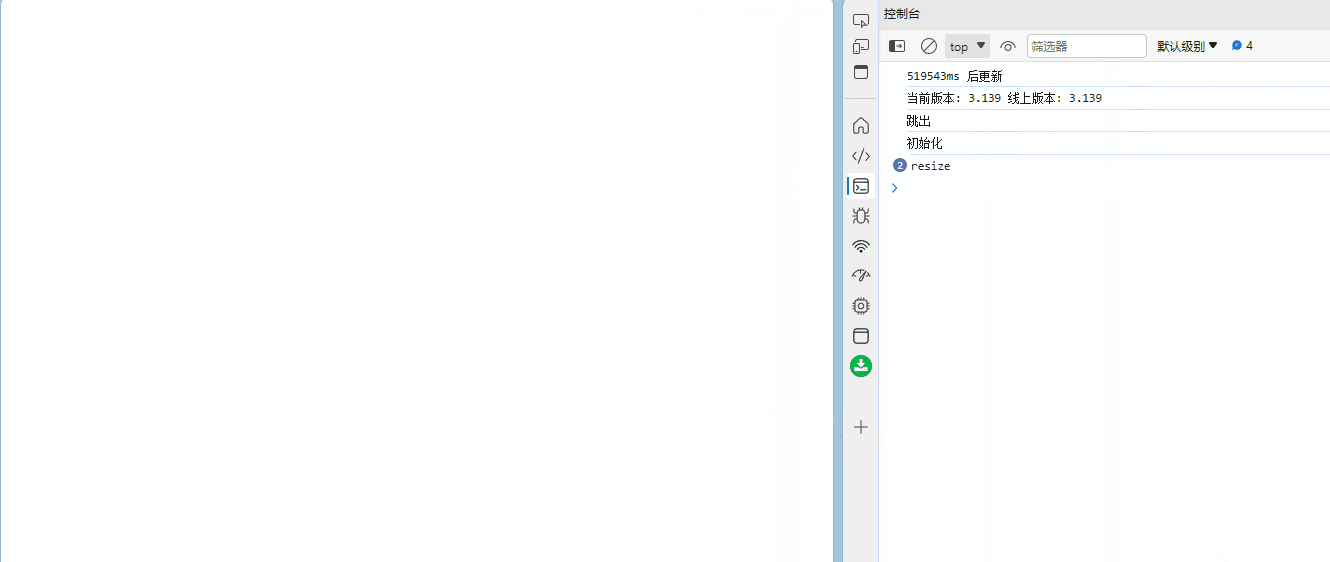
但这个函数十分简陋,没有绑定this,也没有参数传递,接下来我们一步一步来实现这些功能
绑定this与参数
绑定this有两种方式,一种是通过在参数列表中传入this指向,然后通过显式绑定到对应的对象上,还有一种是将返回的箭头函数改成普通函数
- 第一种方式
const debounce = (fn, {delay,that}={}) => {
let timer = null
return () => {
timer && clearTimeout(timer)
timer = setTimeout(fn.apply(that), delay)
}
}
const resize = debounce(() => {
console.log(this)
}, {
delay:1000,
that:window
})
window.addEventListener('resize', resize)
这段代码粗看似乎没什么问题,但实测发现防抖函数无效,因为apply会立即调用函数,解决方法是将apply封装到一个函数中
const debounce = (fn, { delay, that } = {}) => {
let timer = null
return () => {
timer && clearTimeout(timer)
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(that)
}, delay)
}
}
const resize = debounce(() => {
console.log(this)
}, {
delay: 1000,
that: window
})
window.addEventListener('resize', resize)
当我们需要传递的参数过多时可以通过参数解构与默认值的方式获取
2. 第二种方式
const debounce = (fn, delay) => {
let timer = null
return function () {
timer && clearTimeout(timer)
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this)
}, delay)
}
}
const resize = debounce(() => {
console.log(this)
}, 1000)
window.addEventListener('resize', resize)
最后结果都是一样的

参数的绑定十分简单,这里就不再赘述了
const debounce = (fn, delay) => {
let timer = null
return function (...args) {
timer && clearTimeout(timer)
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, args)
}, delay)
}
}
const resize = debounce((event) => {
console.log(this, event)
}, 1000)
window.addEventListener('resize', resize)
取消功能
有时候事件触发了但我们之后又不想函数执行,可以增加一个取消功能,我们可以在返回的函数上直接添加一个属性cancel
const debounce = (fn, delay) => {
let timer = null
const _debounce = function (...args) {
timer && clearTimeout(timer)
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, args)
}, delay)
}
_debounce.cancel = function () {
timer && clearTimeout(timer)
}
return _debounce
}
const resize = debounce((event) => {
console.log(this, event)
}, 1000)
window.addEventListener('resize', resize)
立即执行
立即执行即我们需要在事件触发时的第一次就执行函数
const debounce = (fn, { delay = 1000, immediate = false } = {}) => {
let timer = null
let isInvoke = false
const _debounce = function (...args) {
if (immediate && !isInvoke) {
fn.apply(this, args)
isInvoke = true
return
}
timer && clearTimeout(timer)
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, args)
}, delay)
}
_debounce.cancel = function () {
timer && clearTimeout(timer)
}
return _debounce
}
const resize = debounce((event) => {
console.log(this, event)
}, {
delay: 1000,
immediate: true
})
window.addEventListener('resize', resize)

获取返回值
有时候我们在手动调用防抖函数的时候需要得到函数的返回值就可以这么写,第一种方案是通过回调函数,第二种则是返回一个Promise
- 传入一个
回调函数来获取返回值
const debounce = (fn, { delay = 1000, immediate = false, callback } = {}) => {
let timer = null
let isInvoke = false
const _debounce = function (...args) {
if (immediate && !isInvoke) {
fn.apply(this, args)
isInvoke = true
return
}
timer && clearTimeout(timer)
timer = setTimeout(() => {
let res = fn.apply(this, args)
callback && callback(res)
}, delay)
}
_debounce.cancel = function () {
timer && clearTimeout(timer)
}
return _debounce
}
const resize = debounce((event) => {
console.log(this)
return "resize return"
}, {
delay: 1000,
immediate: false,
callback: (res) => {
console.log(res)
}
})
resize()
- 返回一个
Promise得到返回值
const debounce = (fn, { delay = 1000, immediate = false } = {}) => {
let timer = null
let isInvoke = false
const _debounce = function (...args) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (immediate && !isInvoke) {
fn.apply(this, args)
isInvoke = true
return
}
timer && clearTimeout(timer)
timer = setTimeout(() => {
let res = fn.apply(this, args)
resolve(res)
}, delay)
})
}
_debounce.cancel = function () {
timer && clearTimeout(timer)
}
return _debounce
}
const resize = debounce((event) => {
console.log(this)
return "resize return"
}, {
delay: 1000,
immediate: false
})
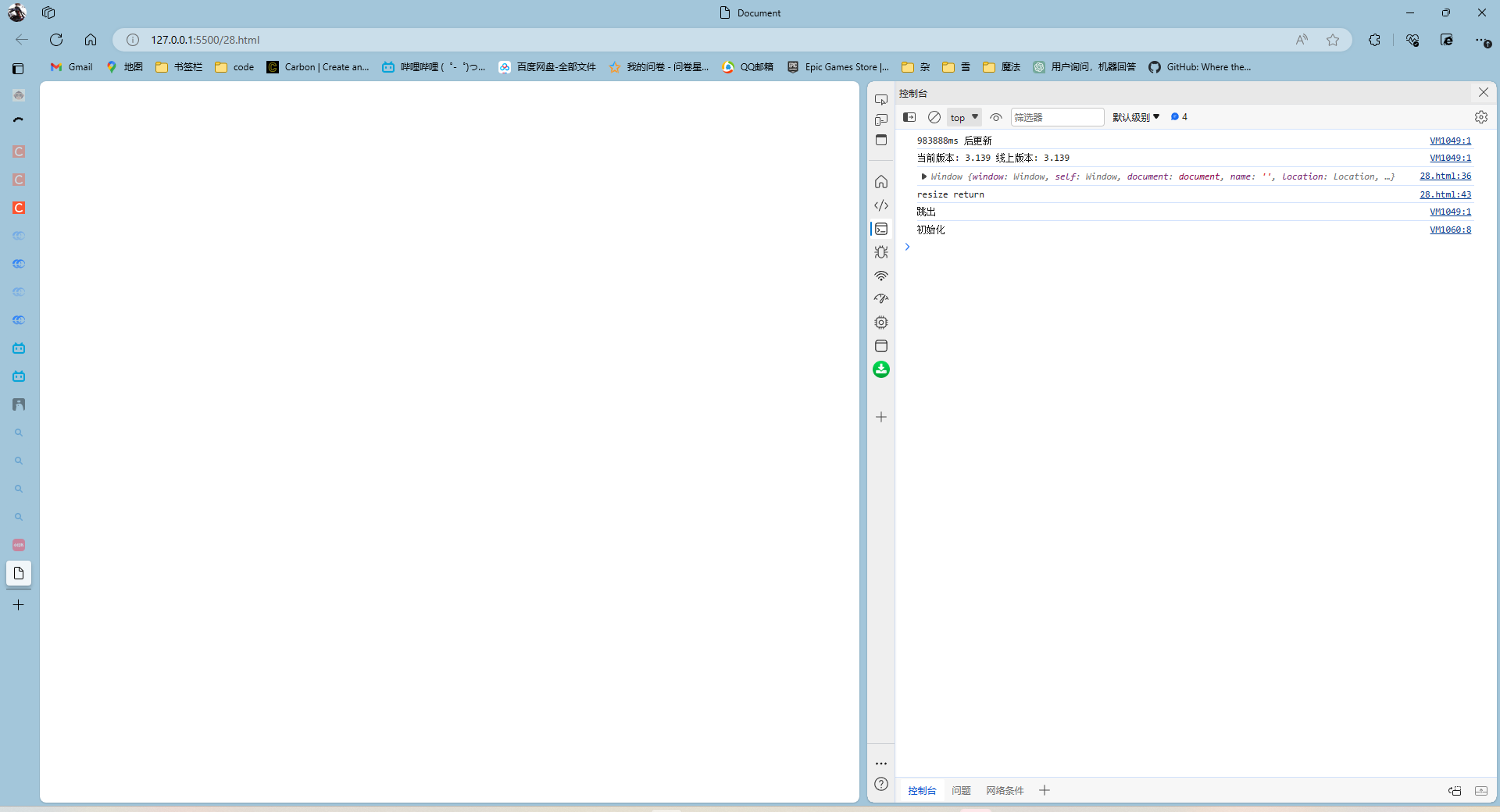
resize().then((res) => {
console.log(res)
})
结果都是一样的
最终版
最后我们将以上代码优化一下就得到了最终版本的防抖函数
const debounce = (fn, { delay = 1000, immediate = false } = {}) => {
let timer = null
let isInvoke = false
const _debounce = function (...args) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
try {
if (immediate && !isInvoke) {
let res = fn.apply(this, args)
isInvoke = true
resolve(res)
return
}
timer && clearTimeout(timer)
timer = setTimeout(() => {
let res = fn.apply(this, args)
timer = null
isInvoke = false
resolve(res)
}, delay)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
})
}
_debounce.cancel = function () {
timer && clearTimeout(timer)
isInvoke = false
timer = null
}
return _debounce
}
手写节流函数
节流函数在实现上和防抖函数稍有不同,不通过定时器而是通过时间戳
以下是一个简略的节流函数实现
const throttle = (fn, { wait = 1000, }) => {
let preTime = 0;
const _throttle = function (...args) {
let nowTime = Date.now();
if (nowTime - preTime > wait) {
fn.apply(this, args);
preTime = nowTime;
}
}
return _throttle
}
const resize = throttle(function () {
console.log("resize")
}, {
wait: 1000,
})
window.addEventListener('resize', resize)
结果如下

至于节流函数的一些优化:
节流函数立即执行与尾部执行添加取消功能获得返回值
与防抖函数的思路大差不差,这里就不再过多赘述,以下是完全版
const throttle = (fn, { wait = 1000, leading = true, trailing = false } = {}) => {
let preTime = 0;
let timer
const _throttle = function (...args) {
return Promise((resolve, reject) => {
try {
let nowTime = Date.now();
if (!leading && preTime == 0) {
preTime = nowTime
}
let interval = wait - (nowTime - preTime)
if (interval <= 0) {
let res = fn.apply(this, args)
resolve(res)
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)
preTime = nowTime
timer = null
return
}
if (trailing && !timer) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
let res = fn.apply(this, args)
resolve(res)
preTime = Date.now()
timer = null
}, interval)
}
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
})
}
_throttle.cancel = function () {
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)
preTime = 0
timer = null
}
return _throttle
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- redis前缀匹配数据迁移数据
- Java时间类型 | 类型转换 及 java.util.Date与java.time.LocalDateTime区别
- 基于ssm流浪动物领养信息系统设计论文
- 从董宇辉小作文风波,我们普通人能学到些什么?
- leetcode1235. 规划兼职工作(java)
- Vred各版本安装指南
- Linux软链接的创建,删除,修改
- vue3+element Plus 清空el-tree复选框选中项
- Hudi数据湖技术引领大数据新风口(四)核心概念
- 从0创建springboot项目并创建GitHub仓库