数据结构实战:变位词侦测
文章目录
一、实战概述
-
本实战通过编写四个Python程序,分别采用逐个比较法、排序比较法、计数比较法和相互包含法来解决变位词检测问题。逐个比较法的时间复杂度为 O ( n 2 ) \text{O}(n^2) O(n2),虽然实现简单但效率较低;排序比较法则利用字符串排序后直接比较,时间复杂度为 O ( n l o g n ) \text{O}(n log n) O(nlogn),效率相对较高;计数比较法则统计字符出现次数进行对比,时间复杂度为 O ( n ) \text{O}(n) O(n),是四种方法中最高效的;而相互包含法则分别检查两个字符串中的字符是否完全包含对方,时间复杂度为 O ( n ? m ) \text{O}(n*m) O(n?m)。
-
在实际应用中,针对不同的场景需求和输入规模,可选择合适的算法以达到时间和空间效率的最佳平衡。例如,在处理大规模字符串时,计数比较法更优;而在较小规模或对内存有限制的场景下,排序比较法可能是更好的选择。同时,强力法由于其极高的时间复杂度( n ! n! n!),不适用于实际问题求解。
二、实战步骤
(一)逐个比较法
1、编写源程序
- 编写Python程序 -
变位词侦测问题解法01-逐个比较法.py

'''
功能:变位词侦测问题解法01-逐个比较法
作者:华卫
日期:2024年01月13日
'''
def anagramSolution1(s1, s2):
stillOK = True
if len(s1) != len(s2):
stillOK = False
alist = list(s2)
pos1 = 0
while pos1 < len(s1) and stillOK:
pos2 = 0
found = False
while pos2 < len(alist) and not found:
if s1[pos1] == alist[pos2]:
found = True
else:
pos2 = pos2 + 1
if found:
alist.pop(pos2)
else:
stillOK = False
pos1 = pos1 + 1
return stillOK
str1 = input('Input the first string: ')
str2 = input('Input the second string: ')
if anagramSolution1(str1, str2):
print(str1, 'and', str2, 'are anagrams.')
else:
print(str1, 'and', str2, 'are not anagrams.')
2、代码解释说明
- 这段代码实现了一个名为
anagramSolution1的函数,用于检测两个输入字符串(s1和s2)是否为变位词。
(1)函数逻辑解释
-
函数首先检查两个字符串的长度是否相等,如果不等,则直接返回False,表示它们不是变位词。
-
将第二个字符串
s2转换为字符列表alist,便于进行元素操作。 -
使用变量
pos1遍历第一个字符串s1的每个字符。a. 初始化一个布尔变量
found为False,用于记录当前字符是否在alist中找到。b. 对于
s1中的每个字符,使用pos2遍历alist,寻找匹配项。-
如果找到匹配项(即
s1[pos1] == alist[pos2]),将found设为True,并跳出内层循环。 -
否则,将
pos2加1继续搜索下一个字符。
c. 如果找到了匹配项,从
alist中移除该字符(alist.pop(pos2));否则,将stillOK设为False,表示无法构成变位词。d. 将
pos1递增,准备处理下一个字符。 -
-
当遍历完
s1的所有字符且stillOK仍为True时,说明s1与s2是变位词,函数返回True;否则返回False。
(2)主程序部分
-
通过
input()获取用户输入的两个字符串str1和str2。 -
调用
anagramSolution1(str1, str2)函数判断这两个字符串是否为变位词。 -
根据函数返回的结果输出相应的信息,如果两个字符串是变位词,则输出"str1 and str2 are anagrams.“,否则输出"str1 and str2 are not anagrams.”。
3、运行程序,查看结果
- 运行两次程序,第一次是同位词,第二次不是同位词
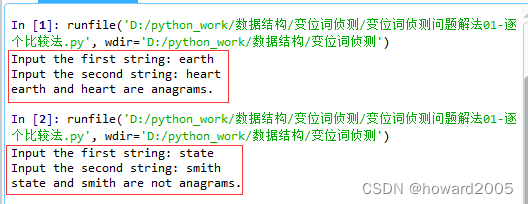
4、计算时间复杂度
-
此程序的时间复杂度为 O ( n 2 ) \text{O}(n^2) O(n2),其中n代表输入字符串s1和s2的长度(假设它们是等长的)。
-
首先检查两个字符串长度,时间复杂度为 O ( 1 ) \text{O}(1) O(1)。
-
将字符串s2转换为列表alist,时间复杂度为 O ( n ) \text{O}(n) O(n)。
-
使用两层循环进行逐个字符比较:
- 外层循环遍历字符串s1,次数为n,时间复杂度为 O ( n ) \text{O}(n) O(n)。
- 内层循环在每一轮外层循环中遍历alist寻找匹配项,最坏情况下需要遍历整个alist,次数也为n,因此内层循环的时间复杂度为 O ( n ) \text{O}(n) O(n)。
- 因此,总的时间复杂度为 O ( n ? n ) \text{O}(n*n) O(n?n),即 O ( n 2 ) \text{O}(n^2) O(n2)。
-
此外,在内层循环找到匹配项后执行的
alist.pop(pos2)操作,虽然在Python中平均时间复杂度为 O ( n ) \text{O}(n) O(n),但在实际应用中(由于每次找到一个匹配项就移除一个元素),其对于整体时间复杂度的影响可以忽略不计,所以整体时间复杂度仍视为 O ( n 2 ) \text{O}(n^2) O(n2)。 -
T ( n ) = ∑ i = 1 n = n ( n + 1 ) 2 ≈ O ( n 2 ) \displaystyle \text{T}(n)=\sum_{i=1}^n=\frac{n(n+1)}{2}\approx \text{O}(n^2) T(n)=i=1∑n?=2n(n+1)?≈O(n2)
(二)排序比较法
1、编写源程序
- 编写Python程序 -
变位词侦测问题解法02-排序比较法.py
'''
功能:变位词侦测问题解法02-排序比较法
作者:华卫
日期:2024年01月13日
'''
def anagramSolution2(s1,s2):
alist1 = list(s1)
alist2 = list(s2)
alist1.sort()
alist2.sort()
pos = 0
matches = True
while pos < len(s1) and matches:
if alist1[pos] == alist2[pos]:
pos = pos + 1
else:
matches = False
return matches
str1 = input('Input the first string: ')
str2 = input('Input the second string: ')
if anagramSolution2(str1, str2):
print(str1, 'and', str2, 'are anagrams.')
else:
print(str1, 'and', str2, 'are not anagrams.')
2、代码解释说明
- 这段代码实现了一个名为
anagramSolution2的函数,用于检测两个输入字符串(s1和s2)是否为变位词。
(1) 函数逻辑解释
-
首先将输入的两个字符串
s1和s2分别转换为字符列表alist1和alist2。 -
对这两个字符列表进行排序操作,排序后的列表中,相同的字符将会按照字典序排列到一起。
-
初始化一个变量
pos为0,表示当前比较的位置;同时初始化布尔值matches为True,用以记录是否所有对应位置的字符都匹配成功。 -
使用while循环遍历两个已排序的字符列表,直到遍历完其中一个列表或发现不匹配为止:
- 如果在相同位置上的字符相等(即
alist1[pos] == alist2[pos]),则将pos加1继续比较下一个字符。 - 否则,将
matches设置为False,跳出循环。
- 如果在相同位置上的字符相等(即
-
循环结束后,根据
matches的值判断两个字符串是否为变位词:- 若
matches为True,则说明原字符串s1和s2是变位词,返回True。 - 若
matches为False,则说明它们不是变位词,返回False。
- 若
(2)主程序部分
-
通过
input()获取用户输入的两个字符串str1和str2。 -
调用
anagramSolution2(str1, str2)函数判断这两个字符串是否为变位词。 -
根据函数返回的结果输出相应的信息,如果两个字符串是变位词,则输出"str1 and str2 are anagrams.“,否则输出"str1 and str2 are not anagrams.”。
3、运行程序,查看结果
- 运行两次程序,第一次是同位词,第二次不是同位词
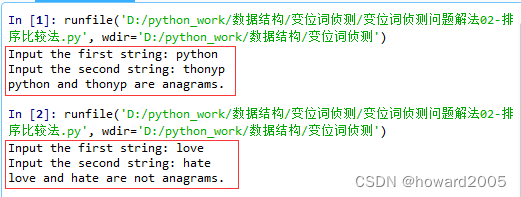
4、计算时间复杂度
- 此程序的时间复杂度主要由两部分组成:
-
排序操作:对输入字符串
s1和s2转换成的字符列表alist1和alist2进行排序。Python内置的sort()方法采用Timsort算法,其平均时间复杂度为 O ( n l o g n ) \text{O}(n log n) O(nlogn),其中 n n n为列表长度(即字符串长度)。 -
遍历比较操作:在排序后的字符列表中,通过一个while循环逐个比较对应位置的字符是否相等,该过程的时间复杂度为 O ( n ) \text{O}(n) O(n)。
- 因此,整个程序的时间复杂度为 O ( n l o g n ) + O ( n ) = O ( n l o g n ) \text{O}(n log n) + \text{O}(n) = \text{O}(n log n) O(nlogn)+O(n)=O(nlogn),其中主要的时间消耗在于排序阶段。不过,在实际情况中,由于遍历比较阶段总是紧跟在排序阶段之后,并且只执行一次,所以整体的时间复杂度通常简记为 O ( n l o g n ) \text{O}(n log n) O(nlogn)。
(三)计数比较法
1、编写源程序
- 编写Python程序 -
变位词侦测问题解法03-计数比较法.py
'''
功能:变位词侦测问题解法03-计数比较法
作者:华卫
日期:2024年01月13日
'''
def anagramSolution4(s1, s2):
c1 = [0] * 26
c2 = [0] * 26
for i in range(len(s1)):
pos = ord(s1[i]) - ord('a')
c1[pos] = c1[pos] + 1
for i in range(len(s2)):
pos = ord(s2[i]) - ord('a')
c2[pos] = c2[pos] + 1
j = 0
stillOK = True
while j < 26 and stillOK:
if c1[j] == c2[j]:
j = j + 1
else:
stillOK = False
return stillOK
str1 = input('Input the first string: ')
str2 = input('Input the second string: ')
if anagramSolution4(str1, str2):
print(str1, 'and', str2, 'are anagrams.')
else:
print(str1, 'and', str2, 'are not anagrams.')
2、代码解释说明
- 这段代码实现了一个名为
anagramSolution4的函数,用于检测两个输入字符串(s1和s2)是否为变位词。该方法采用计数比较法,统计每个字符串中各字符出现的次数,并进行比较。
(1)函数逻辑解释
-
初始化两个长度为26的计数列表
c1和c2,分别用于记录字符串s1和s2中小写字母的出现次数。这里假设输入字符串仅包含小写字母。 -
对于字符串
s1中的每一个字符:- 计算其在字母表中的位置,通过
ord(s1[i]) - ord('a')得到(将字符转换为其ASCII值并减去’a’的ASCII值)。 - 将对应位置的计数加1。
- 计算其在字母表中的位置,通过
-
同样对字符串
s2执行相同的操作,更新计数列表c2。 -
初始化一个变量
j为0,表示当前正在检查的小写字母的位置,以及一个布尔值stillOK,初始值为True,表示目前所有已检查的字符计数都相等。 -
使用while循环遍历26个小写字母,如果在对应的索引位置上
c1[j]与c2[j]相等,则继续检查下一个字母;否则,将stillOK设置为False,跳出循环。 -
循环结束后,根据
stillOK的值判断两个字符串是否为变位词:- 若
stillOK仍为True,说明原字符串s1和s2是变位词,返回True。 - 若
stillOK变为False,则说明它们不是变位词,返回False。
- 若
(2)主程序部分
-
通过
input()获取用户输入的两个字符串str1和str2。 -
调用
anagramSolution4(str1, str2)函数判断这两个字符串是否为变位词。 -
根据函数返回的结果输出相应的信息,如果两个字符串是变位词,则输出"str1 and str2 are anagrams.“,否则输出"str1 and str2 are not anagrams.”。
3、运行程序,查看结果
- 运行两次程序,第一次是同位词,第二次不是同位词
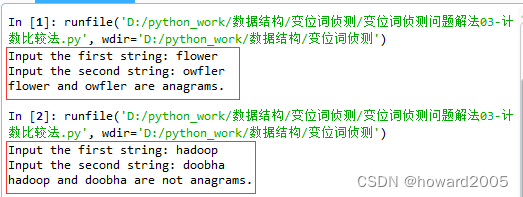
4、计算时间复杂度
-
此程序的时间复杂度为 O ( n ) \text{O}(n) O(n),其中 n n n表示输入字符串的长度。
-
在函数
anagramSolution4中,首先初始化了两个长度为26的列表c1和c2,时间复杂度为 O ( 1 ) \text{O}(1) O(1)。 -
然后对
s1中的每个字符进行遍历,计算其在字母表中的位置并增加相应计数,循环次数为n(假设字符串仅包含小写字母),时间复杂度为 O ( n ) \text{O}(n) O(n)。 -
同样地,对
s2中的每个字符执行相同的操作,时间复杂度也为 O ( n ) \text{O}(n) O(n)。 -
最后,通过一个while循环比较两个计数列表是否相等,循环最多会进行26次(对于所有可能的小写字母),因此这一部分的时间复杂度是 O ( 1 ) \text{O}(1) O(1)级别的。
-
-
综合上述步骤,整个程序的主要时间消耗在于遍历字符串并统计字符出现次数的部分,故总时间复杂度为 O ( n ) \text{O}(n) O(n)。同时,由于空间上只使用了固定大小的计数数组,所以空间复杂度为 O ( 1 ) \text{O}(1) O(1)。
(四)相互包含法
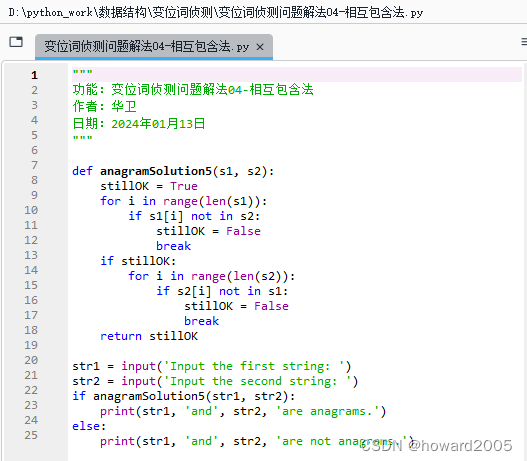
1、编写源程序
- 编写Python程序 -
变位词侦测问题解法04-相互包含法.py
"""
功能:变位词侦测问题解法04-相互包含法
作者:华卫
日期:2024年01月13日
"""
def anagramSolution5(s1, s2):
stillOK = True
for i in range(len(s1)):
if s1[i] not in s2:
stillOK = False
break
if stillOK:
for i in range(len(s2)):
if s2[i] not in s1:
stillOK = False
break
return stillOK
str1 = input('Input the first string: ')
str2 = input('Input the second string: ')
if anagramSolution5(str1, str2):
print(str1, 'and', str2, 'are anagrams.')
else:
print(str1, 'and', str2, 'are not anagrams.')
2、代码解释说明
- 这段代码实现了一个名为
anagramSolution5的函数,用于检测两个输入字符串(s1和s2)是否为变位词。该方法采用了相互包含法,即检查一个字符串中的每个字符是否都出现在另一个字符串中。
(1)函数逻辑解释
-
初始化一个布尔变量
stillOK为True,表示在没有发现不匹配字符的情况下,两个字符串可能是变位词。 -
使用一个for循环遍历字符串
s1中的每个字符:- 如果当前字符不在字符串
s2中,则将stillOK设为False,并使用break语句跳出循环。这意味着s1中存在s2中没有的字符,因此它们不是变位词。
- 如果当前字符不在字符串
-
当遍历完
s1后,如果stillOK仍为True,则继续对字符串s2进行相同的操作:- 用另一个for循环遍历
s2中的每个字符。 - 如果当前字符不在字符串
s1中,则将stillOK设为False,并同样使用break语句跳出循环。这意味着s2中也存在s1中没有的字符,因此它们不是变位词。
- 用另一个for循环遍历
-
在完成所有检查后,返回
stillOK的值。若为True,说明两个字符串是变位词;否则,它们不是变位词。
(2)主程序部分
-
通过
input()获取用户输入的两个字符串str1和str2。 -
调用
anagramSolution5(str1, str2)函数判断这两个字符串是否为变位词。 -
根据函数返回的结果输出相应的信息,如果两个字符串是变位词,则输出"str1 and str2 are anagrams.“,否则输出"str1 and str2 are not anagrams.”。
3、运行程序,查看结果
- 运行两次程序,第一次是同位词,第二次不是同位词
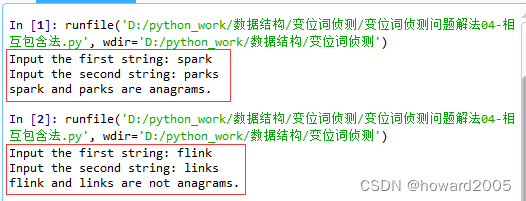
4、计算时间复杂度
-
此程序的时间复杂度为 O ( n ? m ) \text{O}(n*m) O(n?m),其中 n n n和 m m m分别为输入字符串s1和s2的长度。
-
在函数
anagramSolution5中,首先遍历字符串s1,对每个字符执行一次查找操作(即s1[i] not in s2),这需要在字符串s2中进行线性搜索。最坏情况下,对于每个字符都需要遍历整个s2,因此这部分时间复杂度为 O ( m ) \text{O}(m) O(m)。 -
如果
s1中的所有字符都在s2中找到,则继续遍历字符串s2,再次对每个字符执行查找操作(即s2[i] not in s1)。同样地,这部分在最坏情况下也具有 O ( n ) \text{O}(n) O(n)的时间复杂度。
-
-
因此,总时间复杂度为这两部分之和,即 O ( n + m ) \text{O}(n+m) O(n+m),由于两者均与输入字符串的长度相关且相互独立,我们可以将其简化为 O ( n ? m ) \text{O}(n*m) O(n?m),表示随着两个字符串长度同时增加时,程序运行时间的增长趋势。
(五)强力法
- 强力法采用穷尽所有可能性的方式来处理问题。对于长度为n的字符串s1,全排列得到所有字符串,然后去看s2是否出现在s1全排列后构成的字符串列表里。 T ( n ) = n × ( n ? 1 ) × ( n ? 2 ) × . . . . × 2 × 1 = n ! T(n)=n\times(n-1)\times(n-2)\times....\times2\times1= n! T(n)=n×(n?1)×(n?2)×....×2×1=n!, n ! n! n!跑得比 2 n 2^n 2n还要快得多,比如 20 ! = 2432902008176640000 20!= 2432902008176640000 20!=2432902008176640000。如果每秒钟处理一种可能性,那么要花 77 , 146 , 816 , 596 77,146,816,596 77,146,816,596年才能遍历整个列表。显然不是一个好的解决方案。
三、实战总结
- 实战中,我们运用四种不同策略检测变位词:逐个比较法( O ( n 2 ) \text{O}(n^2) O(n2))、排序比较法( O ( n l o g n ) \text{O}(n log n) O(nlogn))、计数比较法( O ( n ) \text{O}(n) O(n))和相互包含法( O ( n ? m ) \text{O}(n*m) O(n?m))。其中,计数比较法效率最高,适合大规模字符串;排序比较法则在小规模数据或对内存有限制时适用。通过实践对比,理解并掌握了针对不同场景选择合适算法的重要性。
?
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 文章解读与仿真程序复现思路——电力自动化设备EI\CSCD\北大核心《计及风电不确定性的多场景多时段安全约束机组组合解耦求解方法》
- 参数优化器
- 深入理解 Nginx 工作原理:Master-Worker 架构与性能优化
- Pytest基础
- R语言【rgdal】——在 2023 年软件包停用/存档之前,rgdal 中累计弃用的函数和方法:readOGR()
- Java 从BigDecimal.setScale 函数的 过期提醒,看编码封装思路 (源码简读)
- STM32F103RCT6使用数据手册及应用示例程序分享
- SRI 哈希生成器( SRI 作为最佳实践)
- Java开发框架和中间件面试题(8)
- C# 使用屏障来使多线程并发操作保持同步