【深度学习目标检测】十三、基于深度学习的血细胞识别(python,目标检测,yolov8)
血细胞计数是医学上一种重要的检测手段,用于评估患者的健康状况,诊断疾病,以及监测治疗效果。而目标检测是一种计算机视觉技术,用于在图像中识别和定位特定的目标。在血细胞计数中,目标检测技术可以发挥重要作用。
首先,血细胞计数通常需要处理大量的血液样本,手动计数每个细胞既耗时又容易出错。使用目标检测算法,可以自动识别和计数图像中的血细胞,大大提高了计数的准确性和效率。
其次,不同的血细胞(如红细胞、白细胞和血小板)具有不同的形态和大小,这使得使用传统的图像处理方法进行区分和计数变得困难。目标检测算法可以通过训练识别不同血细胞的特征,准确地区分和计数各种血细胞。
此外,目标检测算法还可以处理一些特殊情况,如细胞重叠、不规则形状、染色不均等。这些情况可能会影响手动计数的准确性和可靠性。
最后,使用目标检测进行血细胞计数可以帮助医生更准确地分析和解读血液样本,从而为患者提供更准确的诊断和治疗方案。这有助于提高医疗质量和患者满意度。
综上所述,使用目标检测对血细胞计数具有重要的意义,可以提高计数的准确性和效率,为医生提供更可靠的诊断依据,有助于提高医疗质量。
本文介绍使用yolov8进行血细胞检测的方法,其效果如下图:


一、安装YoloV8
yolov8官方文档:主页 - Ultralytics YOLOv8 文档
安装部分参考:官方安装教程
二、数据集准备
本文使用的数据集是BCCD数据集,该数据集包含3个类别:白细胞(WBC)、红细胞(RBC)和血小板(Platelets)。该数据集共364张图片,其中训练集包含205张图片,验证集包含87张图片,测试集包含72张图片。
示例图片如下:
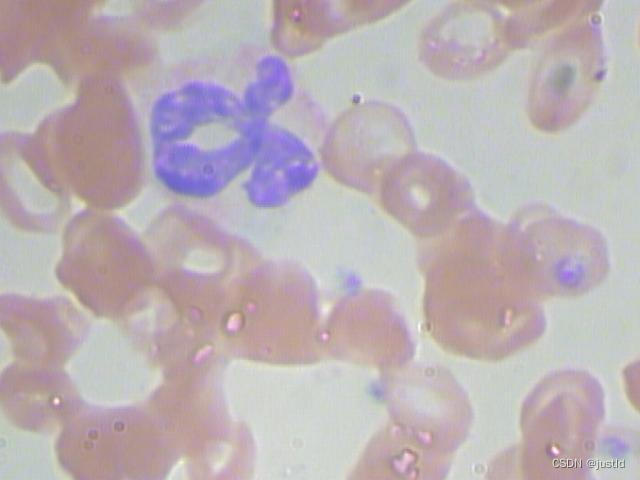
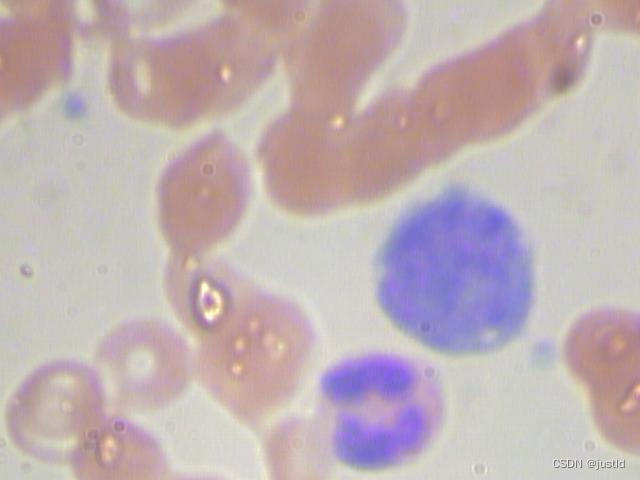
该数据集为VOC格式,本文提供转换好的BCCD数据集YOLO8格式,可以直接用于训练Yolov8模型。BCCD-yolov8数据集
三、模型训练
1、数据集配置文件
在ultralytics/ultralytics/cfg/datasets目录下添加bccd.yaml,添加以下内容(path修改为自己的路径):
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# COCO 2017 dataset http://cocodataset.org by Microsoft
# Example usage: yolo train data=coco.yaml
# parent
# ├── ultralytics
# └── datasets
# └── coco ← downloads here (20.1 GB)
# Train/val/test sets as 1) dir: path/to/imgs, 2) file: path/to/imgs.txt, or 3) list: [path/to/imgs1, path/to/imgs2, ..]
path: datasets/medical/BCCD-yolov8 # dataset root dir
train: images/train # train images (relative to 'path') 118287 images
val: images/val # val images (relative to 'path') 5000 images
test: images/test # 20288 of 40670 images, submit to https://competitions.codalab.org/competitions/20794
# Classes
names:
0: WBC
1: RBC
2: Platelets
2、修改模型配置文件
新建ultralytics/cfg/models/medical/yolov8.yaml?,添加以下内容:
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 3 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
- [[15, 18, 21], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
3、训练模型
使用如下命令训练模型,相关路径更改为自己的路径,建议绝对路径:
yolo detect train project=medical_output name=bccd_yolo8 exist_ok=True optimizer=auto val=True amp=True epochs=100 imgsz=640 model=ultralytics/cfg/models/medical/yolov8.yaml data=ultralytics/cfg/datasets/bccd.yaml
4、验证模型
使用如下命令验证模型,相关路径根据需要修改:
yolo detect val model=medical_output/bccd_yolo8/weights/best.pt data=ultralytics/ultralytics/cfg/datasets/bccd.yaml
其精度如下:
# Ultralytics YOLOv8.0.222 🚀 Python-3.9.18 torch-2.1.2+cu118 CUDA:0 (NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090, 24210MiB)
# YOLOv8 summary (fused): 168 layers, 3006233 parameters, 0 gradients, 8.1 GFLOPs
# val: Scanning /home/yq/aitools/datasets/medical/BCCD-yolov8/labels/val.cache... 87 images, 0 backgrounds, 0 corrupt: 100%|██████████| 87/87 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
# Class Images Instances Box(P R mAP50 mAP50-95): 100%|██████████| 6/6 [00:10<00:00, 1.81s/it]
# all 87 1137 0.833 0.901 0.908 0.612
# WBC 87 87 0.971 1 0.987 0.776
# RBC 87 967 0.745 0.832 0.86 0.604
# Platelets 87 83 0.783 0.87 0.878 0.456
# Speed: 2.3ms preprocess, 6.2ms inference, 0.0ms loss, 6.4ms postprocess per image四、推理
训练好了模型,可以使用如下代码实现推理,将权重放到同级目录:
from PIL import Image
from ultralytics import YOLO
# 加载预训练的YOLOv8n模型
model = YOLO('weights/best.pt')
image_path = 'BloodImage_00014.jpg'
results = model(image_path) # 结果列表
# 展示结果
for r in results:
im_array = r.plot() # 绘制包含预测结果的BGR numpy数组
im = Image.fromarray(im_array[..., ::-1]) # RGB PIL图像
im.show() # 显示图像
im.save('results.jpg') # 保存图像本文提供训练好的权重以及推理代码:【BCCD_yolov8训练结果及预测代码】
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!