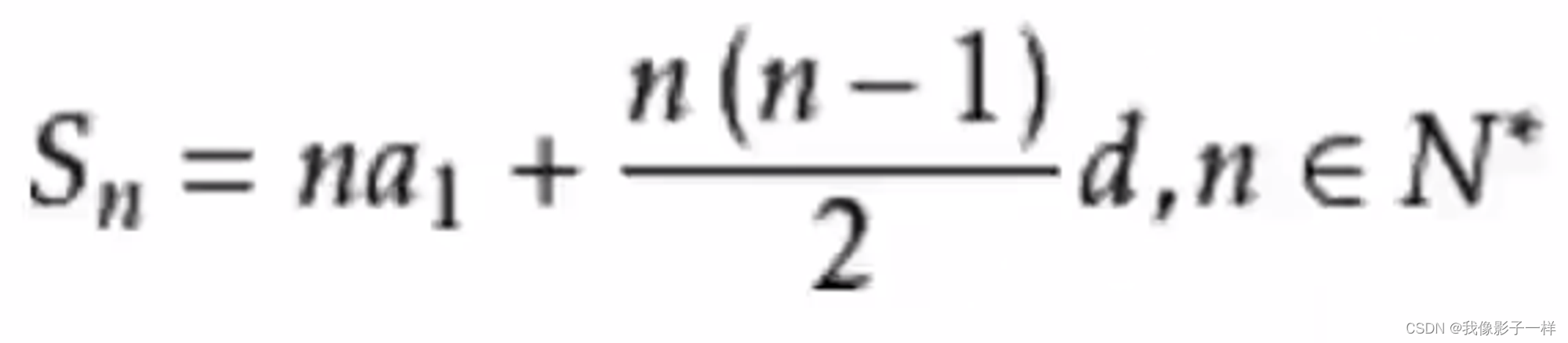第3节 二分、复杂度、动态数组、哈希表
发布时间:2023年12月22日
二分法
入门题目
- 有序数组中找到num
-
package class03; import java.util.Arrays; // 有序数组中找到num public class Code_BSExist { // arr保证有序 public static boolean find(int[] arr, int num) { // 二分法,有缺陷 if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) { // 边界条件 return false; } int L = 0; // 左边界 int R = arr.length - 1; // 有边界 // arr[L....R] 即arr[0...arr.length-1] 这个范围找num while (L <= R) { // <= 是有效范围 int mid = (L + R) / 2; //中点位置 if (arr[mid] == num) { return true; // 找到了 正确 } else if (arr[mid] < num) { // 小于的情况,左边的丢掉,继续找,新的L是mid+1 L = mid + 1; } else { // 大于num的情况,右侧不可能,继续找,新的R是mid-1 R = mid - 1; } } return false; // 以上情况都没找到return false } // for test public static boolean test(int[] arr, int num) { // 对数器 for (int cur : arr) { if (cur == num) { return true; } } return false; } public static int[] generateRandomArray(int maxLen, int maxValue) { int[] arr = new int[(int) ((maxLen + 1) * Math.random())]; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { arr[i] = (int) ((maxValue + 1) * Math.random()) - (int) (maxValue * Math.random()); } return arr; } public static void main(String[] args) { int testTime = 500000; int maxLen = 10; int maxValue = 100; boolean succeed = true; for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) { int[] arr = generateRandomArray(maxLen, maxValue); Arrays.sort(arr); // 排序 int value = (int) ((maxValue + 1) * Math.random()) - (int) (maxValue * Math.random()); if (test(arr, value) != find(arr, value)) { System.out.println("出错了!"); succeed = false; break; } } System.out.println(succeed ? "Nice!" : "Fucking fucked!"); } }
-
- 有序数组中找到>=num最左的位置
-
package class03; import java.util.Arrays; //在有序数组中找到>=num最左的位置 // [1,2,2,2,3,4,5,6,7] >=2 的最左位置的数是索引为1的数2,>=4 的最左位置是索引为5的数4 public class Code_BSNearLeft { // arr有序,找>=num 最左 public static int mostLeftNoLessNumIndex(int[] arr, int num) { if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) { return -1;// -1代表不在里面,返回-1代表没这个概念 } int L = 0; int R = arr.length - 1; int ans = -1; // 最晚发生的ans,令他等于-1 while (L <= R) {// 范围 // 在while里面会更新ans,直到找到符合最左位置的索引,它就跳出循环,return 它 int mid = (L + R) / 2; if (arr[mid] >= num) { ans = mid; // 往左找,需要更新 R = mid - 1; } else { // arr[mid]<num // 中点小于num,ans不更新 L = mid + 1;// 左边砍掉 } } return ans; // 如果没有>=这个数,它将以-1返回,即没这个数。 } // for test public static int test(int[] arr, int value) { //对数器 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { // 从左边开始遍历 if (arr[i] >= value) {// 第一个大于等于value的返回其索引位置 return i; } } return -1; } // for test public static int[] generateRandomArray(int maxSize, int maxValue) { int[] arr = new int[(int) (Math.random() * (maxSize + 1))]; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { arr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * (maxValue + 1)) - (int) (Math.random() * (maxValue)); } return arr; } public static void printArray(int[] arr) { for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); } } public static void main(String[] args) { int maxSize = 10; int maxValue = 100; int testTime = 500000; boolean succeed = true; for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) { int[] arr = generateRandomArray(maxSize, maxValue); Arrays.sort(arr);// 排序 int value = (int) (Math.random() * (maxValue + 1)) - (int) (Math.random() * (maxValue)); if (test(arr, value) != mostLeftNoLessNumIndex(arr, value)) { printArray(arr); System.out.println(value); System.out.println(test(arr, value)); System.out.println(mostLeftNoLessNumIndex(arr, value)); succeed = false; break; } } System.out.println(succeed ? "Nice!" : "Fucking fucked");// 无问题Nice,有问题Fucking fucked } }
-
- 有序数组中找到<=num最右的位置
-
package class03; import java.util.Arrays; public class Code_BSNearRight { //在有序数组中找到<=num最右的位置 // [1,2,2,2,3,4,5,6,7] <=2 的最左位置的数是索引为3的数2,<=4 的最左位置是索引为5的数4 // arr有序,找<=num 最右 public static int mostRightNoLessNumIndex(int[] arr, int num) { if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) { return -1; } int L = 0; int R = arr.length - 1; int ans = -1; while (L <= R) { int mid = (L + R) / 2; if (arr[mid] <= num) { ans = mid; // 更新ans L = mid + 1; // <=num,左边砍掉,找最右的数 } else {//arr[mid]>num R = mid - 1;// 右边砍掉 } } return ans; // 返回正确的结果 } //for test public static int test(int[] arr, int value) {// 对数器 for (int i = arr.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { if (arr[i] <= value) { return i; } } return -1; } // for test public static int[] generateRandomArray(int maxSize, int maxValue) { int[] arr = new int[(int) (Math.random() * (maxSize + 1))]; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { arr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * (maxValue + 1)) - (int) (Math.random() * (maxValue)); } return arr; } public static void printArray(int[] arr) { for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); } } public static void main(String[] args) { int maxSize = 10; int maxValue = 100; int testTime = 500000; // 测试次数 boolean succeed = true; for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) { int[] arr = generateRandomArray(maxSize, maxValue); Arrays.sort(arr); int value = (int) (Math.random() * (maxValue + 1)) - (int) (Math.random() * (maxValue)); if (test(arr, value) != mostRightNoLessNumIndex(arr, value)) { printArray(arr); System.out.println(value); System.out.println(test(arr, value)); System.out.println(mostRightNoLessNumIndex(arr, value)); succeed = false; break; } } System.out.println(succeed ? "Nice" : "Fucking fucked"); } }
-
- 局部最小值问题
-
package class03; // 局部最小值问题(无序数组) // 一个数组,无序,数组有条件,任意两个相邻的数之间不相等 [1,2,3,2,3,4]... /* * 局部最小定义: * 1)[0]<[1] 0位置的数是局部最小 * 2)[N-1]<[N-2] N-1位置的数是局部最小 * 3)左>[i]<右 i位置的数局部最小 * 总结以上三点,0~N-1必存在局部最小。0~1下降,N-2~N-1上升,所以必有 * 问题:返回以上其中一个局部最小即可 * */ public class Code_BSAwesome { // arr整体无序,要满足相邻的数不相等 public static int oneMidIndex(int[] arr) { if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {// 边界条件 return -1; } int N = arr.length; if (N == 1) { return 0;// 一个数,默认0位置最小 } if (arr[0] < arr[1]) { return 0; } if (arr[N - 1] < arr[N - 2]) { return N - 1; } //N > 2 的时候 // 二分 int L = 0; int R = N - 1; // L~R肯定有局部最小 while (L < R - 1) { // (边界条件) 为什么是L<R-1:因为L~R之间要3个数或3个数以上 int mid = (L + R) / 2; // 中点 if (arr[mid] < arr[mid - 1] && arr[mid] < arr[mid + 1]) { // 左>[i]<右 return mid; // 三个数(包括三个数)以上返回mid } else { /* * 不同时小,(我是arr[mid]) * 1)左 > 我 我 > 右 * 2)左 < 我 我 < 右 * 3)左 < 我 我 > 右 * */ // 如果是2、3情况,不用管右边,在左边继续找就行 if (arr[mid] > arr[mid - 1]) { // 砍掉右边,R这时候来到mid-1位置 R = mid - 1;// 更新R的位置 } else { // 否则就是1情况。 arr[mid] > arr[mid+1](必定) // 砍掉左边,L这时候来到mid+1位置 L = mid + 1;// 更新L的位置 } } } // L~R出来之后就是L>=R-1,要么两个数,要么只有一个数 return arr[L] < arr[R] ? L : R;// 如果arr[L]<arr[R] 就返回L,否则是R(如果只有L和R两个相邻位置的数,谁小就返回谁(一定对)) // [3,2,3,2,3] 二分之后只有[3,2],类似这种情况 } // 生成随机数组,且相邻数不相等 public static int[] randomArray(int maxLen, int maxValue) { int len = (int) (Math.random() * maxLen); int[] arr = new int[len]; // 相邻数不相等 if (len > 0) { arr[0] = (int) (Math.random() * maxValue); for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) { do { arr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * maxValue); } while (arr[i] == arr[i - 1]); // 如果相邻数相等,它就返回重做 } } return arr; } // 测试 public static boolean check(int[] arr, int minIndex) { if (arr.length == 0) { return minIndex == -1; } int left = minIndex - 1; // 定义局部最小左边的位置 int right = minIndex + 1; // 定义局部最小右边的位置 boolean leftBigger = left >= 0 ? arr[left] > arr[minIndex] : true; // 如果 left >= 0 时(有效位置),看是不是左边位置的数大于我,<0就越界,则无数不影响 boolean rightBigger = right < arr.length ? arr[right] > arr[minIndex] : true; // 如果 left < arr.length 时(有效位置),看是不是右边位置的数大于我,>arr.length就越界,则不管 return leftBigger && rightBigger; // 同时满足 } public static void printArray(int[] arr) { for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { int testTime = 1000000; int maxLen = 10; int maxValue = 200; System.out.println("测试开始"); for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) { int[] arr = randomArray(maxLen, maxValue); int ans = oneMidIndex(arr); if (!check(arr, ans)) { // 如果有问题就打印以下内容 printArray(arr); // 数组 System.out.println(ans); // 位置 break; } } System.out.println("测试结束"); } }
-
时间复杂度
分析选择、冒泡、插入排序的时间复杂度
- 等差数列求和公式
- 以上公式展开
- n^2/2-(1/2-a1)n
- 时间复杂度定义:整个表达式中最高阶的东西,就是它的复杂度,例如:冒泡的是O(n^2)
- 例1):1/100 n^2 + 1/500 n + 4 时间复杂度 O(n^2)
- 例2):1000万*n + 5000万 时间复杂度O(n)
- 时间复杂度在于数据量很大的情况下,怎么去描述算法时间的关系。 O(n^2) < O(n),O(n) 就是比 O(n^2)好
- 冒泡 可以写成 = a*n^2 + b*n + c a , b , c 是常数 O(n^2)
- 在二分中,它的时间复杂度是 O(㏒2 n) log以2为底n,n=2^? , 0~n 每次砍一半, 最接近n的问号就是它最多砍的次数
- 有的时候底数会省略,直接是O(log n)
- 常数操作是 O(1) (必定的)
- 要假设最差情况估计出来,跟n的关系,不能假设最好的情况,这才叫时间复杂度,才能是O(?)
?常见时间复杂度列表
- 从好到坏
- O(1)→O(logn)→O(n)→O(n*logn)→O(n^2)→O(n^3)→O(n^k)→O(2^n)→O(3^n)→O(k^n)…..→O(n!)
?
动态数组
- 动态数组是什么?
- Arraylist(Java)
- 例子:
- [ ]原先是固定长度为4的数组a
- 现在往里面放数,发现长度不够放了,在Arraylist,它会扩成[ ]长度为8的数组b,把数组a的数拷贝下来,并加新放的数
- 如果还不够,它会继续扩成长度为16的数组c,把b数组的数拷贝下来,并加新放的数。。。。这就是Arraylist
- 动态数组的使用和扩容
- 如果是固定数组,在固定数组找index,它的复杂度是 O(1)
- 现在是Arraylist,它会扩容,讨论扩容这件事会不会影响Arraylist的表现?
- 动态数组的扩容与时间复杂度分析
- 如果加入N个数,扩容的总代价是多少
- O(N)
- 如果加入1个数,扩容的代价是多少
- O(1) (均摊一下)
- 从时间复杂度角度上看,动态数组和固定数组的没有影响,跟固定数组一样好。
- 如果加入N个数,扩容的总代价是多少
?
哈希表和有序表?
- code?
-
package class03; import sun.reflect.generics.tree.Tree; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.TreeMap; public class Code_HashMapTreeMap { public static class Node { public int value; public Node(int v) { value = v; } } // (K,V)表,不管加了多少条数据,它都是常数时间,时间复杂度O(1),固定时间,它的时间比较大 public static void main(String[] args) { // String在HashMap表是按值传递的 // 按值传递,一张哈希表占一个字节 HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("lisifang", "我是李四方"); // 新增数据 System.out.println(map.containsKey("guojiahui")); // 查询是否有guojiahui这个key,上面刚加,所以一定有返回true System.out.println(map.containsKey("guo")); // 无,则返回false System.out.println(map.get("guojiahui")); // 取出K对应的V我是李四方 map.put("guojiahui", "他1是李四方"); // 更新数据 System.out.println(map.get("guojiahui")); // 他是李四方 // put既是新增操作也是更新value操作 // map.remove("guojiahui"); // 删除 // System.out.println(map.containsKey("guojiahui")); // false // System.out.println(map.get("guojiahui")); // 空 null值 String test1 = "guojiahui"; String test2 = "guojiahui"; System.out.println(map.containsKey(test1)); System.out.println(map.containsKey(test2)); HashMap<Integer, String> map2 = new HashMap<>(); map2.put(1234567, "我是1234567"); Integer a = 1234567; Integer b = 1234567; System.out.println(a == b); // false == 比较a的内存地址和b的内存地址是不是一块内存区域。 比较a和b的值用a.equals(b) // 哈希表中不管你的内存地址,只要你的值相等,它就存在 // Integer Double Float String Char 在哈希表中全部按值传递 System.out.println(map2.containsKey(a)); // true System.out.println(map2.containsKey(b)); // true // 非基础类型,非原生类型,哈希表它按引用传递 // 按引用传递,它一个地址占8字节,一张哈希表总共两个,所以它占16字节 Node node1 = new Node(1); Node node2 = new Node(1); HashMap<Node, String> map3 = new HashMap<>(); map3.put(node1,"我进来了"); System.out.println(map3.containsKey(node1)); // true 在 System.out.println(map3.containsKey(node2)); // false 不在 System.out.println("====================="); // 有序表,它的时间复杂度全部是O(logN),比哈希表慢 TreeMap<Integer,String> treeMap1 = new TreeMap<>(); treeMap1.put(3,"我是3"); treeMap1.put(0,"我是3"); treeMap1.put(7,"我是3"); treeMap1.put(2,"我是3"); treeMap1.put(5,"我是3"); treeMap1.put(9,"我是3"); System.out.println(treeMap1.containsKey(7)); // true 存在 System.out.println(treeMap1.containsKey(6)); // false 不存在 System.out.println(treeMap1.get(3)); // 我是3 treeMap1.put(3,"他是3"); //更新 System.out.println(treeMap1.get(3)); // 他是3 treeMap1.remove(3); // 删除 System.out.println(treeMap1.get(3)); // null // 与哈希表不同的 // 内部排好序 System.out.println(treeMap1.firstKey()); // 0 System.out.println(treeMap1.lastKey()); // 9 // <=5 离5最近的key告诉我 System.out.println(treeMap1.floorKey(5)); // 5 // <=6 离6最近的key告诉我 System.out.println(treeMap1.floorKey(6)); // 5 // >=5 离5最近的key告诉我 System.out.println(treeMap1.ceilingKey(5)); // 5 // >=6 离6最近的key告诉我 System.out.println(treeMap1.ceilingKey(6)); // 7 // 以下会报错,自己搞出来的结构,key不可比较,需要自己定义好key // 原生结构它会自己定义好来 Node node3 = new Node(3); Node node4 = new Node(4); TreeMap<Node,String> treeMap2 = new TreeMap<>(); treeMap2.put(node3,"我是node3"); treeMap2.put(node4,"我是node4"); } }
-
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_56181660/article/details/135144386
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- python统计学-两个总体均值差的区间估计
- 如何有效使用360评估
- 亚马逊测评怎么做?
- JavaScript基础
- 数据可视化|Python之Pyecharts将“爬虫数据”绘制饼状图
- 浏览器 标签栏 代码 - 删除
- 百度网盘百度下载倍速方法 亲测有用 无需会员
- 阿里云服务器安装Alibaba Cloud Linux 3.2104 LTS 64位操作系统可以吗?
- 不忘初心,聚焦安全 —— 一名码龄15年的老程序员2023总结
- 编码风格之(5)GNU软件编码风格(3)