【Kafka】开发实战和Springboot集成kafka
消息的发送与接收
生产者
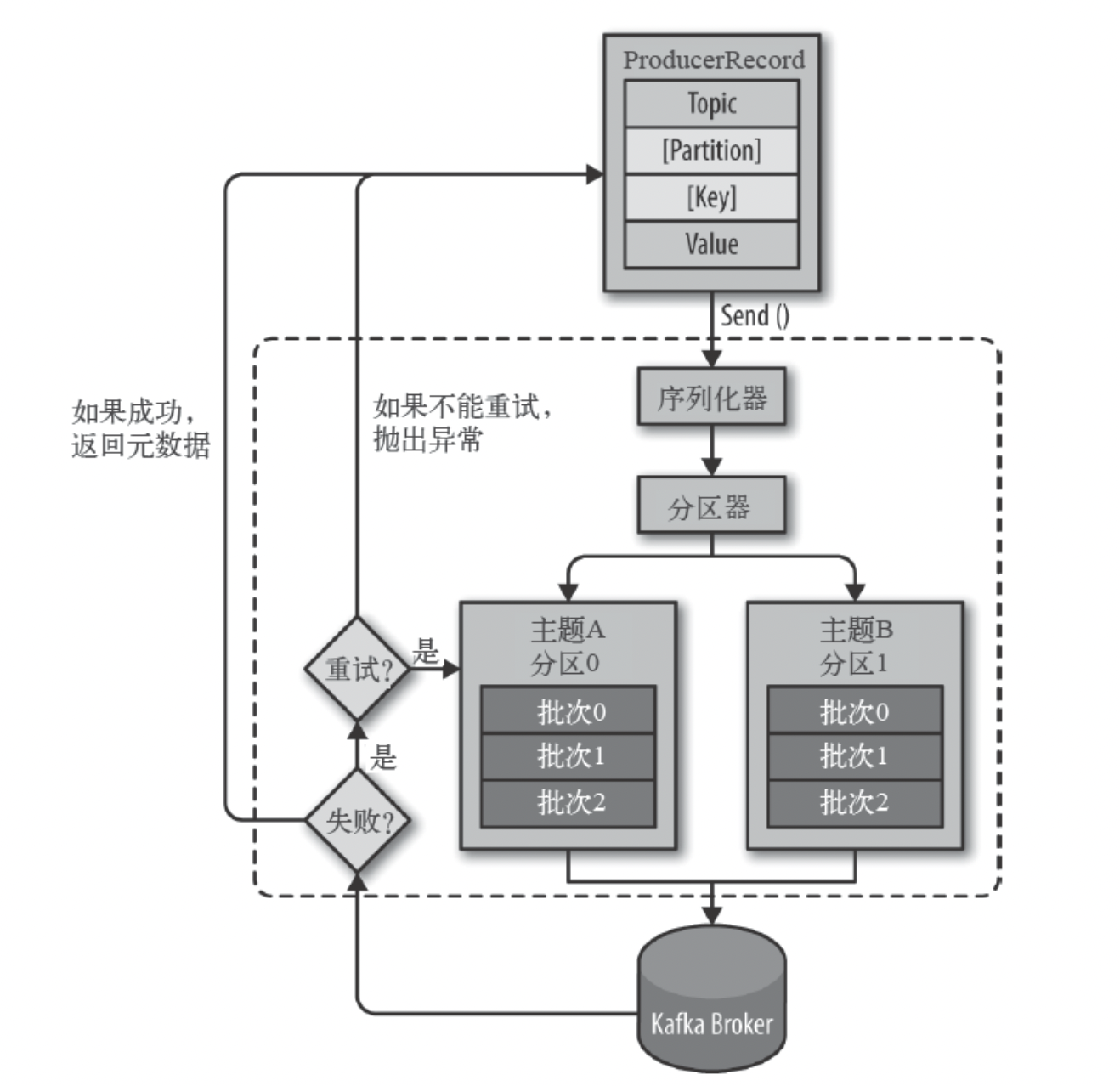
生产者主要的对象有: KafkaProducer , ProducerRecord 。
其中 KafkaProducer 是用于发送消息的类, ProducerRecord 类用于封装Kafka的消息。
KafkaProducer 的创建需要指定的参数和含义:
bootstrap.servers:配置生产者如何与broker建立连接。该参数设置的是初始化参数。如果生产者需要连接的是Kafka集群,则这里配置集群中几个部分broker的地址,而不是全部,当生产者连接上此处指定的broker之后,在通过该连接发现集群中的其他节点。key.serializer:要发送信息的key数据的序列化类。设置的时候可以写类名,也可以使用该类的Class对象。value.serializer:要发送消息的value数据的序列化类。设置的时候可以写类名,也可以使用该类的Class对象。acks:默认值:all。- acks=0:生产者不等待broker对消息的确认,只要将消息放到缓冲区,就认为消息已经发送完成。该情形不能保证broker是否真的收到了消息,retries配置也不会生效。发送的消息的返回的消息偏移量永远是-1。
- acks=1:表示消息只需要写到主分区即可,然后就响应客户端,而不等待副本分区的确认。在该情形下,如果主分区收到消息确认之后就宕机了,而副本分区还没来得及同步该消息,则该消息丢失。
- acks=all:leader分区会等待所有的ISR副本分区确认记录。该处理保证了只要有一个ISR副本分区存活,消息就不会丢失。这是Kafka最强的可靠性保证,等效于 acks=-1。
retries:retries重试次数。当消息发送出现错误的时候,系统会重发消息。跟客户端收到错误时重发一样。如果设置了重试,还想保证消息的有序性,需要设置MAX_IN_FLIGHT_REQUESTS_PER_CONNECTION=1,否则在重试此失败消息的时候,其他的消息可能发送成功了。
其他参数可以从 org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerConfig 中找到。后面的内容会介绍到。
消费者生产消息后,需要broker端的确认,可以同步确认,也可以异步确认。同步确认效率低,异步确认效率高,但是需要设置回调对象。
示例如下:
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.Callback;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerRecord;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.RecordMetadata;
import org.apache.kafka.common.header.Header;
import org.apache.kafka.common.header.internals.RecordHeader;
import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.IntegerSerializer;
import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
public class MyProducer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
Map<String, Object> configs = new HashMap<>();
// 指定初始连接用到的broker地址
configs.put("bootstrap.servers", "192.168.100.101:9092");
// 指定key的序列化类
configs.put("key.serializer", IntegerSerializer.class);
// 指定value的序列化类
configs.put("value.serializer", StringSerializer.class);
// configs.put("acks", "all");
// configs.put("reties", "3");
KafkaProducer<Integer, String> producer = new KafkaProducer<Integer, String>(configs);
// 用于设置用户自定义的消息头字段
List<Header> headers = new ArrayList<>();
headers.add(new RecordHeader("biz.name", "producer.demo".getBytes()));
ProducerRecord<Integer, String> record = new ProducerRecord<Integer, String>(
"topic_1", // topic
0, // 分区
0, // key
"hello lagou 0", // value
headers // headers
);
// 消息的同步确认
final Future<RecordMetadata> future = producer.send(record);
final RecordMetadata metadata = future.get();
System.out.println("消息的主题:" + metadata.topic());
System.out.println("消息的分区号:" + metadata.partition());
System.out.println("消息的偏移量:" + metadata.offset());
// 关闭生产者
producer.close();
}
}
如果需要异步发送,如下:
package com.lagou.kafka.demo.producer;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.Callback;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerRecord;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.RecordMetadata;
import org.apache.kafka.common.header.Header;
import org.apache.kafka.common.header.internals.RecordHeader;
import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.IntegerSerializer;
import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
public class MyProducer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
Map<String, Object> configs = new HashMap<>();
// 指定初始连接用到的broker地址
configs.put("bootstrap.servers", "192.168.100.101:9092");
// 指定key的序列化类
configs.put("key.serializer", IntegerSerializer.class);
// 指定value的序列化类
configs.put("value.serializer", StringSerializer.class);
// configs.put("acks", "all");
// configs.put("reties", "3");
KafkaProducer<Integer, String> producer = new KafkaProducer<Integer, String>(configs);
// 用于设置用户自定义的消息头字段
List<Header> headers = new ArrayList<>();
headers.add(new RecordHeader("biz.name", "producer.demo".getBytes()));
ProducerRecord<Integer, String> record = new ProducerRecord<Integer, String>(
"topic_1", // topic
0, // 分区
0, // key
"hello lagou 0", // value
headers // headers
);
// 消息的异步确认
producer.send(record, new Callback() {
@Override
public void onCompletion(RecordMetadata metadata, Exception exception) {
if (exception == null) {
System.out.println("消息的主题:" + metadata.topic());
System.out.println("消息的分区号:" + metadata.partition());
System.out.println("消息的偏移量:" + metadata.offset());
} else {
System.out.println("异常消息:" + exception.getMessage());
}
}
});
// 关闭生产者
producer.close();
}
}
消费者
kafka不支持消息的推送(当然可以自己已实现),采用的消息的拉取(poll方法)。
消费者主要的对象是kafkaConsumer,用于消费消息的类。
其主要参数:
bootstrap.servers:与kafka建立初始连接的broker地址列表key.deserializer:key的反序列化器value.deserializer:value的反序列化器group.id:指定消费者组id,用于标识该消费者属于哪个消费者组auto.offset.reset:当kafka中没有初始化偏移量或当前偏移量在服务器中不存在(如数据被删除了),处理办法earliest:自动重置偏移量到最早的偏移量latest:自动重置偏移量到最新的偏移量none:如果消费者组原来的偏移量(previous)不存在,向消费者抛出异常anything:向消费者抛异常
ConsumerConfig类中包含了所有的可以给kafkaConsumer的参数。
示例:
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerConfig;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecord;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecords;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.KafkaConsumer;
import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.IntegerDeserializer;
import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
public class MyConsumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Object> configs = new HashMap<>();
// node1对应于192.168.100.101,windows的hosts文件中手动配置域名解析
configs.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, "node1:9092");
// 使用常量代替手写的字符串,配置key的反序列化器
configs.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, IntegerDeserializer.class);
// 配置value的反序列化器
configs.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringDeserializer.class);
// 配置消费组ID
configs.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG, "consumer_demo1");
// 如果找不到当前消费者的有效偏移量,则自动重置到最开始
// latest表示直接重置到消息偏移量的最后一个
configs.put(ConsumerConfig.AUTO_OFFSET_RESET_CONFIG, "earliest");
KafkaConsumer<Integer, String> consumer = new KafkaConsumer<Integer, String>(configs);
// 先订阅,再消费
consumer.subscribe(Arrays.asList("topic_1"));
// 如果主题中没有可以消费的消息,则该方法可以放到while循环中,每过3秒重新拉取一次
// 如果还没有拉取到,过3秒再次拉取,防止while循环太密集的poll调用。
// 批量从主题的分区拉取消息
final ConsumerRecords<Integer, String> consumerRecords = consumer.poll(3_000);
// 遍历本次从主题的分区拉取的批量消息
consumerRecords.forEach(new Consumer<ConsumerRecord<Integer, String>>() {
@Override
public void accept(ConsumerRecord<Integer, String> record) {
System.out.println(record.topic() + "\t"
+ record.partition() + "\t"
+ record.offset() + "\t"
+ record.key() + "\t"
+ record.value());
}
});
consumer.close();
}
}
SpringBoot 集成kafka
这里把生产者和消费者放在一个项目中,实际可能是在两个里的。
1、引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、 配置
spring.application.name=springboot-kafka-02
server.port=8080
# 用于建立初始连接的broker地址
spring.kafka.bootstrap-servers=node1:9092
# producer用到的key和value的序列化类
spring.kafka.producer.key- serializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.IntegerSerializer
spring.kafka.producer.value- serializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
# 默认的批处理记录数
spring.kafka.producer.batch-size=16384
# 32MB的总发送缓存
spring.kafka.producer.buffer-memory=33554432
# consumer用到的key和value的反序列化类
spring.kafka.consumer.key- deserializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.IntegerDeserializer
spring.kafka.consumer.value- deserializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
# consumer的消费组id
spring.kafka.consumer.group-id=spring-kafka-02-consumer
# 是否自动提交消费者偏移量
spring.kafka.consumer.enable-auto-commit=true
# 每隔100ms向broker提交一次偏移量
spring.kafka.consumer.auto-commit-interval=100
# 如果该消费者的偏移量不存在,则自动设置为最早的偏移量
spring.kafka.consumer.auto-offset-reset=earliest
3、启动类
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Demo02SpringbootKafkaApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Demo02SpringbootKafkaApplication.class, args);
}
}
4、生产者
这里我们就写在Controller里就好,如下:
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.RecordMetadata;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.KafkaTemplate;
import org.springframework.kafka.support.SendResult;
import org.springframework.util.concurrent.ListenableFuture;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
@RestController
public class KafkaSyncProducerController {
@Autowired
private KafkaTemplate<Integer, String> template;
@RequestMapping("send/sync/{message}")
public String send(@PathVariable String message) {
final ListenableFuture<SendResult<Integer, String>> future = template.send("topic-spring-01", 0, 0, message);
// 同步发送消息
try {
final SendResult<Integer, String> sendResult = future.get();
final RecordMetadata metadata = sendResult.getRecordMetadata();
System.out.println(metadata.topic() + "\t" + metadata.partition() + "\t" + metadata.offset());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "success";
}
}
上面是同步发送消息,如果异步发送消息,可改为如下:
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.RecordMetadata;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.KafkaTemplate;
import org.springframework.kafka.support.SendResult;
import org.springframework.util.concurrent.ListenableFuture;
import org.springframework.util.concurrent.ListenableFutureCallback;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class KafkaAsyncProducerController {
@Autowired
private KafkaTemplate<Integer, String> template;
@RequestMapping("send/async/{message}")
public String send(@PathVariable String message) {
final ListenableFuture<SendResult<Integer, String>> future = this.template.send("topic-spring-01", 0, 1, message);
// 设置回调函数,异步等待broker端的返回结果
future.addCallback(new ListenableFutureCallback<SendResult<Integer, String>>() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("发送消息失败:" + throwable.getMessage());
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(SendResult<Integer, String> result) {
final RecordMetadata metadata = result.getRecordMetadata();
System.out.println("发送消息成功:" + metadata.topic() + "\t" + metadata.partition() + "\t" + metadata.offset());
}
});
return "success";
}
}
5、消费者
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecord;
import org.springframework.kafka.annotation.KafkaListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyConsumer {
@KafkaListener(topics = "topic-spring-01")
public void onMessage(ConsumerRecord<Integer, String> record) {
System.out.println("消费者收到的消息:"
+ record.topic() + "\t"
+ record.partition() + "\t"
+ record.offset() + "\t"
+ record.key() + "\t"
+ record.value());
}
}
6、kafka配置类
上面当我们启动生产者和消费者时,kafka会自动为我们创建好topic和分区等。那是因为kafka的KafkaAutoConfigration里有个KafkaAdmin,他负责自动检测需要创建的topic和分区等。如果我们想自己创建,或者自定义KafkaTemplate(一般不会这么做),可以使用配置类,如下:
import org.apache.kafka.clients.admin.NewTopic;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerConfig;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.KafkaAdmin;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.KafkaTemplate;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.ProducerFactory;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Configuration
public class KafkaConfig {
@Bean
public NewTopic topic1() {
return new NewTopic("nptc-01", 3, (short) 1);
}
@Bean
public NewTopic topic2() {
return new NewTopic("nptc-02", 5, (short) 1);
}
@Bean
public KafkaAdmin kafkaAdmin() {
Map<String, Object> configs = new HashMap<>();
configs.put("bootstrap.servers", "node1:9092");
KafkaAdmin admin = new KafkaAdmin(configs);
return admin;
}
@Bean
@Autowired
public KafkaTemplate<Integer, String> kafkaTemplate(ProducerFactory<Integer, String> producerFactory) {
// 覆盖ProducerFactory原有设置
Map<String, Object> configsOverride = new HashMap<>();
configsOverride.put(ProducerConfig.BATCH_SIZE_CONFIG, 200);
KafkaTemplate<Integer, String> template = new KafkaTemplate<Integer, String>(
producerFactory, configsOverride
);
return template;
}
}
服务端参数配置
$KAFKA_HOME/config/server.properties文件中的一些配置。
1、zookeeper.connect
该参数用于配置Kafka要连接的Zookeeper/集群的地址。
它的值是一个字符串,使用逗号分隔Zookeeper的多个地址。Zookeeper的单个地址是 host:port形式的,可以在最后添加Kafka在Zookeeper中的根节点路径。
如:
zookeeper.connect=node2:2181,node3:2181,node4:2181/myKafka 1
2、listeners
用于指定当前Broker向外发布服务的地址和端口。
配置项为
listeners=PLAINTEXT://:9092
如下:
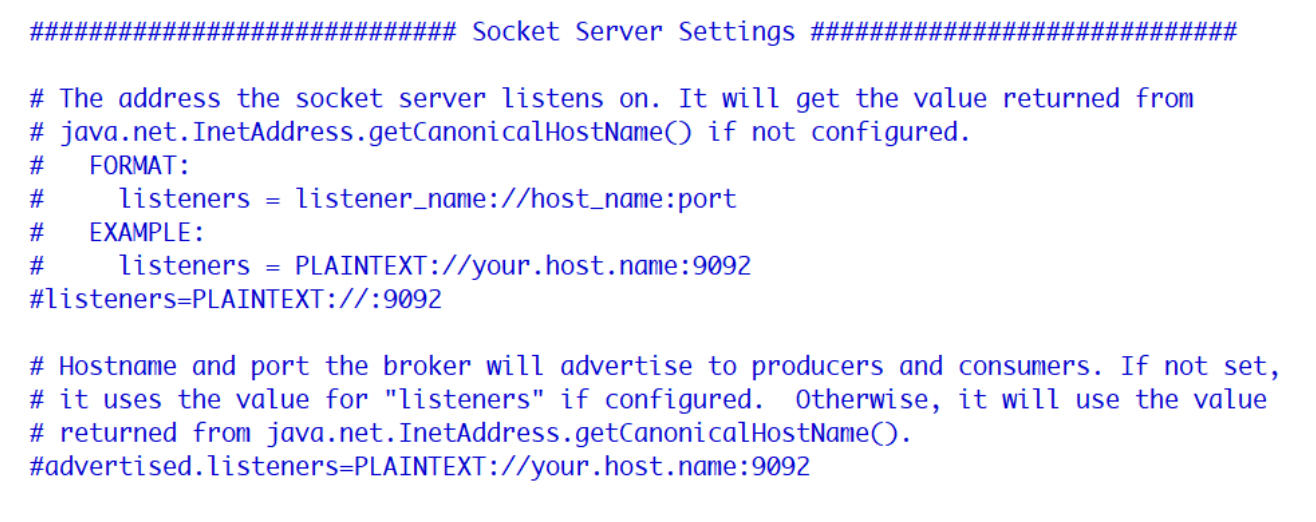
PLAINTEXT是一种协议名称;上面ip地址没写,可以配置成listeners=PLAINTEXT://0.0.0.0:9092,则只有本机可以访问。也可以是其他配置。
可以配置多个,逗号分割。但是多个listener的协议名称不能相同,且端口号不能相同。如果想用一个协议,则需要在listener.security.protocol.map维护听器名称和协议的map。
可以与 advertised.listeners 配合,用于做内外网隔离,比如创建topic和分区的等管理方面的使用一个地址,发送和消费消息则使用另一个地址,即管理和使用分开。
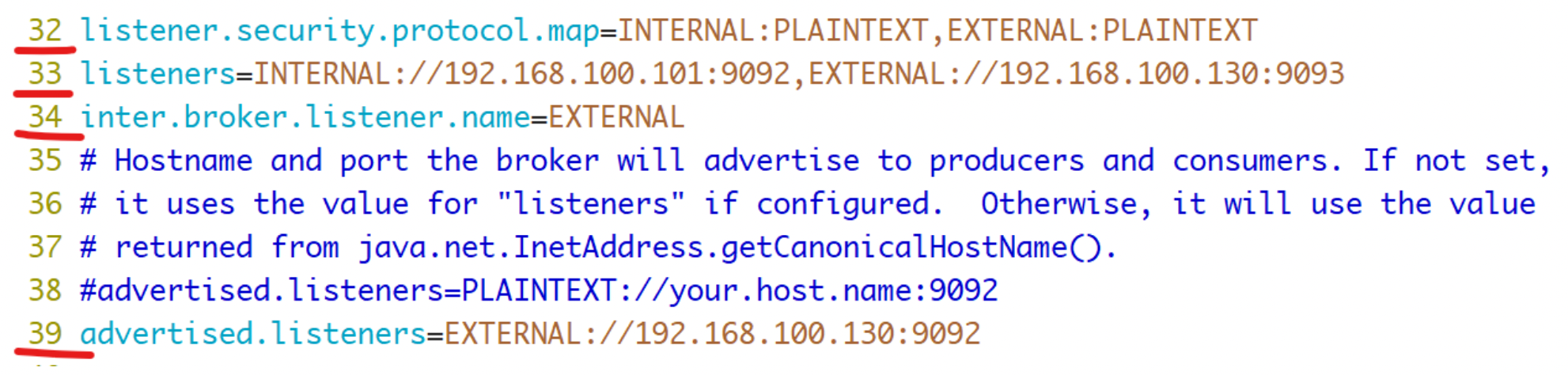
内外网隔离配置:
listener.security.protocol.map
监听器名称和安全协议的映射配置。比如,可以将内外网隔离,即使它们都使用SSL。
listener.security.protocol.map=INTERNAL:SSL,EXTERNAL:SSL
冒号前面代表监听器名称,后面代表真正的协议。每个监听器的名称只能在map中出现一次。
listeners
用于配置broker监听的URI以及监听器名称列表,使用逗号隔开多个URI及监听器名称。如果监听器名称代表的不是安全协议,必须配置listener.security.protocol.map。每个监听器必须使用不同的网络端口。
advertised.listeners
需要将该地址发布到zookeeper供客户端使用。
可以在zookeeper的 get /myKafka/brokers/ids/<broker.id> 中找到。
在IaaS环境,该条目的网络接口得与broker绑定的网络接口不同。
如果不设置此条目,就使用listeners的配置。跟listeners不同,该条目不能使用0.0.0.0网络端口。
advertised.listeners的地址必须是listeners中配置的或配置的一部分。
inter.broker.listener.name
用于配置broker之间通信使用的监听器名称,该名称必须在advertised.listeners列表中。
inter.broker.listener.name=EXTERNAL
典型配置如下:
3、 broker.id
该属性用于唯一标记一个Kafka的Broker,它的值是一个任意integer值。当Kafka以分布式集群运行的时候,尤为重要。
最好该值跟该Broker所在的物理主机有关的,如主机名为 host1.lagou.com ,则 broker.id=1 ;如果主机名为 192.168.100.101 ,则 broker.id=101 等等。
4、 log.dir
通过该属性的值,指定Kafka在磁盘上保存消息的日志片段的目录。它是一组用逗号分隔的本地文件系统路径。
如果指定了多个路径,那么broker 会根据“最少使用”原则,把同一个分区的日志片段保存到同一个路径下。
broker 会往拥有最少数目分区的路径新增分区,而不是往拥有最小磁盘空间的路径新增分区。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!