YOLOv5:指定类别进行评估验证
发布时间:2024年01月05日
前言
- 由于本人水平有限,难免出现错漏,敬请批评改正。
- 更多精彩内容,可点击进入Python日常小操作专栏、OpenCV-Python小应用专栏、YOLO系列专栏、自然语言处理专栏或我的个人主页查看
- 基于DETR的人脸伪装检测
- YOLOv7训练自己的数据集(口罩检测)
- YOLOv8训练自己的数据集(足球检测)
- YOLOv5:TensorRT加速YOLOv5模型推理
- YOLOv5:IoU、GIoU、DIoU、CIoU、EIoU
- 玩转Jetson Nano(五):TensorRT加速YOLOv5目标检测
- YOLOv5:添加SE、CBAM、CoordAtt、ECA注意力机制
- YOLOv5:yolov5s.yaml配置文件解读、增加小目标检测层
- Python将COCO格式实例分割数据集转换为YOLO格式实例分割数据集
- YOLOv5:使用7.0版本训练自己的实例分割模型(车辆、行人、路标、车道线等实例分割)
- 使用Kaggle GPU资源免费体验Stable Diffusion开源项目
前提条件
- 熟悉Python
相关介绍
- Python是一种跨平台的计算机程序设计语言。是一个高层次的结合了解释性、编译性、互动性和面向对象的脚本语言。最初被设计用于编写自动化脚本(shell),随着版本的不断更新和语言新功能的添加,越多被用于独立的、大型项目的开发。
- PyTorch 是一个深度学习框架,封装好了很多网络和深度学习相关的工具方便我们调用,而不用我们一个个去单独写了。它分为 CPU 和 GPU 版本,其他框架还有 TensorFlow、Caffe 等。PyTorch 是由 Facebook 人工智能研究院(FAIR)基于 Torch 推出的,它是一个基于 Python 的可续计算包,提供两个高级功能:1、具有强大的 GPU 加速的张量计算(如 NumPy);2、构建深度神经网络时的自动微分机制。
- YOLOv5是一种单阶段目标检测算法,该算法在YOLOv4的基础上添加了一些新的改进思路,使其速度与精度都得到了极大的性能提升。它是一个在COCO数据集上预训练的物体检测架构和模型系列,代表了Ultralytics对未来视觉AI方法的开源研究,其中包含了经过数千小时的研究和开发而形成的经验教训和最佳实践。
实验环境
- Python 3.x (面向对象的高级语言)
YOLOv5:指定类别进行评估验证
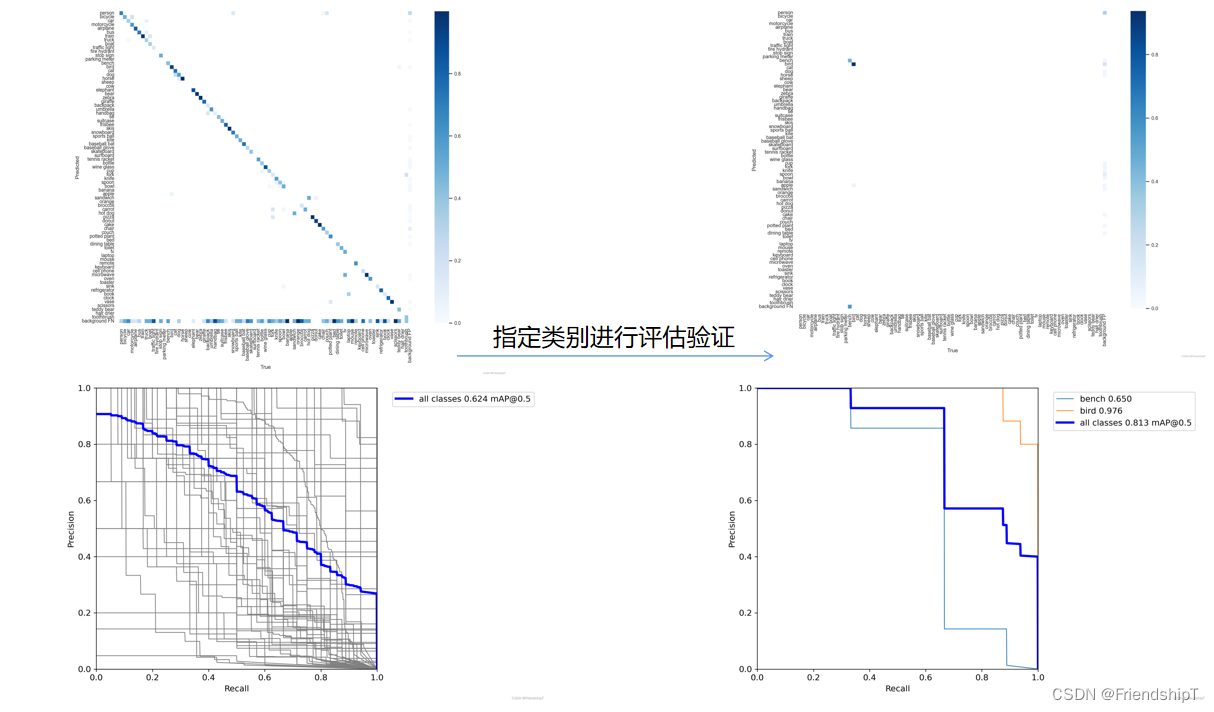
- 背景:在特定场景下,只想关注特定类别的效果,即可指定类别进行评估验证。
- 目录结构示例
代码实现
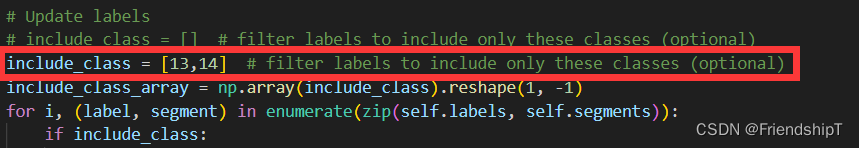
- 主要修改官方代码utils/datasets.py中552行的include_class变量。
# YOLOv5 🚀 by Ultralytics, GPL-3.0 license
"""
Dataloaders and dataset utils
"""
import glob
import hashlib
import json
import math
import os
import random
import shutil
import time
from itertools import repeat
from multiprocessing.pool import Pool, ThreadPool
from pathlib import Path
from threading import Thread
from zipfile import ZipFile
import cv2
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import yaml
from PIL import ExifTags, Image, ImageOps
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, Dataset, dataloader, distributed
from tqdm import tqdm
from utils.augmentations import Albumentations, augment_hsv, copy_paste, letterbox, mixup, random_perspective
from utils.general import (DATASETS_DIR, LOGGER, NUM_THREADS, check_dataset, check_requirements, check_yaml, clean_str,
segments2boxes, xyn2xy, xywh2xyxy, xywhn2xyxy, xyxy2xywhn)
from utils.torch_utils import torch_distributed_zero_first
# Parameters
HELP_URL = 'https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/wiki/Train-Custom-Data'
IMG_FORMATS = ['bmp', 'dng', 'jpeg', 'jpg', 'mpo', 'png', 'tif', 'tiff', 'webp'] # include image suffixes
VID_FORMATS = ['asf', 'avi', 'gif', 'm4v', 'mkv', 'mov', 'mp4', 'mpeg', 'mpg', 'wmv'] # include video suffixes
# ########################################相机设置########################################
# Get orientation exif tag
for orientation in ExifTags.TAGS.keys():
if ExifTags.TAGS[orientation] == 'Orientation':
break
def get_hash(paths):
# Returns a single hash value of a list of paths (files or dirs)
size = sum(os.path.getsize(p) for p in paths if os.path.exists(p)) # sizes
h = hashlib.md5(str(size).encode()) # hash sizes
h.update(''.join(paths).encode()) # hash paths
return h.hexdigest() # return hash
def exif_size(img):
# Returns exif-corrected PIL size
s = img.size # (width, height)
try:
rotation = dict(img._getexif().items())[orientation]
if rotation == 6: # rotation 270
s = (s[1], s[0])
elif rotation == 8: # rotation 90
s = (s[1], s[0])
except Exception:
pass
return s
def exif_transpose(image):
"""
Transpose a PIL image accordingly if it has an EXIF Orientation tag.
Inplace version of https://github.com/python-pillow/Pillow/blob/master/src/PIL/ImageOps.py exif_transpose()
:param image: The image to transpose.
:return: An image.
"""
exif = image.getexif()
orientation = exif.get(0x0112, 1) # default 1
if orientation > 1:
method = {2: Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT,
3: Image.ROTATE_180,
4: Image.FLIP_TOP_BOTTOM,
5: Image.TRANSPOSE,
6: Image.ROTATE_270,
7: Image.TRANSVERSE,
8: Image.ROTATE_90,
}.get(orientation)
if method is not None:
image = image.transpose(method)
del exif[0x0112]
image.info["exif"] = exif.tobytes()
return image
# #######################################################################################
def create_dataloader(path, imgsz, batch_size, stride, single_cls=False, hyp=None, augment=False, cache=False, pad=0.0,
rect=False, rank=-1, workers=8, image_weights=False, quad=False, prefix='', shuffle=False):
'''
在train.py中被调用,用于生成Trainloader, dataset,testloader
自定义dataloader函数: 调用LoadImagesAndLabels获取数据集(包括数据增强) + 调用分布式采样器DistributedSampler +
自定义InfiniteDataLoader 进行永久持续的采样数据
:param path: 图片数据加载路径 train/test 如: ../datasets/VOC/images/train2007
:param imgsz: train/test图片尺寸(数据增强后大小) 640
:param batch_size: batch size 大小 8/16/32
:param stride: 模型最大stride=32 [32 16 8]
:param single_cls: 数据集是否是单类别 默认False
:param hyp: 超参列表dict 网络训练时的一些超参数,包括学习率等,这里主要用到里面一些关于数据增强(旋转、平移等)的系数
:param augment: 是否要进行数据增强 True
:param cache: 是否cache_images False
:param pad: 设置矩形训练的shape时进行的填充 默认0.0
:param rect: 是否开启矩形train/test 默认训练集关闭 验证集开启
:param rank: 多卡训练时的进程编号 rank为进程编号 -1且gpu=1时不进行分布式 -1且多块gpu使用DataParallel模式 默认-1
:param workers: dataloader的numworks 加载数据时的cpu进程数
:param image_weights: 训练时是否根据图片样本真实框分布权重来选择图片 默认False
:param quad: dataloader取数据时, 是否使用collate_fn4代替collate_fn 默认False
:param prefix: 显示信息 一个标志,多为train/val,处理标签时保存cache文件会用到
:param shuffle: 是否乱序,默认False
'''
if rect and shuffle: # rect: 是否开启矩形train/test 默认训练集关闭
LOGGER.warning('WARNING: --rect is incompatible with DataLoader shuffle, setting shuffle=False')
shuffle = False
# 主进程实现数据的预读取并缓存,然后其它子进程则从缓存中读取数据并进行一系列运算。
# 为了完成数据的正常同步, yolov5基于torch.distributed.barrier()函数实现了上下文管理器
with torch_distributed_zero_first(rank): # init dataset *.cache only once if DDP
# 载入文件数据(增强数据集)
dataset = LoadImagesAndLabels(path, imgsz, batch_size,
augment=augment, # augmentation
hyp=hyp, # hyperparameters
rect=rect, # rectangular batches
cache_images=cache,
single_cls=single_cls,
stride=int(stride),
pad=pad,
image_weights=image_weights,
prefix=prefix)
batch_size = min(batch_size, len(dataset))
nd = torch.cuda.device_count() # number of CUDA devices
nw = min([os.cpu_count() // max(nd, 1), batch_size if batch_size > 1 else 0, workers]) # number of workers
# 分布式采样器DistributedSampler
sampler = None if rank == -1 else distributed.DistributedSampler(dataset, shuffle=shuffle)
# 使用InfiniteDataLoader和_RepeatSampler来对DataLoader进行封装, 代替原先的DataLoader, 能够永久持续的采样数据
loader = DataLoader if image_weights else InfiniteDataLoader # only DataLoader allows for attribute updates
return loader(dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=shuffle and sampler is None,
num_workers=nw,
sampler=sampler,
pin_memory=True,
collate_fn=LoadImagesAndLabels.collate_fn4 if quad else LoadImagesAndLabels.collate_fn), dataset
class InfiniteDataLoader(dataloader.DataLoader):
""" Dataloader that reuses workers
Uses same syntax as vanilla DataLoader
当image_weights=False时就会调用这两个函数 进行自定义DataLoader
https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/876
使用InfiniteDataLoader和_RepeatSampler来对DataLoader进行封装, 代替原先的DataLoader, 能够永久持续的采样数据
"""
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
# 调用_RepeatSampler进行持续采样
object.__setattr__(self, 'batch_sampler', _RepeatSampler(self.batch_sampler))
self.iterator = super().__iter__()
def __len__(self):
return len(self.batch_sampler.sampler)
def __iter__(self):
for i in range(len(self)):
yield next(self.iterator)
class _RepeatSampler:
""" Sampler that repeats forever
这部分是进行持续采样
Args:
sampler (Sampler)
"""
def __init__(self, sampler):
self.sampler = sampler
def __iter__(self):
while True:
yield from iter(self.sampler)
class LoadImages:
# YOLOv5 image/video dataloader, i.e. `python detect.py --source image.jpg/vid.mp4`
"""在detect.py中使用
load 文件夹中的图片/视频
定义迭代器 用于detect.py
"""
def __init__(self, path, img_size=640, stride=32, auto=True):
p = str(Path(path).resolve()) # os-agnostic absolute path
if '*' in p:
files = sorted(glob.glob(p, recursive=True)) # glob
elif os.path.isdir(p):
files = sorted(glob.glob(os.path.join(p, '*.*'))) # dir
elif os.path.isfile(p):
files = [p] # files
else:
raise Exception(f'ERROR: {p} does not exist')
images = [x for x in files if x.split('.')[-1].lower() in IMG_FORMATS]
videos = [x for x in files if x.split('.')[-1].lower() in VID_FORMATS]
ni, nv = len(images), len(videos)
self.img_size = img_size
self.stride = stride
self.files = images + videos
self.nf = ni + nv # number of files
self.video_flag = [False] * ni + [True] * nv
self.mode = 'image'
self.auto = auto
if any(videos):
self.new_video(videos[0]) # new video
else:
self.cap = None
assert self.nf > 0, f'No images or videos found in {p}. ' \
f'Supported formats are:\nimages: {IMG_FORMATS}\nvideos: {VID_FORMATS}'
def __iter__(self):
self.count = 0
return self
def __next__(self):
if self.count == self.nf:
raise StopIteration
path = self.files[self.count]
if self.video_flag[self.count]:
# Read video
self.mode = 'video'
ret_val, img0 = self.cap.read()
while not ret_val:
self.count += 1
self.cap.release()
if self.count == self.nf: # last video
raise StopIteration
else:
path = self.files[self.count]
self.new_video(path)
ret_val, img0 = self.cap.read()
self.frame += 1
s = f'video {self.count + 1}/{self.nf} ({self.frame}/{self.frames}) {path}: '
else:
# Read image
self.count += 1
img0 = cv2.imread(path) # BGR
assert img0 is not None, f'Image Not Found {path}'
s = f'image {self.count}/{self.nf} {path}: '
# Padded resize
img = letterbox(img0, self.img_size, stride=self.stride, auto=self.auto)[0]
# Convert
img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1))[::-1] # HWC to CHW, BGR to RGB
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
# 返回路径, resize+pad的图片, 原始图片, 视频对象
return path, img, img0, self.cap, s
def new_video(self, path):
self.frame = 0
self.cap = cv2.VideoCapture(path)
self.frames = int(self.cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
def __len__(self):
return self.nf # number of files
class LoadWebcam: # for inference
# YOLOv5 local webcam dataloader, i.e. `python detect.py --source 0`
def __init__(self, pipe='0', img_size=640, stride=32):
self.img_size = img_size
self.stride = stride
self.pipe = eval(pipe) if pipe.isnumeric() else pipe
self.cap = cv2.VideoCapture(self.pipe) # video capture object
self.cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_BUFFERSIZE, 3) # set buffer size
def __iter__(self):
self.count = -1
return self
def __next__(self):
self.count += 1
if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'): # q to quit
self.cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
raise StopIteration
# Read frame
ret_val, img0 = self.cap.read()
img0 = cv2.flip(img0, 1) # flip left-right
# Print
assert ret_val, f'Camera Error {self.pipe}'
img_path = 'webcam.jpg'
s = f'webcam {self.count}: '
# Padded resize
img = letterbox(img0, self.img_size, stride=self.stride)[0]
# Convert
img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1))[::-1] # HWC to CHW, BGR to RGB
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
return img_path, img, img0, None, s
def __len__(self):
return 0
class LoadStreams:
# YOLOv5 streamloader, i.e. `python detect.py --source 'rtsp://example.com/media.mp4' # RTSP, RTMP, HTTP streams`
def __init__(self, sources='streams.txt', img_size=640, stride=32, auto=True):
self.mode = 'stream'
self.img_size = img_size
self.stride = stride
if os.path.isfile(sources):
with open(sources) as f:
sources = [x.strip() for x in f.read().strip().splitlines() if len(x.strip())]
else:
sources = [sources]
n = len(sources)
self.imgs, self.fps, self.frames, self.threads = [None] * n, [0] * n, [0] * n, [None] * n
self.sources = [clean_str(x) for x in sources] # clean source names for later
self.auto = auto
for i, s in enumerate(sources): # index, source
# Start thread to read frames from video stream
st = f'{i + 1}/{n}: {s}... '
if 'youtube.com/' in s or 'youtu.be/' in s: # if source is YouTube video
check_requirements(('pafy', 'youtube_dl==2020.12.2'))
import pafy
s = pafy.new(s).getbest(preftype="mp4").url # YouTube URL
s = eval(s) if s.isnumeric() else s # i.e. s = '0' local webcam
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(s)
assert cap.isOpened(), f'{st}Failed to open {s}'
w = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
h = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS) # warning: may return 0 or nan
self.frames[i] = max(int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT)), 0) or float('inf') # infinite stream fallback
self.fps[i] = max((fps if math.isfinite(fps) else 0) % 100, 0) or 30 # 30 FPS fallback
_, self.imgs[i] = cap.read() # guarantee first frame
self.threads[i] = Thread(target=self.update, args=([i, cap, s]), daemon=True)
LOGGER.info(f"{st} Success ({self.frames[i]} frames {w}x{h} at {self.fps[i]:.2f} FPS)")
self.threads[i].start()
LOGGER.info('') # newline
# check for common shapes
s = np.stack([letterbox(x, self.img_size, stride=self.stride, auto=self.auto)[0].shape for x in self.imgs])
self.rect = np.unique(s, axis=0).shape[0] == 1 # rect inference if all shapes equal
if not self.rect:
LOGGER.warning('WARNING: Stream shapes differ. For optimal performance supply similarly-shaped streams.')
def update(self, i, cap, stream):
# Read stream `i` frames in daemon thread
n, f, read = 0, self.frames[i], 1 # frame number, frame array, inference every 'read' frame
while cap.isOpened() and n < f:
n += 1
# _, self.imgs[index] = cap.read()
cap.grab()
if n % read == 0:
success, im = cap.retrieve()
if success:
self.imgs[i] = im
else:
LOGGER.warning('WARNING: Video stream unresponsive, please check your IP camera connection.')
self.imgs[i] = np.zeros_like(self.imgs[i])
cap.open(stream) # re-open stream if signal was lost
time.sleep(1 / self.fps[i]) # wait time
def __iter__(self):
self.count = -1
return self
def __next__(self):
self.count += 1
if not all(x.is_alive() for x in self.threads) or cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'): # q to quit
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
raise StopIteration
# Letterbox
img0 = self.imgs.copy()
img = [letterbox(x, self.img_size, stride=self.stride, auto=self.rect and self.auto)[0] for x in img0]
# Stack
img = np.stack(img, 0)
# Convert
img = img[..., ::-1].transpose((0, 3, 1, 2)) # BGR to RGB, BHWC to BCHW
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
return self.sources, img, img0, None, ''
def __len__(self):
return len(self.sources) # 1E12 frames = 32 streams at 30 FPS for 30 years
def img2label_paths(img_paths):
# Define label paths as a function of image paths
sa, sb = os.sep + 'images' + os.sep, os.sep + 'labels' + os.sep # /images/, /labels/ substrings
return [sb.join(x.rsplit(sa, 1)).rsplit('.', 1)[0] + '.txt' for x in img_paths]
class LoadImagesAndLabels(Dataset):
# YOLOv5 train_loader/val_loader, loads images and labels for training and validation
cache_version = 0.6 # dataset labels *.cache version
def __init__(self, path, img_size=640, batch_size=16, augment=False, hyp=None, rect=False, image_weights=False,
cache_images=False, single_cls=False, stride=32, pad=0.0, prefix=''):
"""
初始化过程并没有什么实质性的操作,更多是一个定义参数的过程(self参数),以便在__getitem()__中进行数据增强操作,所以这部分代码只需要抓住self中的各个变量的含义就算差不多了
:param path: 图片数据加载路径 train/test 如: ../datasets/VOC/images/train2007
:param img_size: train/test图片尺寸(数据增强后大小) 640
:param batch_size: batch size 大小 8/16/32
:param augment: 是否要进行数据增强 True
:param hyp: 超参列表dict 网络训练时的一些超参数,包括学习率等,这里主要用到里面一些关于数据增强(旋转、平移等)的系数
:param rect: 是否开启矩形train/test 默认训练集关闭 验证集开启
:param image_weights: 训练时是否根据图片样本真实框分布权重来选择图片 默认False
:param cache_images: 是否cache_images False
:param single_cls: 数据集是否是单类别 默认False
:param stride: 模型最大stride=32 [32 16 8]
:param pad: 设置矩形训练的shape时进行的填充 默认0.0
:param prefix: 显示信息 一个标志,多为train/val,处理标签时保存cache文件会用到
self.img_files: {list: N} 存放着整个数据集图片的相对路径
self.label_files: {list: N} 存放着整个数据集标签的相对路径
cache label -> verify_image_label
self.labels: 如果数据集所有图片中没有一个多边形label labels存储的label就都是原始label(都是正常的矩形label)
否则将所有图片正常gt的label存入labels 不正常gt(存在一个多边形)经过segments2boxes转换为正常的矩形label
self.shapes: 所有图片的shape
self.segments: 如果数据集所有图片中没有一个多边形label self.segments=None
否则存储数据集中所有存在多边形gt的图片的所有原始label(肯定有多边形label 也可能有矩形正常label 未知数)
self.batch: 记载着每张图片属于哪个batch
self.n: 数据集中所有图片的数量
self.indices: 记载着所有图片的index
self.rect=True时self.batch_shapes记载每个batch的shape(同一个batch的图片shape相同)
"""
# 赋值一些基础的self变量 用于后面在__getitem__中调用
self.img_size = img_size # 经过数据增强后的数据图片的大小
self.augment = augment # # 是否启动数据增强 一般train时打开 val时关闭
self.hyp = hyp # # 超参列表
# 图片按权重采样 True就可以根据类别频率(频率高的权重小,反正大)来进行采样 默认False: 不作类别区分
self.image_weights = image_weights # 默认Fales
# 是否启动矩形训练 一般训练时关闭 验证时打开 可以加速
self.rect = False if image_weights else rect
self.mosaic = self.augment and not self.rect # load 4 images at a time into a mosaic (only during training)
# # mosaic增强的边界值 [-320, -320]
self.mosaic_border = [-img_size // 2, -img_size // 2]
self.stride = stride # 最大下采样率 32
self.path = path # 图片路径
self.albumentations = Albumentations() if augment else None
# 得到path路径下的所有图片的路径self.img_files
try:
f = [] # image files
for p in path if isinstance(path, list) else [path]:
# 获取数据集路径path,包含图片路径的txt文件或者包含图片的文件夹路径
# 使用pathlib.Path生成与操作系统无关的路径,因为不同操作系统路径的‘/’会有所不同
p = Path(p) # os-agnostic
# 如果路径path为包含图片的文件夹路径
if p.is_dir(): # dir
# glob.glab: 返回所有匹配的文件路径列表 递归获取p路径下所有文件
f += glob.glob(str(p / '**' / '*.*'), recursive=True)
# f = list(p.rglob('*.*')) # pathlib
# 如果路径path为包含图片路径的txt文件
elif p.is_file(): # file
with open(p) as t:
# 获取图片路径,更换相对路径
t = t.read().strip().splitlines()
# 获取数据集路径的上级父目录 os.sep为路径里的分隔符(不同路径的分隔符不同,os.sep可以根据系统自适应)
parent = str(p.parent) + os.sep
f += [x.replace('./', parent) if x.startswith('./') else x for x in t] # local to global path
# f += [p.parent / x.lstrip(os.sep) for x in t] # local to global path (pathlib)
else:
raise Exception(f'{prefix}{p} does not exist')
# 破折号替换为os.sep,os.path.splitext(x)将文件名与扩展名分开并返回一个列表
# 筛选f中所有的图片文件
self.img_files = sorted(x.replace('/', os.sep) for x in f if x.split('.')[-1].lower() in IMG_FORMATS)
# self.img_files = sorted([x for x in f if x.suffix[1:].lower() in IMG_FORMATS]) # pathlib
assert self.img_files, f'{prefix}No images found'
except Exception as e:
raise Exception(f'{prefix}Error loading data from {path}: {e}\nSee {HELP_URL}')
# Check cache
# 根据imgs路径找到labels的路径self.label_files
self.label_files = img2label_paths(self.img_files) # labels
# cache label 下次运行这个脚本的时候直接从cache中取label而不是去文件中取label 速度更快
cache_path = (p if p.is_file() else Path(self.label_files[0]).parent).with_suffix('.cache')
try:
# 如果有cache文件,直接加载 exists=True: 是否已从cache文件中读出了nf, nm, ne, nc, n等信息
cache, exists = np.load(cache_path, allow_pickle=True).item(), True # load dict
# 如果图片版本信息或者文件列表的hash值对不上号 说明本地数据集图片和label可能发生了变化 就重新cache label文件
assert cache['version'] == self.cache_version # same version
assert cache['hash'] == get_hash(self.label_files + self.img_files) # same hash
except Exception:
# 否则调用cache_labels缓存标签及标签相关信息
cache, exists = self.cache_labels(cache_path, prefix), False # cache
# Display cache
# 打印cache的结果 nf nm ne nc n = 找到的标签数量,漏掉的标签数量,空的标签数量,损坏的标签数量,总的标签数量
nf, nm, ne, nc, n = cache.pop('results') # found, missing, empty, corrupt, total
# 如果已经从cache文件读出了nf nm ne nc n等信息,直接显示标签信息 msgs信息等
if exists:
d = f"Scanning '{cache_path}' images and labels... {nf} found, {nm} missing, {ne} empty, {nc} corrupt"
tqdm(None, desc=prefix + d, total=n, initial=n) # display cache results
if cache['msgs']:
LOGGER.info('\n'.join(cache['msgs'])) # display warnings
# 数据集没有标签信息 就发出警告并显示标签label下载地址help_url
assert nf > 0 or not augment, f'{prefix}No labels in {cache_path}. Can not train without labels. See {HELP_URL}'
# Read cache
# Read cache 从cache中读出最新变量赋给self 方便给forward中使用
# cache中的键值对最初有: cache[img_file]=[l, shape, segments] cache[hash] cache[results] cache[msg] cache[version]
# 先从cache中去除cache文件中其他无关键值如:'hash', 'version', 'msgs'等都删除
[cache.pop(k) for k in ('hash', 'version', 'msgs')] # remove items
# pop掉results、hash、version、msgs后只剩下cache[img_file]=[l, shape, segments]
# cache.values(): 取cache中所有值 对应所有l, shape, segments
# labels: 如果数据集所有图片中没有一个多边形label labels存储的label就都是原始label(都是正常的矩形label)
# 否则将所有图片正常gt的label存入labels 不正常gt(存在一个多边形)经过segments2boxes转换为正常的矩形label
# shapes: 所有图片的shape
# self.segments: 如果数据集所有图片中没有一个多边形label self.segments=None
# 否则存储数据集中所有存在多边形gt的图片的所有原始label(肯定有多边形label 也可能有矩形正常label 未知数)
# zip 是因为cache中所有labels、shapes、segments信息都是按每张img分开存储的, zip是将所有图片对应的信息叠在一起
labels, shapes, self.segments = zip(*cache.values()) # # segments: 都是[]
self.labels = list(labels) # labels to list
self.shapes = np.array(shapes, dtype=np.float64) # image shapes to float64
# 更新所有图片的img_files信息 update img_files from cache result
self.img_files = list(cache.keys()) # update
# 更新所有图片的label_files信息(因为img_files信息可能发生了变化)
self.label_files = img2label_paths(cache.keys()) # update
n = len(shapes) # number of images
bi = np.floor(np.arange(n) / batch_size).astype(np.int) # batch index
nb = bi[-1] + 1 # number of batches
self.batch = bi # batch index of image
self.n = n
self.indices = range(n)
# Update labels
# include_class = [] # filter labels to include only these classes (optional)
include_class = [13,14] # filter labels to include only these classes (optional)
include_class_array = np.array(include_class).reshape(1, -1)
for i, (label, segment) in enumerate(zip(self.labels, self.segments)):
if include_class:
j = (label[:, 0:1] == include_class_array).any(1)
self.labels[i] = label[j]
if segment:
self.segments[i] = segment[j]
if single_cls: # single-class training, merge all classes into 0
self.labels[i][:, 0] = 0
if segment:
self.segments[i][:, 0] = 0
# Rectangular Training
# 为Rectangular Training作准备
# 这里主要是注意shapes的生成 这一步很重要 因为如果采样矩形训练那么整个batch的形状要一样 就要计算这个符合整个batch的shape
# 而且还要对数据集按照高宽比进行排序 这样才能保证同一个batch的图片的形状差不多相同 再选则一个共同的shape代价也比较小
if self.rect:
# Sort by aspect ratio
s = self.shapes # wh
ar = s[:, 1] / s[:, 0] # aspect ratio
irect = ar.argsort() # 根据高宽比排序
self.img_files = [self.img_files[i] for i in irect] # 获取排序后的img_files
self.label_files = [self.label_files[i] for i in irect] # 获取排序后的label_files
self.labels = [self.labels[i] for i in irect] # 获取排序后的labels
self.shapes = s[irect] # wh # 获取排序后的wh
ar = ar[irect] # 获取排序后的aspect ratio
# Set training image shapes
# 计算每个batch采用的统一尺度 Set training image shapes
shapes = [[1, 1]] * nb
for i in range(nb):
ari = ar[bi == i] # bi: batch index
mini, maxi = ari.min(), ari.max() # 获取第i个batch中,最小和最大高宽比
# 如果高/宽小于1(w > h),将w设为img_size(保证原图像尺度不变进行缩放)
if maxi < 1:
shapes[i] = [maxi, 1]
# 如果高/宽大于1(w < h),将h设置为img_size(保证原图像尺度不变进行缩放)
elif mini > 1:
shapes[i] = [1, 1 / mini]
# 计算每个batch输入网络的shape值(向上设置为32的整数倍)
# 要求每个batch_shapes的高宽都是32的整数倍,所以要先除以32,取整再乘以32(不过img_size如果是32倍数这里就没必要了)
self.batch_shapes = np.ceil(np.array(shapes) * img_size / stride + pad).astype(np.int) * stride
# Cache images into RAM/disk for faster training (WARNING: large datasets may exceed system resources)
# 是否需要cache image 一般是False 因为RAM会不足 cache label还可以 但是cache image就太大了 所以一般不用
# Cache images into memory for faster training (WARNING: large datasets may exceed system RAM)
self.imgs, self.img_npy = [None] * n, [None] * n
if cache_images:
if cache_images == 'disk':
self.im_cache_dir = Path(Path(self.img_files[0]).parent.as_posix() + '_npy')
self.img_npy = [self.im_cache_dir / Path(f).with_suffix('.npy').name for f in self.img_files]
self.im_cache_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
gb = 0 # Gigabytes of cached images
self.img_hw0, self.img_hw = [None] * n, [None] * n
results = ThreadPool(NUM_THREADS).imap(self.load_image, range(n))
pbar = tqdm(enumerate(results), total=n)
for i, x in pbar:
if cache_images == 'disk':
if not self.img_npy[i].exists():
np.save(self.img_npy[i].as_posix(), x[0])
gb += self.img_npy[i].stat().st_size
else: # 'ram'
self.imgs[i], self.img_hw0[i], self.img_hw[i] = x # im, hw_orig, hw_resized = load_image(self, i)
gb += self.imgs[i].nbytes
pbar.desc = f'{prefix}Caching images ({gb / 1E9:.1f}GB {cache_images})'
pbar.close()
def cache_labels(self, path=Path('./labels.cache'), prefix=''):
# Cache dataset labels, check images and read shapes
"""用在__init__函数中 cache数据集label
加载label信息生成cache文件 Cache dataset labels, check images and read shapes
:params path: cache文件保存地址
:params prefix: 日志头部信息(彩打高亮部分)
:return x: cache中保存的字典
包括的信息有: x[im_file] = [l, shape, segments]
一张图片一个label相对应的保存到x, 最终x会保存所有图片的相对路径、gt框的信息、形状shape、所有的多边形gt信息
im_file: 当前这张图片的path相对路径
l: 当前这张图片的所有gt框的label信息(不包含segment多边形标签) [gt_num, cls+xywh(normalized)]
shape: 当前这张图片的形状 shape
segments: 当前这张图片所有gt的label信息(包含segment多边形标签) [gt_num, xy1...]
hash: 当前图片和label文件的hash值 1
results: 找到的label个数nf, 丢失label个数nm, 空label个数ne, 破损label个数nc, 总img/label个数len(self.img_files)
msgs: 所有数据集的msgs信息
version: 当前cache version
"""
x = {} # dict # 初始化最终cache中保存的字典dict
# 初始化number missing, found, empty, corrupt, messages
# 初始化整个数据集: 漏掉的标签(label)总数量, 找到的标签(label)总数量, 空的标签(label)总数量, 错误标签(label)总数量, 所有错误信息
nm, nf, ne, nc, msgs = 0, 0, 0, 0, [] # number missing, found, empty, corrupt, messages
desc = f"{prefix}Scanning '{path.parent / path.stem}' images and labels..."
# 多进程调用verify_image_label函数
with Pool(NUM_THREADS) as pool:
# 定义pbar进度条
# pool.imap_unordered: 对大量数据遍历多进程计算 返回一个迭代器
# 把self.img_files, self.label_files, repeat(prefix) list中的值作为参数依次送入(一次送一个)verify_image_label函数
pbar = tqdm(pool.imap(verify_image_label, zip(self.img_files, self.label_files, repeat(prefix))),
desc=desc, total=len(self.img_files))
# im_file: 当前这张图片的path相对路径
# l: [gt_num, cls+xywh(normalized)]
# 如果这张图片没有一个segment多边形标签 l就存储原label(全部是正常矩形标签)
# 如果这张图片有一个segment多边形标签 l就存储经过segments2boxes处理好的标签(正常矩形标签不处理 多边形标签转化为矩形标签)
# shape: 当前这张图片的形状 shape
# segments: 如果这张图片没有一个segment多边形标签 存储None
# 如果这张图片有一个segment多边形标签 就把这张图片的所有label存储到segments中(若干个正常gt 若干个多边形标签) [gt_num, xy1...]
# nm_f(nm): number missing 当前这张图片的label是否丢失 丢失=1 存在=0
# nf_f(nf): number found 当前这张图片的label是否存在 存在=1 丢失=0
# ne_f(ne): number empty 当前这张图片的label是否是空的 空的=1 没空=0
# nc_f(nc): number corrupt 当前这张图片的label文件是否是破损的 破损的=1 没破损=0
# msg: 返回的msg信息 label文件完好=‘’ label文件破损=warning信息
for im_file, lb, shape, segments, nm_f, nf_f, ne_f, nc_f, msg in pbar:
nm += nm_f # 累加总number missing label
nf += nf_f # 累加总number found label
ne += ne_f # 累加总number empty label
nc += nc_f # 累加总number corrupt label
if im_file:
x[im_file] = [lb, shape, segments] # 信息存入字典 key=im_file value=[l, shape, segments]
if msg:
msgs.append(msg) # # 将msg加入总msg
pbar.desc = f"{desc}{nf} found, {nm} missing, {ne} empty, {nc} corrupt"
pbar.close() # 关闭进度条
# 日志打印所有msg信息
if msgs:
LOGGER.info('\n'.join(msgs))
# 一张label都没找到 日志打印help_url下载地址
if nf == 0:
LOGGER.warning(f'{prefix}WARNING: No labels found in {path}. See {HELP_URL}')
# 将当前图片和label文件的hash值存入最终字典dist
x['hash'] = get_hash(self.label_files + self.img_files)
# 将nf, nm, ne, nc, len(self.img_files)存入最终字典dist
x['results'] = nf, nm, ne, nc, len(self.img_files)
# 将所有数据集的msgs信息存入最终字典dist
x['msgs'] = msgs # warnings
# 将当前cache version存入最终字典dist
x['version'] = self.cache_version # cache version
try:
np.save(path, x) # save cache for next time
path.with_suffix('.cache.npy').rename(path) # remove .npy suffix
LOGGER.info(f'{prefix}New cache created: {path}')
except Exception as e:
LOGGER.warning(f'{prefix}WARNING: Cache directory {path.parent} is not writeable: {e}') # not writeable
return x
def __len__(self):
'''
求数据集图片的数量。
'''
return len(self.img_files)
# def __iter__(self):
# self.count = -1
# print('ran dataset iter')
# #self.shuffled_vector = np.random.permutation(self.nF) if self.augment else np.arange(self.nF)
# return self
def __getitem__(self, index):
"""
这部分是数据增强函数,一般一次性执行batch_size次。
训练 数据增强: mosaic(random_perspective) + hsv + 上下左右翻转
测试 数据增强: letterbox
:return torch.from_numpy(img): 这个index的图片数据(增强后) [3, 640, 640]
:return labels_out: 这个index图片的gt label [6, 6] = [gt_num, 0+class+xywh(normalized)]
:return self.img_files[index]: 这个index图片的路径地址
:return shapes: 这个batch的图片的shapes 测试时(矩形训练)才有 验证时为None for COCO mAP rescaling
"""
index = self.indices[index] # linear, shuffled, or image_weights
hyp = self.hyp
mosaic = self.mosaic and random.random() < hyp['mosaic']
if mosaic:
# Load mosaic
img, labels = self.load_mosaic(index)
shapes = None
# MixUp augmentation
if random.random() < hyp['mixup']:
img, labels = mixup(img, labels, *self.load_mosaic(random.randint(0, self.n - 1)))
else:
# Load image
img, (h0, w0), (h, w) = self.load_image(index)
# Letterbox
shape = self.batch_shapes[self.batch[index]] if self.rect else self.img_size # final letterboxed shape
img, ratio, pad = letterbox(img, shape, auto=False, scaleup=self.augment)
shapes = (h0, w0), ((h / h0, w / w0), pad) # for COCO mAP rescaling
labels = self.labels[index].copy()
if labels.size: # normalized xywh to pixel xyxy format
labels[:, 1:] = xywhn2xyxy(labels[:, 1:], ratio[0] * w, ratio[1] * h, padw=pad[0], padh=pad[1])
if self.augment:
img, labels = random_perspective(img, labels,
degrees=hyp['degrees'],
translate=hyp['translate'],
scale=hyp['scale'],
shear=hyp['shear'],
perspective=hyp['perspective'])
nl = len(labels) # number of labels
if nl:
labels[:, 1:5] = xyxy2xywhn(labels[:, 1:5], w=img.shape[1], h=img.shape[0], clip=True, eps=1E-3)
if self.augment:
# Albumentations
img, labels = self.albumentations(img, labels)
nl = len(labels) # update after albumentations
# HSV color-space
augment_hsv(img, hgain=hyp['hsv_h'], sgain=hyp['hsv_s'], vgain=hyp['hsv_v'])
# Flip up-down
if random.random() < hyp['flipud']:
img = np.flipud(img)
if nl:
labels[:, 2] = 1 - labels[:, 2]
# Flip left-right
if random.random() < hyp['fliplr']:
img = np.fliplr(img)
if nl:
labels[:, 1] = 1 - labels[:, 1]
# Cutouts
# labels = cutout(img, labels, p=0.5)
# nl = len(labels) # update after cutout
labels_out = torch.zeros((nl, 6))
if nl:
labels_out[:, 1:] = torch.from_numpy(labels)
# Convert
img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1))[::-1] # HWC to CHW, BGR to RGB
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
return torch.from_numpy(img), labels_out, self.img_files[index], shapes
def load_image(self, i):
"""用在LoadImagesAndLabels模块的__getitem__函数和load_mosaic模块中
从self或者从对应图片路径中载入对应index的图片 并将原图中hw中较大者扩展到self.img_size, 较小者同比例扩展
loads 1 image from dataset, returns img, original hw, resized hw
:params self: 一般是导入LoadImagesAndLabels中的self
:param index: 当前图片的index
:return: img: resize后的图片
(h0, w0): hw_original 原图的hw
img.shape[:2]: hw_resized resize后的图片hw(hw中较大者扩展到self.img_size, 较小者同比例扩展)
"""
# loads 1 image from dataset index 'i', returns (im, original hw, resized hw)
im = self.imgs[i]
if im is None: # not cached in RAM
npy = self.img_npy[i]
if npy and npy.exists(): # load npy
im = np.load(npy)
else: # read image
f = self.img_files[i]
im = cv2.imread(f) # BGR
assert im is not None, f'Image Not Found {f}'
h0, w0 = im.shape[:2] # orig hw
r = self.img_size / max(h0, w0) # ratio
if r != 1: # if sizes are not equal
im = cv2.resize(im,
(int(w0 * r), int(h0 * r)),
interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR if (self.augment or r > 1) else cv2.INTER_AREA)
return im, (h0, w0), im.shape[:2] # im, hw_original, hw_resized
else:
return self.imgs[i], self.img_hw0[i], self.img_hw[i] # im, hw_original, hw_resized
def load_mosaic(self, index):
"""用在LoadImagesAndLabels模块的__getitem__函数 进行mosaic数据增强
将四张图片拼接在一张马赛克图像中 loads images in a 4-mosaic
:param index: 需要获取的图像索引
:return: img4: mosaic和随机透视变换后的一张图片 numpy(640, 640, 3)
labels4: img4对应的target [M, cls+x1y1x2y2]
"""
# YOLOv5 4-mosaic loader. Loads 1 image + 3 random images into a 4-image mosaic
labels4, segments4 = [], []
s = self.img_size
yc, xc = (int(random.uniform(-x, 2 * s + x)) for x in self.mosaic_border) # mosaic center x, y
indices = [index] + random.choices(self.indices, k=3) # 3 additional image indices
random.shuffle(indices)
for i, index in enumerate(indices):
# Load image
img, _, (h, w) = self.load_image(index)
# place img in img4
if i == 0: # top left
img4 = np.full((s * 2, s * 2, img.shape[2]), 114, dtype=np.uint8) # base image with 4 tiles
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), max(yc - h, 0), xc, yc # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (large image)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), h - (y2a - y1a), w, h # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (small image)
elif i == 1: # top right
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, max(yc - h, 0), min(xc + w, s * 2), yc
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, h - (y2a - y1a), min(w, x2a - x1a), h
elif i == 2: # bottom left
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), yc, xc, min(s * 2, yc + h)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), 0, w, min(y2a - y1a, h)
elif i == 3: # bottom right
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, yc, min(xc + w, s * 2), min(s * 2, yc + h)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, 0, min(w, x2a - x1a), min(y2a - y1a, h)
img4[y1a:y2a, x1a:x2a] = img[y1b:y2b, x1b:x2b] # img4[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
padw = x1a - x1b
padh = y1a - y1b
# Labels
labels, segments = self.labels[index].copy(), self.segments[index].copy()
if labels.size:
labels[:, 1:] = xywhn2xyxy(labels[:, 1:], w, h, padw, padh) # normalized xywh to pixel xyxy format
segments = [xyn2xy(x, w, h, padw, padh) for x in segments]
labels4.append(labels)
segments4.extend(segments)
# Concat/clip labels
labels4 = np.concatenate(labels4, 0)
for x in (labels4[:, 1:], *segments4):
np.clip(x, 0, 2 * s, out=x) # clip when using random_perspective()
# img4, labels4 = replicate(img4, labels4) # replicate
# Augment
img4, labels4, segments4 = copy_paste(img4, labels4, segments4, p=self.hyp['copy_paste'])
img4, labels4 = random_perspective(img4, labels4, segments4,
degrees=self.hyp['degrees'],
translate=self.hyp['translate'],
scale=self.hyp['scale'],
shear=self.hyp['shear'],
perspective=self.hyp['perspective'],
border=self.mosaic_border) # border to remove
return img4, labels4
def load_mosaic9(self, index):
"""用在LoadImagesAndLabels模块的__getitem__函数 替换mosaic数据增强
将九张图片拼接在一张马赛克图像中 loads images in a 9-mosaic
:param self:
:param index: 需要获取的图像索引
:return: img9: mosaic和仿射增强后的一张图片
labels9: img9对应的target
"""
# YOLOv5 9-mosaic loader. Loads 1 image + 8 random images into a 9-image mosaic
labels9, segments9 = [], []
s = self.img_size
indices = [index] + random.choices(self.indices, k=8) # 8 additional image indices
random.shuffle(indices)
hp, wp = -1, -1 # height, width previous
for i, index in enumerate(indices):
# Load image
img, _, (h, w) = self.load_image(index)
# place img in img9
if i == 0: # center
img9 = np.full((s * 3, s * 3, img.shape[2]), 114, dtype=np.uint8) # base image with 4 tiles
h0, w0 = h, w
c = s, s, s + w, s + h # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (base) coordinates
elif i == 1: # top
c = s, s - h, s + w, s
elif i == 2: # top right
c = s + wp, s - h, s + wp + w, s
elif i == 3: # right
c = s + w0, s, s + w0 + w, s + h
elif i == 4: # bottom right
c = s + w0, s + hp, s + w0 + w, s + hp + h
elif i == 5: # bottom
c = s + w0 - w, s + h0, s + w0, s + h0 + h
elif i == 6: # bottom left
c = s + w0 - wp - w, s + h0, s + w0 - wp, s + h0 + h
elif i == 7: # left
c = s - w, s + h0 - h, s, s + h0
elif i == 8: # top left
c = s - w, s + h0 - hp - h, s, s + h0 - hp
padx, pady = c[:2]
x1, y1, x2, y2 = (max(x, 0) for x in c) # allocate coords
# Labels
labels, segments = self.labels[index].copy(), self.segments[index].copy()
if labels.size:
labels[:, 1:] = xywhn2xyxy(labels[:, 1:], w, h, padx, pady) # normalized xywh to pixel xyxy format
segments = [xyn2xy(x, w, h, padx, pady) for x in segments]
labels9.append(labels)
segments9.extend(segments)
# Image
img9[y1:y2, x1:x2] = img[y1 - pady:, x1 - padx:] # img9[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
hp, wp = h, w # height, width previous
# Offset
yc, xc = (int(random.uniform(0, s)) for _ in self.mosaic_border) # mosaic center x, y
img9 = img9[yc:yc + 2 * s, xc:xc + 2 * s]
# Concat/clip labels
labels9 = np.concatenate(labels9, 0)
labels9[:, [1, 3]] -= xc
labels9[:, [2, 4]] -= yc
c = np.array([xc, yc]) # centers
segments9 = [x - c for x in segments9]
for x in (labels9[:, 1:], *segments9):
np.clip(x, 0, 2 * s, out=x) # clip when using random_perspective()
# img9, labels9 = replicate(img9, labels9) # replicate
# Augment
img9, labels9 = random_perspective(img9, labels9, segments9,
degrees=self.hyp['degrees'],
translate=self.hyp['translate'],
scale=self.hyp['scale'],
shear=self.hyp['shear'],
perspective=self.hyp['perspective'],
border=self.mosaic_border) # border to remove
return img9, labels9
@staticmethod
def collate_fn(batch):
"""这个函数会在create_dataloader中生成dataloader时调用:
整理函数 将image和label整合到一起
:return torch.stack(img, 0): 如[16, 3, 640, 640] 整个batch的图片
:return torch.cat(label, 0): 如[15, 6] [num_target, img_index+class_index+xywh(normalized)] 整个batch的label
:return path: 整个batch所有图片的路径
:return shapes: (h0, w0), ((h / h0, w / w0), pad) for COCO mAP rescaling
pytorch的DataLoader打包一个batch的数据集时要经过此函数进行打包 通过重写此函数实现标签与图片对应的划分,一个batch中哪些标签属于哪一张图片,形如
[[0, 6, 0.5, 0.5, 0.26, 0.35],
[0, 6, 0.5, 0.5, 0.26, 0.35],
[1, 6, 0.5, 0.5, 0.26, 0.35],
[2, 6, 0.5, 0.5, 0.26, 0.35],]
前两行标签属于第一张图片, 第三行属于第二张。。。
注意:这个函数一般是当调用了batch_size次 getitem 函数后才会调用一次这个函数,
对batch_size张图片和对应的label进行打包。
强烈建议这里大家debug试试这里return的数据是不是我说的这样定义的。
"""
img, label, path, shapes = zip(*batch) # transposed
for i, lb in enumerate(label):
lb[:, 0] = i # add target image index for build_targets()
return torch.stack(img, 0), torch.cat(label, 0), path, shapes
@staticmethod
def collate_fn4(batch):
"""同样在create_dataloader中生成dataloader时调用:
这里是yolo-v5作者实验性的一个代码 quad-collate function 当train.py的opt参数quad=True 则调用collate_fn4代替collate_fn
作用: 如之前用collate_fn可以返回图片[16, 3, 640, 640] 经过collate_fn4则返回图片[4, 3, 1280, 1280]
将4张mosaic图片[1, 3, 640, 640]合成一张大的mosaic图片[1, 3, 1280, 1280]
将一个batch的图片每四张处理, 0.5的概率将四张图片拼接到一张大图上训练, 0.5概率直接将某张图片上采样两倍训练
"""
img, label, path, shapes = zip(*batch) # transposed
n = len(shapes) // 4
img4, label4, path4, shapes4 = [], [], path[:n], shapes[:n]
ho = torch.tensor([[0.0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0]])
wo = torch.tensor([[0.0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0]])
s = torch.tensor([[1, 1, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5]]) # scale
for i in range(n): # zidane torch.zeros(16,3,720,1280) # BCHW
i *= 4
if random.random() < 0.5:
im = F.interpolate(img[i].unsqueeze(0).float(), scale_factor=2.0, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)[
0].type(img[i].type())
lb = label[i]
else:
im = torch.cat((torch.cat((img[i], img[i + 1]), 1), torch.cat((img[i + 2], img[i + 3]), 1)), 2)
lb = torch.cat((label[i], label[i + 1] + ho, label[i + 2] + wo, label[i + 3] + ho + wo), 0) * s
img4.append(im)
label4.append(lb)
for i, lb in enumerate(label4):
lb[:, 0] = i # add target image index for build_targets()
return torch.stack(img4, 0), torch.cat(label4, 0), path4, shapes4
# Ancillary functions --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
def create_folder(path='./new'):
# Create folder
if os.path.exists(path):
shutil.rmtree(path) # delete output folder
os.makedirs(path) # make new output folder
def flatten_recursive(path=DATASETS_DIR / 'coco128'):
# Flatten a recursive directory by bringing all files to top level
new_path = Path(str(path) + '_flat')
create_folder(new_path)
for file in tqdm(glob.glob(str(Path(path)) + '/**/*.*', recursive=True)):
shutil.copyfile(file, new_path / Path(file).name)
def extract_boxes(path=DATASETS_DIR / 'coco128'): # from utils.datasets import *; extract_boxes()
# Convert detection dataset into classification dataset, with one directory per class
path = Path(path) # images dir
shutil.rmtree(path / 'classifier') if (path / 'classifier').is_dir() else None # remove existing
files = list(path.rglob('*.*'))
n = len(files) # number of files
for im_file in tqdm(files, total=n):
if im_file.suffix[1:] in IMG_FORMATS:
# image
im = cv2.imread(str(im_file))[..., ::-1] # BGR to RGB
h, w = im.shape[:2]
# labels
lb_file = Path(img2label_paths([str(im_file)])[0])
if Path(lb_file).exists():
with open(lb_file) as f:
lb = np.array([x.split() for x in f.read().strip().splitlines()], dtype=np.float32) # labels
for j, x in enumerate(lb):
c = int(x[0]) # class
f = (path / 'classifier') / f'{c}' / f'{path.stem}_{im_file.stem}_{j}.jpg' # new filename
if not f.parent.is_dir():
f.parent.mkdir(parents=True)
b = x[1:] * [w, h, w, h] # box
# b[2:] = b[2:].max() # rectangle to square
b[2:] = b[2:] * 1.2 + 3 # pad
b = xywh2xyxy(b.reshape(-1, 4)).ravel().astype(np.int)
b[[0, 2]] = np.clip(b[[0, 2]], 0, w) # clip boxes outside of image
b[[1, 3]] = np.clip(b[[1, 3]], 0, h)
assert cv2.imwrite(str(f), im[b[1]:b[3], b[0]:b[2]]), f'box failure in {f}'
def autosplit(path=DATASETS_DIR / 'coco128/images', weights=(0.9, 0.1, 0.0), annotated_only=False):
""" Autosplit a dataset into train/val/test splits and save path/autosplit_*.txt files
Usage: from utils.datasets import *; autosplit()
Arguments
path: Path to images directory
weights: Train, val, test weights (list, tuple)
annotated_only: Only use images with an annotated txt file
"""
path = Path(path) # images dir
files = sorted(x for x in path.rglob('*.*') if x.suffix[1:].lower() in IMG_FORMATS) # image files only
n = len(files) # number of files
random.seed(0) # for reproducibility
indices = random.choices([0, 1, 2], weights=weights, k=n) # assign each image to a split
txt = ['autosplit_train.txt', 'autosplit_val.txt', 'autosplit_test.txt'] # 3 txt files
[(path.parent / x).unlink(missing_ok=True) for x in txt] # remove existing
print(f'Autosplitting images from {path}' + ', using *.txt labeled images only' * annotated_only)
for i, img in tqdm(zip(indices, files), total=n):
if not annotated_only or Path(img2label_paths([str(img)])[0]).exists(): # check label
with open(path.parent / txt[i], 'a') as f:
f.write('./' + img.relative_to(path.parent).as_posix() + '\n') # add image to txt file
def verify_image_label(args):
# Verify one image-label pair
im_file, lb_file, prefix = args
nm, nf, ne, nc, msg, segments = 0, 0, 0, 0, '', [] # number (missing, found, empty, corrupt), message, segments
try:
# verify images
im = Image.open(im_file)
im.verify() # PIL verify
shape = exif_size(im) # image size
assert (shape[0] > 9) & (shape[1] > 9), f'image size {shape} <10 pixels'
assert im.format.lower() in IMG_FORMATS, f'invalid image format {im.format}'
if im.format.lower() in ('jpg', 'jpeg'):
with open(im_file, 'rb') as f:
f.seek(-2, 2)
if f.read() != b'\xff\xd9': # corrupt JPEG
ImageOps.exif_transpose(Image.open(im_file)).save(im_file, 'JPEG', subsampling=0, quality=100)
msg = f'{prefix}WARNING: {im_file}: corrupt JPEG restored and saved'
# verify labels
if os.path.isfile(lb_file):
nf = 1 # label found
with open(lb_file) as f:
lb = [x.split() for x in f.read().strip().splitlines() if len(x)]
if any([len(x) > 8 for x in lb]): # is segment
classes = np.array([x[0] for x in lb], dtype=np.float32)
segments = [np.array(x[1:], dtype=np.float32).reshape(-1, 2) for x in lb] # (cls, xy1...)
lb = np.concatenate((classes.reshape(-1, 1), segments2boxes(segments)), 1) # (cls, xywh)
lb = np.array(lb, dtype=np.float32)
nl = len(lb)
if nl:
assert lb.shape[1] == 5, f'labels require 5 columns, {lb.shape[1]} columns detected'
assert (lb >= 0).all(), f'negative label values {lb[lb < 0]}'
assert (lb[:, 1:] <= 1).all(), f'non-normalized or out of bounds coordinates {lb[:, 1:][lb[:, 1:] > 1]}'
_, i = np.unique(lb, axis=0, return_index=True)
if len(i) < nl: # duplicate row check
lb = lb[i] # remove duplicates
if segments:
segments = segments[i]
msg = f'{prefix}WARNING: {im_file}: {nl - len(i)} duplicate labels removed'
else:
ne = 1 # label empty
lb = np.zeros((0, 5), dtype=np.float32)
else:
nm = 1 # label missing
lb = np.zeros((0, 5), dtype=np.float32)
return im_file, lb, shape, segments, nm, nf, ne, nc, msg
except Exception as e:
nc = 1
msg = f'{prefix}WARNING: {im_file}: ignoring corrupt image/label: {e}'
return [None, None, None, None, nm, nf, ne, nc, msg]
def dataset_stats(path='coco128.yaml', autodownload=False, verbose=False, profile=False, hub=False):
""" Return dataset statistics dictionary with images and instances counts per split per class
To run in parent directory: export PYTHONPATH="$PWD/yolov5"
Usage1: from utils.datasets import *; dataset_stats('coco128.yaml', autodownload=True)
Usage2: from utils.datasets import *; dataset_stats('path/to/coco128_with_yaml.zip')
Arguments
path: Path to data.yaml or data.zip (with data.yaml inside data.zip)
autodownload: Attempt to download dataset if not found locally
verbose: Print stats dictionary
"""
def round_labels(labels):
# Update labels to integer class and 6 decimal place floats
return [[int(c), *(round(x, 4) for x in points)] for c, *points in labels]
def unzip(path):
# Unzip data.zip TODO: CONSTRAINT: path/to/abc.zip MUST unzip to 'path/to/abc/'
if str(path).endswith('.zip'): # path is data.zip
assert Path(path).is_file(), f'Error unzipping {path}, file not found'
ZipFile(path).extractall(path=path.parent) # unzip
dir = path.with_suffix('') # dataset directory == zip name
return True, str(dir), next(dir.rglob('*.yaml')) # zipped, data_dir, yaml_path
else: # path is data.yaml
return False, None, path
def hub_ops(f, max_dim=1920):
# HUB ops for 1 image 'f': resize and save at reduced quality in /dataset-hub for web/app viewing
f_new = im_dir / Path(f).name # dataset-hub image filename
try: # use PIL
im = Image.open(f)
r = max_dim / max(im.height, im.width) # ratio
if r < 1.0: # image too large
im = im.resize((int(im.width * r), int(im.height * r)))
im.save(f_new, 'JPEG', quality=75, optimize=True) # save
except Exception as e: # use OpenCV
print(f'WARNING: HUB ops PIL failure {f}: {e}')
im = cv2.imread(f)
im_height, im_width = im.shape[:2]
r = max_dim / max(im_height, im_width) # ratio
if r < 1.0: # image too large
im = cv2.resize(im, (int(im_width * r), int(im_height * r)), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
cv2.imwrite(str(f_new), im)
zipped, data_dir, yaml_path = unzip(Path(path))
with open(check_yaml(yaml_path), errors='ignore') as f:
data = yaml.safe_load(f) # data dict
if zipped:
data['path'] = data_dir # TODO: should this be dir.resolve()?
check_dataset(data, autodownload) # download dataset if missing
hub_dir = Path(data['path'] + ('-hub' if hub else ''))
stats = {'nc': data['nc'], 'names': data['names']} # statistics dictionary
for split in 'train', 'val', 'test':
if data.get(split) is None:
stats[split] = None # i.e. no test set
continue
x = []
dataset = LoadImagesAndLabels(data[split]) # load dataset
for label in tqdm(dataset.labels, total=dataset.n, desc='Statistics'):
x.append(np.bincount(label[:, 0].astype(int), minlength=data['nc']))
x = np.array(x) # shape(128x80)
stats[split] = {'instance_stats': {'total': int(x.sum()), 'per_class': x.sum(0).tolist()},
'image_stats': {'total': dataset.n, 'unlabelled': int(np.all(x == 0, 1).sum()),
'per_class': (x > 0).sum(0).tolist()},
'labels': [{str(Path(k).name): round_labels(v.tolist())} for k, v in
zip(dataset.img_files, dataset.labels)]}
if hub:
im_dir = hub_dir / 'images'
im_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
for _ in tqdm(ThreadPool(NUM_THREADS).imap(hub_ops, dataset.img_files), total=dataset.n, desc='HUB Ops'):
pass
# Profile
stats_path = hub_dir / 'stats.json'
if profile:
for _ in range(1):
file = stats_path.with_suffix('.npy')
t1 = time.time()
np.save(file, stats)
t2 = time.time()
x = np.load(file, allow_pickle=True)
print(f'stats.npy times: {time.time() - t2:.3f}s read, {t2 - t1:.3f}s write')
file = stats_path.with_suffix('.json')
t1 = time.time()
with open(file, 'w') as f:
json.dump(stats, f) # save stats *.json
t2 = time.time()
with open(file) as f:
x = json.load(f) # load hyps dict
print(f'stats.json times: {time.time() - t2:.3f}s read, {t2 - t1:.3f}s write')
# Save, print and return
if hub:
print(f'Saving {stats_path.resolve()}...')
with open(stats_path, 'w') as f:
json.dump(stats, f) # save stats.json
if verbose:
print(json.dumps(stats, indent=2, sort_keys=False))
return stats
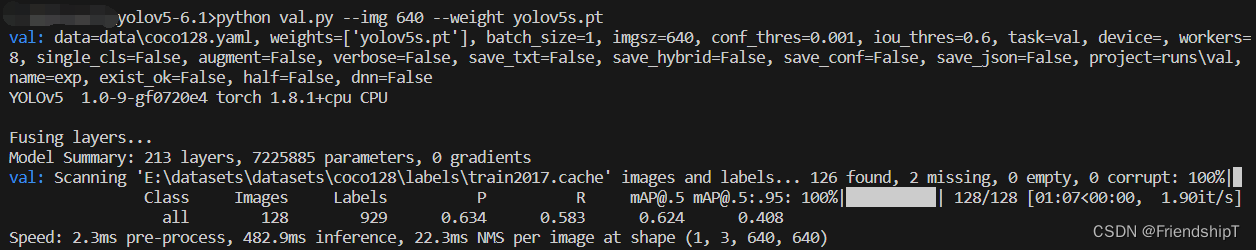
进行验证
python val.py --img 640 --weight yolov5s.pt
没有指定的结果
include_class = [] # filter labels to include only these classes (optional)
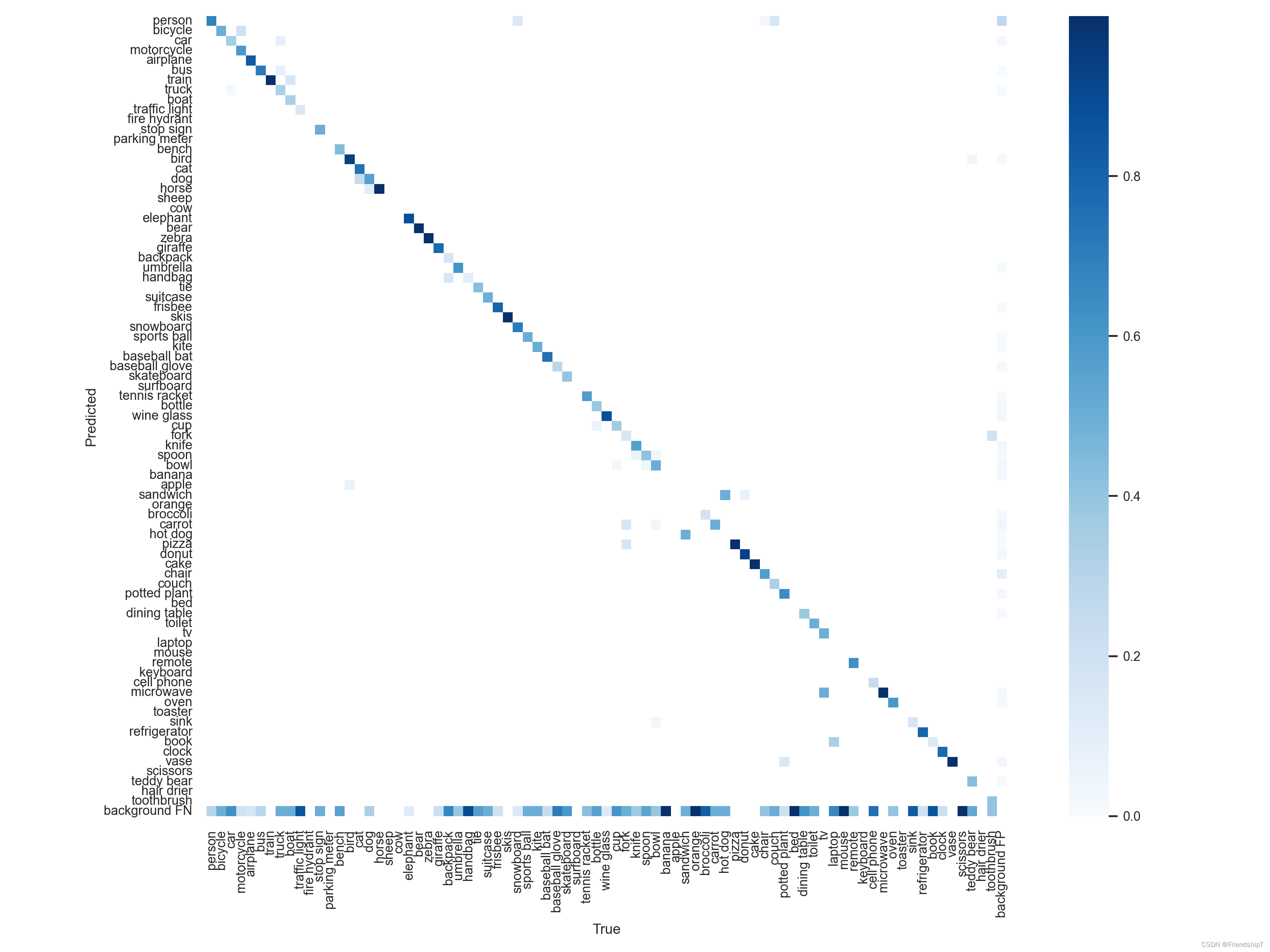
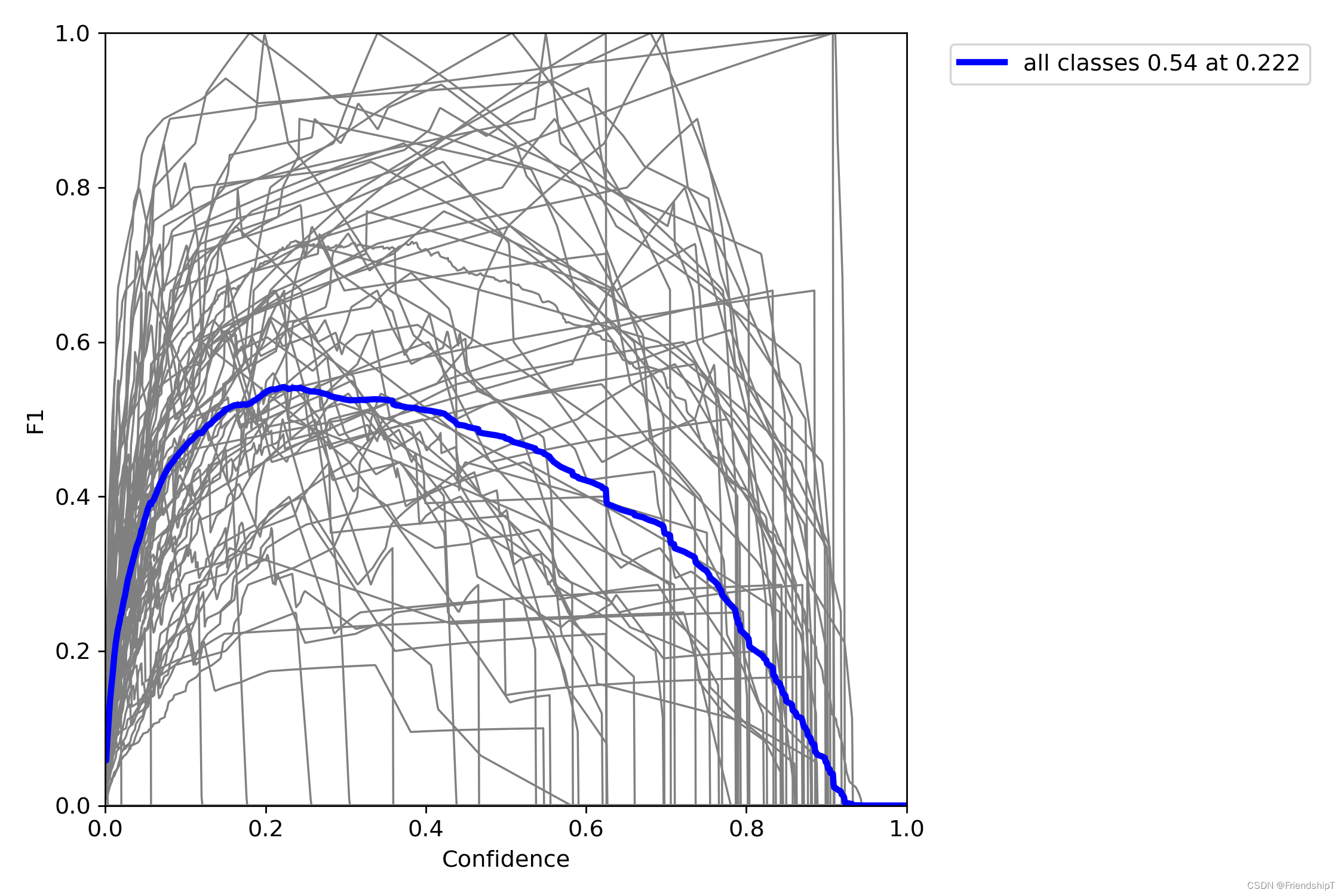
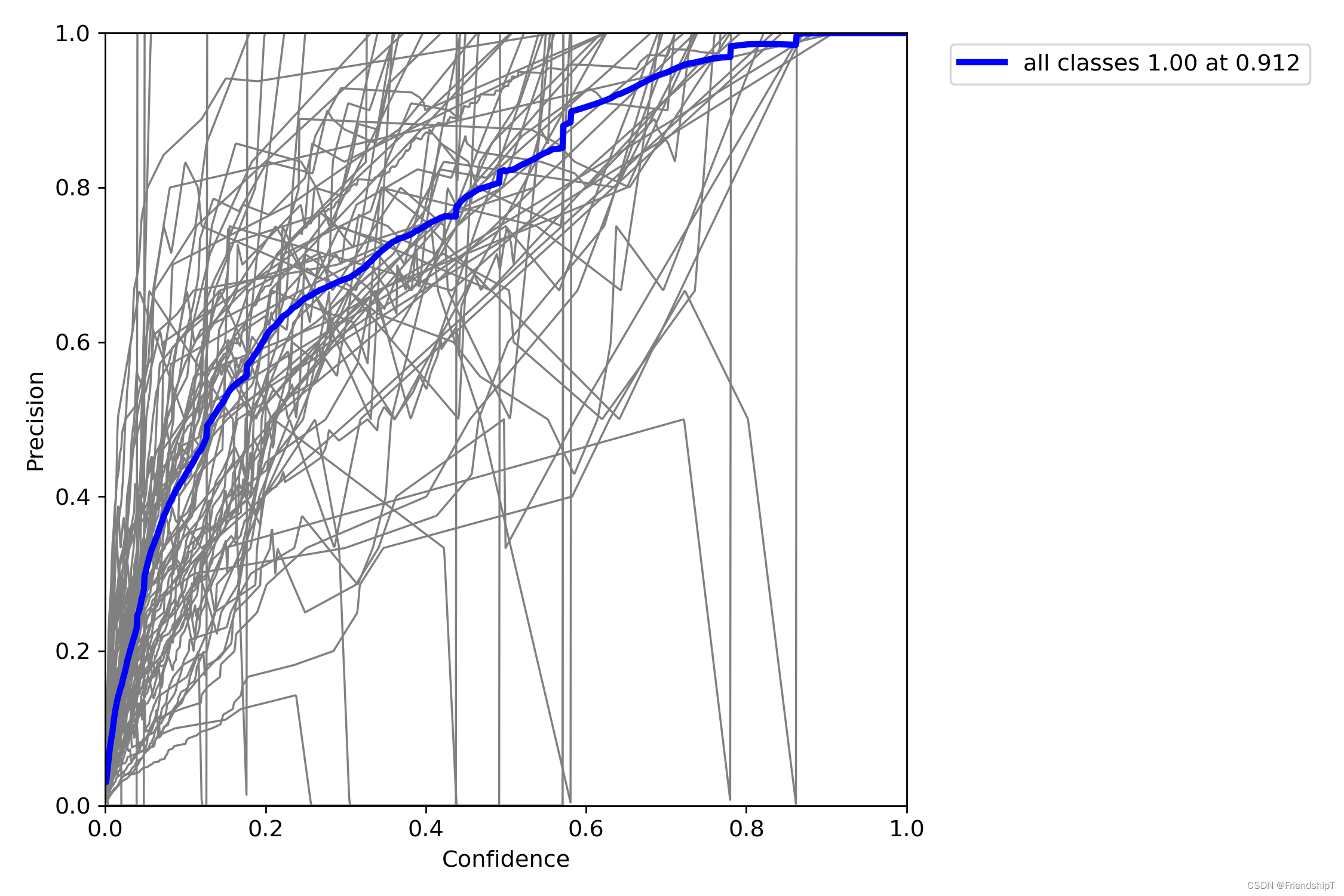
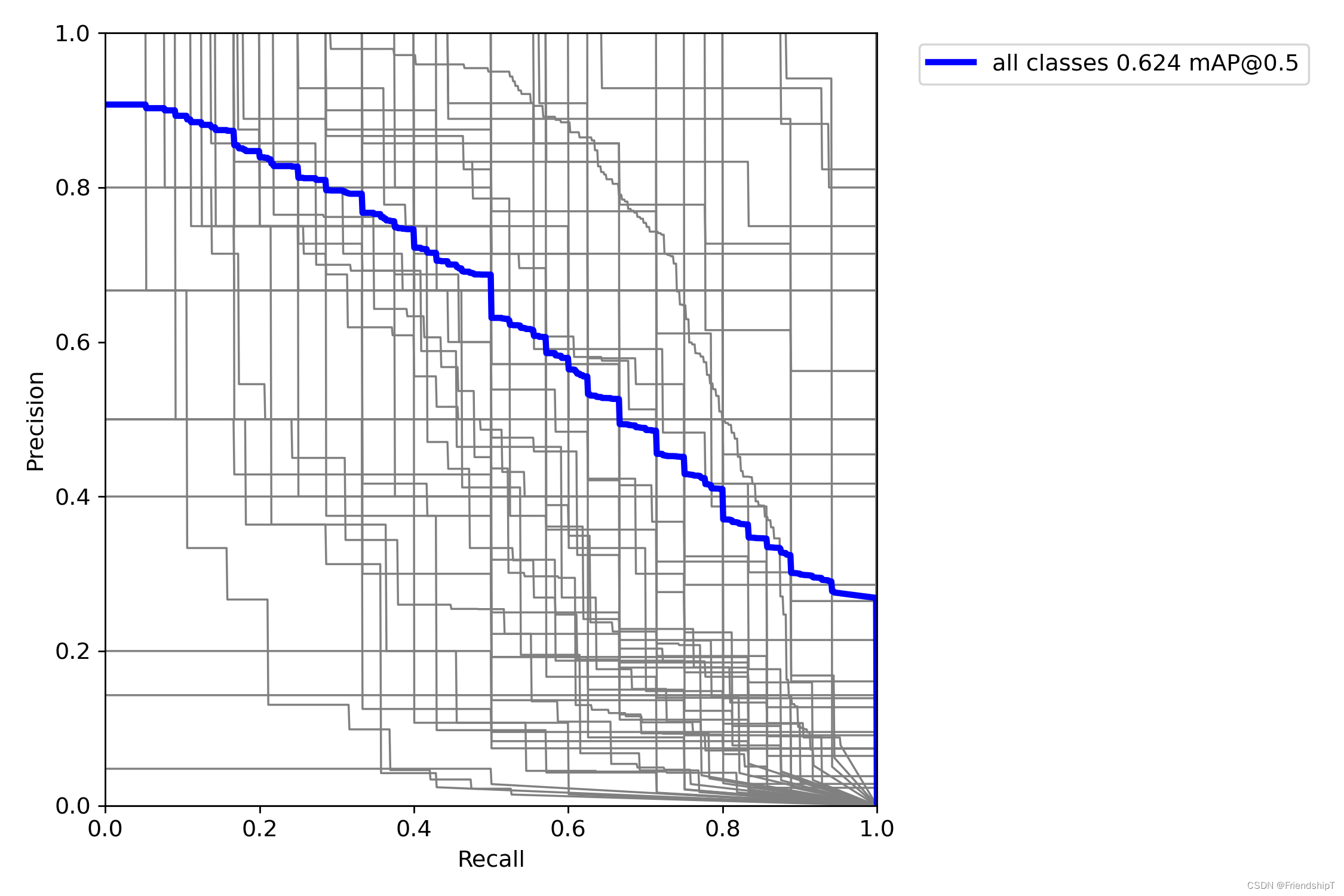
指定类别的结果
# 指定第13,14类
include_class = [13,14] # filter labels to include only these classes (optional)
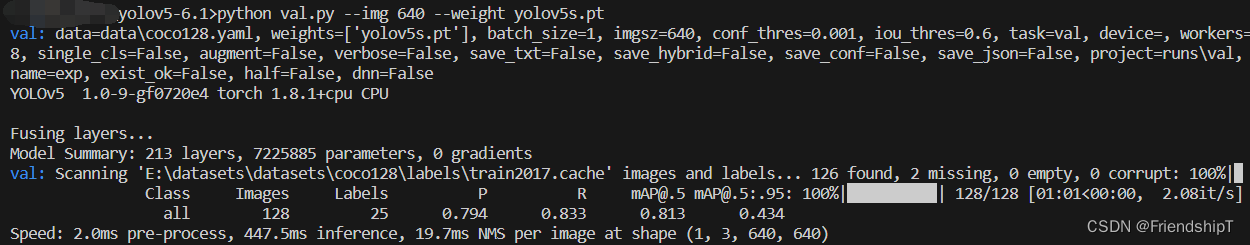
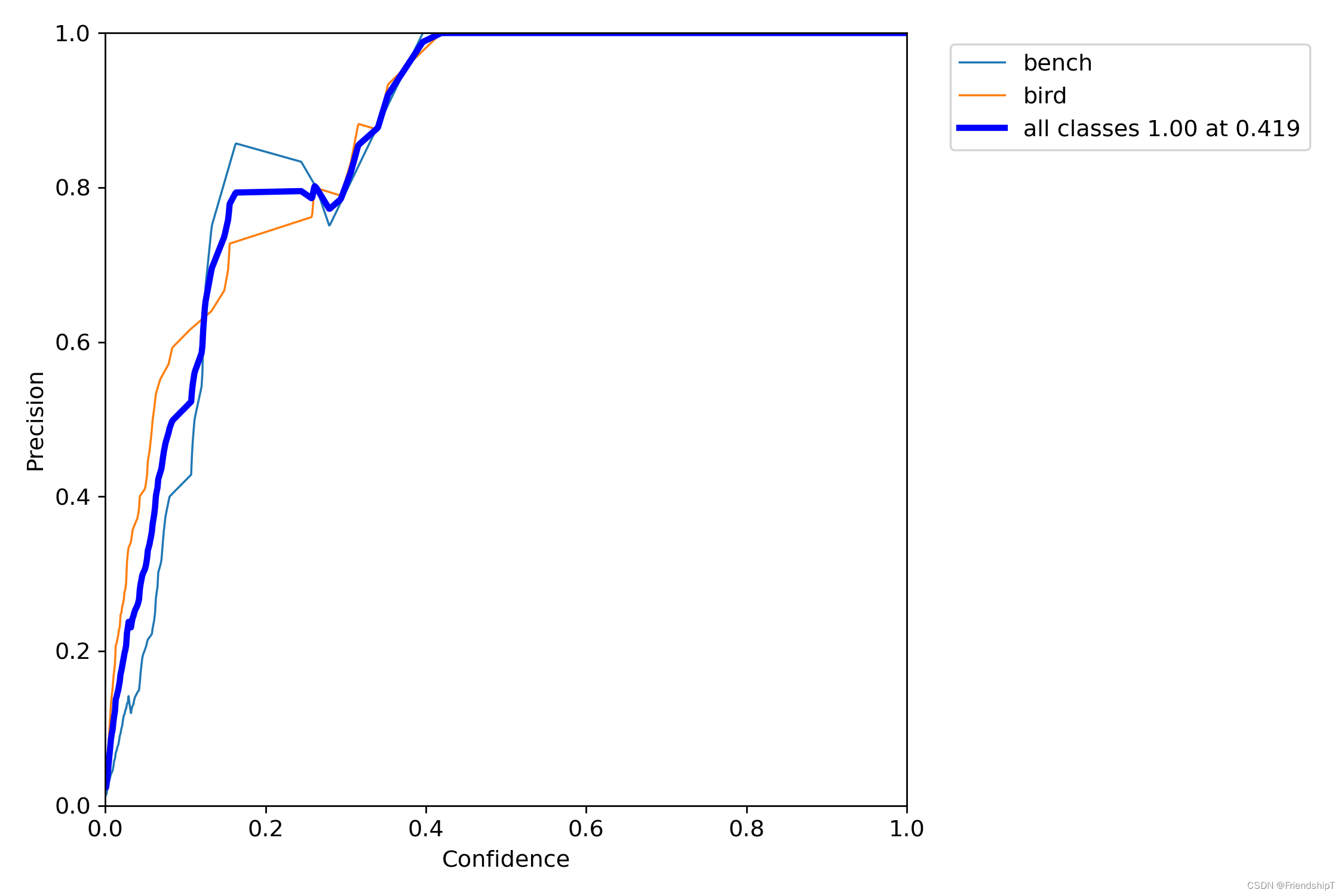
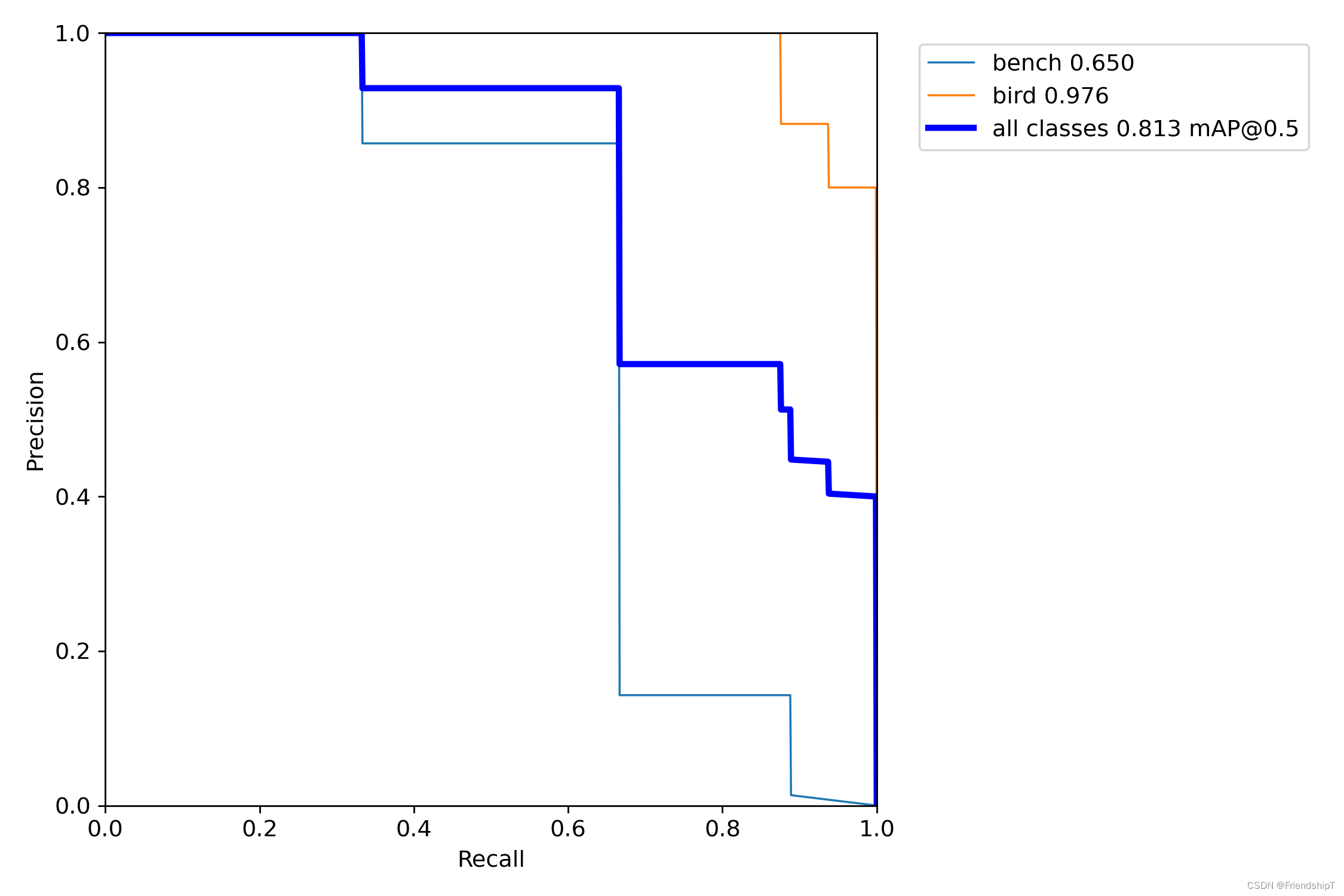
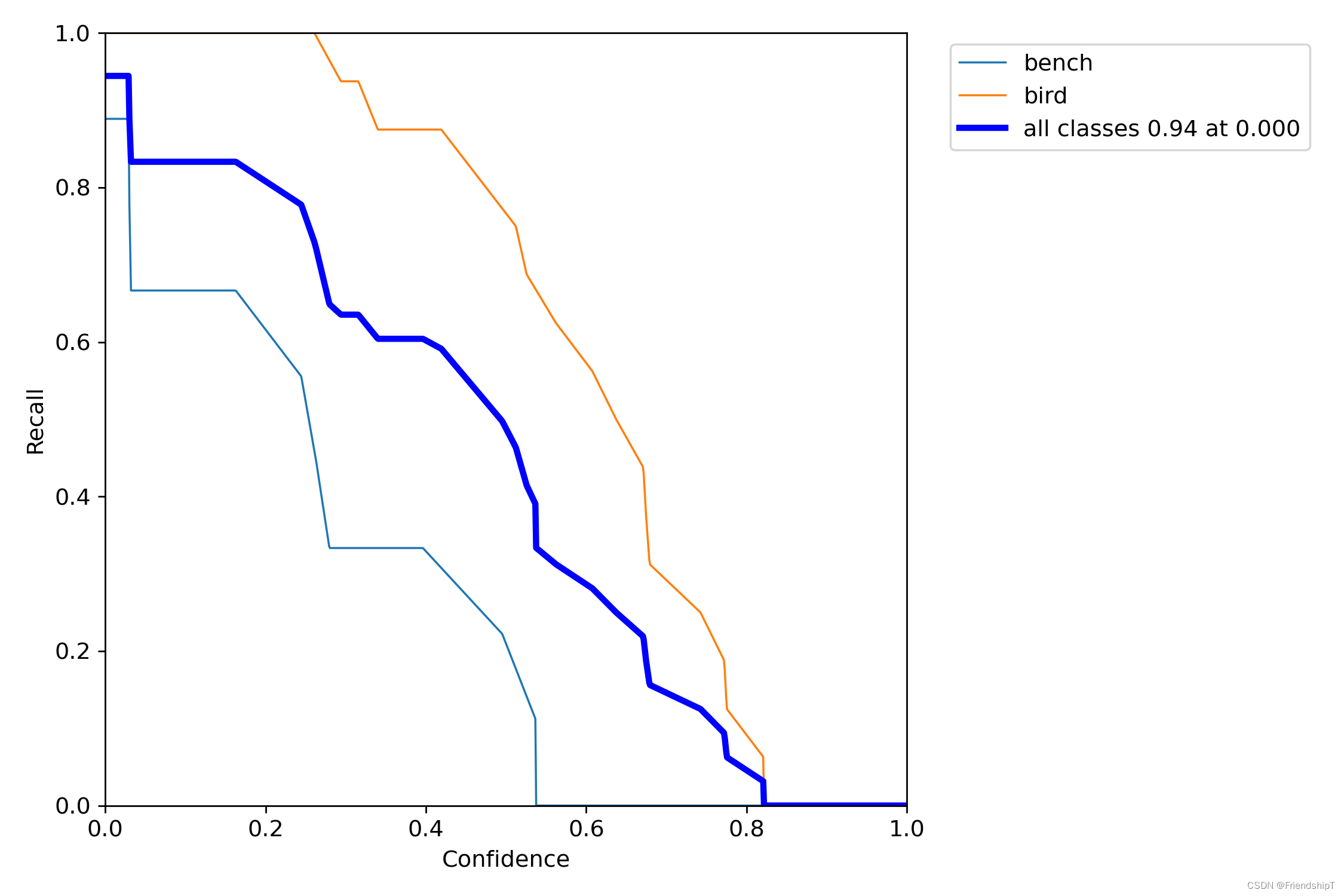
- 由于本人水平有限,难免出现错漏,敬请批评改正。
- 更多精彩内容,可点击进入Python日常小操作专栏、OpenCV-Python小应用专栏、YOLO系列专栏、自然语言处理专栏或我的个人主页查看
- 基于DETR的人脸伪装检测
- YOLOv7训练自己的数据集(口罩检测)
- YOLOv8训练自己的数据集(足球检测)
- YOLOv5:TensorRT加速YOLOv5模型推理
- YOLOv5:IoU、GIoU、DIoU、CIoU、EIoU
- 玩转Jetson Nano(五):TensorRT加速YOLOv5目标检测
- YOLOv5:添加SE、CBAM、CoordAtt、ECA注意力机制
- YOLOv5:yolov5s.yaml配置文件解读、增加小目标检测层
- Python将COCO格式实例分割数据集转换为YOLO格式实例分割数据集
- YOLOv5:使用7.0版本训练自己的实例分割模型(车辆、行人、路标、车道线等实例分割)
- 使用Kaggle GPU资源免费体验Stable Diffusion开源项目
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/FriendshipTang/article/details/135398613
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 华为HUAWEI笔记本MateBook 16s 2023款 i7 集显(CREFG-16)原装出厂Windows11系统22H2
- 石油化工行业常用PFA镊子本底低无溶出析出防污染样品
- mysql的gtid主从复制,从库误操作更新操作,
- Vue created()和 activated()区别和作用调用顺序
- 【工具使用-A2B】使用A2B配置32通道车载音频系统
- CC工具箱使用指南:【属性映射】
- c# 实现PID参数调节
- 气压计LPS28DFW开发(1)----轮询获取气压计数据
- 【云原生kubernets】Ingress 功能与应用
- 企业信息防泄漏管理的理念是什么?